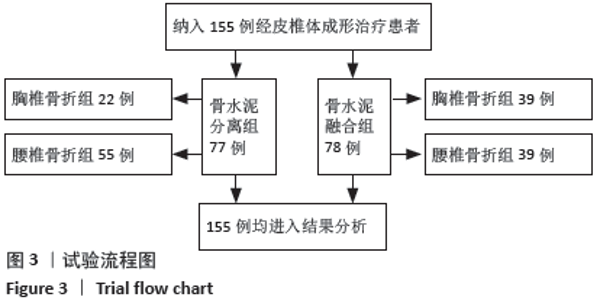
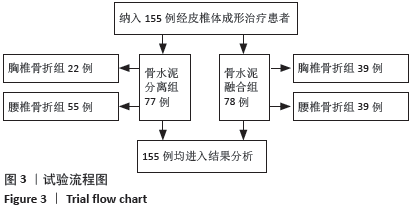
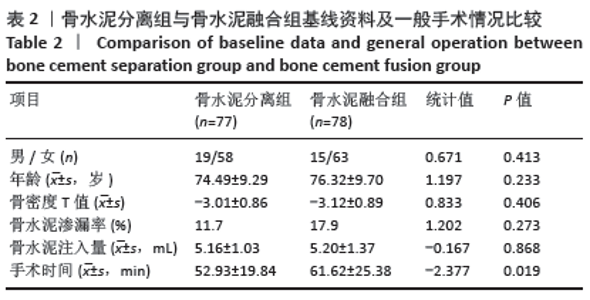
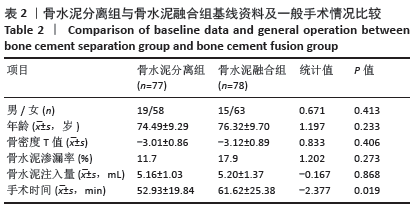
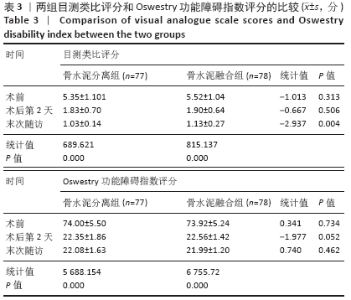
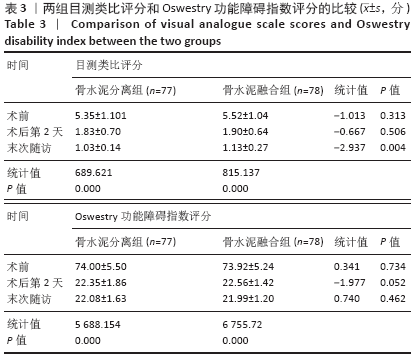
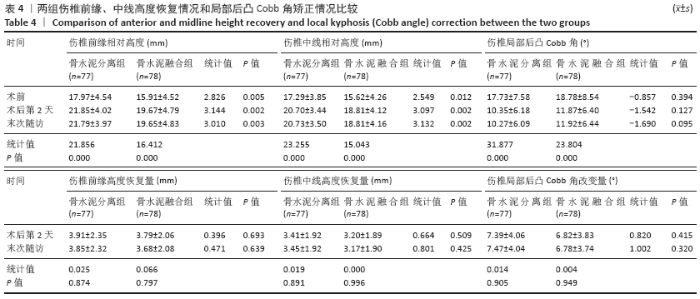
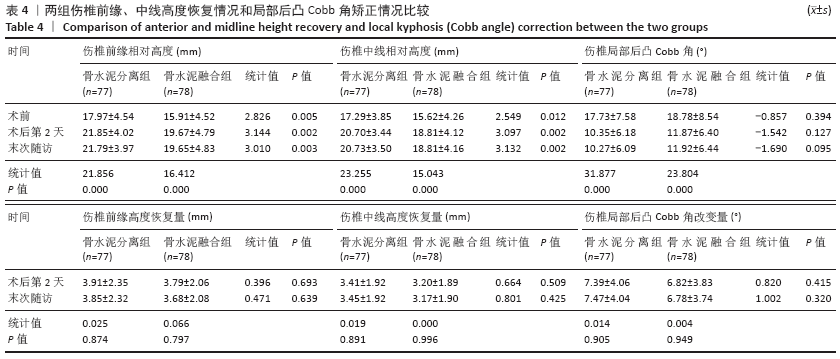
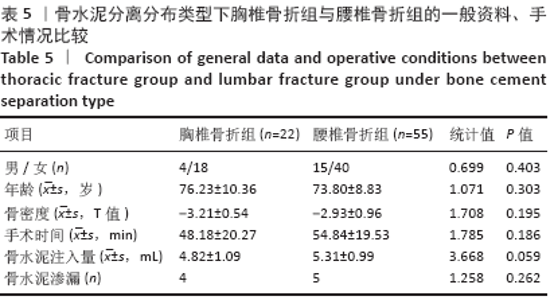
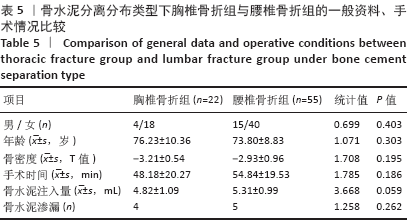
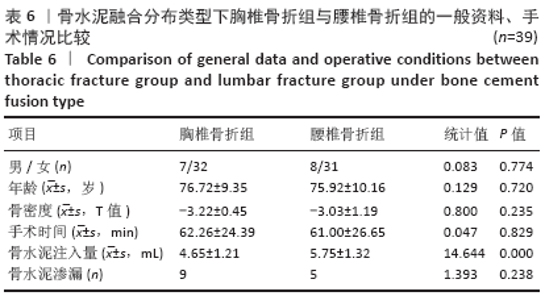
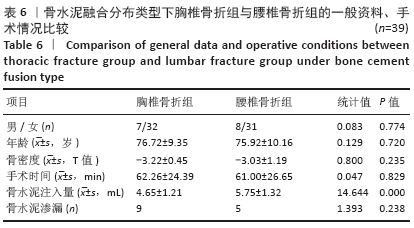
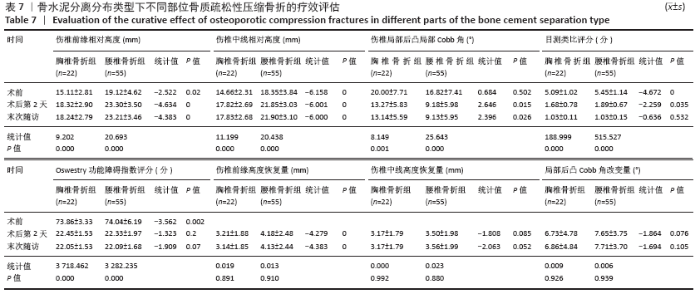
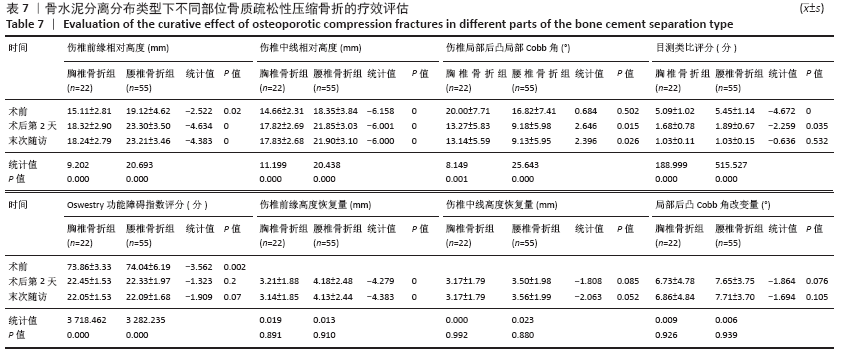
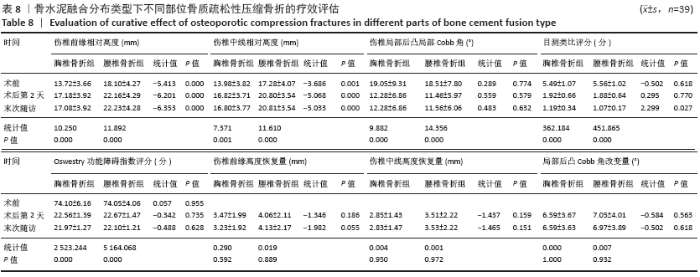
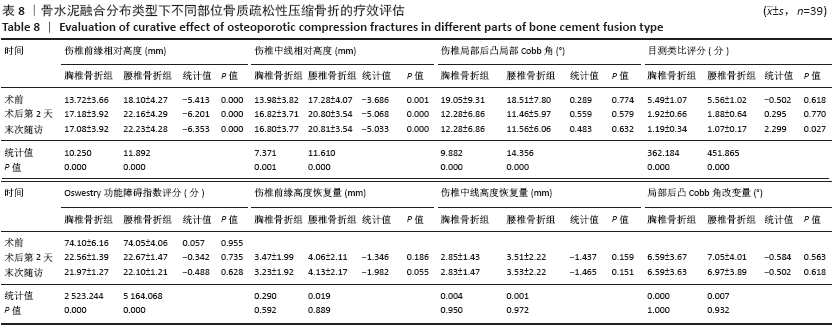
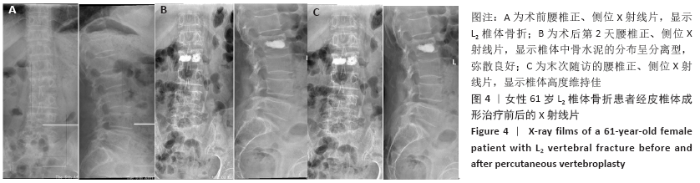
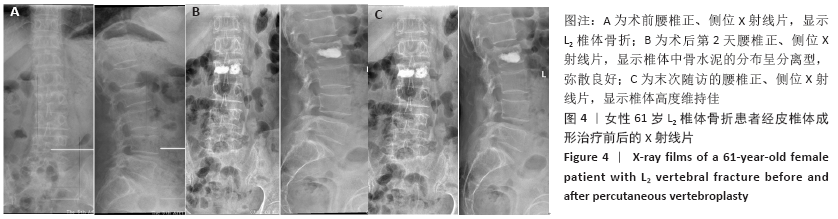
