Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (4): 593-599.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2374
Previous Articles Next Articles
Comparison of tantalum and titanium (alloy) as orthopedic materials: physical and chemical indexes, antibacterial and osteogenic ability
Shi Xiaoxiu, Mao Shilong, Liu Yang, Ma Xingshuang, Luo Yanfeng
- Key Laboratory of Biorheological Science and Technology of Ministry of Education, College of Bioengineering, Chongqing University, Chongqing 400044, China
-
Received:2020-02-11Revised:2020-02-20Accepted:2020-04-03Online:2021-02-08Published:2020-11-23 -
Contact:Luo Yanfeng, Professor, Key Laboratory of Biorheological Science and Technology of Ministry of Education, College of Bioengineering, Chongqing University, Chongqing 400044, China -
About author:Shi Xiaoxiu, Master candidate, Key Laboratory of Biorheological Science and Technology of Ministry of Education, College of Bioengineering, Chongqing University, Chongqing 400044, China -
Supported by:the National Key Research and Development Plan of China during the 13th Five-Year Plan Period, No. 2016YFB1101401
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Shi Xiaoxiu, Mao Shilong, Liu Yang, Ma Xingshuang, Luo Yanfeng. Comparison of tantalum and titanium (alloy) as orthopedic materials: physical and chemical indexes, antibacterial and osteogenic ability[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 593-599.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
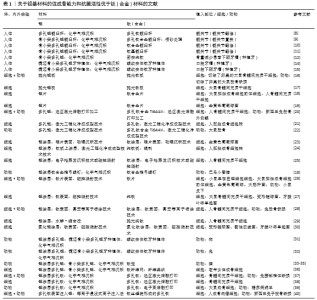
2.1 钽基材料促成骨活性和抗菌活性明显优于钛(合金)材料的研究报道 2.1.1 临床研究 在临床应用研究方面,VUTESU等[8]对637例多孔钛及159例多孔钽全髋关节置换修复患者进行了至少2年的随访研究,发现多孔钽修复效果良好,没有出现失败案例,而多孔钛出现了失败案例。WEGRZYN等[9]通过对1998年1月至1999年12月进行髋关节置换的130例患者进行了平均12年的随访,发现多孔钽人工关节组存活率为100%,而多孔钛人工关节组中有2%的患者出现无菌性松动。JAFARI等[10]回顾性研究了207例共214个钛基髋关节臼杯无水泥翻修手术和79例81个多孔钽臼杯翻修手术患者的资料,最少随访时间24个月(钛基平均51.8个月,范围24-98个月;多孔钽平均35.4个月,范围24-63个月),发现因力学性能引起的手术失败比例钽为6%、钛为8%;在小骨缺损修复中的失败率钛为6%、钽为4%,而在大骨缺损中的失败率钛为24%、钽为12%,表明多孔钽在临床髋关节翻修手术中具有更好的固定效果。TOKARSKI等[11]系统研究了全髋关节置换翻修手术用多孔钽模块和钛基模块的抗菌情况,临床随访了2000至2013年间进行了翻修手术的966例共990个髋关节,平均随访时间40.2个月(3个月-13.1年),男性平均年龄62.3岁,女性平均年龄65.1岁,其中多孔钽454个,钛基关节杯536个(66个为长入性表面)。随访发现失败率多孔钽为4.4%、钛基为9.9%,在144个因感染而翻修手术中(多孔钽为64个,钛基为80个)的再次感染率,多孔钽为3.1% (2/64)、钛基为17.5% (14/80),根据随访结果,作者认为多孔钽自身具有抗感染能力。HEFNI等[12]在1例人体试验中采用反转录?聚合酶链反应检测发现,钽和钛都可激活骨相关基因,但前者激活骨相关基因的时间早于钛。捷迈公司生产的中段为骨小梁金属多孔钽的牙科种植体及螺纹实体钛牙种植体在牙科中被广泛使用,多孔钽是采用化学气相沉积技术在钛表面沉积形成的[13]。EDELMANN等[14]回顾性研究了82例患者共205个种植牙(44个骨小梁金属多孔钽种植体和161个螺纹实体钛牙种植体)周围的骨重建情况,发现多孔钽种植体周围的骨量损失小于钛基种植体,多孔钽种植体的成功率为100%,钛基种植体成功率为98.1%。BENCHARIT等[15]比较了多孔钽种植体与螺纹实体钛牙种植体在植入人体口腔下额牙槽后2,4周的血管形成、创伤愈合和骨长入情况,发现多孔钽种植体组中与血管新生、创伤愈合和成骨相关的基因表达水平更高,其骨形态蛋白、胶原和生长因子的基因表达水平也更高,提示多孔钽种植体作为牙种植体时在初期可以通过改变基因表达情况来增强牙槽的初期愈合。