Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (7): 1113-1118.doi: 10.12307/2022.153
Previous Articles Next Articles
Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing
Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong
- Department of Burns, the Second Affiliated Hospital, Kunming Medical University, Burn Institute of Yunnan Province, Kunming 650101, Yunnan Province, China
-
Received:2020-09-27Revised:2020-09-28Accepted:2020-11-09Online:2022-03-08Published:2021-10-29 -
Contact:Wang Hong, Master, Chief physician, Department of Burns, the Second Affiliated Hospital, Kunming Medical University, Burn Institute of Yunnan Province, Kunming 650101, Yunnan Province, China -
About author:Zhang Jinglin, Master candidate, Physician, Department of Burns, the Second Affiliated Hospital, Kunming Medical University, Burn Institute of Yunnan Province, Kunming 650101, Yunnan Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China Regional Science Foundation Supported Project, No. 81660321 (to WH); Yunnan Provincial Department of Science and Technology - Kunming Medical University Applied Basic Research Joint Special Funding Project, No. 2017FE468(-177) (to WH)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
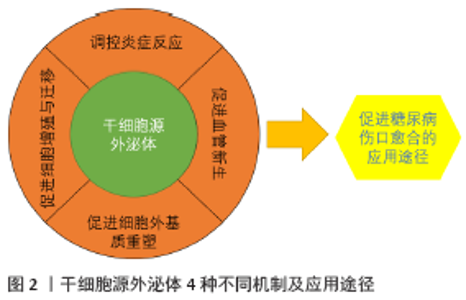
外泌体内常含具有生物活性的蛋白质和遗传信息,在进入靶细胞后可以对糖尿病创面愈合发挥一些作用。干细胞源外泌体促进糖尿病创面愈合的机制可为4类,见图2。 2.1 调控炎症反应 炎症在协调伤口愈合和再生中具有重要作用。间充质干细胞(mesenchymal stem cells,MSCs)具有强大的免疫调节功能,所以间充质干细胞分泌的外泌体可以产生适合炎症消退的微环境以促进组织修复[9]。间充质干细胞来源外泌体被证实具有抗炎和抗凋亡的功能,且具有多种调节炎症的方式。 间充质干细胞来源外泌体内含有具有调节炎症反应的功能性miRNA。例如,骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体中含有抑制促炎细胞因子的miR-210[10];人脐带间充质干细胞来源外泌体中有miR-21,miR-146a和miR-181三种与调节炎症有关的特定免疫相关miRNA[9]。过表达miR-210的间充质干细胞来源外泌体通过NF-κB信号通路降低了白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α的表达。miR-21在炎症消融中起着重要作用。在调控炎症过程中,miR-21会沉默PTEN和GSK3β表达,抑制NF-κB的激活,提高c-jun/AP1活性,从而控制炎症反应并促进伤口愈合。在面对细菌感染时,miR-21抑制抗炎巨噬细胞中的PTEN表达,导致AKT激活,使炎症缓解和伤口愈合。间充质干细胞来源外泌体中的 miR-146a在限制过度炎症反应方面可能具有多种关键作用,miR-146a可以作为先天免疫反应的关键调节因子,阻止几种促炎因子的表达,包括肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6和干扰素γ,还可能调节单核细胞亚群的动态变化。据报道,巨噬细胞和单核细胞中miR-146的转录增强可以减弱单核/巨噬细胞的激活,并抑制促炎巨噬细胞的反应,从而抑制NF-κB介导的炎症[11]。 间充质干细胞来源外泌体还可以通过拮抗炎症因子、抑制促炎因子的分泌来缓解炎症。据报道,间充质干细胞来源外泌体增强了s-GAG的合成,而白细胞介素1β抑制s-GAG的合成,并且间充质干细胞来源外泌体抑制了促炎因子白细胞介素1β诱导的一氧化氮和基质金属蛋白酶13的产生[12]。 间充质干细胞来源外泌体可通过诱导M1向M2型巨噬细胞极化来解决炎症[13]。有报道称,间充质干细胞来源外泌体能显著降低脂多糖诱导的巨噬细胞 M1 型活化标志肿瘤坏死因子α和一氧化氮合酶水平,提高 M2 型活化标志白细胞介素 10 和精氨酸酶 1 水平,调控巨噬细胞向 M2 型极化,从而发挥组织修复的功能[14]。 在调控高糖水平的炎症方面,干细胞源性外泌体发挥着不俗的作用。有报道称,脂肪间充质干细胞衍生的外泌体对链脲佐菌素诱导的1型糖尿病具有免疫调节T细胞炎症反应和减轻临床症状的作用,且免疫调节T细胞炎症主要表现在使白细胞介素4、白细胞介素10和转化生长因子β水平显著增加,白细胞介素17和干扰素γ水平下降等方面[15]。间充质干细胞来源外泌体可介导巨噬细胞激活,而巨噬细胞源性外泌体又可通过抑制促炎酶和肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6的分泌发挥抗炎作用。此外,巨噬细胞源性外泌体还显著增强了磷酸化AKT和血管内皮生长因子的表达,使高糖培养人静脉内皮细胞中AKT/VEGF信号通路激活,从而加速糖尿病伤口愈合[16]。 2.2 促进血管新生 缺血组织血管修复的主要机制是血管生成和血管新生[17]。血管生成是指在胚胎形成过程中,内皮祖细胞迁移到血管化部位,分化为内皮细胞,并聚集形成初始血管丛,而血管新生则是在愈合过程中为了恢复血循环,从现有血管的新毛细血管分支中生出萌芽[17]。