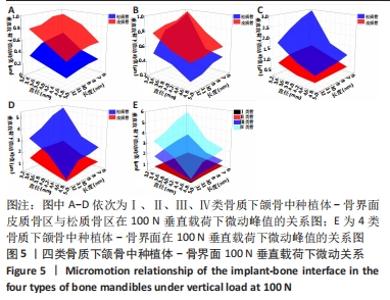
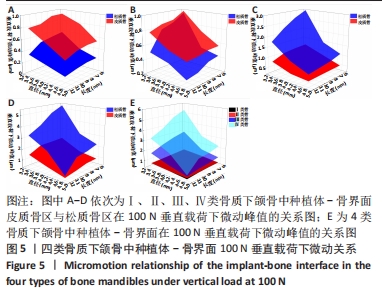
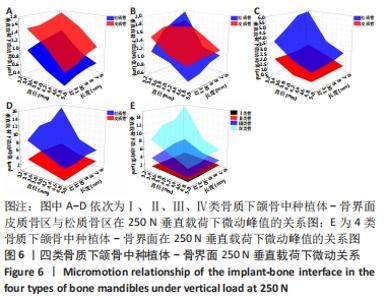
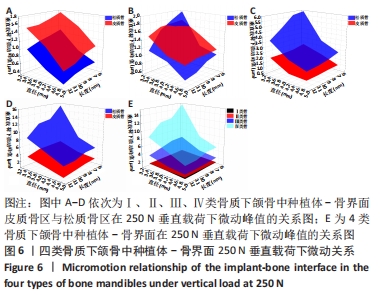
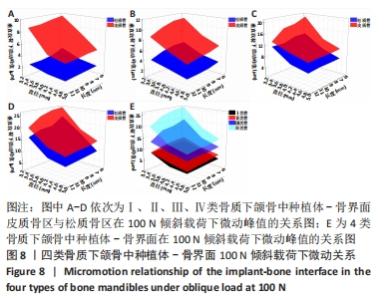
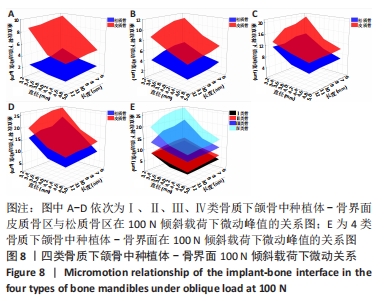
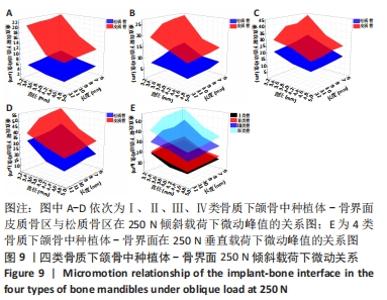
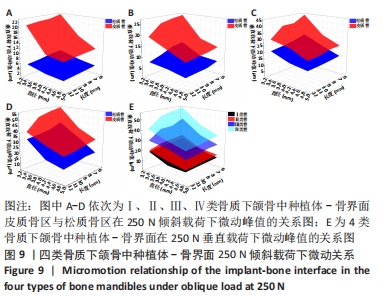
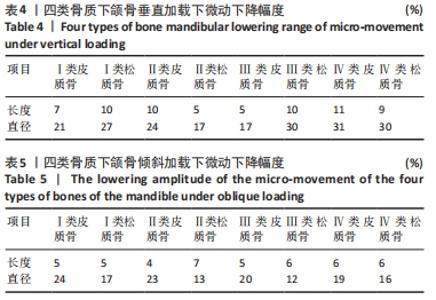
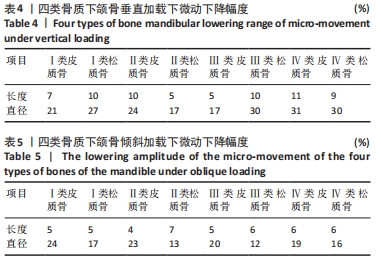
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (6): 875-880.doi: 10.12307/2022.169
Previous Articles Next Articles
Finite element analysis on the effect of implant length and diameter on initial stability under different bone conditions
Gao Wenbo, Ma Zongmin, Li Shuxian, Nie Xiuji
- School of Mechanical Engineering, Dalian University, Dalian 116622, Liaoning Province, China
-
Received:2021-04-27Revised:2021-05-06Accepted:2021-06-30Online:2022-02-28Published:2021-12-07 -
Contact:Ma Zongmin, MD, Associate professor, School of Mechanical Engineering, Dalian University, Dalian 116622, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Gao Wenbo, Master candidate, School of Mechanical Engineering, Dalian University, Dalian 116622, Liaoning Province, China -
Supported by:the Liaoning Provincial Department of Education Scientific Research Fund Project, No. jyt-dldxfw202004 (to LSX); the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 11602047 (to LSX); the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 11572066 (to MZM)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Gao Wenbo, Ma Zongmin, Li Shuxian, Nie Xiuji. Finite element analysis on the effect of implant length and diameter on initial stability under different bone conditions[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 875-880.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] RAIKAR S, TALUKDAR P, KUMARI S, et al. Factors Affecting the Survival Rate of Dental Implants: A Retrospective Study. J Int Soc Prev Community Dent. 2017; 7(6):351-355. [2] ESPOSITO M, GRUSOVIN MG, COULTHARD P, et al. Different loading strategies of dental implants: a Cochrane systematic review of randomised controlled clinical trials. Eur J Oral Implantol. 2008;1(4):259-276. [3] ROMANOS GE. Surgical and prosthetic concepts for predictable immediate loading of oral implants. J Calif Dent Assoc. 2004;32(12):991-1001. [4] 庞琴,王超,马小娟,等.IT与ISQ能反映种植体初期稳定性吗[J].口腔医学研究,2017,33(2):150-153. [5] 许竞.种植初期稳定性的意义及其参数标准[J].口腔疾病防治,2021,29(1): 1-10. [6] 方菊,吴涛.植入扭矩与种植体骨结合的研究进展[J].中国口腔种植学杂志,2020,25(4):187-191. [7] 陈子强,周文娟,柳忠豪.共振频率分析技术在口腔种植中的应用[J].中国口腔种植学杂志,2020,25(1):47-50. [8] NORTON MR. The Influence of Low Insertion Torque on Primary Stability, Implant Survival, and Maintenance of Marginal Bone Levels: A Closed-Cohort Prospective Study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2017;32(4):849-857. [9] MATYS J, ŚWIDER K, FLIEGER R, et al. Assessment of the primary stability of root analog zirconia implants designed using cone beam computed tomography software by means of the Periotest® device: An ex vivo study. A preliminary report. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2017;26(5):803-809. [10] REA M, LANG NP, RICCI S, et al. Healing of implants installed in over- or under-prepared sites--an experimental study in dogs. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2015; 26(4):442-446. [11] WIECZOREK K, HARZER W, WEHRBEIN H, et al. Predictive values of resonance frequency analysis as a diagnostic tool in palatal implant loss. Angle Orthod. 