Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (27): 4376-4382.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2776
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of advanced glycation end products on metabolism of bone tissue cells
Liu Chang, Wang Na, Li Yukun, Xue Peng
- Second Department of Endocrinology, the Third Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050001, Hebei Province, China
-
Received:2020-01-14Revised:2020-01-17Accepted:2020-02-26Online:2020-09-28Published:2020-09-10 -
Contact:Xue Peng, MD, Associate professor, Second Department of Endocrinology, the Third Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050001, Hebei Province, China -
About author:Liu Chang, Master candidate, Second Department of Endocrinology, the Third Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050001, Hebei Province, China -
Supported by:the High-Level Talent Support Project of Hebei Province, No. A2017003079; the Basic Research Cooperation Project of Beijing, Tianjin and Hebei Province, No. 19JCZDJC65500Z; the Medical Applicable Technology Following Project of Hebei Province, No. G2019008; the Developing Program for Young and Middle-aged Doctors with Osteoporosis and Bone Mineral Diseases, No. GX20191107
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Chang, Wang Na, Li Yukun, Xue Peng. Effect of advanced glycation end products on metabolism of bone tissue cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(27): 4376-4382.
share this article

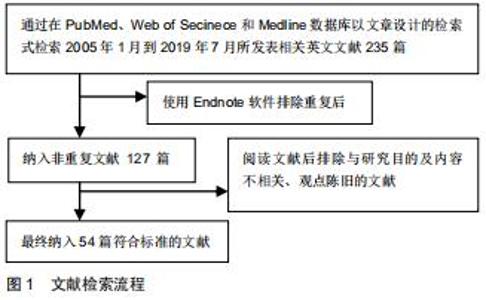
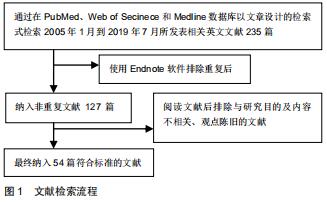
综上所述,骨骼中晚期糖基化终末产物的积累在一定程度上对骨骼生物力学性能产生一定的负性影响,它与Ⅰ型胶原的合成及降解有关,打破了Ⅰ型胶原合成和降解之间的平衡,降低骨组织强度,增加骨脆性及骨折风险[15]。另外,在细胞分子水平上,晚期糖基化终末产物可与多个受体结合发生作用,增加氧化应激和炎症反应[16],抑制正常的酶促胶原交联反应,导致胶原结构破坏。同时氧化应激反应也可导致晚期糖基化终末产物增多,进一步加剧胶原结构破坏。近年来在这些受体中发现,RAGE是最具特征的受体之一,可在成骨细胞、破骨细胞及骨细胞中表达[17-18],通过多种机制刺激晚期糖基化终末产物产生活性氧和炎症[19],并使产生的炎症信号持续存在,造成骨组织细胞病理改变[20-21],见表1。 "

|
[1] YAMAMOTO M, SUGIMOTO T. Advanced Glycation End Products, Diabetes, and Bone Strength. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2016;14(6):320-326.
[2] SANGUINETI R, PUDDU A, MACH F, et al. Advanced glycation end products play adverse proinflammatory activities in osteoporosis. Mediators Inflamm. 2014;2014:975872.
[3] GARNERO P, BOREL O, GINEYTS E, et al. Extracellular post-translational modifications of collagen are major determinants of biomechanical properties of fetal bovine cortical bone. Bone. 2006;38(3):300-309.
[4] VASHISHTH D. The role of the collagen matrix in skeletal fragility. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2007;5(2):62-66.
[5] SEMBA RD, NICKLETT EJ, FERRUCCI L. Does accumulation of advanced glycation end products contribute to the aging phenotype? J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2010; 65(9):963-975.
[6] GRIMSBY JL, LUCERO HA, TRACKMAN PC, et al. Role of lysyl oxidase propeptide in secretion and enzyme activity. J Cell Biochem. 2010;111(5):1231-1243.
[7] BANSE X, SIMS TJ, BAILEY AJ. Mechanical properties of adult vertebral cancellous bone: correlation with collagen intermolecular cross-links. J Bone Miner Res. 2002;17(9): 1621-1628.
[8] OXLUND H, BARCKMAN M, ORTOFT G, et al. Reduced concentrations of collagen cross-links are associated with reduced strength of bone. Bone. 1995;17(4 Suppl): 365S-371S.
[9] EVERTS V, KORPER W, DOCHERTY AJ, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors block osteoclastic resorption of calvarial bone but not the resorption of long bone. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1999;878:603-606.
