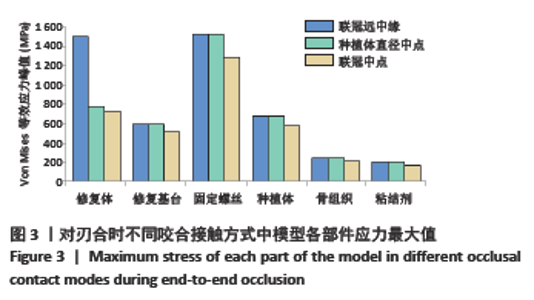
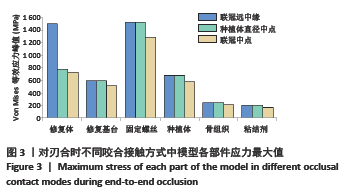
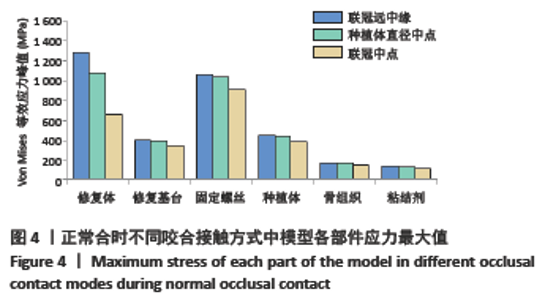
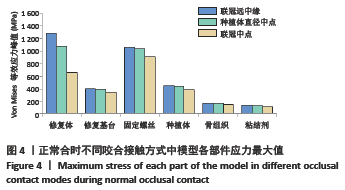
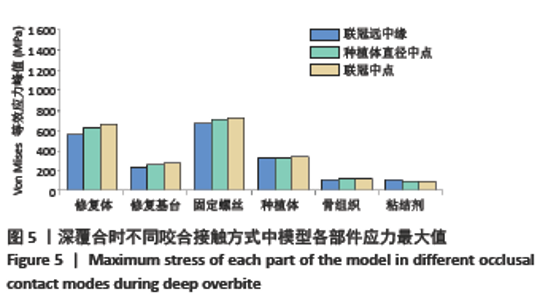
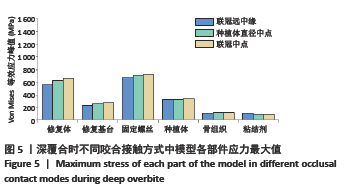
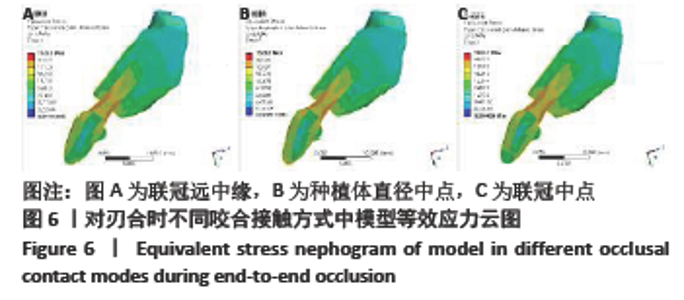
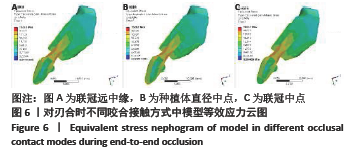
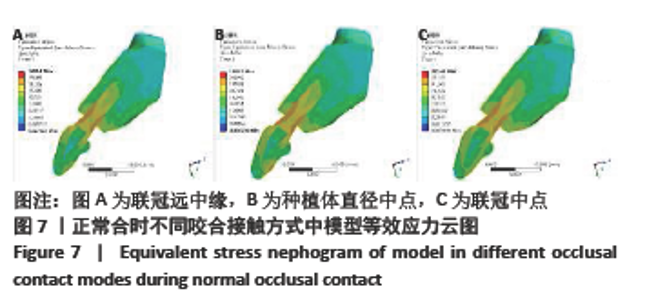
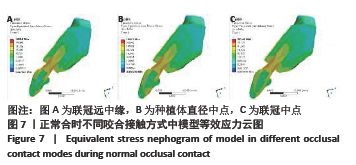
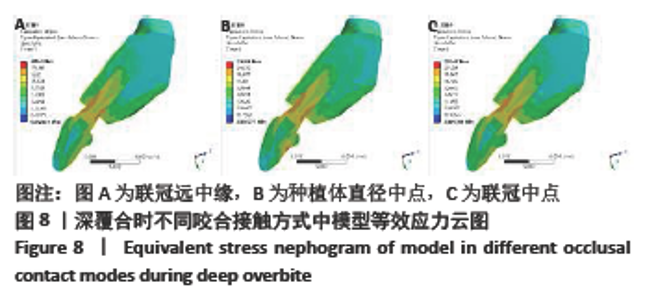
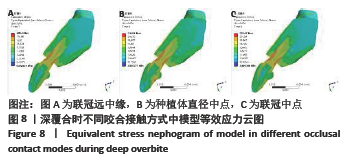
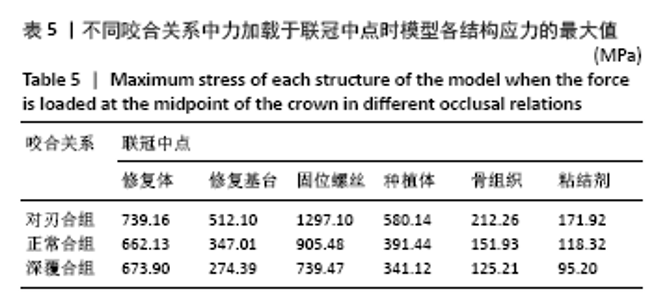
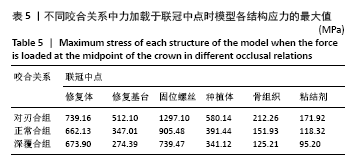
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (4): 567-572.doi: 10.12307/2022.093
Previous Articles Next Articles
Stress analysis of maxillary central incisor crown implant restoration in different occlusal modes
Baibujiafu·Yelisi, Renaguli·Maihemuti, Aizimaitijiang·Saiyiti, Wang Junxiang, Nijiati·Tuerxun
- Department of Stomatology, Second Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830063, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2020-10-27Revised:2020-10-30Accepted:2020-12-07Online:2022-02-08Published:2021-11-03 -
Contact:Nijiati·Tuerxun, Master, Chief physician, Associate professor, Department of Stomatology, Second Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830063, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Baibujiafu·Yelisi, Master candidate, Department of Stomatology, Second Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830063, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, No. 2016D01C192 (to NT)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Baibujiafu·Yelisi, Renaguli·Maihemuti, Aizimaitijiang·Saiyiti, Wang Junxiang, Nijiati·Tuerxun. Stress analysis of maxillary central incisor crown implant restoration in different occlusal modes[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 567-572.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] PRADO FB, ROSSI AC, FREIRE AR, et al. The application of finite element analysis in the skull biomechanics and dentistry Indian. J Dent Res. 2014; 253(3): 390-397. [2] VAN STADEN RC, GUAN H, LOO YC. Application of the finite element method in dental implant research. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2006;9(4): 257-270. [3] TRIVEDI S. Finite element analysis: A boon to dentistry. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2014;4(3):200-203. [4] 韩丽会,邱晓霞,邢旭娜,等.上颌前牙区种植方案中角度设计的三维有限元分析[J].上海口腔医学,2015,24(2):157-163. [5] 王淑英,江青松,蒋向华,等.钛基台支持的CAD/CAM全瓷单冠不同载荷位置的三维有限元应力分析[J].北京口腔医学,2019,27(2):72-75. [6] 魏玮,张寒,陈梦琦,等.钛材料仿生天然磨牙的三维有限元分析[J].南京医科大学学报(自然科学版),2019,39(7):1057-1061. [7] SHURBAJI MOZAYEK R, ALLAF M, ABUHARB MB. Efficacy of adding a supporting implant in stress distribution of long-span fixed partial dentures: a 3D finite element analysis. J Dent Res Dent Clin Dent Prospects. 