Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (9): 1371-1376.doi: 10.12307/2023.209
Previous Articles Next Articles
Three-dimensional finite element model analysis of intramedullary nailing fixation design for large femoral defects in Beagle dogs
Wen Xinghua1, Ding Huanwen1, 2, Cheng Kai1, 2, Yan Xiaonan1, Peng Yuanhao1, 2, Wang Yuning1, Liu Kang1, Zhang Huiwu3
- 1South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510641, Guangdong Province, China; 2Guangzhou First People’s Hospital, Guangzhou 510180, Guangdong Province, China; 3Sichuan Orthopedic Hospital, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2021-12-11Accepted:2022-01-19Online:2023-03-28Published:2022-07-01 -
Contact:Ding Huanwen, MD, Professor, Chief physician, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510641, Guangdong Province, China; Guangzhou First People’s Hospital, Guangzhou 510180, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Wen Xinghua, Master candidate, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510641, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:Fundamental and Applied Basic Research Fund Project of Guangdong Province, No. 2021A1515012564 (to DHW); Guangzhou Science and Technology Plan Project, No. 202007020002 (to DHW); Sichuan Science and Technology Plan Project, No. 2019YFS0446 (to ZHW)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wen Xinghua, Ding Huanwen, Cheng Kai, Yan Xiaonan, Peng Yuanhao, Wang Yuning, Liu Kang, Zhang Huiwu. Three-dimensional finite element model analysis of intramedullary nailing fixation design for large femoral defects in Beagle dogs[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1371-1376.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
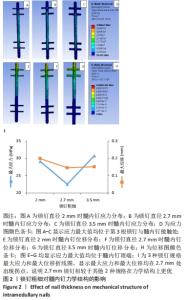
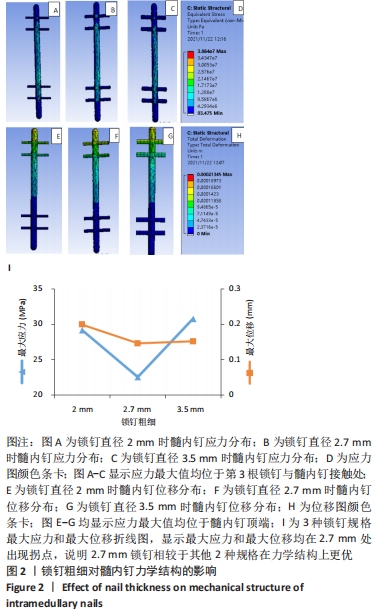
有限元结果显示,3.5 mm直径锁钉的最大Von Mises应力值最大,达到30.82 MPa;2 mm锁钉次之,为29.15 MPa;2.7 mm锁钉最大Von Mises应力值最小,为22.53 MPa。分析原因髓内钉直径固定时,锁钉越粗,髓内钉与锁钉接触位置的开孔越大,壁薄而容易导致断裂;相反,锁钉越细,髓内钉上最大应力值减小,但由于锁钉相对较细,受到的反作用力较大,而位于中间粗细的锁钉其对应的髓内钉最大应力值最小。因此得出结论:在髓内钉大小确定后,锁钉的粗细不应过粗,也不应过细,而位于髓内钉直径一半左右时所受应力最小,效果最好。 2.1.2 位移分析 所有模型的位移分布规律相似,股骨沿长轴的最大位移均位于股骨近端,即施加载荷处,且向股骨远端逐渐降低,髓内钉及锁钉的最大位移出现在髓内钉顶端,及离施力端最近处,见图2。 分析手术过程模型,2 mm锁钉位移最大值相较其他最大,值为0.199 mm;3.5 mm锁钉最大位移值次之,为0.152 mm;2.7 mm锁钉值最小,为0.146 mm。位移随着最大应力变化而变化,同样2.7 mm锁钉的最大位移在3个模型里是最小的。 2.2 锁钉数量对假体应力的影响 2.2.1 应力分析 同上所述,观察髓内钉及锁钉受力,由有限元结果可知,3种模型的髓内钉最大应力均位于植入体下端第1个锁钉处,并且向周围分散见图3。 "
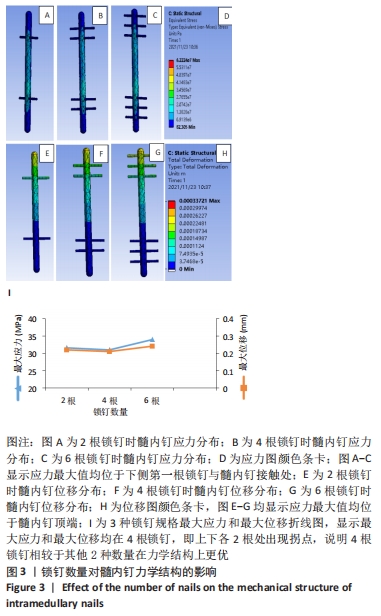
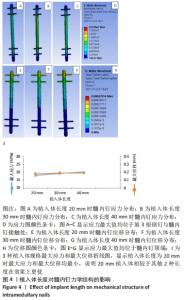
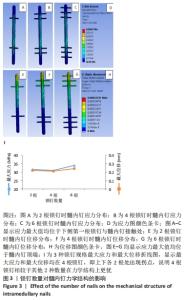
