Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (7): 1130-1136.doi: 10.12307/2022.156
Previous Articles Next Articles
Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration
An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu
- First Department of Orthopedics, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150000, Heilongjiang Province, China
-
Received:2020-12-23Revised:2020-12-25Accepted:2021-02-22Online:2022-03-08Published:2021-10-29 -
Contact:Liu Jianyu, MD, Chief physician, Professor, First Department of Orthopedics, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150000, Heilongjiang Province, China -
About author:An Weizheng, Master candidate, First Department of Orthopedics, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150000, Heilongjiang Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81971828 (to LJY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
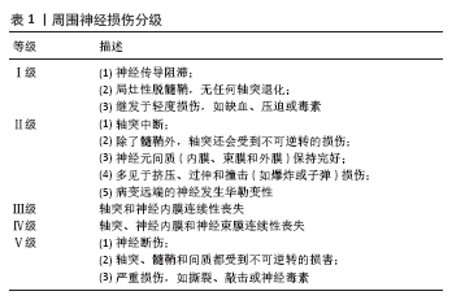
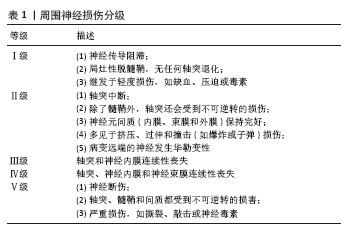
2.1 周围神经损伤简介 流行病学研究表明,周围神经损伤的发生率可高达所有创伤患者的3%[1-2]。周围神经从内到外可分为3层:神经内膜、神经束膜和神经外膜。结缔组织为神经纤维提供机械支持,并含有为神经纤维提供营养支持的血管。周围神经损伤的治疗效果取决于周围神经的轴突、神经内膜、神经束膜和神经外膜的损伤程度和支持结构的完整性,以及神经功能检查结果[3-5]。周围神经损伤分级见表1,桑德兰Ⅰ级周围神经损伤表示一过性神经疾病,Ⅱ级周围神经损伤的特点是神经轴突断裂,神经内膜及神经束膜完整。桑德兰Ⅰ级和Ⅱ级周围神经损伤可以在不干预的情况下恢复。桑德兰Ⅲ级周围神经损伤的特点是轴突和内膜管断裂,但神经束膜保持完整。由于神经内膜管的破坏,导致结构紊乱,桑德兰Ⅲ级损伤有自行恢复的可能性,但由于神经内膜瘢痕化,恢复常不完全[6]。桑德兰Ⅳ级周围神经损伤的特点是神经束膜完全断裂,只有神经外膜相连,神经外观连续性仍存在。在桑德兰Ⅴ级周围神经损伤中,所有的支持结构都严重受损,并伴随着明显的出血和间隙瘢痕形成。Ⅳ,Ⅴ级周围神经损伤自然恢复的机会非常低,需要手术探查和修复[7]。 2.2 周围神经损伤的治疗 2.2.1 非手术治疗方法 非手术治疗方法对于桑德兰Ⅰ-Ⅲ级周围神经损伤有许多优点,但由于损伤类型和严重程度的不同,非手术治疗的效果往往不确定。 (1)物理疗法:物理疗法(如电刺激、磁刺激、激光光疗)被认为是最广泛使用和最有效的非手术治疗方法之一[8]。低频电刺激可以促进神经功能的恢复,但其最佳使用频率和持续时间以及不良反应尚不明确,不适当的应用甚至可能导致不良结果[9]。