2016;10(2):81-86. [8] 雍苓,黄仕禄,刘洪,等.不同骨缺损类型牙种植体的三维有限元分析[J].医用生物力学,2016,31(2):148-153. [9] HUSSEIN FA, SALLOOMI KN, ABDULRAHMAN BY, et al. Effect of thread depth and implant shape on stress distribution in anterior and posterior regions of mandible bone: A finite element analysis. Dent Res J. 2019;16(3):200-207. [10] OZAN O, KURTULMUS-YILMAZ S. Biomechanical comparison of different implant inclinations and cantilever lengths in all-on-4 treatment concept by three-dimensional finite element analysis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2018;33(1):64-71. [11] DU L, LI Z, CHANG X, et al. Effects of the screw-access hole diameter on the biomechanical behaviors of 4 types of cement-retained implant prosthodontic systems and their surrounding cortical bones: A 3D finite element analysis. Implant Dent. 2018;27(5):555-563. [12] SHERIDAN RA, DECKER AM, PLONKA AB, et al. The role of occlusion in implant therapy: A comprehensive updated review. Implant Dent. 2016;25(6):829-838. [13] NIROOMAND MR, ARABBEIKI M. Effect of the dimensions of implant body and thread on bone resorption and stability in trapezoidal threaded dental implants: a sensitivity analysis and optimization. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Eng. 2020;(5):1-9. [14] JIANG X, YAO Y, TANG W, et al. Design of dental implants at materials level: An overview. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2020;108(8):1634-1661. [15] ROBERTS SD, KAPADIA H, GREENLEE G, et al. Midfacial and dental changes associated with nasal positive airway pressure in children with obstructive sleep apnea and craniofacial conditions. J Clin Sleep Med. 2016;12(4):469-475. [16] 罗强,丁茜,张磊,等.后牙种植冠桥修复后局部咬合变化的定量分析[J].北京大学学报(医学版),2019,51(6):1119-1123. [17] LEE DJ, LEE JM, KIM EJ, et al. Bio-implant as a novel restoration for tooth loss. Sci Rep. 2017; 7(1): 7414. [18] 甘雪琦,肖宇,马瑞阳,等.种植体的生物力学研究[J].华西口腔医学杂志, 2019,37(2):115-123. [19] 张永丽.四种不同形状种植体应力分布比较的三维有限元分析[D].济南:山东大学,2003. [20] 赵宝红,张娇, 蔺增,等.种植体长度与直径对骨界面应力分布影响的三维有限元分析[J].口腔医学,2014,34(1):22-27. [21] LIU ZY, ZHAO L, YANG LY, et al. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of different endodontic access methods and full crown restoration in the maxillary central incisor. West China Stomatol. 2019;37(6):642-647. [22] BAYRAK A, YARAMANOLU P, KLARSLAN MA, et al. Biomechanical comparison of a new triple cylindrical implant design and a conventional cylindrical implant design on the mandible by three-dimensional finite element analysis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2020;35(2):257-264. [23] KANG X, LI Y, WANG Y, et al. Relationships of stresses on alveolar bone and abutment of dental implant from