6根锁钉的最大Von Mises应力值最大,达到34.0 MPa;2根锁钉次之,为31.64 MPa;4根锁钉最大Von Mises应力值最小,为31.03 MPa。分析原因髓内钉和锁钉规格固定时,并不是锁钉数量越多越好,要同时考虑到对应髓内钉打孔数,打孔越多,髓内钉的力学结构随之受到破环,相同的载荷导致打孔处应力增强,但锁钉数量较少时,承担在每个锁钉的应力会相应增大。因此得出结论:在髓内钉确定后,锁钉的数量不应过多,也不应过少,而4根锁钉时所受应力最小,效果最好。 2.2.2 位移分析 所有模型的位移分布规律相似,股骨沿长轴的最大位移位于股骨近端,即施加载荷处,且向股骨远端逐渐降低,髓内钉及锁钉的最大位移出现在髓内钉顶端,及离施力端最近处,见图3。 6根锁钉位移最大值相较其他最大,为0.24 mm;2根锁钉最大位移值次之,为0.22 mm;4根锁钉值最小,为0.21 mm。位移随着最大应力变化而变化,同样4根锁钉的最大位移在3个模型里是最小的。 2.3 植入体长度对假体应力的影响 2.3.1 应力分析 同上所述,观察髓内钉及锁钉受力。由分析结果可知,3种模型的髓内钉最大应力均位于植入体下端第1个锁钉,即第3个锁钉处,并且向周围分散见图4。 "
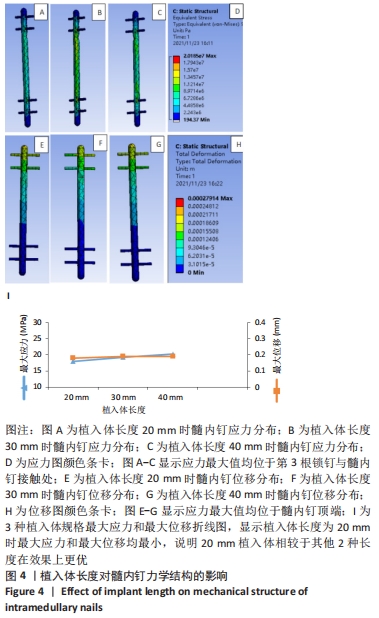
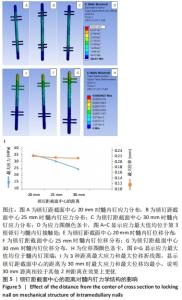
植入体长度为40 mm的最大Von Mises应力值最大,达到20.19 MPa;长度为30 mm锁钉次之,为19.24 MPa;长度为20 mm最大Von Mises应力值最小,为17.94 MPa。得出结论:在缺损大小和锁钉位置固定时,植入体越长髓内钉承受力越大,也即植入体长度在刚好连接上下骨缺损创口时为最佳,设计植入体时不应扩大缺损位置。 2.3.2 位移分析 所有模型的位移分布规律相似,股骨沿长轴的最大位移位于股骨近端,即施加载荷处,且向股骨远端逐渐降低,髓内钉及锁钉的最大位移出现在髓内钉顶端,及离施力端最近处,见图4。 分析手术过程模型,植入体长度为40 mm最大位移值最大,为0.20 mm;长度为30 mm最大位移值次之,为 0.19 mm;长度为20 mm最大位移值最小,为0.18 mm。位移随着最大应力变化而变化,同样植入体长度在20 mm时最大位移在3个模型里是最小的。 2.4 锁钉离截面中心的距离对假体应力的影响 2.4.1 应力分析 同上所述,观察髓内钉及锁钉受力。由有限元结果可知,3种模型的髓内钉最大应力均位于植入体下端第1个锁钉,即第3个锁钉处,并且向周围分散见图5。 "


距离截面中心20 mm的最大Von Mises应力值最大,达到34.89 MPa;距离截面中心25 mm锁钉次之,为30.35 MPa;距离截面中心30 mm最大Von Mises应力值最小,为24.69 MPa。得出结论:在髓内钉长度和锁钉直径固定时,锁钉离截面中心越远承受力越小,也即锁钉在考虑髓内钉的力学结构前提下,使用时尽可能地固定在髓内钉的末端处。 2.4.2 位移分析 所有模型的位移分布规律相似,股骨沿长轴的最大位移位于股骨近端,即施加载荷处,且向股骨远端逐渐降低,髓内钉及锁钉的最大位移出现在髓内钉顶端,及离施力端最近处,见图5。 距离截面中心20 mm位移最大值相较其他最大,为0.22 mm;距离截面中心25 mm最大位移值次之,为0.214 mm;距离截面中心30 mm值最小,为0.212 mm。位移随着最大应力变化而变化,同样距离截面中心30 mm的模型最大位移在3个模型里是最小的。 "

| [1] SAHIJWANI H, SALUNKE AA, WARIKOO V, et al. Use of Free Anterolateral Thigh Flap in Reconstruction of Soft Tissue Defects in Orthopedic Oncology: What are the Outcomes? Indian J Orthop. 2020;55:246-255. [2] FERNÁNDEZ GARRIDO M, PEREIRA N, LÓPEZ FERNÁNDEZ S, et al. Turbocharged bilateral pedicled DIEP flap for reconstruction of thigh defect without recipient vessels: A case report. Microsurgery. 2018; 38(3):324-327. [3] MYEROFF C, ARCHDEACON M. Autogenous bone graft: donor sites and techniques. J Bone Joint Surg. 2011;93(23):2227-2236. [4] WANG F, JIA S, LI M, et al. Effect of the medial collateral ligament and the lateral ulnar collateral ligament injury on elbow stability: a finite element analysis. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2021; 24(13):1517-1529. [5] SPYROU LA, AGORAS M, DANAS K, et al. A homogenization model of the Voigt type for skeletal muscle. J Theor Biol. 2017;414:50-61. [6] 张帅,屠重棋,段宏,等.股骨近端骨缺损与骨折相关性的有限元分析[J].四川大学学报(医学版),2011,42(2):273-276+279. [7] DESYATOVA A, POULSON W, MACTAGGART J, et al. Cross-sectional pinching in human femoropopliteal arteries due to limb flexion, and stent design optimization for maximum cross-sectional opening and minimum intramural stresses. J R Soc Interface. 