血管新生是一种内源性修复机制,对伤口愈合和组织再生起关键性作用,而外泌体是细胞诱导的血管新生的关键旁分泌成分,所以要完成血管新生需要依赖外泌体来发挥作用。干细胞源外泌体可通过多种方式来促进血管新生,修复糖尿病创面。 干细胞源外泌体可通过传递促血管生成相关分子蛋白,刺激血管内皮细胞的增殖、迁移和管形成能力,以促进伤口愈合。例如,经内皮祖细胞衍生外泌体刺激的内皮细胞会增加成纤维细胞生长因子1、血管内皮生长因子A、血管内皮生长因子受体2、血管生成素1、E-选择素、趋化因子16、内皮型一氧化氮合酶和白细胞介素8等血管生成相关分子的表达[18]。据报道,间充质干细胞来源外泌体在体外增加血管内皮生长因子和缺氧诱导因子1α的表达,显著增强了股骨骨折大鼠模型的血管新生[19]。月经血间充质干细胞来源外泌体通过上调血管内皮生长因子A表达增强新血管生成[13]。 这些血管生成相关分子会刺激内皮祖细胞迁移及形成毛细血管网,从而促进大鼠伤口愈合[20]。内皮祖细胞衍生的外泌体不仅可以通过表达血管新生分子促进正常小鼠的创面愈合过程,还可以促进糖尿病大鼠皮肤伤口的修复和再生[18,21]。 人类尿液干细胞来源外泌体中也富含与伤口愈合相关的生物过程调控相关蛋白质。JIANG等[22]发现尿液干细胞来源外泌体包含转化生长因子β1、血管生成素和骨形态发生蛋白7等,它们可能与血管新生和细胞存活有关。尿液干细胞来源外泌体中含有促血管生成蛋白DMBT1,可通过转移DMBT1蛋白促进糖尿病小鼠伤口愈合[23]。 干细胞来源外泌体中有促进血管新生的关键功能性 miRNA,将其转运至靶细胞以改善功能或激活内源性修复机制来治疗糖尿病创面。据报道,来自脐血的人内皮祖细胞系和来自永生的脂肪源间充质干细胞系的微囊泡中存在促血管生成的miRNA:miR-126、miR-296、miR-378和miR-210[24]。例如,内皮祖细胞来源外泌体中miR-126激活Raf/ERK信号,通过下调SPRED1表达,促进了内皮细胞的增殖、迁移和血管生成能力[25]。脂肪间充质干细胞来源外泌体中含有一些促血管生成的微小RNA如miR-126,miR-130a和miR-132,从而使其表现出体外促血管生成特性[26]。诱导多能干细胞衍生的内皮细胞源外泌体中富含miR-199b-5p,其可增强缺血部位的微血管密度和血液灌注[27]。人类胚胎干细胞的外泌体中高度富集miR-200a,通过下调Keap1负调控Nrf2的表达,可促进衰老小鼠的背部压力性溃疡伤口闭合并增强血管新生[28]。 干细胞来源外泌体发挥促进血管新生的途径也各有不同。间充质干细胞来源外泌体通过调节AKT/eNOS途径促进了靶向受体内皮细胞增强血管生成的功能[29]。间充质干细胞来源外泌体也可激活Wnt/β-catenin诱导血管生成,Wnt4会在内皮细胞中诱导β-catenin核转位并发挥促血管生成作用[30]。 内皮祖细胞来源外泌体是通过激活Erk1/2信号传导来改变基因表达,从而显著促进内皮细胞的增殖、迁移[21]。LI等[31] 发现脂肪间充质干细胞来源外泌体过表达Nrf2时,可通过SDF-1/CXCR7的介导而增加对内皮祖细胞显著的保护作用,促进血管新生修复[32],并且Nrf2过表达可以在高葡萄糖环境中促进内皮祖细胞的增殖和血管生成,治疗糖尿病大鼠脚上的伤口溃疡[31]。 干细胞来源外泌体经过处理后促进血管新生作用更加明显,且促进糖尿病创面愈合的效果也更明显。据报道, 455 nm的蓝光可有效促进与间充质干细胞共培养的人脐静脉血管内皮细胞的管形成,蓝光可以通过上调miR-135b-5p和miR-499a-3p增强其促血管生成能力,从而改善人脐带间充质干细胞来源外泌体的治疗效果[33]。通过Akt修饰的间充质干细胞来源外泌体显著加速内皮细胞增殖和迁移,通过激活血小板衍生生长因子D,增强体外管状结构形成和体内血管形成[34]。低氧诱导的间充质干细胞来源外泌体中miR-214表达增加,可以通过抑制ATM基因的表达从而促进血管新生[35]。 116MMU_CIRC_0000250修饰的脂肪间充质干细胞来源外泌体通过miR-128-3p/SIRT1轴通路调节促进糖尿病小鼠创面愈合[36]。由去铁胺预处理的间充质干细胞来源外泌体通过 miR-126介导的PTEN下调激活PI3K/AKT信号通路,从而在体外刺激糖尿病大鼠的伤口愈合和血管生成[37]。 2.3 促进细胞增殖与迁移 干细胞源性外泌体可介导信息传递,促进成纤维细胞增殖,调节角质形成细胞的迁移,从而促进糖尿病伤口的愈合。 干细胞源性外泌体在促进成纤维细胞的增殖和迁移方面具有重要作用,并且不同干细胞来源的外泌体可通过不同方式分泌生长因子促进创面愈合。间充质干细胞来源外泌体激活了伤口愈合过程中几种重要的信号通路,例如Akt通路、ERK通路和STAT3通路等,并诱导了多种生长因子蛋白的表达,如肝细胞生长因子、胰岛素样生长因子1、神经生长因子和基质细胞衍生因子1等来实现创面修复[38]。滑膜间充质干细胞在糖尿病大鼠模型中具有促进成纤维细胞增殖的能力。miR-126-3p过表达的滑膜间充质干细胞来源外泌体以剂量依赖方式刺激了人真皮成纤维细胞的增殖,导致体内上皮再生加速,促进胶原蛋白成熟[39]。人诱导多能干细胞来源的间充质干细胞外泌体在体外以剂量依赖方式刺激了人皮肤成纤维细胞的增殖和迁移,且随着外泌体浓度的增加,Ⅰ、Ⅲ型胶原和弹性蛋白的分泌以及成纤维细胞的mRNA表达也增加[40]。脂肪间充质干细胞来源外泌体可以被成纤维细胞吸收并内化,通过PI3K/Akt信号通路促进成纤维细胞增殖和迁移并优化胶原蛋白沉积[41],使基质金属蛋白酶1、碱性成纤维细胞生长因子、转化生长因子β1的mRNA和蛋白水平均升高,同时增加N-钙黏蛋白、细胞周期蛋白1、增殖细胞核抗原和Ⅰ,Ⅲ胶原蛋白的基因表达[42]。人羊膜间充质干细胞来源外泌体中的miR-135a可促进成纤维细胞迁移,抑制E-钙黏着蛋白、N-钙黏着蛋白、大型肿瘤抑制因子2的表达,并促进α-平滑肌肌动蛋白的表达[43]。 在再上皮化过程中角质形成细胞的迁移对于伤口愈合至关重要。干细胞源外泌体可通过不同的方式促进角质形成细胞的迁移,从而导致糖尿病创面愈合。例如,人循环纤维细胞分泌的外泌体能诱导糖尿病角质形成细胞的迁移和增殖,促进糖尿病小鼠创面的愈合[8]。有报道称,间充质干细胞来源外泌体可能通过调控ERK、AKT 和 STAT3 蛋白的磷酸化而促进角质形成细胞增殖与迁移,且在处理时间为48 h和质量浓度为50 mg/L时效果最明显[44]。脂肪间充质干细胞来源外泌体可促进HaCaT细胞的增殖和迁移,抑制其凋亡。脂肪间充质干细胞来源外泌体可能通过Wnt/β-catenin信号传导在皮肤伤口愈合中发挥积极作用[45]。脂肪间充质干细胞来源外泌体中高表达miR-21,其可以显著加速伤口愈合过程,并促进HaCaT细胞的迁移和增殖,此过程可能通过PI3K/AKT途径影响基质金属蛋白酶2和金属蛋白酶组织抑制剂1蛋白表达,从而起到加速伤口愈合的作用[46]。 