Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (2): 309-314.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.02.026
Previous Articles Next Articles
Research progress of strontium-doped biomedical titanium alloys
- Second Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun 130041, Jilin Province, China
-
Received:2016-10-28Online:2017-01-18Published:2017-02-27 -
Contact:Qin Yan-guo, Associate professor, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Second Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun 130041, Jilin Province, China -
About author:Li Rui-yan, Studying for master’s degree, Second Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun 130041, Jilin Province, China -
Supported by:a grant from the Provincial Industry Innovation Project of Jilin Province, No. 2016C037; the Science and Technology Development Program of Jilin Province, No. 20150414006G H
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Rui-yan, Liu Guan-cong, Liang Hao-jun, Qin Yan-guo.
share this article
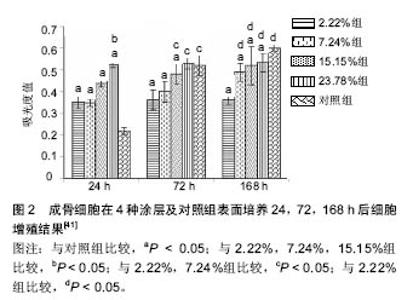
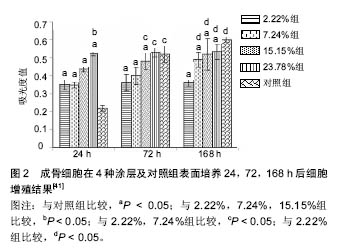
2.1 单纯引入锶元素进行改性 2.1.1 物理喷涂 物理喷涂可以将锶盐或锶的氧化物喷涂在钛合金表面进行改性,且喷涂后的表面较粗糙利于细胞黏附。Andersen等[11]研究应用喷涂技术先在钛合金表面制备一层100 nm的Ti基础涂层,然后用50% SrTiO3和50% Ti粉末制备不同厚度的掺锶涂层(50,200,1 000,1 500 nm),涂层厚度不同掺入锶离子的量也不同,探讨其生物相容性。结果显示1 000 nm和 1 500 nm厚度生物活性较好,1 500 nm组新骨生成量最大,研究中不同厚度涂层均未发现细胞毒性。 Yang等[12]通过等离子喷涂及微弧氧化技术制备了粗糙多孔的钛合金医用支架材料,并对比不同表面处理方法的生物效应,最终发现含锶涂层可以促进细胞增殖和碱性磷酸酶的分泌,其中含锶磷酸钙涂层具有类细胞外基质结构,是合理的医用涂层处理方法。 Offermanns等[13]应用磁控共溅镀技术在钛表面喷镀SrTiO3和Ti混合物,制作Ti-Sr-O涂层。调节SrTiO3的含量可以控制锶含量。该研究评估了这一涂层的锶离子体外缓释,并通过大鼠模型评估该涂层材料植入物与骨接触反应以及新骨形成。结果发现涂层中锶含量8.9%组锶离子缓释时间最久,新生成骨量达60.1%,骨植入物接触量为91.6%,而作为对照的钛合金新生成骨量仅有16.6%,骨植入物接触量为70.6%。新生成骨量的多少与锶的含量有关。高麒等[14]应用酸蚀复合磁共溅技术在纯钛种植体表面合成纳米结构掺锶仿生涂层,发现该涂层可以促进种植体与骨组织的早期结合。 物理喷涂方法简单易行,各组分含量较易控制,但物理结合易因长期负重活动而造成涂层部分剥脱,影响涂层长期效果。 2.1.2 热液合成方法 热液合成方法可以通过系列的化学反应在钛合金表面合成含锶的涂层。Xin等[15]在钛植入物表面合成氧化钛纳米管,经简单的热液处理合成SrTiO3纳米管,处理后纳米管结构得以保留,该涂层具有较好的生物相容性,可以促进材料在模拟体液中羟基磷灰石的沉积,并可长期缓释锶离子,同时这一纳米管结构为负载其他功能物质提供了可能。Wang等[16]采用相似的技术经表面阳极氧化处理后在钛合金表面形成一层TiO2涂层,再通过热液处理的方法在其表面修饰一层SrTiO3纳米颗粒,最终形成异质结构的涂层。结果发现此异质结构中合适比例的SrTiO3可以促进成骨细胞丝状伪足的分泌,进而增强细胞黏附、固定和增殖。 2.1.3 锶替代羟基磷灰石 因羟基磷灰石和骨组织固体相组成结构类似,大量的实验证明羟基磷灰石具有良好的生物相容性,掺锶羟基磷灰石较纯羟基磷灰石涂层机械强度更好,硬度更高,有更高的抗脆性[17]。目前有多种方法将锶元素掺入羟基磷灰石中即含锶羟基磷灰石,进一步提高材料的生物活性[18-19]。如Renaudin等[20]应用凝胶溶胶法将锶掺入β-磷酸三钙和羟基磷灰石中,其研究发现锶可以抗骨质疏松抑制炎症并促进成骨细胞生长。Oliveir等[21]用模拟体液在钛合金表面沉积羟基磷灰石涂层,随后用SrCl2置换羟基磷灰石中的钙,最终合成部分锶离子替代钙的羟基磷灰石涂层,其结构与人体骨组织固体相组成结构相近,有望增强骨组织形成和骨整合。Capuccin等[22]应用加热脉冲激光沉积技术在钛合金支架表面合成含锶磷灰石涂层,其研究发现该涂层促进成骨细胞分化,抑制破骨细胞分化。Vahabzadeh等[23]通过电感耦合射频等离子喷涂技术在纯钛表面制备混合SrO和羟基磷灰石粉末的涂层。在pH=7.4的PBS中进行牛血清白蛋白释放实验发现掺锶羟基磷灰石涂层释放可达92%,而纯羟基磷灰石涂层仅能达到72%。