上述临床跟踪结果表明,多孔钽优于多孔钛。 2.1.2 细胞和动物实验研究 为了进一步验证钽基材料优于钛(合金)基材料并阐明其机制,研究人员在细胞和动物水平开展了大量研究。 2D钽片与钛(合金)片材间的比较:LU等[16]用切除卵巢大鼠的骨髓间充质干细胞为模型细胞,从细胞黏附、增殖、分化等方面研究了细胞在抛光钽板和抛光钛板上的生物活性,发现钽板比钛板具有更优的促细胞黏附、增殖和成骨分化的能力;进一步利用无卵巢大鼠股骨缺损为动物模型研究了抛光钛板和钽板在骨质疏松型骨缺损中的修复情况,发现植入8周后钽板表面的新骨形成量明显高于钛板表面,且骨-植入体的界面接触面积也略高于钛板。为了阐明其机制,该课题组进一步研究了正常大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞与两板材共培养之后的骨钙素(7,14 d)和Ⅰ型胶原(7,14 d)的基因表达与蛋白分泌情况及钙结节(14,21 d)形成情况,发现钽表面都高于钛表面;结合各表面上细胞的整合素亚基 (Integrin α5和Integrin β1)及胞外信号调节激酶(ERK1/2)的基因表达情况,作者认为钽表面可激活整合素亚基integrin α5β1/ERK1/2信号通路,从而使钽表面比钛表面具有更高的成骨诱导活性[17]。SHI等[18]以大鼠胚胎成骨细胞前体细胞和人骨髓间充质干细胞为模型细胞时也发现钽片表面的成骨分化更佳,但他们认为钽介导成骨分化是通过Wnt/β-catenin和TGF-β/smad信号通路来实现的。该研究进一步发现钽表面对破骨细胞活性有更强的抑制作用,正是钽涂层的促进成骨和抑制破骨共同成就了钽表面在体内表现出优良的骨长入和骨整合能力。有研究还发现,钽片表面对金黄色葡萄球菌的抗黏附活性高于钛合金表面[19]。 3D多孔钽与钛(合金)间的比较:除钽片以外,由于增材制造技术可以较精确地控制样品外形和孔结构,被越来越广泛地应用于多孔钛和多孔钽的加工,其中最广泛应用的是电子束熔融打印、选区激光熔融打印和激光工程化净成成型等。例如,GUO等[20]采用选区激光熔融打印技术加工了多孔钽和多孔钛合金Ti6Al4V,发现人骨髓间充质干细胞在多孔钽上的体外黏附、增殖、骨分化能力更好,对新西兰兔的体内骨融合更优。BALLA等[21]采用激光工程化净成成型技术加工孔隙率为27%-55%的多孔钽和多孔钛,考查各多孔材料表面对人胚胎成骨细胞的黏附、增殖、分化等指标的影响,发现多孔钽有更好的生物相容性。BANDYOPADHYAY等[22]采用激光工程化净成成型技术加工具有相同孔隙的多孔钽和多孔钛合金Ti6Al4V(平均孔隙30%),植入大鼠股骨缺损5,12周后也发现多孔钽与骨的界面融合明显优于多孔钛合金。 2D钽涂层与钛(合金)间的比较:由于纯钽的密度大、价格贵,目前商用的含钽植入体几乎都是钽涂层产品。为此,更多的研究是在钛(合金)表面或其他基质表面沉积钽涂层,然后研究钽涂层的体内外生物活性。钽涂层的沉积方法包括化学气相沉积 [18]、物理气相沉积技术[23]、激光工程化净成成型[21,24]、电子枪蒸发沉积技术 [25]、磁控溅射[26-27]、真空等离子喷涂技术 [28]、水解-缩合等[29]。例如,BALLA 等[24]在纯钛辊压板上采用激光工程化净成成型技术沉积厚度为1.5-2.0 mm钽涂层,在保证钛板表面和钽涂层表面粗糙度相近的情况下考查了人成骨细胞株的黏附和增殖活性,发现细胞在钽涂层表面具有更好的黏附和增殖。STIEHLER等[25]采用电子枪蒸发沉积技术和磁控溅射技术制备了光滑的钛涂层和钽涂层,发现钛涂层表面促进人骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖而钽涂层表面促进成骨分化。ZHU等[27]采用磁控溅射技术在纯钛表面制备了钽涂层,发现钽涂层表面不仅能促进大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的初期黏附和铺展,而且对变形链球菌和牙龈卟啉单胞菌也有很好的抗菌活性。当细胞与细菌共存时,钽涂层可以选择性促进细胞-材料作用。YANG等[26]也采用磁控溅射技术在纯钛片表面沉积高纯钽,发现钽涂层与钛片的体外抗菌活性无显著差异,但钽涂层的体内抗菌活性明显高于钛片,钽涂层的体内抗菌活性与钽涂层可增强中性粒细胞对细菌的巨噬作用、降低中性粒细胞裂解、增强巨噬细胞释放促炎细胞因子进而增强机体局部先天免疫能力有关。当在钛表面分别溅射上氮化钽涂层和氮化钛涂层时,与纯钛和氮化钛涂层相比,氮化钽涂层显著增强了材料的抗微生物诱导腐蚀性[30]。TANG等[28]采用真空等离子喷涂技术在纯钛表面沉积钽涂层和钛涂层,发现人骨髓间充质干细胞在钽涂层表面的黏附、增殖和成骨分化都优于钛涂层;植入兔股骨缺损部位后,钽涂层表面的成骨速率和质量都明显优于钛涂层。SUN等[29]采用水解-缩合法在纯钛表面沉积钽氧化物涂层,观察到人骨髓间充质干细胞在钽涂层表面的黏附和铺展更优。SHI等[18]比较了钛合金椎弓螺钉和钽涂层钛合金椎弓螺钉植入巴马小香猪体内后的骨整合情况,发现后者的骨长入情况更佳,拔出力更强,骨整合性更强。 3D多孔钽涂层与钛(合金)间的比较:大量研究也对捷迈公司的中段骨小梁金属多孔钽和螺纹实体钛牙种植体在动物水平的成骨活性进行了比较。例如,LEE等[31]以狗为动物模型将骨小梁金属多孔钽和螺纹实体钛牙种植体植入狗的新鲜牙窝,观察植入2,4,8,12周后的新骨长入速率,发现多孔钽的骨长入速度和程度都明显优于钛基牙种植体,种植体的稳定性也更好。FRASER等[32]采用兔胫骨间隙愈合模型(即植入体与骨之间有0.5 mm间隙)研究了中段骨小梁金属多孔钽与螺纹实体钛牙种植体在植入4,8,12周后的骨长入情况,研究发现植入4周后多孔钽上的细胞成骨活性更高,所有时间段上多孔钽的骨-植入体界面接触面积更高,植入8,12周后多孔钽的拔出扭矩更高,表明骨小梁金属多孔钽比钛基种植体具有更好的促骨长入能力。骨小梁金属多孔钽除用作种植体或骨缺损植入体以外也被用作椎间融合器。有研究比较了多孔钽、钛笼、碳纤维笼在猪椎间融合中的应用情况,发现多孔钽的椎间融合性明显高于钛笼椎间融合器[33-35],与钛纤维网相比,多孔钽更能促进老年女性成骨细胞的增殖和分化[36]。