various bite forces by three-dimensional finite element analysis. BioMed Res Int. 2020;2020(2):1-9. [24] MORITA J, WADA M, MAMENO T, et al. Ideal placement of an implant considering the positional relationship to an opposing tooth in the first molar region: a three-dimensional finite element analysis. Int J Implant Dent. 2020;6(1):31. [25] TRIBST JPM, DAL PIVA AMO, BORGES APLS, et al. Does the prosthesis weight matter? 3D finite element analysis of a fixed implant-supported prosthesis at different weights and implant numbers. J Adv Prosthodont. 2020;12(2):67-74. [26] 连颂峰,林敬凯,蔡坤灿,等.CAD/CAM纯钛烤瓷冠的抗疲劳性与抗折性分析[J].上海口腔医学,2019,28(2):118-122. [27] AZCARATE-VELÁZQUEZ F, CASTILLO-OYAGÜE R, OLIVEROS-LÓPEZ LG, et al. Influence of bone quality on the mechanical interaction between implant and bone: A finite element analysis. J Dent. 2019;88:103161. [28] TOIA M, STOCCHERO M, JINNO Y, et al. Effect of misfit at implant-level framework and supporting bone on internal connection implants: Mechanical and finite element analysis[J]. International J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2019; 34(2): 320-328. [29] 邹英楠,王屹博,丁超,等.动态载荷下双种植体单冠修复下颌磨牙的三维有限元分析[J].口腔医学,2019,39(12):1078-1081+1094. [30] DELGADO-RUIZ RA, CALVO-GUIRADO JL, ROMANOS GE. Effects of occlusal forces on the peri‐implant‐bone interface stability. Periodontology. 2019;81(1):179-193. [31] RODRIGUES EDS, BENETTI P, CARLI JP, et al. A Comparison of torque stress on abutment screw of external hexagon and morse taper implant. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2018;19(11):1306-1311. [32] MANEA A, BACIUT G, BACIUT M, et al. New dental implant with 3D shock absorbers and tooth-like mobility—prototype development, finite element analysis (FEA), and mechanical testing. Materials. 2019;12(20):3444. |
| [1] | Wang Jianping, Zhang Xiaohui, Yu Jinwei, Wei Shaoliang, Zhang Xinmin, Xu Xingxin, Qu Haijun. Application of knee joint motion analysis in machanism based on three-dimensional image registration and coordinate transformation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(在线): 1-5. |
| [2] | Wei Guoqiang, Li Yunfeng, Wang Yi, Niu Xiaofen, Che Lifang, Wang Haiyan, Li Zhijun, Shi Guopeng, Bai Ling, Mo Kai, Zhang Chenchen, Xu Yangyang, Li Xiaohe. Biomechanical analysis of non-uniform material femur under different loads [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1318-1322. |
| [3] | Zhang Yufang, Lü Meng, Mei Zhao. Construction and verification of a full spine biomechanical model of adolescent scoliosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1351-1356. |
| [4] | Zhang Jichao, Dong Yuefu, Mou Zhifang, Zhang Zhen, Li Bingyan, Xu Xiangjun, Li Jiayi, Ren Meng, Dong Wanpeng. Finite element analysis of biomechanical changes in the osteoarthritis knee joint in different gait flexion angles [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1357-1361. |