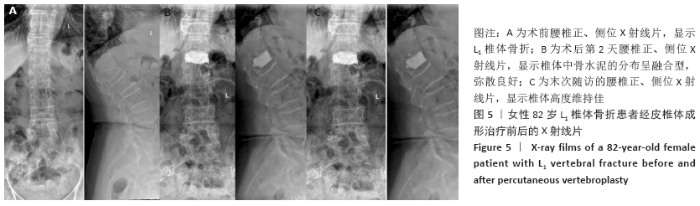
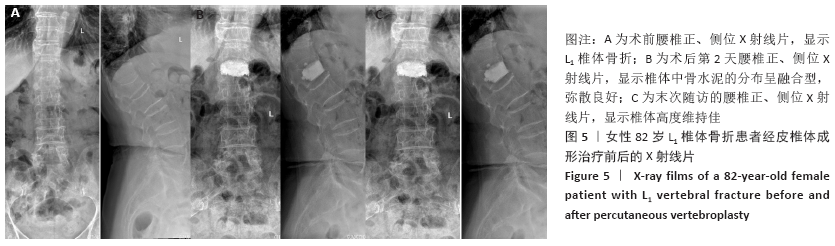
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (22): 3450-3457.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.3180
Previous Articles Next Articles
How does bone cement dispersion affect the early outcome of percutaneous vertebroplasty
Feng Guancheng, Fang Jianming, Lü Haoran, Zhang Dongsheng, Wei Jiadong, Yu Bingbing
- Department of Orthopedics, the Fifth Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou 510700, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2020-05-20Revised:2020-05-22Accepted:2020-07-09Online:2021-08-08Published:2021-01-19 -
Contact:Lü Haoran, MD, Associate professor, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Department of Orthopedics, the Fifth Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou 510700, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Feng Guancheng, Master candidate, Physician, Department of Orthopedics, the Fifth Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou 510700, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the Science and Technology Project of Guangdong Province, No. 2017A090905038 (to LHR)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Feng Guancheng, Fang Jianming, Lü Haoran, Zhang Dongsheng, Wei Jiadong, Yu Bingbing. How does bone cement dispersion affect the early outcome of percutaneous vertebroplasty[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3450-3457.