2019;89(5):721-726. [12] WAECHTER J, MADRUGA MM, CARMO FILHO LCD, et al. Comparison between tapered and cylindrical implants in the posterior regions of the mandible: A prospective, randomized, split-mouth clinical trial focusing on implant stability changes during early healing. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2017;19(4):733-741. [13] TURKYILMAZ I, TOZUM TF. Enhancing primary implant stability by undersizing implant site preparation: A human cadaver study. J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2020;121(1):58-62. [14] DÍAZ-CASTRO MC, FALCAO A, LÓPEZ-JARANA P, et al. Repeatability of the resonance frequency analysis values in implants with a new technology. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2019;24(5):e636-e642. [15] BAFIJARI D, BENEDETTI A, STAMATOSKI A, et al. Influence of Resonance Frequency Analysis (RFA) Measurements for Successful Osseointegration of Dental Implants During the Healing Period and Its Impact on Implant Assessed by Osstell Mentor Device. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2019;7(23):4110-4115. [16] LEE J, PYO SW, CHO HJ, et al. Comparison of implant stability measurements between a resonance frequency analysis device and a modified damping capacity analysis device: an in vitro study. J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2020;50(1): 56-66. [17] HUANG HM, CHEE TJ, LEW WZ, et al. Modified surgical drilling protocols influence osseointegration performance and predict value of implant stability parameters during implant healing process. Clin Oral Investig. 2020;24(10):3445-3455. [18] BAVETTA G, BAVETTA G, RANDAZZO V, et al. A Retrospective Study on Insertion Torque and Implant Stability Quotient (ISQ) as Stability Parameters for Immediate Loading of Implants in Fresh Extraction Sockets. Biomed Res Int. 2019;11(3):1-10. [19] VELMURUGAN D, ALPHIN M S. Micromotion of Immediately Loaded Zirconia Dental Implants for Various Parametric Conditions: A Three-Dimensional Finite Element Study. J Biomater Tiss Eng. 2018;8(7):962-971. [20] 吕佳,刘翠玲,蓝菁,等.动态载荷下种植体位置和直径对悬臂梁种植固定义齿应力影响的三维有限元研究[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2013,31(6):552-556. [21] 安尼卡尔·安尼瓦尔,帕丽黛姆·图尔迪,阿迪力·麦木提敏,等.上颌前牙区不同种植修复体在不同咬合受力下的三维有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(16):2531-2536. [22] LI Z, GAO S, CHEN H, et al. Micromotion of implant-abutment interfaces (IAI) after loading: correlation of finite element analysis with in vitro performances. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2019;57(5):1133-1144. [23] 缑小蕊,周政,姜丹丹,等.种植覆盖义齿修复不同骨质类型的Kennedy Ⅰ类缺失的三维有限元分析[J].口腔医学研究,2020,36(9):855-860. [24] 葛奕辰,蒋少康,李轻如,等.”All-on-4”在不同骨质条件下应力分布的三维有限元分析[J].口腔医学研究,2016,32(12):1252-1256. [25] Ding X, Zhu XH, Liao SH,et al.Implant-bone interface stress distribution in immediately loaded implants of different diameters: a three-dimensional finite element analysis. J Prosthodont. 2009;18(5):393-402. [26] 游嘉,周乐峰,彭伟,等.面向即刻种植的种植体的初期稳定性研究[J].中国生物医学工程学报,2016,35(3):324-329. [27] BAGGI L, CAPPELLONI I, DI GIROLAMO M, et al. The influence of implant diameter and length on stress distribution of osseointegrated implants related to crestal bone geometry: a three-dimensional finite element analysis. J Prosthet Dent. 2008;100(6):422-431. [28] MESNARD M, RAMOS A, SIMÕES JA. Influences of implant condyle geometry on bone and screw strains in a temporomandibular implant. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2014;42(3):194-200. [29] FAVERANI LP, BARÃO VA, RAMALHO-FERREIRA G, et al. The influence of bone quality on the biomechanical behavior of full-arch implant-supported fixed prostheses. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2014;37:164-170. [30] 张杨,王超,张晓南,等.动态载荷下不同骨质对天然牙-种植体联合修复应力分布的影响[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2015,33(3):286-290. [31] TETTAMANTI L, ANDRISANI C, BASSI MA, et al. Immediate loading implants: review of the critical aspects. Oral Implantol (Rome). 2017;10(2):129-139. [32] FERNANDES EDE L, UNIKOWSKI IL, TEIXEIRA ER, et al. Primary stability of turned and acid-etched screw-type implants: a removal torque and histomorphometric study in rabbits. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2007;22(6):886-892. [33] OVERMANN AL, APARICIO C, RICHARDS JT, et al. Orthopaedic osseointegration: Implantology and future directions. J Orthop Res. 2020;38(7):1445-1454. [34] IKAR M, GROBECKER-KARL T, KARL M, et al. Mechanical stress during implant surgery and its effects on marginal bone: a literature review. Quintessence Int. 2020;51(2):142-150. [35] MERHEB J, TEMMERMAN A, RASMUSSON L, et al. Influence of Skeletal and Local Bone Density on Dental Implant Stability in Patients with Osteoporosis. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2016;18(2):253-260. [36] 莫嘉骥,姒蜜思,周仲豪,等.Straumann种植体早期稳定性相关因素的研究[J].中国口腔颌面外科杂志,2012(5):381-385. [37] 刘东,吴煜农.旋入扭矩值与共振频率分析对种植体初期稳定性的相关性研究[J].口腔医学,2020,40(5):426-431. [38] ARAGONESES JM, SUÁREZ A, BRUGAL VA, et al. Frequency Values and Their Relationship With the Diameter of Dental Implants. Prospective Study of 559 Implants. Implant Dent. 2019;28(3):279-288. [39] MELLADO-VALERO A, FERRER-GARCÍA JC, CALVO-CATALÁ J, et al. Implant treatment in patients with osteoporosis. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2010; 15(1):e52-e57. [40] 彭伟,周乐峰,徐旭,等.多根牙种植体初期稳定性的有限元分析[J].浙江工业大学学报,2016,44(3):283-287. [41] DELIVERSKA E, YORDANOV B. Osseodensification as an Alternative Approach in Dental Implantology for Implant Sites with Insufficient Available Bone. J IMAB. 2019;25(3):2606-2610. [42] RUES S, SCHMITTER M, KAPPEL S, et al. Effect of bone quality and quantity on the primary stability of dental implants in a simulated bicortical placement. Clin Oral Investig. 2021;25(3):1265-1272. [43] 钱文涛,张瑛,浦益萍,等.下颌后牙区骨组织与种植体初期稳定性的相关性研究[J].中国口腔种植学杂志,2013,18(1):1-6. [44] BARIKANI H, RASHTAK S, AKBARI S, et al. The effect of implant length and diameter on the primary stability in different bone types. J Dent (Tehran). 2013; 10(5):449-455. [45] 李璐丽,张松,房玉杰.牙种植体植入扭矩影响因素的分析及预测模型[J].工具技术,2019,53(7):31-36. [46] FAZEL A, AALAI S, RISMANCHIAN M. Effect of macro-design of immediately loaded implants on micromotion and stress distribution in surrounding bone using finite element analysis. Implant Dent. 2009;18(4):345-352. [47] GÓMEZ-POLO M, ORTEGA R, GÓMEZ-POLO C, et al. Does Length, Diameter, or Bone Quality Affect Primary and Secondary Stability in Self-Tapping Dental Implants. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2016;74(7):1344-1353. |
| [1] | Li Chenjie, Lü Linwei, Song Yang, Liu Jingna, Zhang Chunqiu. Measurement and statistical analysis of trabecular morphological parameters of titanium alloy peri-prosthesis under preload [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 516-520. |