WANG等[37]采用化学气相沉积技术在电子束熔融打印加工的多孔钛表面沉积钽涂层,发现钽涂层多孔钛的促干细胞增殖和成骨分化能力都强于对应的无钽涂层多孔钛;当用于兔腰部椎体缺损的修复时,发现其术后8周和12周的骨形成情况也明显优于无钽涂层的钛合金椎体。DOU等[38]采用化学气相沉积技术在选区激光熔融打印加工的多孔钛合金表面沉积钽,体外研究表明骨髓间充质干细胞在钽涂层多孔钛表面的黏附(1 d)、增殖(3,5,7 d)以及碱性磷酸酶、成骨相关转录因子抗体、Ⅰ型胶原、骨连蛋白和骨钙素的mRNA表达水平明显高于多孔钛,且多孔钽可能通过激活MAPK/ERK信号通路来调控成骨基因的高表达,从而促进骨髓间充质干细胞的体外成骨分化。在糖尿病环境条件下,钽涂层多孔钛可显著提高大鼠成骨细胞的黏附、增殖和成骨分化,降低细胞凋亡;植入糖尿病绵羊后发现,钽涂层多孔钛比多孔钛具有更好的体内骨整合性;钽涂层多孔钛呈现更好的骨整合性与钽涂层能够抑制反应性氧簇介导的p38 MAPK通路有关[39]。除钽涂层以外,有研究采用等离子浸没式离子注入法在多孔钛表面注入钽,体外研究发现浸钽表面对人成骨肉瘤细胞具有更强的促细胞增殖能力,显著上调成骨相关基因,动物实验表明浸钽多孔钛的骨长入情况更佳,拔出力更强[40]。 上述研究表明,钽具有明显优于钛(合金)的体内外骨诱导活性、促骨长入活性、对骨的机械附着性和固定性,植入体内后骨缺损修复质量更佳(表1)。此外,钽自身具有明显高于钛(合金)的抗菌活性,这也是钽基材料植入体内后其成功率更高的重要原因。 "
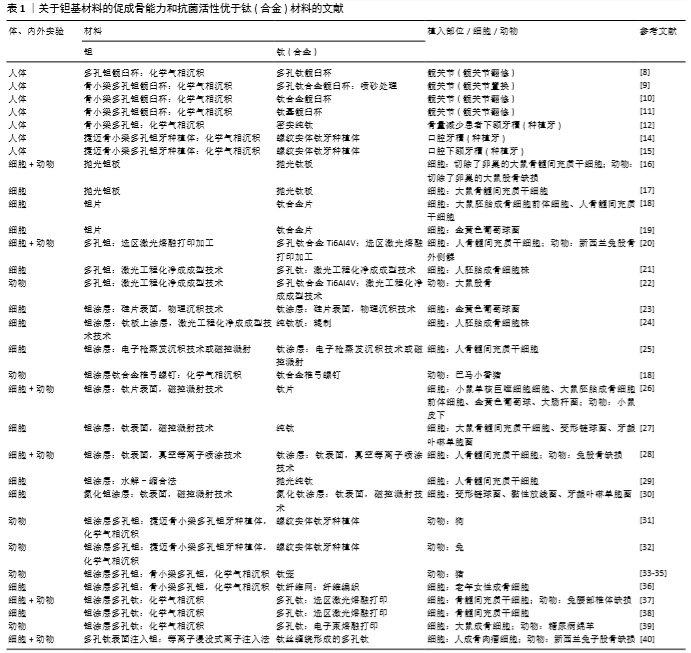
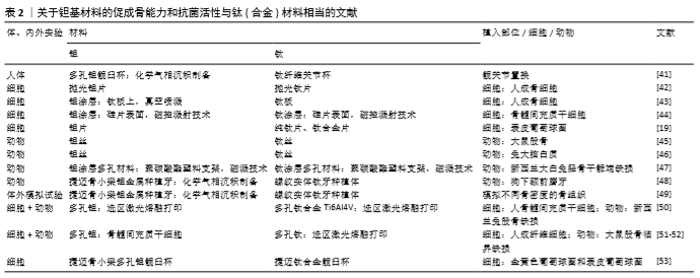
2.2 钽基材料的促成骨活性和抗菌活性与钛(合金)相当的研究报道 尽管大量研究表明,纯钽(钽片和3D打印多孔钽)、钽涂层(钽涂层片和钽涂层多孔材料)都具有明显优于钛或钛涂层的促成骨活性和抗菌活性,但也有研究表明,钽的促成骨活性和抗菌活性与钛(合金)相当(表2)。 2.2.1 临床研究 在临床研究方面,AYERS等[41]采用放射立体照相测量分析技术研究了46例实行了髋关节置换患者的关节杯的滑移情况,随访5年后发现钛纤维多孔关节杯与多孔钽钽关节杯的滑移情况无显著差异 (P > 0.19),具有相似的骨固定能力。 2.2.2 细胞与动物实验研究 2D钽片(涂层)与钛(合金)片材间的比较:FINDLAY等[42]比较了具有相似表面粗糙度的抛光钽片(均方根粗糙度为0.29 μm)和抛光钛片(均方根粗糙度为0.37 μm)与正常人成骨细胞的黏附、增殖和矿化情况,发现钽片与钛片间无显著差异。FRANDSEN等[43]比较了钛板和采用真空喷溅技术在钛板上沉积的钽涂层与人成骨细胞的相容性,细胞形态、增殖、碱性磷酸酶分泌、钙结节形成、矿化速率等指标表明钛板与钽涂层间并无显著差异。MYLLYMAA等[44]采用磁控溅射技术在硅片表面沉积钽涂层后,发现钽涂层表面除碱性磷酸酶分泌更多以外,其骨钙素分泌及矿化情况与钛涂层表面相当。此外,尽管有研究指出钽自身具有抗菌活性[11,26],但SCHILDHAUER等[19]比较了捷迈公司提供的纯钽片与纯钛和钛合金(Ti6Al4V)的抗菌活性,发现虽然纯钽片对金黄色葡萄球菌的抗黏附性高于钛合金,但其与纯钛相当;钽片对表皮葡萄球菌的抗黏附性也与纯钛和钛合金表面没有显著差异。除钽片和钽涂层以外,有研究也比较了钽丝与钛丝的生物相容性。2001年日本学者MATSUNO等[45]将直径为1.0 mm、长度为7.0 mm的钛丝和钽丝植入大鼠股骨干骨骨髓,观察植入2周和4周后的新骨形成情况,结果发现钽丝和钛丝都具有良好的生物相容性,植入物周围的新骨厚度相当,与植入物的接触面积相当。将钽丝和钛丝植入大鼠大脑白质时,发现钛丝和钽丝都没有组织反应,钽丝有色素沉着而钛丝没有,表明钽丝并不具有优于钛丝的生物相容性[46]。 3D多孔钽(涂层)与钛(合金)间的比较:在多孔材料方面,JOHANSSON等[47]早在1990年就将钽、铌、钛喷溅到聚碳酸酯塑料支架表面形成涂层后植入兔子径骨骺端,观察支架周围的多核巨噬细胞和纤维形成情况,结果发现植入3个月后,多孔钽和多孔钛表面都没有明显的异物反应且骨-植入物界面的胶原纤维厚度相当,多孔钽与多孔钛的界面整合性差异并不明显。尽管前面已提到,有研究在人体和动物实验中都观察到中段骨小梁金属多孔钽比螺纹实体钛具有更优的促骨长入能力[13,15],但KIM等[48]将骨小梁多孔钽和螺纹实体钛植入狗的下额前磨牙,采用组织形态学观察和背散射扫描电镜观察植入2,4,8,12周后种植体的稳定性,发现两种种植体的稳定性相当。ROMANOS等[49]在体外考察了中段骨小梁多孔钽和螺纹实体钛的直径(3.7 mm & 4.1 mm)与植入部位骨密度对植入稳定性的影响,发现在密质骨部位大直径多孔钽和螺纹实体钛都比对应的小直径植入体的稳定性更好,小直径多孔钽和螺纹实体钛在密质骨的稳定性没有显著差异,而在骨质软的植入部位螺纹实体钛比骨小梁多孔钽的植入稳定性更好。最近,重庆医科大学口腔医院王超团队比较了选区激光熔融打印加工的多孔钛和多孔钽的体内外成骨活性[50]。多孔钽与多孔钛的孔径、丝径和孔隙率相当,分别为500 μm、400 μm 和70%。骨髓间充质干细胞在多孔材料上体外培养3,5,7 d后的细胞形态和增殖情况没有显著差异,培养7,21 d的碱性磷酸酶分泌、钙结节形成和成骨相关基因的表达都没有显著差异。进一步以新西兰兔股骨缺损(直径5 mm、深度8 mm)为动物模型考查多孔钽和多孔钛的体内成骨情况,发现植入2周内多孔钛的新骨长入速度更快,2-4周多孔钽的骨长入速度更快,但8周后二者的骨长入速度相当,并无显著差异。同样,WAUTHLE等[51]和VAN DER STOK等[52]采用选区激光熔融打印加工的多孔钛和多孔钽进行体内外研究,也表现多孔钽与多孔钛都没有细胞毒性,且都具有良好的骨整合性。此外,HARRISON等[53]在系统研究了金黄色葡萄球菌和表皮葡萄球菌在钽髋臼杯翻修垫块和钛髋臼杯上培养24 h后的菌落情况和生物膜形成情况,发现二者并没有显著差异,指出钽本身并不具有抗菌活性,临床上观察到的抑菌现象应该有其他原因。"