通过植入大鼠股骨远端的实验观察发现,植入7周后掺锶羟基磷灰石涂层植入物表面就出现了骨质沉积,纯羟基磷灰石涂层在12周时才出现新生骨质,而纯钛组一直无新骨生成。植入16周后羟基磷灰石组和掺锶羟基磷灰石组骨质完全矿化。Yang等[24]用电化学手段在多孔钛上制备纳米级锶替代羟基磷灰石涂层,植入家兔体内4、8周后,发现锶替代羟基磷灰石涂层材料与骨的结合更好,促进了骨整合。 2.1.4 离子交换 用NaOH溶液处理金属钛,随后在CaCl2和SrCl2混合溶液中进行离子交换,在600 ℃加热处理后在钛表面形成含锶钙钛酸盐层。该处理方法可使处理后的材料在PBS溶液中7 d释放0.92 ppm锶离子,且1 d即可在模拟体液中沉积羟基磷灰石。这一材料既富含钙离子又能缓释锶离子,具有良好的生物活性,可以使植入物和周围骨组织紧密结合,其促进羟基磷灰石沉积的特性又可以促进骨生成[25]。 Lindahl等[26]将钛合金在含不同浓度锶(0,0.06,0.6,1.2 mmol/L)的磷酸盐缓冲液中制备不同锶浓度的掺锶磷酸钙盐涂层,该涂层释放的锶质量浓度从0到2.37 mg/L不等。SAOS-2细胞实验发现这种涂层和羟基磷灰石相比同样具有良好的生物相容性,而即使最低浓度的含锶量仍明显促进了碱性磷酸酶的分泌。 2.1.5 其他掺锶方法 Lovati等[27]制备骨小梁结构钛合金复合羧甲基纤维素凝胶(CMCA)富集SrCl2材料,在大鼠背部进行异位成骨实验。通过micro-CT、扫描电镜、拉出实验检测发现,这种富集锶元素和人骨髓间充质干细胞的材料展示出卓越的组织长入性能,提高了骨小梁金属的骨量沉积和骨整合性。 Wang等[28]通过粉末冶金技术制备0%,1%,3%,5%的SrO和Titanium金属复合材料。复合材料的压缩强度和弹性模量以及显微硬度均随SrO的含量而升高,而相应的极限应变随之降低,其中抗压强度从982 MPa提高到1 753 MPa,显微硬度从59%提高到190%。MTS实验证明SrO含量3%的复合材料增强了类成骨细胞的增殖,但长达10 d的对比发现Ti-SrO表面对碱性磷酸酶分泌的影响和纯钛组无明显差异。经扫描电镜和激光共聚焦显微镜观察证实SrO含量3%的复合材料表现出良好的生物相容性。 2.2 联合其他改性方法 锶的单独应用可以促进骨髓干细胞成骨分化,促进植入物骨整合,而联合其他功能元素或生物活性好的材料可以达到优势叠加或互补的效果。 2.2.1 联合其他元素 Karthika等[29]在电子束处理的钛合金表面合成3种二价金属(锶、镁、锌)替代的羟基磷灰石凝胶涂层,并研究其机械性能、耐腐蚀性、抗菌性能和生物活性。结果发现其具有良好的机械性能和耐腐蚀性,且可以抑制金黄色葡萄球菌和大肠埃希杆菌菌落生长,此外通过细胞增殖及活死细胞染色发现该涂层可以促进MT3C3-E1细胞和成纤维干细胞的生长,最终证明其为良好有效的植入物材料。Huang等[30]通过电化学沉积的方法在钛植入物支架上制备含ZnO和掺锶羟基磷灰石的复合涂层,结果表明SrHAp/ZnO复合涂层致密程度明显高于羟基磷灰石涂层,并增强了基底材料的耐腐蚀性,体外细胞实验证明生物相容性也进一步提高。 F元素也是人体骨骼和牙齿组成的重要微量元素,F可以促进骨组织生成时磷酸钙盐的沉积和矿化。用溶胶凝胶法在钛合金表面合成FHA和SrHA涂层,FHA作为不可溶成分,SrHA作为可溶成分,两种成分复合降低了涂层溶解速率,调节凝胶中SrHA的量可以调节两种元素的含量,最终所获得的复合涂层稳定性更好,可以缓释Sr,Ca和F元素。当SrHA和FHA比例为1∶2时对成骨细胞的功能有更显著的影响[31]。 银离子一直以来被认为可以起到抑菌的作用,目前有很多研究引入银离子涂层以求利用其抑菌效果减少感染的发生。但银离子具有潜在的细胞毒性,这一问题影响了掺银抗菌的应用。Fielding等[32]用2.0%Ag2O和1.0%SrO掺杂羟基磷灰石以等离子喷涂技术制备同时含银锶2种功能元素的涂层。该改性涂层可以有效抑制细菌增殖。同时锶离子的引入不但逆转了银的潜在生物毒性还明显增强了细胞增殖和分化,相比纯羟基磷灰石涂层明显提高了材料的生物活性。Cheng等[33]在纳米微管结构的钛支架上制备同时含银和锶两种元素的涂层,获得的生物活化材料不但可以促进成骨相关细胞增殖黏附,也上调了成骨相关基因表达,且缓释的银离子有很好的抗菌作用。 2.2.2 联合有机复合涂层 Liu等[34]用微弧氧化技术处理钛合金在其表面形成磷酸钙涂层和锶磷酸钙涂层,再经一系列反应在其外沉积多巴胺涂层,最终制备无机-有机复合涂层来提高钛合金植入物的表面活性以改善细胞反应。实验结果发现多巴胺涂层可以促进细胞最初的黏附和增殖,最里层的含锶涂层不断释放锶离子可以促进细胞分化,这一涂层方法可以同时强化植入物表面的多种生物活性。 Boanini等[35]在钛合金支架上合成不同含量级别的锶替代羟基磷灰石和唑来膦酸改性的羟基磷灰石涂层,并以MG63细胞在涂层上进行长达21 d的共培养。结果发现锶离子抵消了Ⅰ型胶原产量相对较高的副作用并促进碱性磷酸酶的合成分泌。唑来膦酸对于osteoprotegerin/RANKL比例的作用要强于锶离子。这一涂层方法可以调节不同组分的含量进而促进骨组织生长和原位骨修复。 为了提高钛合金材料的抗腐蚀性和生物相容性,用电极沉积的方法同时将锶元素(Sr)、明胶(GLT)合并到磷酸钙盐(Ca-P)中,制备Sr-Ca-P/GLT混合涂层材料。该复合涂层呈多孔结构,具有花纹状和鳞片状形貌。涂层均匀一致约10 μm厚。Sr-Ca-P/GLT混合涂层比裸钛有更好的抗腐蚀性。体外细胞实验验证Sr-Ca-P/GLT混合涂层有比Ca-P涂层有更好的生物相容性[36]。 2.3 掺锶改性剂量的研究 2.3.1 骨骼中锶的含量 目前的研究在骨骼中发现的锶含量结果不一,由于研究的对象既有不同动物也有人的不同部位,所以无法进行直接比较[37]。Boivin等[38]以猴为研究对象发现,骨骼中钙锶比例最大值为10∶1,所以目前掺锶羟基磷灰石涂层材料大多以钙锶比例10∶1为最适量。 2.3.2 局部微环境锶浓度的研究 锶在较低浓度时可以促进骨骼矿化,而在高浓度时反而不利于骨骼矿化[39]。此外在细胞培养实验中发现培养液中锶含量达到20 mg/L以上时就会对成骨细胞的活性产生消极作用[40]。 