[10] 秦健,王志辉,毕仕强.绝经后妇女血清基质金属蛋白酶-2、-9与骨转换生化指标及骨密度的关系[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2009, 15(4):292-295.
[11] LI W, LING W, TENG X, et al. Effect of advanced glycation end products, extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer and matrix metalloproteinases on type-I collagen metabolism. Biomed Rep. 2016;4(6):691-693.
[12] YAMAMOTO T, OZONO K. Role of advanced glycation endproducts in adynamic bone disease. Clin Calcium. 2001; 11(8):1044-1047. [13] 谢斌,陈允震,刘海春.骨胶原在骨质疏松中的作用[J].中国老年学杂志,2009,29(16):2057-2059.
[14] KNOTT L, WHITEHEAD CC, FLEMING RH, et al. Biochemical changes in the collagenous matrix of osteoporotic avian bone. Biochem J. 1995;310 (Pt 3):1045-1051.
[15] HEIN G, WIEGAND R, LEHMANN G, et al. Advanced glycation end-products pentosidine and N epsilon-carboxymethyllysine are elevated in serum of patients with osteoporosis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2003;42(10): 1242-1246.
[16] GEFTER JV, SHAUFL AL, FINK MP, et al. Comparison of distinct protein isoforms of the receptor for advanced glycation end-products expressed in murine tissues and cell lines. Cell Tissue Res. 2009;337(1):79-89.
[17] MERCER N, AHMED H, ETCHEVERRY SB, et al. Regulation of advanced glycation end product (AGE) receptors and apoptosis by AGEs in osteoblast-like cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 2007;306(1-2):87-94.
[18] TANAKA K, YAMAGUCHI T, KANAZAWA I, et al. Effects of high glucose and advanced glycation end products on the expressions of sclerostin and RANKL as well as apoptosis in osteocyte-like MLO-Y4-A2 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;461(2):193-199.
[19] RAMASAMY R, YAN SF, SCHMIDT AM. Advanced glycation endproducts: from precursors to RAGE: round and round we go. Amino Acids. 2012;42(4):1151-1161.
[20] LIU J, MAO J, JIANG Y, et al. AGEs Induce Apoptosis in Rat Osteoblast Cells by Activating the Caspase-3 Signaling Pathway Under a High-Glucose Environment In Vitro. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2016;178(5):1015-1027.
[21] YANG X, GANDHI C, RAHMAN MM, et al. Age-Related Effects of Advanced Glycation End Products (Ages) in Bone Matrix on Osteoclastic Resorption. Calcif Tissue Int. 2015; 97(6):592-601.
[22] OKAZAKI K, YAMAGUCHI T, TANAKA K, et al. Advanced glycation end products (AGEs), but not high glucose, inhibit the osteoblastic differentiation of mouse stromal ST2 cells through the suppression of osterix expression, and inhibit cell growth and increasing cell apoptosis. Calcif Tissue Int. 2012; 91(4):286-296.
[23] NOTSU M, YAMAGUCHI T, OKAZAKI K, et al. Advanced glycation end product 3 (AGE3) suppresses the mineralization of mouse stromal ST2 cells and human mesenchymal stem cells by increasing TGF-β expression and secretion. Endocrinology. 2014;155(7):2402-2410.
[24] TANAKA K, YAMAGUCHI T, KAJI H, et al. Advanced glycation end products suppress osteoblastic differentiation of stromal cells by activating endoplasmic reticulum stress. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;438(3):463-467.
[25] MENG HZ, ZHANG WL, LIU F, et al. Advanced Glycation End Products Affect Osteoblast Proliferation and Function by Modulating Autophagy Via the Receptor of Advanced Glycation End Products/Raf Protein/Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase/Extracellular Signal-regulated Kinase Kinase/Extracellular Signal-regulated Kinase (RAGE/Raf/MEK/ERK) Pathway. J Biol Chem. 2015;290(47): 28189-28199. [26] LI G, XU J, LI Z. Receptor for advanced glycation end products inhibits proliferation in osteoblast through suppression of Wnt, PI3K and ERK signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012;423(4):684-689.
[27] ALIKHANI M, ALIKHANI Z, BOYD C, et al. Advanced glycation end products stimulate osteoblast apoptosis via the MAP kinase and cytosolic apoptotic pathways. Bone. 2007; 40(2):345-353.
[28] WEINBERG E, MAYMON T, WEINREB M. AGEs induce caspase-mediated apoptosis of rat BMSCs via TNFα production and oxidative stress. J Mol Endocrinol. 2014; 52(1):67-76.