| [1] HAN Q, WANG C, CHEN H, et al. Porous tantalum and titanium in orthopedics: A review. Acs Biomater Sci Eng.2019;5(11):5798-5824. [2] PAŁKA K, POKROWIECKI R. Porous titanium implants: A review. Adv Eng Mater. 2018;20(5):1700648. [3] 赵德伟,李军雷.多孔ta的制备及其作为骨植入材料的应用进展[J].金属学报,2017,53(10):1303-1310. [4] 任军帅,张英明,谭江,等.生物医用钛合金材料发展现状及趋势[J].材料导报,2016,30(S2):384-388. [5] 于晓明,谭丽丽,杨柯.钽金属的医学应用研究进展[J].材料导报,2012,26 (1): 79-82. [6] BLACK J. Biological performance of tantalum.Clin Mater.1994;16(3):167-173. [7] ARNOULD C, KORÁNYI TI, DELHALLE J, et al. Fabrication of tantalum oxide/carbon nanotubes thin film composite on titanium substrate.J Colloid Interf Sci. 2010;344(2):390-394. [8] VUTESCU ES, HSIUE P, PAPROSKY W, et al. Comparative survival analysis of porous tantalum and porous titanium acetabular components in total hip arthroplasty. Hip Int.2017;27(5):505-508. [9] WEGRZYN J, KAUFMAN KR, HANSSEN AD, et al. Performance of porous tantalum vs. titanium cup in total hip arthroplasty: randomized trial with minimum 10-year follow-up.J Arthroplasty.2015;30(6): 1008-1013. [10] JAFARI SM, BENDER B, COYLE C, et al. Do tantalum and titanium cups show similar results in revision hip arthroplasty? Clin Orthop Relat Res.2010;468(2):459-465. [11] TOKARSKI AT, NOVACK TA, PARVIZI J. Is tantalum protective against infection in revision total hip arthroplasty? Bone Joint J.2015;97-B(1):45-49. [12] HEFNI E, BENCHARIT S, KIM S, et al. Transcriptomic profiling of tantalum metal implant osseointegration in osteopenic patients.BDJ Open.2018;4:17042. [13] BENCHARIT S, BYRD WC, ALTARAWNEH S, et al. Development and applications of porous tantalum trabecular metal-enhanced titanium dental implants.Clin Implant Dent R.2014;16(6):817-826. [14] EDELMANN AR, PATEL D, ALLEN RK, et al. Retrospective analysis of porous tantalum trabecular metal–enhanced titanium dental implants.J Prosthet Dent.2019;121(3):404-410. [15] BENCHARIT S, MORELLI T, BARROS S, et al. Comparing initial wound healing and osteogenesis of porous tantalum trabecular metal and titanium alloy materials.J Oral Implantol.2019;45(3):173-180. [16] LU M, WU P, GUO X, et al. Osteoinductive effects of tantalum and titanium on bone mesenchymal stromal cells and bone formation in ovariectomized rats.Eur Rev Med Pharmaco.2018;22(21):7087-7104. [17] LU M, ZHUANG X, TANG K, et al.Intrinsic surface effects of tantalum and titanium on Integrin α5β1/ ERK1/2 pathway-mediated osteogenic differentiation in rat bone mesenchymal stromal cells. Cell Physiol Biochem.2018;51(2):589-609. [18] SHI LY, WANG A, ZANG F, et al. Tantalum-coated pedicle screws enhance implant integration. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces.2017;160:22-32. [19] SCHILDHAUER TA, ROBIE B, MUHR G, et al. Bacterial adherence to tantalum versus commonly used orthopedic metallic implant materials.J Orthop Trauma. 2006;20(7):476-484. [20] GUO Y, XIE K, JIANG W, et al.In vitro and in vivo study of 3D-printed porous tantalum scaffolds for repairing bone defects.Acs Biomater Sci Eng.2019;5:1123-1133. [21] BALLA VK, BODHAK S, BOSE S, et al. Porous tantalum structures for bone implants: fabrication, mechanical and in vitro biological properties.Acta Biomater. 2010;6(8):3349-3359. [22] BANDYOPADHYAY A, MITRA I, SHIVARAM A, et al. Direct comparison of additively manufactured porous titanium and tantalum implants towards in vivo osseointegration.Addit Manuf.2019;28:259-266. [23] LEVON J, MYLLYMAA K, KOURI V, et al.Patterned macroarray plates in comparison of bacterial adhesion inhibition of tantalum, titanium, and chromium compared with diamond-like carbon. J Biomed Mater Res A.2010;92A(4):1606-1613. [24] BALLA VK, BANERJEE S, BOSE S, et al. Direct laser processing of a tantalum coating on titanium for bone replacement structures.Acta Biomater. 2010;6(6):2329-2334. [25] STIEHLER M, LIND M, MYGIND T, et al. Morphology, proliferation, and osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells cultured on titanium, tantalum, and chromium surfaces.J Biomed Mater Res A.2008; 6A(2):448-458. [26] YANG C, LI J, ZHU C, et al. Advanced antibacterial activity of biocompatible tantalum nanofilm via enhanced local innate immunity.Acta Biomater.2019;89:403-418. [27] ZHU YZ, GU Y, QIAO S, et al. Bacterial and mammalian cells adhesion to tantalum-decorated micro-/nano-structured titanium.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2017;105(3):871-878. [28] TANG Z, XIE Y, YANG F, et al. Porous tantalum coatings prepared by vacuum plasma spraying enhance BMSCs osteogenic differentiation and bone regeneration in vitro and in vivo.PLoS One.2013; 8(6): e66263. [29] SUN YS, CHANG JH, HUANG HH. Corrosion resistance and biocompatibility of titanium surface coated with amorphous tantalum pentoxide.Thin Solid Films. 2013;528(3):130-135. [30] ZHANG Y, ZHENG Y, LI Y, et al. Tantalum nitride-decorated titanium with enhanced resistance to microbiologically induced corrosion and mechanical property for dental application. PLoS One. 2015; 10(6): e130774. [31] LEE JW, WEN HB, GUBBI P, et al. New bone formation and trabecular bone microarchitecture of highly porous tantalum compared to titanium implant threads: A pilot canine study.Clin Oral Implan Res.2018;29(2):164-174. [32] FRASER D, MENDONCA G, SARTORI E, et al. Bone response to porous tantalum implants in a gap healing model.Clin Oral Implan Res.2019;30(2):156-168. [33] BÜNGER MH, FOSS M, ERLACHER K, et al. Bone nanostructure near titanium and porous tantalum implants studied by scanning small angle X-ray scattering.Eur Cell Mater.2006;12:81-91. [34] LI H, ZOU X, WOO C, et al. Experimental anterior lumbar interbody fusion with an osteoinductive bovine bone collagen extract.