2018;15(145): 20180475. [8] TUNCER M, COBB JP, HANSEN UN, et al. Validation of multiple subject-specific finite element models of unicompartmental knee replacement. Med Eng Phys. 2013;35:1457-1464. [9] WEI X, ZHAO L, XU Z, et al. Effects of cortical bone thickness at different healing times on microscrew stability. Angle Orthod. 2011;81(5):760-766. [10] PLENERT T, GARLICHS G, NOLTE I, et al. Biomechanical comparison of a new expandable intramedullary nail and conventional intramedullary nails for femoral osteosynthesis in dogs. PloS One. 2020;15(5): e0231823. [11] MAUFFREY C, BARLOW BT, SMITH W. Management of segmental bone defects. Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2015;23(3):143-153. [12] SILVESTRI C, HEATH D, RUPAREL T, et al. Validation of a biofidelic LS-DYNA model and comparison vs. a traditional ATD finite element model for assessing knee-thigh-hip injuries. Vehicle Safety. 2010;5:21-34. [13] XIE S, CONLISK N, HAMILTON D, et al. A finite element analysis of tibial tritanium cones without stems in varying bone defects. Knee. 2020; 27(3):656-666. [14] 董衍生. 可吸收锁钉鞘预防带锁髓内钉应力遮挡的有限元分析[D].天津:天津理工大学,2018. [15] 檀臻炜,汪丙昂,姚一民,等.兔膝关节力学有限元分析及软骨缺损模型的建立[J].西南国防医药,2018,28(12):1213-1217. [16] ZHANG T, WEI Q, ZHOU H, et al. Three-dimensional-printed individualized porous implants: A new “implant-bone” interface fusion concept for large bone defect treatment. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(11): 3659-3670. [17] ACCADBLED F, THEVENIN LEMOINE C, POINSOT E, et al. Bone reconstruction after malignant tumour resection using a motorized lengthening intramedullary nail in adolescents: preliminary results. J Child Orthop. 2019;13(3):324-329. [18] ATTIAS N, THABET AM, PRABHAKAR G, et al. Management of extra-articular segmental defects in long bone using a titanium mesh cage as an adjunct to other methods of fixation. Bone Joint J. 2018;100-B(5): 646-651. [19] 贾超,喻胜鹏,吴宏日,等.Masquelet技术二期髓内钉固定重建术治疗胫骨感染性骨缺损[J].局解手术学杂志,2020,29(1):29-33. [20] 韩世翀,李昌,刑海洋,等.胫骨近端关节外骨折两种内固定方式的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(15):2329-2333. [21] XU L, ZHOU J, WANG Z, et al. Reconstruction of bone defect with allograft and retrograde intramedullary nail for distal tibia osteosarcoma. Foot Ankle Surg. 2018;24(2):149-153. [22] 李智,王臻,孙峥.