share this article
| [1] LIU T, LI Z, SU Q, et al. Cement leakage in osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures with cortical defect using high-viscosity bone cement during unilateral percutaneous kyphoplasty surgery. Medicine. 2017;96(25):e7216. [2] PINHEIRO MM, REIS NETO ET, MACHADO FS, et al. Risk factors for osteoporotic fractures and low bone density in pre and postmenopausal women. Rev Saude Publica. 2010;44(3):479-485. [3] KLOTZBUECHER CM, ROSS PD, LANDSMAN PB, et al. Patients with prior fractures have an increased risk of future fractures: A suary of the literature and statistical synthesis. J Bone Miner Res. 2000;15(4):721-739. [4] LIANG L, CHEN X, JIANG W, et al. Balloon kyphoplasty or percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture? An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Saudi Med. 2016;36(3):165-174. [5] ZHAO G, LIU X, LI F. Balloon kyphoplasty versus percutaneous vertebroplasty for treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures(OVCFs). Osteoporosis Int. 2016;27(9):2823-2834. [6] GUO SM, LUO WJ, HUANG YM, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty and percutaneous balloon kyphoplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture:A metaanalysis. Indian J Orthop. 2015;49(4): 377-387. [7] ZHOU Z, WANG Y, SUN Z, et al. Safety of Cement Distribution Patterns in Metastatic Vertebral Tumors:A Retrospective Study. Med Sci Monit. 2019;25:7228-7234. [8] MA X, XING D, MA J, et al. Risk factors for new vertebral compression fractures after percutaneous vertebroplasty: qualitative evidence synthesized from a systematic review. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013; 38(12):E713-722. [9] HADLEY C, AWAN OA, ZOARSKI GH. Biomechanics of Vertebral Bone Augmentation. Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 2010;20(2):159-167. [10] STEINMANN J, TINGEY CT, CRUZ G, et al. Biomechanical comparison of unipedicular versus bipedicular kyphoplasty. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30(2):201-205. [11] 邱贵兴,裴福兴,胡侦明,等.中国骨质疏松性骨折诊疗指南—骨质疏松性骨折诊断及治疗原则[J].黑龙江科学,2018,9(2):85-88,95. [12] 邵珂,吉立新.不同程度椎体压缩骨折行经皮穿刺椎体成形术后骨水泥的弥散分布规律[J].创伤外科杂志,2019,21(7):508-512. [13] STEVENSON M, GOMERSALL T, LLOYD JONES M, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty and percutaneous balloon kyphoplasty for the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral fractures: a systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis. Health Technol Assess. 2014;18(17):1-290. [14] 赵小龙,史会明,张志忠,等.不同黏度骨水泥在PVP治疗椎体压缩骨折的临床应用[J].北京医学,2019,41(12):1113-1115. [15] 吴四军,刘正,姚洪春,等.应用高黏度骨水泥PVP治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折与传统PKP的临床疗效比较[J].中华骨科杂志, 2017,37(2):74-79. [16] 李春海,刘尚礼,叶伟,等.高黏度骨水泥在经皮椎体成形术中的应用[J].中华骨科杂志, 2007,27(4):259-262. [17] 卢海川,吴益奇,黄春辉,等.经皮球囊扩张式椎体成形术治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折疗效研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2013,21(4): 403-405. [18] LONG QL, MI SJ, LI HY. Biomechanical changes following vertebroplasty by unilateral or bilateral approach:Finite element analysis. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2009;22(13):4277-4280. [19] HEINI PF, WÄLCHLI B, BERLEMANN U. Percutaneous transpedicular vertebroplasty with PMMA:operative technique and early results. A prospective study for the treatment of osteoporotic compression fractures. Eur Spine J. 2000;9(5):445-450. [20] MATHIS JM. Percutaneous vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty:which one do I choose? Skeletal Radiol. 2006;35(9):629-631. [21] COSAR M, SASANI M, OKTENOGLU T, et al. The major complications of transpedicular vertebroplasty. J Neurosurg Spine. 2009;11(5):607-613. [22] 徐磊,杨惠林,姜为民,等.单侧经皮聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯骨水泥椎体 成形治疗中骨水泥注入位置、注入量与疗效的相关性[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,16(21):3833-3837. [23] MOLLOY S, MATHIS JM, BELKOFF SM. The effect of vertebral body percentage fill on mechanical behavior during percutaneous vertebroplasty. Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2003;28(14):1549-1554. [24] ERKAN S, WU C, MEHBOD AA, et al. Transfeldt EE.Biomechanical comparison of transpedicular versus extrapedicular vertebroplasty using polymethylmetacrylate. Spinal Disord Tech. 2010;23(3):180-185. [25] BELKOFF SM, MATHIS JM, FENTON DC, et al. An ex vivo biomechanical evaluation of an inflatable bone tamp used in the treatment of compression fracture. Spine (PhilaPa 1976). 2001;26:151-156. [26] 张磊,汪凌骏,杨惠林,等.椎体后凸成形骨水泥注射治疗不同部位骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的疗效分析[J].中国组织工程研究, 2019,23(14):2140-2146. [27] KAUFMANN TJ, TROUT AT, KALLMES DF. The effects of cement volume on clinicaloutcomes of percutaneous vertebroplasty. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2006;27(9):1933-1937. [28] 罗学勤.椎体成形术中采用高黏度骨水泥治疗胸腰椎重度骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折[J].