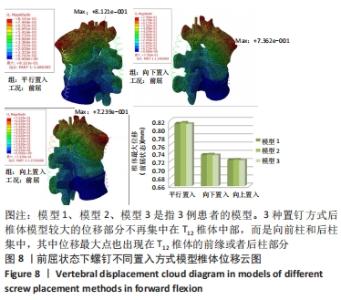
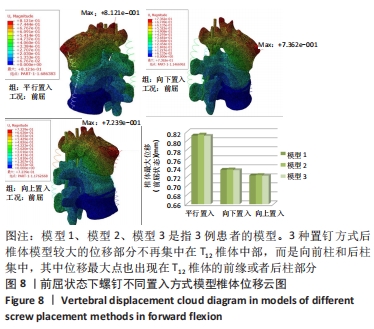
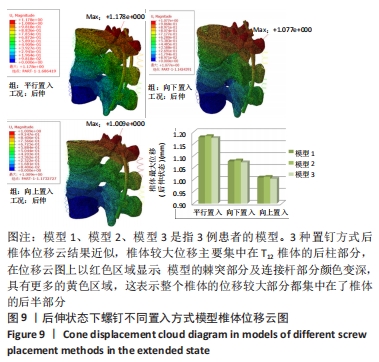
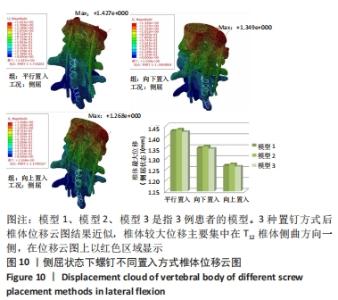
[1] Bouyer B, Vassal M, Zairi F, et al. Surgery in vertebral fracture: epidemiology and functional and radiological results in a prospective series of 518 patients at 1 year’s follow-up. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2015;101:11-15.
[2] 李祖昌,崔冠宇,行勇刚,等.椎弓根螺钉固定强度的影响因素和骨质疏松椎体中增加固定强度的方法[J].骨科临床与研究杂志, 2018,3(1):43-47.
[3] 郝申申,赵如元,刘志斌,等.有限元分析胸腰段脊柱骨折经伤椎置钉的固定[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(31):5060-5065.
[4] 刘观燚.枢椎单侧棘突螺钉联合对侧椎弓根螺钉固定的生物力学有限元分析[D].杭州:浙江大学,2018.
[5] matsukawa k, yato y, imabayashi h, et al. Biomechanical Evaluation of Cross Trajectory Technique for Pedicle Screw Insertion: Combined Use of Traditional Trajectory and Cortical Bone Trajectory. Orthopa Surg. 2015;7(4):1041-1048.
[6] 徐海栋.胸腰椎骨折有限元分析及优化置钉方案研究[D].上海:第二军医大学,2015:1-109.
[7] WU WW, ZHU YB, CHEN W, et al. Bone Hardness of Different Anatomical Regions of Human Radius and its Impact on the Pullout Strength of Screws. Orthop Surg. 2019;11(2):270-276.
[8] shja tm, laun j, gonzalez-blohm sa, et al. Designs and techniques that improve the pullout strength of pedicle screws in osteoporotic vertebrae: current status. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014: 748393.
[9] YING SH, KAO HC, LIU CL. Fixation strength of PMMA-augmented pedicle screws after depth adjustment in a synthetic bone model of osteoporosis. Orthopedics. 2012;35:e1511-1516.
[10] LIU D, SHENG J, LUO Y, et al. Biomechanical comparative study of the stability of injectable pedicle screws with different lateral holes augmented with different volumes of polymethylmethacrylate in osteoporotic lumbar vertebrae. Spine J. 2018;18(9):1637-1644.
[11] 魏兵,许泽川,常山.有限元法分析腰椎椎弓根螺钉的生物力学特征[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(19):3091-3096.
[12] MAHATO NK, DHASON R, RAM DR. Quantifying Range of Motion and Stress Patterns at the Transitional Lumbosacral Junction: Pilot Study Using a Computational Model for Load-Bearing at Accessory L5-S1 Articulation. Spine. 2019;13(1):17-23.
[13] LI Y, FOGEL GR, LIAO Z, et al. Finite element model predicts the biomechanical performance of cervical disc replacement and fusion hybrid surgery with various geometry of ball-and-socket artificial disc. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2017;12(8):1399-1409.
[14] MU X, LI Z, YIN D, et al. Biomechanical Effects of Fixation of Different Segments of Goat Lumbar Spine on Adjacent Segmental Motion and Intradiscal Pressure Change. Med Sci Monit. 2019;25:4885-4891.
[15] FAN W, GUO LX, ZHAO D. Stress analysis of the implants in transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion under static and vibration loadings: a comparison between pedicle screw fixation system with rigid and flexible rods. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2019;30(10):118.
[16] JIE L, HUAN L. Finite Element Analysis of a New Pedicle Screw-Plate System for Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion. PLoS One. 2015;11:1371-1470.
[17] 李浩.老年胸腰椎骨折的有限元分析及其临床应用[D].上海:上海交通大学,2014.
[18] CHOSA E, TAJIMA N. A biomechanical study of lumbarspondy-lolysis based on a 3-dimensional finite element method. Orthop Res. 2004; 22(1):158-163.
[19] JENDOUBI K, KHADRI Y, BENDJABALLAH M, et al. Effects of the Insertion Type and Depth on the Pedicle Screw Pullout Strength: A Finite Element Study. Appl Bionics Biomech. 2018;2018:1460195.
[20] KINER DW, BARTOL SW, VAIDYA R. Biomechanicalanalysis of different techniques in revision spinal instrumentation: larger diameter screws versus cement augmentation. Spine. 2008;33:2618-2622.
[21] SENGUPTA DK. Pedicle screw-based posterior dynamic stabilization:literature review. Adv Orthop. 2012:4242-4268.
[22] ABSHIRE BB, KAMBIC HE. Characteristics of pullout failure in conical and cylindrical pedicle screws after full insertion and back-out. Spine J. 2001;1:408-414.
[23] NAKASHIMA D, ISHII K, NISHIWAKI Y, et al. Quantitative CT-based bone strength parameters for the prediction of novel spinal implant stability using resonance frequency analysis: a cadaveric study involving experimental micro-CT and clinical multislice CT. Eur Radiol Exp. 2019; 3(1):1-8.
[24] 杜炜,钱明权.椎弓根螺钉植入椎体深度与其稳定性的生物力学分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(9):1289-1294.
[25] ROY-CAMILLE R, MAZEL C. Internal fixation of the lumbar spine with pedicle screw plating. Clin Orthop. 1986;(203):7-17.
[26] MAGERL FP. Stabilization of the lower thoracic and lumbar spine with external skeletal fixation. Clin Orthop. 1984;(189):125-141.
[27] KRAG MH, BEYNNON BD. Placement of transpedicular vertebral screws close to anterior vertebral cortex.Description of method. Spine. 1989;14(8):879-883.
[28] KORKMAZ MF, ERDEM MN, OZEVREN H, et al. Determining the Optimal Length and Safety of Pedicle Screws in the T12 Vertebra: A Morphometric Study. Cureus. 2018;10(2):e2156.
[29] MULLER ME, ALLGOWER M, SCHNEIDER R. Manual of internal fixation techniques recommended by the AO ASIF group. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 1991:666-670.
[30] 王正,沈国平,陈伟兵,等.椎弓根螺钉内固定稳定性的生物力学测试[J].医用生物力学,2002,17(2):80-84.
|