磁刺激和激光光疗也是应用广泛的物理疗法,可以促进周围神经损伤的恢复[10-11]。 (2)药物治疗:根据动物实验,有几种药物已被证明能促进损伤后周围神经功能的恢复。然而,只有少数药物应用于临床,如神经营养因子3、胶质细胞源性神经营养因子、胶质生长因子、睫状神经营养因子和亮肽素[12]。此外,B族维生素和甲钴胺等也常用于周围神经损伤的治疗。一些研究表明,物理疗法和药物疗法相结合可以促进神经的再生,例如电刺激和皮质类固醇的结合[13]。 2.2.2 手术治疗方法 手术治疗的目的是重建神经内膜、神经束膜和神经外膜的连续性,从而支持神经的再生。损伤严重程度可在术中确定,因此治疗效果比非手术治疗更具特异性。 (1)神经缝合:神经缝合术是将神经外膜和/或神经束膜的近端和远端缝合在一起的最基本和最常用的外科方法[14]。 神经缝合适用于无缺损或有微小缺损的神经,范围从5 mm到20 mm。如果有中、大的神经间隙,由于缝合后张力过大,恢复效果较弱,需要神经移植或神经移位[15]。 (2)神经移位:神经移位被定义为通过使用近端的 “外来”神经作为供体来修复远端损伤[16]。健康的供体神经被切断后,转移到更关键的受损神经上重建功能,常用于上肢功能恢复和臂丛神经修复等。然而,由于供体神经缺损造成的功能缺失以及移位后神经支配、调控需要协调过程,神经移位术没有得到广泛应用。 (3)自体神经移植:一直被认为是治疗周围神经中大型缺损的“金标准”[17]。通常用于移植的神经有腓肠神经、肋间神经、腓浅神经和腓深神经[18]。与其他方法相比,自体神经移植更有效,但是依然有诸多缺点,如供体神经可用性有限、供区感觉障碍、神经瘤形成、供体神经与缺损神经之间的匹配性差[19],自体神经移植只有40%-50%的成功率。同种异体神经移植可以避免自体移植引起的供区病变,临床应用更加灵活,但主要缺点是免疫调节治疗的相关并发症以及传播疾病的可能。 2.2.3 光遗传学 光遗传学是一种治疗周围神经损伤的新疗法[20],它涉及到利用光来控制活组织中的细胞[21]。靶向神经细胞首先被基因修饰以表达光敏离子通道或离子泵[22],光激活蛋白被特定波长的光激活和失活。光遗传学可以极其精确地控制神经的激活和抑制,而不需要与神经进行物理接触[23]。2016年,WARD和他的同事发表了第一份关于光遗传促进THY-1-ChR2/YFP小鼠周围神经横断后运动轴突再生的报告[23]。THY-1-ChR2/YFP小鼠坐骨神经经1 ms持续时间的蓝光脉冲(473 nm)预处理1 h后进行横断和即刻显微外科修复,术后组织学和电生理学观察到光刺激神经元的轴突再生和肌肉再神经支配都有积极的效果[23]。基于光遗传学治疗会给周围神经损伤带来革命性的变化,目前还处于实验阶段,仍然需要进一步研究,以确定如何更好地将这项技术转化为人类临床使用。 2.2.4 神经导管 使用生物材料神经导管治疗节段性神经损伤,具有防止周围组织长入及减少神经瘤发生等优点,通过这种方式可以将轴突从近端引导到远端,从而使受损的突触得以正确连接。应用组织工程化的神经导管来桥接神经缺损已经成为一种替代策略。大量的组织工程学研究集中在开发新型的神经引导管,旨在促进神经损伤后的轴突再生。目前已经报道了各种自体或人工材料,如静脉[24]、外斜肌的外膜[25]、纤维蛋白[26]、生物可降解的聚乙醇酸管[27],以及使用各种材料三维打印的神经导管[28]。 2.2.5 干细胞治疗 干细胞在一定条件下能无限制自我更新与增殖分化,因此在再生医学中受到了广泛的研究。胚胎干细胞因其多能性和显著的自我更新能力而备受青睐,但由于监管限制、伦理因素、可能的肿瘤形成等因素,胚胎干细胞的应用受到许多潜在的限制。相反,成体干细胞更容易获得,从自体组织中获得时完全免疫兼容;此外,它们较少有各种伦理因素的担忧[29]。 成体干细胞可以从多种组织中分离出来,并被诱导分化为多种细胞系。临床治疗环境中,理想的干细胞应该能够以可调节的方式维持和再生组织,可通过微创手术获得,供体部位发病率低,并可安全地移植到自体或异体宿主。