| [2] | Shi Xiaoxiu, Mao Shilong, Liu Yang, Ma Xingshuang, Luo Yanfeng. Comparison of tantalum and titanium (alloy) as orthopedic materials: physical and chemical indexes, antibacterial and osteogenic ability [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 593-599. |
| [3] | Yang Ruimin, Wu Wenzheng, Zheng Yongze, Zheng Xiaohui. Finite element analysis of the effect of different cancellous bone volume fraction on the apparent mechanical response of proximal femur [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(36): 5765-5770. |
| [4] | Huo Hua, Cheng Yuting, Zhou Qian, Qi Yuhan, Wu Chao, Shi Qianhui, Yang Tongjing, Liao Jian, Hong Wei. Effects of drug coating on implant surface on the osseointegration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3558-3564. |
| [5] | Liu Chang, Wang Na, Li Yukun, Xue Peng. Effect of advanced glycation end products on metabolism of bone tissue cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(27): 4376-4382. |
| [6] |
Dong Xiling, Zhang Xiaoming, Liu Tongbin.
Recombinant human parathyroid hormone (1-34): pro-osteogenic action and application in oral field [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(26): 4231-4236. |
| [7] | Zhang Lan, Wang Xiang, Liu Jun, Zhang Chunqiu, Ye Jinduo, Liu Lu. Tensile properties of three-dimensional printed porous titanium alloy trabecular bone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(22): 3498-3503. |
| [8] | Fan Shifeng, Qie Hui, Zhang Wenxuan, Hou Xiaowei, Wang Lijie, Zheng Yu. Comparison of the effects of topical application of zoledronic acid and silver nanoparticles on osseointegration of immediate implant [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(10): 1547-1552. |
| [9] | Wu Yeke, Gao Ranran, Zhao Lixing. Orthodontic micro-implant stability under continuous or intermittent loading: a histomorphometric and biomechanical evaluation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(22): 3488-3494. |
| [10] | He Tao, Zhang Yunhui, Zhang Chao, Xu Zhiguo, Dong Yuqi. Evaluation of osseointegration of plasma electrolytic oxidation coated titanium implants in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(34): 5469-5476. |
| [11] |
Sun Zhi-hui, Zheng Yu, Wang Li-jie, Fan Shi-feng, Hou Xiao-wei.
The local application of recombinant human parathyroid hormone (1-34) promotes osseointegration of an immediate implant
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(26): 4210-4216.
|
| [12] |
Li Rui-yan, Liu Guan-cong, Liang Hao-jun, Qin Yan-guo.
Research progress of strontium-doped biomedical titanium alloys
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(2): 309-314.
|
| [13] | Liang Hao-jun, Li Rui-yan, Liu Guan-cong, Qin Yan-guo. Design of the porous orthopedic implants: research and application status [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(15): 2410-2417. |
| [14] | Liang Yao-zhong1, Chen Shu2, Yang Yu-hao1, Lan Chun-hai1, Zhang Guo-wei1, Ji Zhi-sheng1, . Atorvastatin promotes implant osseointegration via the activation of Wnt/β-catenin signal pathway in osteoporotic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(20): 2940-2948. |
| [15] | Lin Yang-dong, Wu Ye-ke. Factors affecting the stability of mini-implants [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(8): 1295-1300. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||