| [5] | Bai Zixing, Cao Xuhan, Sun Chengyi, Yang Yanjun, Chen Si, Wen Jianmin, Lin Xinxiao, Sun Weidong. Construction and biomechanical analysis of ankle joint finite element model in gait cycle [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1362-1366. |
| [6] | Liu Feng, Feng Yi. Finite element analysis of different Kirschner wire tension bands on transverse patella fractures during gait cycle [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1367-1371. |
| [7] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [8] | Duan Chao, Shang Xiaoqiang, Duan Xianglin, Yang Ping, Tao Shengxiang. Stability of patellar claw versus loop plate combined with patellar claw for the treatment of comminuted fractures of the lower pole of the patella [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 934-937. |
| [9] | Li Guijun, Fang Xiaohui, Kong Weifeng, Yuan Xiaoqing, Jin Rongzhong, Yang Jun. Finite element analysis of the treatment of hallux valgus deformity by microplate combined with super strong suture elastic fixation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 938-942. |
| [10] | Wen Mingtao, Liang Xuezhen, Li Jiacheng, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Mechanical stability of Sanders II type calcaneal fractures fixed by two internal fixation methods [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 838-842. |
| [11] | Wang Hailong, Li Long, Maihemuti·Yakufu, Chen Hongtao, Liu Xu, Yilihamu·Tuoheti. Finite element analysis of stress distribution of acetabular prosthesis in the Lewinnek safety zone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 843-847. |
| [12] | Huang Hao, Hong Song, Wa Qingde. Finite element analysis of the effect of femoral component rotation on patellofemoral joint contact pressure in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 848-852. |
| [13] | Zheng Yongze, Zheng Liqin, He Xingpeng, Chen Xinmin, Li Musheng, Li Pengfei, Lin Ziling. Extended finite element modeling analysis of femoral neck fracture based on ABAQUS software [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 853-857. |
| [14] | Li Shuo, Su Peng, Zhang Li, Wu Qiulong, Hu Xiangyu, Lai Yuliang. Positive effect of supracondylar femoral osteotomy on the correction of knee varus based on three-dimensional reconstruction and finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 858-863. |
| [15] | Wei Bing, Chang Shan. Finite element analysis of different angles of nail placement in sagittal plane of spinal fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 864-869. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||