Wang等[16]的研究中,经热液合成法在钛合金表面合成SrTiO3纳米管,研究中分别合成了含锶浓度低(1.4-Sr/TNTs)和含锶浓度高(6.3-Sr/TNTs)两组涂层,在培养液中释放锶的质量浓度为1.4 mg/L,6.3 mg/L,用成骨细胞(SaOS2)检测其细胞增殖及黏附行为,结果表明低质量浓度SrTiO3纳米管涂层可以促进细胞增殖,而高质量浓度反而抑制细胞增殖。 Wang等[28]的研究中,通过粉末冶金技术利用含不同比例SrO的钛粉制备合金材料,得出结论认为含3%SrO的合金材料生物相容性最好。王薇等[41]就不同含锶浓度的羟基磷灰石涂层对骨细胞影响进行研究,依据锶原子数百分比[Sr/(Sr+Ca)]分别制备浓度为2.22%,7.24%,15.15%和23.78%的涂层,研究发现15.15%和23.78%组细胞增殖和附着更佳,而低浓度组(2.22%,7.24%)碱性磷酸酶活性更好,研究中不同浓度锶对细胞增殖的影响结果如图2所示。 目前关于锶剂量的研究众多,但所使用的含锶材料各不相同,且培养液中固定锶浓度并不能代表材料在培养液中逐渐缓释的锶浓度,且在体内环境下,体液不断循环代谢,锶的浓度也是变化的,所以目前并没有明确的研究指出局部锶浓度的毒性标准。"
| [1]Ungersboeck A,Geret V,Pohler O, et al.Tissue reaction to bone plates made of pure titanium: a prospective, quantitative clinical study.J Materials Sci Materials Med. 1995; 6(4): 223-229.[2]Geethaa M, Singhb AK, Asokamania R, et al. Ti based biomaterials, the ultimate choice for orthopaedic implants – A review. Progress in Materials Science.2009;54(3):397-425.[3]Harris WH.Wear and periprosthetic osteolysis: the problem. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001;(393):66-70.[4]Porter JA, von Fraunhofer JA. Success or failure of dental implants? A literature review with treatment considerations. Gen Dent. 2005;53(6):423-432[5]Navarro M, Michiardi A, Castaño O, et al. Biomaterials in orthopaedics. J R Soc Interface. 2008;5(27):1137-1158.[6]Park JW, Kim HK, Kim YJ, et al. Osteoblast response and osseointegration of a Ti-6Al-4V alloy implant incorporating strontium. Acta Biomater. 2010;6(7):2843-2851.[7]Marie PJ, Ammann P, Boivin G, et al. Mechanisms of action and therapeutic potential of strontium in bone. Calcif Tissue Int. 2001;69(3):121-129.[8]Canalis E, Hott M, Deloffre P, et al. The divalent strontium salt S12911 enhances bone cell replication and bone formation in vitro. Bone. 1996;18(6):517-523.[9]陈齐勇,梁清,林煜,等.雷奈酸锶对钛颗粒刺激单核/巨噬细胞分泌溶骨因子及其RANK表达的影响[J].风湿病与关节炎, 2015,4(5):5-8.[10]Lu YC, Chang TK, Yeh ST, et al. The potential role of strontium ranelate in treating particle-induced osteolysis. Acta Biomater. 2015;20:147-154.[11]Andersen OZ, Offermanns V, Sillassen M, et al. Accelerated bone ingrowth by local delivery of strontium from surface functionalized titanium implants. Biomaterials. 2013;34(24):5883-5890.[12]Yang SP, Lee TM, Lui TS. Biological response of Sr-containing coating with various surface treatments on titanium substrate for medical applications. Applied Surface Science. 2015;346:554-561.[13]Offermanns V, Andersen OZ, Falkensammer G, et al. Enhanced osseointegration of endosseous implants by predictable sustained release properties of strontium. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2015;103(5):1099-1106.[14]高麒,牛强,李永锋,等.掺锶仿生涂层用于促进种植体早期骨结合的初步研究[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志, 2014, 24(4):216-220.