[29] DING KH, WANG ZZ, HAMRICK MW, et al. Disordered osteoclast formation in RAGE-deficient mouse establishes an essential role for RAGE in diabetes related bone loss. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006;340(4):1091-1097.
[30] KOGIANNI G, MANN V, NOBLE BS. Apoptotic bodies convey activity capable of initiating osteoclastogenesis and localized bone destruction. J Bone Miner Res. 2008;23(6):915-927.
[31] VALCOURT U, MERLE B, GINEYTS E, et al. Non-enzymatic glycation of bone collagen modifies osteoclastic activity and differentiation. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(8):5691-5703.
[32] LI Z, LI C, ZHOU Y, et al. Advanced glycation end products biphasically modulate bone resorption in osteoclast-like cells. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2016;310(5):E355-E366.
[33] NOTSU M, KANAZAWA I, TAKENO A, et al. Advanced Glycation End Product 3 (AGE3) Increases Apoptosis and the Expression of Sclerostin by Stimulating TGF-β Expression and Secretion in Osteocyte-Like MLO-Y4-A2 Cells. Calcif Tissue Int. 2017;100(4):402-411.
[34] CHEN H, LIU W, WU X, et al. Advanced glycation end products induced IL-6 and VEGF-A production and apoptosis in osteocyte-like MLO-Y4 cells by activating RAGE and ERK1/2, P38 and STAT3 signalling pathways. Int Immunopharmacol. 2017;52:143-149.
[35] KUME S, KATO S, YAMAGISHI S, et al. Advanced glycation end-products attenuate human mesenchymal stem cells and prevent cognate differentiation into adipose tissue, cartilage, and bone. J Bone Miner Res. 2005;20(9):1647-1658.
[36] FRANKE S, RÜSTER C, PESTER J, et al. Advanced glycation end products affect growth and function of osteoblasts. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2011;29(4):650-660.
[37] MOMMA H, NIU K, KOBAYASHI Y, et al. Skin advanced glycation end-product accumulation is negatively associated with calcaneal osteo-sono assessment index among non-diabetic adult Japanese men. Osteoporos Int. 2012;23(6): 1673-1681.
[38] YANG X, MOSTAFA AJ, APPLEFORD M, et al. Bone Formation is Affected by Matrix Advanced Glycation End Products (AGEs) In Vivo. Calcif Tissue Int. 2016;99(4): 373-383.
[39] YANG L, MENG H, YANG M. Autophagy protects osteoblasts from advanced glycation end products-induced apoptosis through intracellular reactive oxygen species.J Mol Endocrinol. 2016;56(4):291-300. [40] CARAMÉS B, TANIGUCHI N, OTSUKI S, et al. Autophagy is a protective mechanism in normal cartilage, and its aging-related loss is linked with cell death and osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62(3):791-801.
[41] HOCKING LJ, WHITEHOUSE C, HELFRICH MH. Autophagy: a new player in skeletal maintenance? J Bone Miner Res. 2012;27(7):1439-1447.
[42] ZHOU Z, IMMEL D, XI CX, et al. Regulation of osteoclast function and bone mass by RAGE. J Exp Med. 2006;203(4): 1067-1080.
[43] PHILIP BK, CHILDRESS PJ, ROBLING AG, et al. RAGE supports parathyroid hormone-induced gains in femoral trabecular bone. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2010; 298(3):E714-E725.
[44] MIYATA T, NOTOYA K, YOSHIDA K, et al. Advanced glycation end products enhance osteoclast-induced bone resorption in cultured mouse unfractionated bone cells and in rats implanted subcutaneously with devitalized bone particles. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1997;8(2):260-270.
[45] BONEWALD LF, JOHNSON ML. Osteocytes, mechanosensing and Wnt signaling. Bone. 2008;42(4): 606-615.
[46] BELLIDO T. Osteocyte-driven bone remodeling. Calcif Tissue Int. 2014;94(1):25-34.
[47] WEINSTEIN RS, NICHOLAS RW, MANOLAGAS SC. Apoptosis of osteocytes in glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis of the hip. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000;85(8): 2907-2912.
[48] DUNSTAN CR, SOMERS NM, EVANS RA. Osteocyte death and hip fracture. Calcif Tissue Int. 1993;53 Suppl 1: S113-S117.
[49] JILKA RL, O'BRIEN CA, ROBERSON PK, et al. Dysapoptosis of osteoblasts and osteocytes increases cancellous bone formation but exaggerates cortical porosity with age. J Bone Miner Res. 2014;29(1):103-117.