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2005;30(8): 890-896. [35] ZOU X, LI H, TENG X, et al. Pedicle screw fixation enhances anterior lumbar interbody fusion with porous tantalum cages:an experimental study in pigs.Spine(Phila Pa 1976).2005;30(14): E392-E399. [36] SAGOMONYANTS KB, HAKIM-ZARGAR M, JHAVERI A, et al. Porous tantalum stimulates the proliferation and osteogenesis of osteoblasts from elderly female patients.J Orthop Res.2011;29(4):609-616. [37] WANG F, WANG L, FENG Y, et al. Evaluation of an artificial vertebral body fabricated by a tantalum-coated porous titanium scaffold for lumbar vertebral defect repair in rabbits.Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):8927. [38] DOU X, WEI X, LIU G, et al. Effect of porous tantalum on promoting the osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in vitro through the MAPK/ERK signal pathway.J Orthop Translat.2019;19:81-93. [39] WANG L, HU X, MA X, et al. Promotion of osteointegration under diabetic conditions by tantalum coating-based surface modification on 3-dimensional printed porous titanium implants. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces.2016;148:440-452. [40] WANG Q, QIAO Y, CHENG M, et al. Tantalum implanted entangled porous titanium promotes surface osseointegration and bone ingrowth.Sci Rep.2016;6(1):26248. [41] AYERS DC, GREENE M, SNYDER B, et al. Radiostereometric analysis study of tantalum compared with titanium acetabular cups and highly cross-linked compared with conventional liners in young patients undergoing total hip replacement.J Bone Joint Surg Am.2015;97(8):627-634. [42] FINDLAY DM, WELLDON K, ATKINS GJ, et al. The proliferation and phenotypic expression of human osteoblasts on tantalum metal.Biomaterials. 2004;25(12):2215-2227. [43] FRANDSEN CJ, BRAMMER KS, NOH K, et al. Tantalum coating on TiO2 nanotubes induces superior rate of matrix mineralization and osteofunctionality in human osteoblasts.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2014; 37: 332-341. [44] MYLLYMAA S, KAIVOSOJA E, MYLLYMAA K, et al. Adhesion, spreading and osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells cultured on micropatterned amorphous diamond, titanium, tantalum and chromium coatings on silicon.