2.4 促进细胞外基质重塑 细胞外基质主要由胶原蛋白、纤维蛋白、弹性蛋白,层粘蛋白等组成,给细胞提供适宜的微环境,从而诱导细胞黏附、迁移、分化[47]。在愈合早期,胶原沉淀较为重要;而在愈合后期,基质重塑更为重要。细胞外基质的重塑通常需要持续2周至1年,而细胞外基质的产生和重塑是决定瘢痕形成程度的关键。 干细胞源外泌体可以调控细胞外基质,促进胶原的生成,从而减少瘢痕。有报道称,间充质干细胞来源外泌体可以增加Ⅲ型胶原与Ⅰ型胶原的比例及转化生长因子β3与转化生长因子β1的比例;间充质干细胞来源外泌体还可以降低Ⅰ型胶原与Ⅲ型胶原比例导致瘢痕形成较少。此外,间充质干细胞来源外泌体激活ERK/MAPK信号通路,导致基质金属蛋白酶3的表达增加、基质金属蛋白酶3/金属蛋白酶组织抑制剂1比例增加,从而促进细胞外基质的重建,减少瘢痕形 成,提高创伤愈合质量[48]。 在皮肤伤口愈合期间,肌成纤维细胞聚集是导致瘢痕过多的重要因素,干细胞源性外泌体可抑制肌成纤维细胞的生长和聚集从而抑制瘢痕形成。间充质干细胞来源外泌体可抑制成纤维细胞向肌成纤维细胞分化。人脐带间充质干细胞来源外泌体中的miR-21、miR-23a、miR-125b和miR-145通过TGF-β2/ SMAD2途径抑制α-平滑肌肌动蛋白和胶原沉积以此来抑制肌成纤维细胞生长,以达到抗瘢痕效果[49]。人脐带间充质干细胞来源外泌体不仅起到促进伤口愈合的信号加速器作用,而且还起到抑制瘢痕的信号制动作用。有报道称,人脐带间充质干细胞来源外泌体在皮肤再生的重塑阶段还能促进Wnt/β-catenin信号的自我调节,通过调节YAP表达来协调皮肤再生,限制皮肤细胞过度膨胀和抑制胶原蛋白沉淀[50]。 2.5 干细胞源外泌体在治疗糖尿病创面中的应用途径 干细胞源外泌体在治疗糖尿病伤口时,可配合换药、负压疗法等传统治疗方法加速伤口愈合。有报道称,外泌体移植可能适合于糖尿病足溃疡治疗的临床应用[31]。内皮祖细胞来源外泌体可促进皮肤损伤区的血管新生和成熟、激活Erk1/2信号通路、增强人微血管内皮细胞的成血管功能,从而提高糖尿病大鼠皮肤伤口愈合率,增强新生血管形成、表皮和胶原组织再生[51]。 在对大面积糖尿病伤口进行皮瓣修复时应用干细胞源外泌体可以减少皮瓣坏死。有报道称,对缺血性坏死的组织缺损进行皮瓣移植时,间充质干细胞来源外泌体可以有效促进缺血皮瓣成活,减少皮瓣坏死[52]。脂肪间充质干细胞来源外泌体可通过转运白细胞介素6来激活STAT3通路从而显著提高皮瓣的毛细血管密度和皮瓣的存活率[53]。 将干细胞来源外泌体结合到多功能敷料中,在伤口愈合这一方面有巨大潜力。为了解决如何让外泌体在组织中持续释放的问题,研究人员研发出了具有刺激响应性的脂肪间充质干细胞来源外泌体的FHE水凝胶和FEP水凝胶支架,经证实其确有使创面快速愈合的能力且效果优于单一外泌体治疗,并减少瘢痕形成[54-55]。 此外,在将干细胞源外泌体作为新型无细胞疗法治疗各种疾病时,评估其安全性和毒性是非常重要的。研究人员用脂肪间充质干细胞分泌的外泌体来评估毒理学特征,包括皮肤过敏、光敏化、眼睛和皮肤刺激以及急性口服毒性,结果表明脂肪间充质干细胞来源外泌体可以安全用于局部治疗,并且可以潜在地用作治疗剂、化妆品成分或用于其他生物学用途[56]。 "
| [1] CHEN B, CAI J, WEI Y, et al. Exosomes Are Comparable to Source Adipose Stem Cells in Fat Graft Retention with Up-Regulating Early Inflammation and Angiogenesis. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2019;144(5):816e-827e. [2] THÉRY C, WITWER KW, AIKAWA E, et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): a position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J Extracell Vesicles. 2018;7(1):1535750. [3] HUANG G, LIN G, ZHU Y, et al. Emerging technologies for profiling extracellular vesicle heterogeneity. Lab Chip. 2020;20(14):2423-2437. [4] HUANG X, YUAN T, TSCHANNEN M, et al. Characterization of human plasma-derived exosomal RNAs by deep sequencing. BMC Genomics. 2013;14:319. [5] ZABEO D, CVJETKOVIC A, LÄSSER C, et al. Exosomes purified from a single cell type have diverse morphology. J Extracell Vesicles. 2017; 6(1):1329476. [6] MAIONE AG, SMITH A, KASHPUR O, et al. Altered ECM deposition by diabetic foot ulcer-derived fibroblasts implicates fibronectin in chronic wound repair. Wound Repair Regen. 2016;24(4):630-643. [7] CATRINA SB, ZHENG X. Disturbed hypoxic responses as a pathogenic mechanism of diabetic foot ulcers. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2016; 32 Suppl 1:179-185. [8] GEIGER A, WALKER A, NISSEN E. Human fibrocyte-derived exosomes accelerate wound healing in genetically diabetic mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;467(2):303-309. [9] TI D, HAO H, FU X, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomal microRNAs contribute to wound inflammation. Sci China Life Sci. 2016; 59(12):1305-1312. [10] HE L, CHEN Y, KE Z, et al. Exosomes derived from miRNA-210 overexpressing bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells protect lipopolysaccharide induced chondrocytes injury via the NF-κB pathway. Gene. 2020;751:144764. [11] ETZRODT M, CORTEZ-RETAMOZO V, NEWTON A, et al. Regulation of monocyte functional heterogeneity by miR-146a and Relb. Cell Rep. 2012;1(4):317-324. [12] ZHANG S, TEO KYW, CHUAH SJ, et al. MSC exosomes alleviate temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis by attenuating inflammation and restoring matrix homeostasis. Biomaterials. 2019;200:35-47. [13] DALIRFARDOUEI R, JAMIALAHMADI K, JAFARIAN AH, et al. Promising effects of exosomes isolated from menstrual blood-derived mesenchymal stem cell on wound-healing process in diabetic mouse model. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2019;13(4):555-568. [14] 宋玉仙,张东亚,许玉君,等.人脐带间充质干细胞来源外泌体可调控巨噬细胞的极化[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(13): 2002-2008. [15] NOJEHDEHI S, SOUDI S, HESAMPOUR A, et al. Immunomodulatory effects of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes on experimental type-1 autoimmune diabetes. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119(11):9433-9443. [16] LI M, WANG T, TIAN H, et al. Macrophage-derived exosomes accelerate wound healing through their anti-inflammation effects in a diabetic rat model. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2019;47(1):3793-3803. [17] 张静,易阳艳,阳水发,等.脂肪干细胞来源外泌体对人脐静脉血管内皮细胞增殖、迁移及管样分化的影响[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2018,32(10):1351-1357. [18] LI X, JIANG C, ZHAO J. Human endothelial progenitor cells-derived exosomes accelerate cutaneous wound healing in diabetic rats by promoting endothelial function. J Diabetes Complications. 2016;30(6): 986-992. [19] ZHANG Y, HAO Z, WANG P, et al. Exosomes from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells enhance fracture healing through HIF-1α-mediated promotion of angiogenesis in a rat model of stabilized fracture. Cell Prolif. 2019;52(2):e12570. [20] 徐兵,李海乐,刘丹平,等.骨髓源内皮祖细胞分泌的外泌体对大鼠创伤性皮肤缺损修复的促进作用[J].吉林大学学报(医学版), 2017,43(4): 672-678,857-858. [21] ZHANG J, CHEN C, HU B, et al. Exosomes Derived from Human Endothelial Progenitor Cells Accelerate Cutaneous Wound Healing by Promoting Angiogenesis Through Erk1/2 Signaling. Int J Biol Sci. 2016;12(12):1472-1487. [22] JIANG ZZ, LIU YM, NIU X, et al. Exosomes secreted by human urine-derived stem cells could prevent kidney complications from type I diabetes in rats. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;7:24. [23] CHEN CY, RAO SS, REN L, et al. Exosomal DMBT1 from human urine-derived stem cells facilitates diabetic wound repair by promoting angiogenesis. Theranostics. 