有限接触式带锁髓内钉的有限元分析及临床应用[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2006,14(14):1082-1085+1037. [23] YU JJ, ZHANG C, LI L, et al. Internal fixation treatments for intertrochanteric fracture: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized evidence. Sci Rep. 2015;5(1):18195. [24] SIPAHIOGLU S, ZEHIR S, SARIKAYA B, et al. Comparision of the expandable nail with locked nail in the treatment of closed diaphyseal fractures of femur. Niger J Clinical Prac. 2017;20(7):792-798. [25] BASARAN T, CALBIYIK M, BASARAN PO, et al. Blade expandable intramedullary nails for fixation of tibial shaft fractures. Acta Orthop Belg. 2019;85(4):472-476. [26] PLENERT T, GARLICHS G, NOLTE I, et al. Biomechanical comparison of a new expandable intramedullary nail and conventional intramedullary nails for femoral osteosynthesis in dogs. PLOS ONE. 2020;15(5):e0231823. [27] GALVAIN T, CHITNIS A, PAPAROUNI K, et al. The economic burden of infections following intramedullary nailing for a tibial shaft fracture in England. BMJ Open. 2020;10(8):e035404. [28] TAKASHIMA K, NAKAHARA I, UEMURA K, et al. Clinical outcomes of proximal femoral fractures treated with a novel carbon fiber-reinforced polyetheretherketone intramedullary nail. Injury. 2020;51(3):678-682. [29] MITCHELL P, LEE AK, COLLINGE CA, et al. Jahangir A. Early comparative outcomes of carbon fiber-reinforced polymer plate in the fixation of distal femur fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2018;32:386-390. [30] 徐国平.四肢创伤骨折后骨不连的植入物内固定术治疗的临床对照分析[J].临床医药文献电子杂志,2018,5(28):60-61. [31] 孙晓亮,孙有声,刘志伟,等.交锁髓内钉治疗胫骨近端骨折(附46例报告)[J].骨与关节损伤杂志,2000,15(6):451-452. |
| [1] | Zhong Yizheng, Huang Peizhen, Cai Qunbin, Zheng Liqin, He Xingpeng, Dong Hang. Microstructural indexes that determine the trabecular bone maximum stress of micro-finite element models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1313-1318. |
| [2] | Wu Taoguang, Nie Shaobo, Chen Hua, Zhu Zhengguo, Qi Lin, Tang Peifu. Biomechanical characteristics of a new multi-dimensional cross locking plate in the treatment of subtrochanteric nonunion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1330-1334. |
| [3] | Peng Zhixin, Yan Wengang, Wang Kun, Zhang Zhenjiang. Finite element analysis and structural optimization design of 3D printed forearm braces [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1340-1345. |
| [4] | Wu Tianliang, Tao Xiuxia, Xu Hongguang. Influence of different bone mineral densities on cage subsidence after stand-alone oblique lateral interbody fusion: three-dimensional finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1352-1358. |
| [5] | Liu Jinyu, Zhang Hanshuo, Cui Hongpeng, Pan Lingzhi, Zhao Boran, Li Fei, Ding Yu. Finite element biomechanical analysis of minimally invasive treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy and accurate exercise rehabilitation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1359-1364. |