[15]Xin Y, Jiang J, Huo K, et al. Bioactive SrTiO(3) nanotube arrays: strontium delivery platform on Ti-based osteoporotic bone implants. ACS Nano. 2009;3(10):3228-3234.[16]Wang Y, Zhang D, Wen C, et al. Processing and Characterization of SrTiO?-TiO? Nanoparticle-Nanotube Heterostructures on Titanium for Biomedical Applications. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015;7(29):16018-16026.[17]Machado CP, Sartoretto SC, Alves AT, et al. Histomorphometric evaluation of strontium-containing nanostructured hydroxyapatite as bone substitute in sheep. Braz Oral Res. 2016;30(1):e45.[18]Christoffersen J, Christoffersen MR, Kolthoff N, et al. Effects of strontium ions on growth and dissolution of hydroxyapatite and on bone mineral detection. Bone. 1997;20(1):47-54.[19]刘茂林,张晶,陈赟,等.钛表面电化学法制备掺锶羟基磷灰石涂层及其形貌控制[J]. 材料科学与工程学报, 2016, 34(1):18-24.[20]Renaudin G, Laquerrière P, Filinchuk Y, et al. Structural characterization of sol–gel derived Sr-substituted calcium phosphates with anti-osteoporotic and anti-inflammatory properties. Journal of Materials Chemistry. 2008; 18(30):3593-3600.[21]Oliveira AL, Reis RL, Li P. Strontium-substituted apatite coating grown on Ti6Al4V substrate through biomimetic synthesis. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2007;83(1): 258-265.[22]Capuccini C, Torricelli P, Sima F, et al. Strontium-substituted hydroxyapatite coatings synthesized by pulsed-laser deposition: in vitro osteoblast and osteoclast response. Acta Biomater. 2008;4(6):1885-1893.[23]Vahabzadeh S, Roy M, Bandyopadhyay A, et al. Phase stability and biological property evaluation of plasma sprayed hydroxyapatite coatings for orthopedic and dental applications. Acta Biomater. 2015;17:47-55.[24]Yang GL, Song LN, Jiang QH, et al. Effect of strontium-substituted nanohydroxyapatite coating of porous implant surfaces on implant osseointegration in a rabbit model. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2012 ;27(6):1332-1339.[25]Yamaguchi S, Nath S, Matsushita T, et al. Controlled release of strontium ions from a bioactive Ti metal with a Ca-enriched surface layer. Acta Biomater. 2014;10(5):2282-2289.[26]Lindahl C, Pujari-Palmer S, Hoess A, et al. The influence of Sr content in calcium phosphate coatings. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2015;53:322-330.[27]Lovati AB, Lopa S, Talò G, et al. In vivo evaluation of bone deposition in macroporous titanium implants loaded with mesenchymal stem cells and strontium-enriched hydrogel. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2015;103(2):448-456.[28]Wang Y, Wong C, Wen C, et al. Ti-SrO metal matrix composites for bone implant materials. J Mater Chem B. 2014; 2(35):5854-5861.