2018;8(6):1607-1623. [24] KRAWCZENKO A, BIELAWSKA-POHL A, PAPROCKA M, et al. Microvesicles from Human Immortalized Cell Lines of Endothelial Progenitor Cells and Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells of Adipose Tissue Origin as Carriers of Bioactive Factors Facilitating Angiogenesis. Stem Cells Int. 2020;2020:1289380. [25] JIA Y, ZHU Y, QIU S, et al. Exosomes secreted by endothelial progenitor cells accelerate bone regeneration during distraction osteogenesis by stimulating angiogenesis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):12. [26] ZHU LL, HUANG X, YU W, et al. Transplantation of adipose tissue-derived stem cell-derived exosomes ameliorates erectile function in diabetic rats. Andrologia. 2018;50(2):e12871. [27] YE M, NI Q, QI H, et al. Exosomes Derived from Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells-Endothelia Cells Promotes Postnatal Angiogenesis in Mice Bearing Ischemic Limbs. Int J Biol Sci. 2019;15(1): 158-168. [28] CHEN B, SUN Y, ZHANG J, et al. Human embryonic stem cell-derived exosomes promote pressure ulcer healing in aged mice by rejuvenating senescent endothelial cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):142. [29] QIU X, LIU J, ZHENG C, et al. Exosomes released from educated mesenchymal stem cells accelerate cutaneous wound healing via promoting angiogenesis. Cell Prolif. 2020;53(8):e12830. [30] ZHANG B, WU X, ZHANG X, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell exosomes enhance angiogenesis through the Wnt4/β-catenin pathway. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2015;4(5):513-522. [31] LI X, XIE X, LIAN W, et al. Exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells overexpressing Nrf2 accelerate cutaneous wound healing by promoting vascularization in a diabetic foot ulcer rat model. Exp Mol Med. 2018; 50(4):29. [32] DAI X, YAN X, ZENG J, et al. Elevating CXCR7 Improves Angiogenic Function of EPCs via Akt/GSK-3β/Fyn-Mediated Nrf2 Activation in Diabetic Limb Ischemia. Circ Res. 2017;120(5):e7-e23. [33] YANG K, LI D, WANG M, et al. Exposure to blue light stimulates the proangiogenic capability of exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):358. [34] MA J, ZHAO Y, SUN L, et al. Exosomes Derived from Akt-Modified Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Improve Cardiac Regeneration and Promote Angiogenesis via Activating Platelet-Derived Growth Factor D. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017;6(1):51-59. [35] 张烨,肖轶,余国龙.间充质干细胞来源外泌体促心肌梗死血管新生及其机制研究进展[J].生命科学研究,2020,24(2):153-159. [36] SHI R, JIN Y, HU W, et al. Exosomes derived from mmu_circ_0000250-modified adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells promote wound healing in diabetic mice by inducing miR-128-3p/SIRT1-mediated autophagy. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2020;318(5):C848-C856. [37] DING J, WANG X, CHEN B, et al. Exosomes Derived from Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Stimulated by Deferoxamine Accelerate Cutaneous Wound Healing by Promoting Angiogenesis. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019:9742765. [38] SHABBIR A, COX A, RODRIGUEZ-MENOCAL L, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Exosomes Induce Proliferation and Migration of Normal and Chronic Wound Fibroblasts, and Enhance Angiogenesis In Vitro. Stem Cells Dev. 2015;24(14):1635-1647. [39] TAO SC, GUO SC, LI M, et al. Chitosan Wound Dressings Incorporating Exosomes Derived from MicroRNA-126-Overexpressing Synovium Mesenchymal Stem Cells Provide Sustained Release of Exosomes and Heal Full-Thickness Skin Defects in a Diabetic Rat Model. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017;6(3):736-747. [40] ZHANG J, GUAN J, NIU X, et al. Exosomes released from human induced pluripotent stem cells-derived MSCs facilitate cutaneous wound healing by promoting collagen synthesis and angiogenesis. J Transl Med. 2015;13:49. [41] ZHANG W, BAI X, ZHAO B, et al. Cell-free therapy based on adipose tissue stem cell-derived exosomes promotes wound healing via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Exp Cell Res. 2018;370(2):333-342. [42] HU L, WANG J, ZHOU X, et al. Exosomes derived from human adipose mensenchymal stem cells accelerates cutaneous wound healing via optimizing the characteristics of fibroblasts. Sci Rep. 2016;6:32993. [43] CHEN T, GAO S, HAO Y, et al. Experimental study of human amniotic mesenchymal stem cell exosome promoting fibroblasts migration through microRNA-135a. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2020;34(2):234-239. [44] 田新立,江波,颜洪.脂肪间充质干细胞来源外泌体对角质形成细胞增殖和迁移的影响与机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(1): 68-73. [45] MA T, FU B, YANG X, et al. Adipose mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promote cell proliferation, migration, and inhibit cell apoptosis via Wnt/β-catenin signaling in cutaneous wound healing. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(6):10847-10854. [46] YANG C, LUO L, BAI X, et al. Highly-expressed micoRNA-21 in adipose derived stem cell exosomes can enhance the migration and proliferation of the HaCaT cells by increasing the MMP-9 expression through the PI3K/AKT pathway. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2020;681:108259. [47] 郭昊宇,李伟权,刘开源,等.基于细胞外基质仿生工程心肌构建的研究进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(10):1577-1584. [48] 胡丽.人脂肪间充质干细胞来源的外泌体通过调控细胞外基质重建促进皮肤无瘢痕愈合[C].北京:中华口腔医学会口腔医学科研管理分会第二次学术年会,2017. [49] FANG S, XU C, ZHANG Y, et al. Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomal MicroRNAs Suppress Myofibroblast Differentiation by Inhibiting the Transforming Growth Factor-β/SMAD2 Pathway During Wound Healing. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016;5(10): 1425-1439. [50] ZHANG B, SHI Y, GONG A, et al. HucMSC Exosome-Delivered 14-3-3ζ Orchestrates Self-Control of the Wnt Response via Modulation of YAP During Cutaneous Regeneration. Stem Cells. 2016;34(10):2485-2500. [51] 陈春媛.