从骨 髓[30]、脐血[31] 、皮肤[32]、毛囊[33]、脂肪组织分离出的成体干细胞具有能在体外诱导成神经和/或胶质表型的潜能[34-35]。然而,骨髓采集是一种有创操作,获得的骨髓间充质干细胞产量往往不足。外周血、脂肪和其他组织很容易获得,但它们分化成多个谱系的能力不足[36]。 多能神经干细胞是具有自我更新潜能的原始神经细胞,能够分化为3种成熟的神经细胞(即神经元、星形胶质细胞和少突胶质细胞)[37]。神经干细胞具有可塑性强、迁移率高、免疫原性低等特点,已被应用于组织工程[38-39]。然而,来源有限、获取困难和有限扩增能力限制了它们的广泛应用。针对这些局限性,近年来研究人员将注意力转向骨骼肌作为成体干细胞的来源。从小鼠或人肌肉组织中分离出的肌源干细胞具有强大的自我更新能力、多向分化能力以及免疫特权等行为。 2.3 肌源干细胞治疗周围神经损伤 2.3.1 肌源干细胞简介 肌源干细胞可以定义为存在于骨骼肌间质组织中的所有具有干细胞和/或祖细胞特性的细胞[40];肌源干细胞在分离、培养、分化潜能等方面均不同于肌卫星细胞。肌源干细胞是圆形、非贴壁或最少贴壁的细胞,能自发收缩,在各种培养条件下形成集落[41-42]。骨骼肌占人体总质量的30%-40%,其来源丰富且容易获取,骨骼肌组织来源干细胞有望成为理想的组织工程种子细胞。 成体肌肉含有不同的祖细胞群体,研究最广泛的是卫星细胞和肌源干细胞。卫星细胞是“肌源性前体细胞”,能够在损伤后再生肌肉并经历自我更新;然而,它们被认为致力于肌源性谱系,并未被证明可以分化为其他谱系[43-44]。肌源干细胞被认为是卫星细胞的前身,表现出更高的再生能力、更高的细胞存活率,以及比卫星细胞更广泛的多系分化能力[45]。从小鼠和人类分离的肌源干细胞都表现出高抗氧化性能[45-46]。此外,肌源干细胞在体外能够进行多达200个代数的倍增,同时保持其干细胞特性和再生能力[47]。 在一定培养条件下,肌源干细胞可以分化为肌肉细胞[48]、成脂细胞[49]、成骨细胞[50]、软骨细胞[51]、内皮细胞[52]、 肝脏细胞[53]、造血细胞[54]、许旺细胞和神经细胞[55-58]。肌源干细胞的多能性引起了人们的广泛兴趣,它们在再生医学中具有广阔的应用前景。由于周围神经损伤常伴有严重的创伤性肌肉损伤、出血和骨折,因此,多能肌源干细胞在修复受损的组织器官方面具有独特的优势。 2.3.2 肌源干细胞的分离与鉴定 目前人们已经从人和一些动物如大鼠、小鼠等体内分离得到肌源干细胞[59-62],但是由于肌源干细胞的异质性和技术手段等因素,有时不能分离得到纯度较高的肌源干细胞,甚至导致无法正确获得目的干细胞。 肌源干细胞的分离方法包括预贴壁[61]、冻融技术[63]、流式细胞术[64]、磁珠分选法等[65]。到目前为止,肌源干细胞的分离普遍采用非依赖于标记的预贴壁方法。基于表面标记谱、免疫染色和流式细胞术的细胞分选不仅有利于肌源干细胞的分离,而且有助于其特性的确定。CD34抗原是一种跨膜细胞表面糖蛋白,已在不同物种中被鉴定为造血干细胞标记物,它通常由肌源干细胞表达[65-66]。SCA-1是一种在鼠造血干细胞中表达的蛋白质,目前它也被认为是鼠肌源干细胞的一种表面标志,但也有学者报道分离的肌源干细胞不表达SCA-1。研究总结认为具有较强成肌潜能的小鼠卫星细胞表达Pax7而不表达为CD34和SCA-1,而多潜能肌源干细胞表达CD34、SCA-1而不表达Pax7。结蛋白也被认为是常见标记物[66-69]。此外鼠肌源干细胞还表达间充质干细胞标记物CD44,而几乎不表达造血干细胞标记物CD45[51]。研究人员已经筛选出人肌源干细胞[70],人肌源干细胞表达最多的标志物是结蛋白(>70%),其次是CD105和波形蛋白。此外,CD45、血管内皮生长因子受体2(FLK1/KDR)、CD31、血管内皮细胞钙粘连蛋白(VE-cadherin)和血管性血友病因子均为阴性。虽然AC133/CD133的百分率很低,但AC133/CD133持续表达,这一标记在造血干细胞和血管干细胞以及神经干细胞中非常常见[71]。