| [6] | He Yujie, Kang Zhijie, Xue Mingming, Jin Feng, Li Zhijun, Wang Xing, Xu Yangyang, Gao Mingjie, Li Jiawei, Li Xiaohe, Wang Haiyan. Finite element analysis of transarticular screw fixation of adolescent thoracic vertebra [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1365-1370. |
| [7] | Li Shihao, Li Qi, Li Zhen, Zhang Yuanyuan, Liu Miaomiao, Ouyang Yi, Xu Weiguo. Plantar pressure and gait analysis in patients with anterior cruciate ligament injury and reconstruction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Liu Qinghua, Cai Yongqiang, Jin Feng, Yu Jinghong, Wang Haiyan, Zhang Yunfeng, Wang Lidong, Li Jiawei, Wang Xing, He Yujie, Dai Lina, Wang Jianzhong, Wu Chao, Tong Ling, Kang Zhijie, Li Zhijun, Li Xiaohe. Finite element model of the 12-year-old child whole cervical spine: establishment and validity verification based on CT data [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 500-504. |
| [9] | Li Yaping, Liu Hong, Gao Zhen, Chen Xiaolin, Huang Wujie, Jiang Zheng. Three-dimensional motion analysis of lower limb biomechanical performance in Tai Chi practitioners accompanied by knee joint pain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 520-526. |
| [10] | Xu Xiangjun, Wang Chao, Song Qunshan, Li Bingyan, Zhang Jichao, Wang Guodong, Dong Yuefu. Optimal angle for prosthesis implantation in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 612-618. |
| [11] | Zhan Yi, Wang Biao, Ma Yuli, He Simin, Sun Honghui, Hao Dingjun. Biomechanical comparison between a novel bone cement screw system and common surgical methods for the treatment of Kummell’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 385-390. |
| [12] | Lu Hui, Wu Qimei, Liu Rong. Finite element analysis and application of unilateral and bilateral bone-filling mesh container in treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 391-397. |
| [13] | Wang Junxiang, Sun Jiangwei, Bai Bujiafu·Yellisi, Wang Zhaoxin, Nijati·Turson. Effect of three abutment materials on bone stress around maxillary angle implant under dynamic loading [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 398-405. |
| [14] | Chen Jingqiao, Li Ying, Meng Maohua, Xu Xingxing, Wang Qinying, Wang Huan, Lu Jing, Shu Jiayu, Dong Qiang. Research progress in platelet-rich fibrin in stomatology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 441-446. |
| [15] | Wang Kaiyu, Hu Peng, Wei Zairong, Huang Guangtao, Zhou Jian, He Guijia, Nie Kaiyu. Use of expanders and implants in breast reconstruction complicated with infection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 461-469. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||