[29]Karthika A, Kavitha L, Surendiran M, et al. Fabrication of divalent ion substituted hydroxyapatite/gelatin nanocomposite coating on electron beam treated titanium: mechanical, anticorrosive, antibacterial and bioactive evaluations. Rsc Advances. 2015; 5(59):47341-47352.[30]Huang Y, Zeng H, Wang X, et al. Corrosion resistance and biocompatibility of SrHAp/ZnO composite implant coating on titanium. Applied Surface Science. 2014; 290(4):353-358.[31]Yin P, Feng FF, Lei T, et al. Osteoblastic cell response on biphasic fluorhydroxyapatite/strontium-substituted hydroxyapatite coatings. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2014;102(3): 621-627.[32]Fielding GA, Roy M, Bandyopadhyay A, et al. Antibacterial and biological characteristics of silver containing and strontium doped plasma sprayed hydroxyapatite coatings. Acta Biomater. 2012;8(8):3144-3152.[33]Cheng H, Xiong W, Fang Z, et al. Strontium (Sr) and silver (Ag) loaded nanotubular structures with combined osteoinductive and antimicrobial activities. Acta Biomater. 2016;31:388-400.[34]Liu YT, Kung KC, Yang CY, et al. Engineering three-dimensional structures using bio-inspired dopamine and strontium on titanium for biomedical application. J Mater Chem B. 2014; 2(45):7927-7935.[35]Boanini E, Torricelli P, Sima F, et al. Strontium and zoledronate hydroxyapatites graded composite coatings for bone prostheses. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2015;448:1-7.[36]Huang Y, Yan Y, Pang X, et al. Bioactivity and corrosion properties of gelatin-containing and strontium-doped calcium phosphate composite coating. Applied Surface Science. 2013; 282(5):583-589.[37]Dahl SG, Allain P, Marie PJ, et al. Incorporation and distribution of strontium in bone. Bone. 2001;28(4):446-453.[38]Boivin G, Deloffre P, Perrat B, et al. Strontium distribution and interactions with bone mineral in monkey iliac bone after strontium salt (S 12911) administration. J Bone Miner Res. 1996;11(9):1302-1311.[39]Grynpas MD, Hamilton E, Cheung R, et al. Strontium increases vertebral bone volume in rats at a low dose that does not induce detectable mineralization defect. Bone. 1996; 18(3):253-259.[40]Verberckmoes SC, De Broe ME, D'Haese PC. Dose-dependent effects of strontium on osteoblast function and mineralization.Kidney Int. 2003;64(2):534-543.[41]王薇,张玉梅,闫钧,等.不同掺锶浓度羟基磷灰石涂层对成骨细胞生物学行为的影响[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志, 2010,20(2): 71-75. |
| [1] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [2] | Xue Yadong, Zhou Xinshe, Pei Lijia, Meng Fanyu, Li Jian, Wang Jinzi . Reconstruction of Paprosky III type acetabular defect by autogenous iliac bone block combined with titanium plate: providing a strong initial fixation for the prosthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1424-1428. |