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2010;21(1):329-341. [45] MATSUNO H, YOKOYAMA A, WATARI F, et al. Biocompatibility and osteogenesis of refractory metal implants, titanium, hafnium, niobium, tantalum and rhenium.Biomaterials.2001;22(11): 1253-1262. [46] Von HOLST H, COLLINS P, STEINER L. Titanium, silver, and tantalum clips in brain tissue. Acta Neurochir.1981;56(3-4):239-242. [47] JOHANSSON CB, HANSSON HA, ALBREKTSSON T. Qualitative interfacial study between bone and tantalum, niobium or commercially pure titanium.Biomaterials.1990;11(4):277-280. [48] KIM DG, HUJA SS, TEE BC, et al. Bone ingrowth and initial stability of titanium and porous tantalum dental implants: a pilot canine study.Implant Dent. 2013;22(4):399-405. [49] ROMANOS GE, DELGADO-RUIZ RA, SACKS D, et al. Influence of the implant diameter and bone quality on the primary stability of porous tantalum trabecular metal dental implants: an in vitro biomechanical study.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2018;29(6):649-655. [50] WANG H, SU K, SU L, et al. Comparison of 3D-printed porous tantalum and titanium scaffolds on osteointegration and osteogenesis.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;104:109908. [51] WAUTHLE R, van der STOK J, AMIN YAVARI S, et al. Additively manufactured porous tantalum implants. Acta Biomater.2015;14:217-225. [52] VAN DER STOK J, VAN DER JAGT OP, AMIN YAVARI S, et al. Selective laser melting-produced porous titanium scaffolds regenerate bone in critical size cortical bone defects.J Orthop Res.2013; 31(5):792-799. [53] HARRISON PL, HARRISON T, STOCKLEY I, et al.Does tantalum exhibit any intrinsic antimicrobial or antibiofilm properties? Bone Joint J.2017;99-B(9):1153-1156. [54] SHARMA CP, PAUL W. Protein interaction with tantalum: changes with oxide layer and hydroxyapatite at the interface.J Biomed Mater Res.1992;26(9):1179-1184. [55] BAKRI MM, LEE SH, LEE JH. Improvement of biohistological response of facial implant materials by tantalum surface treatment.Maxillofac Plast Reconstr Surg. 2019;41(1):52. [56] HEMMERSAM AG, FOSS M, CHEVALLIER J, et al. Adsorption of fibrinogen on tantalum oxide, titanium oxide and gold studied by the QCM-D technique.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces.2005;43(3-4): 208-215. [57] CHANG YY, HUANG HL, CHEN HJ, et al. Antibacterial properties and cytocompatibility of tantalum oxide coatings.Surf Coat Tech.2014;259(2):193-198. [58] FENG B, WENG J, YANG BC, et al. Characterization of surface oxide films on titanium and adhesion of osteoblast.Biomaterials.2003;24(25):4663-4670. [59] HOOK F, VOROS J, RODAHL M, et al. A comparative study of protein adsorption on titanium oxide surfaces using in situ ellipsometry, optical waveguide lightmode spectroscopy, and quartz crystal microbalance/dissipation.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces.2002;24(2):155-170. [60] DONKOV N, MATEEV E, ZYKOVA A, et al. Biocompatibility of dielectric Ta2O5 coatings in in vitro tests.J Phys Conf Ser.2010;223:12030. |