脊柱外科杂志,2020,18(1):34-37. [29] NIEUWENHUIJSE MJ, MUIJS SP, VAN ERKEL AR, et al. A clinical comparative study on low versus medium viscosity polymethylmetacrylate bone cement in percutaneous vertebroplasty: viscosity associated with cement leakage. Spine (PhilaPa 1976). 2010;35(20):E1037-1044. [30] 刘士昭.不同骨密度防腐标本椎体成形术后生物力学及渗漏率、弥散性的研究[D].石家庄市:河北医科大学,2017. [31] 张亮,高梁斌,李健,等.椎体成形术中椎体骨密度对骨水泥弥散体积的影响[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2011,21(11):915-918. [32] 吴强,莫世赞,包拥政,等.椎体成形治疗后骨水泥在椎体内弥散的影响因素[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(43):6922-6928. [33] 席新华,吴强,包拥政,等.骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折程度及骨水泥黏度对骨水泥在椎体内弥散的影响[J].河南医学研究,2016, 25(8):1425-1426. [34] CLCLARK W, BIRD P, GONSKI P, et al.Safety and efficacy of vertebroplasty for acute painful osteoporotic fractures (VAPOUR): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2016;388(10052):1408-1416. [35] 刘长枫,宋文慧,刘昌文,等.经皮椎体成形术骨水泥分布评价及影响因素分析[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2019,29(11):1001-1008. [36] HADJIPAVLOU AG, TZERMIADIANOS MN, KATONIS PG, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty and balloon kyphoplasty for the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures and osteolytic tumours. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005;87(12):1595-1604. [37] HULME PA, KREBS J, FERGUSON SJ, et al. Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty:a systematic review of 69 clinical studies. Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(17):1983-2001. [38] GEORGY BA. Clinical experience with High-Viscosity cements for percutaneous vertebral body augmentation: occurrence, degree, and location of cement leakage compared with kyphoplasty. Am J Neuroradiol. 2010;31(3):504-508. [39] 杨森,徐韬,盛伟斌,等.单双侧球囊灌注骨水泥椎体成形修复骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的系统评价[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(8):1306-1312. [40] XIE W, JIN D, MA H, et al. Cement leakage in percutaneous vertebral augmentation for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: analysis of risk factors. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2016;29(4):E171-176. [41] 李波,余雨,钟斌,等.高压分步注射骨水泥选择性经皮椎体成形术治疗骨质疏松性多发椎体骨折[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2010,12(5):486-488. |
| [1] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [2] | Jiang Yong, Luo Yi, Ding Yongli, Zhou Yong, Min Li, Tang Fan, Zhang Wenli, Duan Hong, Tu Chongqi. Von Mises stress on the influence of pelvic stability by precise sacral resection and clinical validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1318-1323. |
| [3] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [4] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [5] | Wei Wei, Li Jian, Huang Linhai, Lan Mindong, Lu Xianwei, Huang Shaodong. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [6] | Wang Jinjun, Deng Zengfa, Liu Kang, He Zhiyong, Yu Xinping, Liang Jianji, Li Chen, Guo Zhouyang. Hemostatic effect and safety of intravenous drip of tranexamic acid combined with topical application of cocktail containing tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [7] | Xiao Guoqing, Liu Xuanze, Yan Yuhao, Zhong Xihong. Influencing factors of knee flexion limitation after total knee arthroplasty with posterior stabilized prostheses [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1362-1367. |
| [8] | Huang Zexiao, Yang Mei, Lin Shiwei, He Heyu. Correlation between the level of serum n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and quadriceps weakness in the early stage after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1375-1380. |
| [9] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [10] | Wang Haiying, Lü Bing, Li Hui, Wang Shunyi. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: prediction of functional prognosis of patients based on spinopelvic parameters [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1393-1397. |
| [11] | Lü Zhen, Bai Jinzhu. A prospective study on the application of staged lumbar motion chain rehabilitation based on McKenzie’s technique after lumbar percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1398-1403. |
| [12] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [13] | Du Xiupeng, Yang Zhaohui. Effect of degree of initial deformity of impacted femoral neck fractures under 65 years of age on femoral neck shortening [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1410-1416. |
| [14] | Zhang Shangpu, Ju Xiaodong, Song Hengyi, Dong Zhi, Wang Chen, Sun Guodong. Arthroscopic suture bridge technique with suture anchor in the treatment of acromioclavicular dislocation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1417-1422. |
| [15] | Liang Yan, Zhao Yongfei, Xu Shuai, Zhu Zhenqi, Wang Kaifeng, Liu Haiying, Mao Keya. Imaging evaluation of short-segment fixation and fusion for degenerative lumbar scoliosis assisted by highly selective nerve root block [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1423-1427. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||