[50] CHEUNG WY, SIMMONS CA, YOU L. Osteocyte apoptosis regulates osteoclast precursor adhesion via osteocytic IL-6 secretion and endothelial ICAM-1 expression. Bone. 2012; 50(1):104-110.
[51] JILKA RL, NOBLE B, WEINSTEIN RS. Osteocyte apoptosis. Bone. 2013;54(2):264-271.
[52] WAUTIER MP, GUILLAUSSEAU PJ, WAUTIER JL. Activation of the receptor for advanced glycation end products and consequences on health. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2017;11(4): 305-309.
[53] TEISSIER T, BOULANGER É. The receptor for advanced glycation end-products (RAGE) is an important pattern recognition receptor (PRR) for inflammaging. Biogerontology. 2019;20(3):279-301. [54] YONEKURA H, YAMAMOTO Y, SAKURAI S, et al. Novel splice variants of the receptor for advanced glycation end-products expressed in human vascular endothelial cells and pericytes, and their putative roles in diabetes-induced vascular injury. Biochem J. 2003;370(Pt 3):1097-1109. |
| [1] | Tang Hui, Yao Zhihao, Luo Daowen, Peng Shuanglin, Yang Shuanglin, Wang Lang, Xiao Jingang. High fat and high sugar diet combined with streptozotocin to establish a rat model of type 2 diabetic osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1207-1211. |
| [2] | Li Zhongfeng, Chen Minghai, Fan Yinuo, Wei Qiushi, He Wei, Chen Zhenqiu. Mechanism of Yougui Yin for steroid-induced femoral head necrosis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1256-1263. |
| [3] | Hou Guangyuan, Zhang Jixue, Zhang Zhijun, Meng Xianghui, Duan Wen, Gao Weilu. Bone cement pedicle screw fixation and fusion in the treatment of degenerative spinal disease with osteoporosis: one-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 878-883. |
| [4] | Li Shibin, Lai Yu, Zhou Yi, Liao Jianzhao, Zhang Xiaoyun, Zhang Xuan. Pathogenesis of hormonal osteonecrosis of the femoral head and the target effect of related signaling pathways [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 935-941. |
| [5] | Xiao Fangjun, Chen Shudong, Luan Jiyao, Hou Yu, He Kun, Lin Dingkun. An insight into the mechanism of Salvia miltiorrhiza intervention on osteoporosis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 772-778. |
| [6] | Liu Bo, Chen Xianghe, Yang Kang, Yu Huilin, Lu Pengcheng. Mechanism of DNA methylation in exercise intervention for osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 791-797. |
| [7] | Zhong Yuanming, Wan Tong, Zhong Xifeng, Wu Zhuotan, He Bingkun, Wu Sixian. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of percutaneous curved vertebroplasty and unilateral pedicle approach percutaneous vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 456-462. |
| [8] | Nie Shaobo, Li Jiantao, Sun Jien, Zhao Zhe, Zhao Yanpeng, Zhang Licheng, Tang Peifu. Mechanical stability of medial support nail in treatment of severe osteoporotic intertrochanteric fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 329-333. |
| [9] | Zhu Yun, Chen Yu, Qiu Hao, Liu Dun, Jin Guorong, Chen Shimou, Weng Zheng. Finite element analysis for treatment of osteoporotic femoral fracture with far cortical locking screw [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3832-3837. |
| [10] | Feng Guancheng, Fang Jianming, Lü Haoran, Zhang Dongsheng, Wei Jiadong, Yu Bingbing. How does bone cement dispersion affect the early outcome of percutaneous vertebroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3450-3457. |
| [11] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [12] | Cai Qunbin, Yang Lijuan, Li Qiumin, Chen Xinmin, Zheng Liqin, Huang Peizhen, Lin Ziling, Jiang Ziwei . Feasibility of internal fixation removal of intertrochanteric fractures in elderly patients based on fracture mechanics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3313-3318. |
| [13] | Liu Yulin, Li Guotai. Combined effects of hyperbaric oxygen, vibration training and astaxanthin on bone mineral density, glucose metabolism and oxidative stress in diabetic osteoporosis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3117-3124. |
| [14] | Lin Haishan, Mieralimu Muertizha, Li Peng, Ma Chao, Wang Li. Correlation between skeletal muscle fiber characteristics and bone mineral density in postmenopausal women with hip fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3144-3149. |
| [15] | Hu Guang, Guan Zhiyu, Zhang Kaiwei . Mechanism underlying the interventional effect of Panax Notoginsenosides on ovariectomized osteoporotic fracture rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 172-177. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||