| [1] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [2] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [3] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [4] | Jiang Yong, Luo Yi, Ding Yongli, Zhou Yong, Min Li, Tang Fan, Zhang Wenli, Duan Hong, Tu Chongqi. Von Mises stress on the influence of pelvic stability by precise sacral resection and clinical validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1318-1323. |
| [5] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [6] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [7] | Wei Wei, Li Jian, Huang Linhai, Lan Mindong, Lu Xianwei, Huang Shaodong. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [8] | Wang Jinjun, Deng Zengfa, Liu Kang, He Zhiyong, Yu Xinping, Liang Jianji, Li Chen, Guo Zhouyang. Hemostatic effect and safety of intravenous drip of tranexamic acid combined with topical application of cocktail containing tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [9] | Xiao Guoqing, Liu Xuanze, Yan Yuhao, Zhong Xihong. Influencing factors of knee flexion limitation after total knee arthroplasty with posterior stabilized prostheses [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1362-1367. |
| [10] | Huang Zexiao, Yang Mei, Lin Shiwei, He Heyu. Correlation between the level of serum n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and quadriceps weakness in the early stage after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1375-1380. |
| [11] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [12] | Wang Haiying, Lü Bing, Li Hui, Wang Shunyi. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: prediction of functional prognosis of patients based on spinopelvic parameters [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1393-1397. |
| [13] | Lü Zhen, Bai Jinzhu. A prospective study on the application of staged lumbar motion chain rehabilitation based on McKenzie’s technique after lumbar percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1398-1403. |
| [14] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [15] | Du Xiupeng, Yang Zhaohui. Effect of degree of initial deformity of impacted femoral neck fractures under 65 years of age on femoral neck shortening [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1410-1416. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||