人EPCs来源外泌体修复糖尿病大鼠皮肤缺损的作用及机制[D].南昌:南昌大学,2016. [52] 胡玄,易阳艳,朱元正,等.脂肪干细胞来源外泌体促进大鼠皮瓣移植后血管新生的研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2019,33(12): 1560-1565. [53] PU CM, LIU CW, LIANG CJ, et al. Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Protect Skin Flaps against Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury via IL-6 Expression. J Invest Dermatol. 2017;137(6):1353-1362. [54] WANG C, WANG M, XU T, et al. Engineering Bioactive Self-Healing Antibacterial Exosomes Hydrogel for Promoting Chronic Diabetic Wound Healing and Complete Skin Regeneration. Theranostics. 2019;9(1):65-76. [55] WANG M, WANG C, CHEN M, et al. Efficient Angiogenesis-Based Diabetic Wound Healing/Skin Reconstruction through Bioactive Antibacterial Adhesive Ultraviolet Shielding Nanodressing with Exosome Release. ACS Nano. 2019;13(9):10279-10293. [56] HA DH, KIM SD, LEE J, et al. Toxicological evaluation of exosomes derived from human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem/stromal cells. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 2020;115:104686. [57] DUSCHER D, BARRERA J, WONG VW, et al. Stem Cells in Wound Healing: The Future of Regenerative Medicine? A Mini-Review. Gerontology. 2016;62(2):216-225. [58] GUAY C, KRUIT JK, ROME S, et al. Lymphocyte-Derived Exosomal MicroRNAs Promote Pancreatic β Cell Death and May Contribute to Type 1 Diabetes Development. Cell Metab. 2019;29(2):348-361. [59] ROBBINS PD, DORRONSORO A, BOOKER CN. Regulation of chronic inflammatory and immune processes by extracellular vesicles. J Clin Invest. 2016;126(4):1173-1180. [60] VAN DER POL E, BÖING AN, HARRISON P, et al. Classification, functions, and clinical relevance of extracellular vesicles. Pharmacol Rev. 2012; 64(3):676-705. [61] NAIR S, SALOMON C. Extracellular vesicles and their immunomodulatory functions in pregnancy. Semin Immunopathol. 2018;40(5):425-437. [62] LAMICHHANE TN, SOKIC S, SCHARDT JS, et al. Emerging roles for extracellular vesicles in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2015;21(1):45-54. [63] NEWTON WC, KIM JW, LUO JZQ, et al. Stem cell-derived exosomes: a novel vector for tissue repair and diabetic therapy. J Mol Endocrinol. 2017;59(4):R155-R165. [64] SUN Y, SHI H, YIN S, et al. Human Mesenchymal Stem Cell Derived Exosomes Alleviate Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus by Reversing Peripheral Insulin Resistance and Relieving β-Cell Destruction. ACS Nano. 2018; 12(8):7613-7628. [65] YANG M, SHENG L, ZHANG TR, et al. Stem cell therapy for lower extremity diabetic ulcers: where do we stand? Biomed Res Int. 2013; 2013:462179. [66] BUI TQ, BUI QVP, NÉMETH D, et al. Epidermal Growth Factor is Effective in the Treatment of Diabetic Foot Ulcers: Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019;16(14):2584. |
| [1] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1316-1322. |
| [2] | Xiao Hao, Liu Jing, Zhou Jun. Research progress of pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1323-1329. |