| [3] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [4] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [5] | Gao Wenbo, Ma Zongmin, Li Shuxian, Nie Xiuji. Finite element analysis on the effect of implant length and diameter on initial stability under different bone conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 875-880. |
| [6] | Hu Weifan, Zheng Li, Li Dadi, Sun Yang, Zhao Fengchao. Overexpression of miR-25 downregulates titanium particle-induced osteoclast differentiation through the NFATc1 signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 682-687. |
| [7] | Chen Xiaoxu, Luo Yaxin, Bi Haoran, Yang Kun. Preparation and application of acellular scaffold in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 591-596. |
| [8] | Kang Kunlong, Wang Xintao. Research hotspot of biological scaffold materials promoting osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 597-603. |
| [9] | Shen Jiahua, Fu Yong. Application of graphene-based nanomaterials in stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 604-609. |
| [10] | Zhang Tong, Cai Jinchi, Yuan Zhifa, Zhao Haiyan, Han Xingwen, Wang Wenji. Hyaluronic acid-based composite hydrogel in cartilage injury caused by osteoarthritis: application and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 617-625. |
| [11] | Li Hui, Chen Lianglong. Application and characteristics of bone graft materials in the treatment of spinal tuberculosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 626-630. |
| [12] | Gao Cangjian, Yang Zhen, Liu Shuyun, Li Hao, Fu Liwei, Zhao Tianyuan, Chen Wei, Liao Zhiyao, Li Pinxue, Sui Xiang, Guo Quanyi. Electrospinning for rotator cuff repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 637-642. |
| [13] | Qiu Peng, Fu Qilin, Liu Min, Lan Yuyan, Wang Pin. Comparison of oral micro-adhesion on polyetheretherketone, zirconium dioxide, and pure titanium abutment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 540-545. |
| [14] | Chen Shuo, Xiao Dongqin, Li Xingping, Ran Bin, Shi Feng, Zhang Chengdong, Deng Li, Huang Nanxiang, Liu Kang, Feng Gang, Duan Ke. Preparation and characterization of tantalum functional coating on titanium implant [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 546-552. |
| [15] | He Yunying, Li Lingjie, Zhang Shuqi, Li Yuzhou, Yang Sheng, Ji Ping. Method of constructing cell spheroids based on agarose and polyacrylic molds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 553-559. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||