[1] 杜传超,张衡,海宝,等.脊柱阶段性解剖特点及其损伤的力学机制与诊疗策略[J].创伤外科杂志,2019,21(7):552-557.
[2] KIM Y, KHUYAGBAATAR B, KIM K. Recent advances in finite element modeling of the human cervical spine. J Mechanical Sci Technol. 2018;32(1):1-10.
[3] LI Z, SONG G, SU Z, et al. Development, validation, and application of ligamentous cervical spinal segment C6-C7 of a six-year-old child and an adult. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2020;183:105080.
[4] HERRON MR, PARK J, DAILEY AT, et al. Febio finite element models of the human cervical spine. J Biomech. 2020;113:110077.
[5] 孙枫原,李宗远,何希,等.有限元分析在脊柱侧凸生物力学研究中的应用及进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(32):5221-5226.
[6] 郭群峰,陈方经,倪斌,等.带有颅底的全颈椎三维有限元模型的建立及分析[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2014,24(6):550-554.
[7] 陈群响,倪斌,郭群峰,等.带肌肉组织全颈椎三维有限元模型的建立及分析[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2019,29(4):348-355.
[8] SHIRAZI-ADL A, AHMED AM, SHRIVASTAVA SC, et al. Mechanical response of a lumbar motion segment in axial torque alone and combined with compression. Spine. 1986;11(9):914-927.
[9] SCHMIDT H, HEUER F, DRUMM J, et al. Application of a calibration method provides more realistic results for a finite element model of a lumbar spinal segment. Clin Biomech. 2007;22(4):377-384
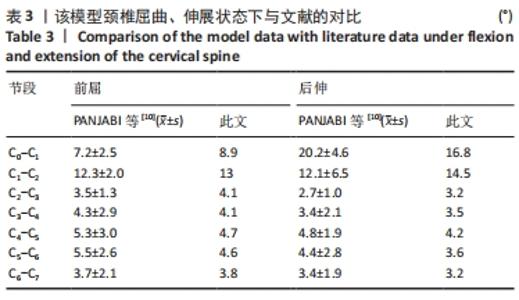
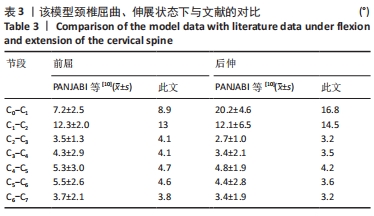
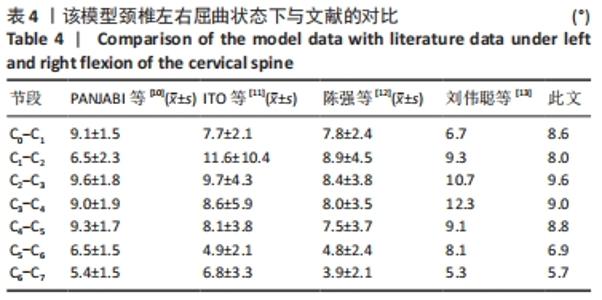
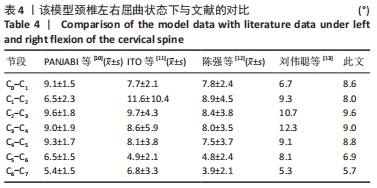
[10] PANJABI MM, CRISCO JJ, VASAVADA A, et al. Mechanical properties of the human cervical spine as shown by three-dimensional load–displacement curves. Spine. 2001;26(24):2692-2700.
[11] ITO S, IVANCIC PC, PANJABI MM, et al. Soft Tissue Injury Threshold During Simulated Whiplash. Spine. 2004;29(9):979-987.
[12] 陈强. 挥鞭样损伤的生物力学和临床研究[D].上海:第二军医大学,2005.
[13] 刘伟聪,陈雄生,周盛源,等.正常人体C0-T1全颈椎有限元模型的构建及意义[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(11):1707-1712.
[14] 张瑜,李忠海.三维有限元法在脊柱生物力学中的应用现状[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2020,9(3):220-224.
[15] BREKELMANS WAM, POORT HW, SLOOFF T. A new method to analyse the mechanical behaviour of skeletal parts. Acta Orthop Scand. 1972;43(5):301-317.
[16] BELYTSCHKO T, KULAK RF, SCHULTZ AB, et al. Finite element stress analysis of an intervertebral disc. J Biomech. 1974;7(3):277-285.
[17] YOGANANDAN N, KUMARESAN S, PINTAR FA. Pediatric cervical spine biomechanics using finite element models. Research Council on the Biomechanics of Impact , Goteborg , Sweden.1998.
[18] MEYER F, ROTH S, WILLINGER R. Child neck FE model development and validation. International Journal of Human Factors Modelling and Simulation. 2008;1(2):244-257.
[19] MEYER F, ROTH S, WILLINGER R. Three-year-old child head-neck finite element modelling: simulation of the interaction with airbag in frontal and side impact. Int J Veh Saf. 2009;4(4). doi: info:doi/10.1504/IJVS.2009.032757
[20] 曹立波,魏嵬,张冠军.3岁儿童C4-C5颈椎有限元模型开发及拉伸、弯曲验证[J].中国生物医学工程学报,2015,34(1):37-45.
[21] 吕文乐,阮世捷,李海岩,等.6岁儿童全颈有限元模型的构建及验证[J].医用生物力学,2016,31(2):95-101.
[22] DONG L, LI G, MAO H, et al. Development and validation of a 10-year-old child ligamentous cervical spine finite element model. Ann Biomed Eng. 2013; 41(12): 2538-2552.
[23] 韩晓强. 6岁儿童颈部建模及汽车尾撞工况下损伤研究[D].北京:北京交通大学,2018.
[24] 惠耀敏,王嘉,何洁铭.颈椎骨质增生特点与不同年龄颈椎退变规律CT影像观察[J].现代仪器与医疗,2019,25(1):9-12.
[25] ARYAN HE, NEWMAN CB, NOTTMEIER EW, et al. Stabilization of the atlantoaxial complex via C-1 lateral mass and C-2 pedicle screw fixation in a multicenter clinical experience in 102 patients: modification of the Harms and Goel techniques. J Neurosurg Spine. 2008;8(3):222-229.
[26] WANG X, FENG M, HU Y. Establishment and finite element analysis of a three‐dimensional dynamic model of upper cervical spine instability. Orthop Surg. 2019; 11(3):500-509.
[27] GOPINATHAN N R, VISWANATHAN V K, CRAWFORD A I H. Cervical spine evaluation in pediatric trauma: a review and an update of current concepts.Indian J Orthop. 2018;52(5):489-500.
|