| [3] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [4] | Fan Yiming, Liu Fangyu, Zhang Hongyu, Li Shuai, Wang Yansong. Serial questions about endogenous neural stem cell response in the ependymal zone after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1137-1142. |
| [5] | Wen Dandan, Li Qiang, Shen Caiqi, Ji Zhe, Jin Peisheng. Nocardia rubra cell wall skeleton for extemal use improves the viability of adipogenic mesenchymal stem cells and promotes diabetes wound repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1038-1044. |
| [6] | Zhu Bingbing, Deng Jianghua, Chen Jingjing, Mu Xiaoling. Interleukin-8 receptor enhances the migration and adhesion of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells to injured endothelium [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1045-1050. |
| [7] | Luo Xiaoling, Zhang Li, Yang Maohua, Xu Jie, Xu Xiaomei. Effect of naringenin on osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1051-1056. |
| [8] | Xiong Tinglin, Ying Menghui, Zhang Lisha, Zhang Xiaogang, Yang Yan. Electrophysiological characteristics of cardiomyocytes differentiated from induced pluripotent stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1063-1067. |
| [9] | Wang Xinmin, Liu Fei, Xu Jie, Bai Yuxi, Lü Jian. Core decompression combined with dental pulp stem cells in the treatment of steroid-associated femoral head necrosis in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1074-1079. |
| [10] | Fang Xiaolei, Leng Jun, Zhang Chen, Liu Huimin, Guo Wen. Systematic evaluation of different therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in the treatment of ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1085-1092. |
| [11] | Guo Jia, Ding Qionghua, Liu Ze, Lü Siyi, Zhou Quancheng, Gao Yuhua, Bai Chunyu. Biological characteristics and immunoregulation of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1093-1101. |
| [12] | Wu Weiyue, Guo Xiaodong, Bao Chongyun. Application of engineered exosomes in bone repair and regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1102-1106. |
| [13] | Huang Chenwei, Fei Yankang, Zhu Mengmei, Li Penghao, Yu Bing. Important role of glutathione in stemness and regulation of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1119-1124. |
| [14] | Hui Xiaoshan, Bai Jing, Zhou Siyuan, Wang Jie, Zhang Jinsheng, He Qingyong, Meng Peipei. Theoretical mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine theory on stem cell induced differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1125-1129. |
| [15] | Liang Xuezhen, Yang Xi, Li Jiacheng, Luo Di, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Bushen Huoxue capsule regulates osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via Hedgehog signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1020-1026. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||