根据CD34和CD29的表达可以把人肌源干细胞分为2个主要群体,分别是有较强成肌潜能的CD34-/CD45-/CD29+(Sk-DN/29+)细胞和多向分化潜能的CD34+/CD45-(Sk-34)细胞[70]。然而由于培养条件的不同,细胞表面标志物在体外可能有不同程度的上调或下调,这使得识别肌源干细胞的原始标志物变得困难[33]。因此,目前肌源干细胞尤其是人肌源干细胞的原始标志物仍有争议,进一步的研究对于确定不同肌源干细胞群体之间的分子差异和相似性至关重要。 2.3.3 肌源干细胞的体外研究 研究人员在体外主要研究了肌源干细胞的分化潜能尤其是神经及胶质表型细胞的分化潜能。许旺细胞在神经再生过程中扮演着很重要的角色。神经损伤后,远端神经通过华勒变性而降解,而近端神经萌发出新神经。许旺细胞通过增殖并形成Bungner带作为新生神经纤维的引导支架来支持神经再生[72]。此外,他们还合成细胞黏附分子,通过基底板支持轴突的生长[73-74]。由于许旺细胞来源有限、获取困难,限制了其广泛应用。相比之下,以干细胞尤其是肌源干细胞为基础的疗法,可以潜在地增强许旺细胞介导的神经修复。 鉴于许旺细胞在神经再生过程中的重要作用,最初人们猜想肌源干细胞主要是通过直接分化为许旺细胞或神经细胞而发挥作用的,并尝试将肌源干细胞诱导分化为具有神经表型的细胞。到目前为止,关于肌源干细胞神经分化的有效培养和诱导方案还没有达成共识[75]。目前,神经培养基和神经球方案被广泛用于神经干细胞的分化[75],它们已被应用于将肌源干细胞向神经系分化:用神经鸡尾酒诱导方案处理扁平单层的肌源干细胞,以及悬浮培养形成肌源干细胞的生长球体,使用这两种方案,研究人员都成功地将肌源干细胞诱导成神经表型[63,76]。培养方案各有不同,生长因子包括:神经营养因子3、维甲酸、腺苷酸环化酶激活剂、碱性成纤维细胞生长因子和表皮细胞生长因子,结合血小板衍生生长因子BB、血管内皮生长因子或胰岛素样生长因子、脑源性神经营养因子、睫状神经营养因子和丹参等[55,65,71,76-79]。为了评价神经分化的有效率,测定了不同神经标志物的表达水平。常用的神经元标记物包括β-微管蛋白Ⅲ(β-tubulin)、磷酸化神经丝、Tuj1、NF68、神经元特异性烯醇化酶、巢蛋白和突触囊泡蛋白突触素;星形胶质细胞标记物胶质纤维酸性蛋白;少突胶质细胞标记物CNPase和MOSP[63]。研究人员对啮齿动物肌源干细胞的神经分化进行了深入研究,并使用与鼠肌源干细胞相似的程序分离人骨骼肌源性干细胞,分析了诱导神经发生后的多能性。在暴露于神经培养基后,人骨骼肌源性干细胞显示出间充质标志物波形蛋白表达增加,以及β-微管蛋白Ⅲ、CNPase和胶质纤维酸性蛋白的显著表达[71]。 然而,由于分离和鉴定技术的差异,不同培养基的诱导效率不能直接进行比较。总体而言,脑源性神经营养因子、碱性成纤维细胞生长因子、表皮生长因子等生长因子的有效性被确立。 此外,骨形态发生蛋白4可以促进成骨[69],而神经营养因子和血管内皮生长因子分别诱导肌源干细胞向神经源性和内皮分化[80]。神经生长因子对肌源干细胞的刺激显著提高了肌营养不良小鼠模型的植入效率[81],这表明神经发生和肌肉发生之间存在联系,并证实了环境在干细胞分化中的作用。 肌源干细胞的体外培养过程受到多种因素的影响,其中培养基的选择非常关键。肌源干细胞在不同培养基中的增殖特征不同,在添加了细胞因子的培养基中肌源干细胞增殖较快,并保持小而圆的细胞形态,维持成肌、成内皮和成神经分化潜能[62]。 2.3.4 肌源干细胞的移植研究 目前肌源干细胞移植治疗周围神经损伤的研究都采用动物模型,将分离自人和动物的肌源干细胞单独或者联合导管等移植到周围神经损伤动物模型体内。日本学者TAMAKI等[82]报道了利用培养7 d的小鼠肌源干细胞优先和全面重建了严重受损的坐骨神经,在这项研究中,比较了肌源干细胞、骨髓间充质干细胞以及新鲜分离的损伤坐骨神经细胞对受损神经重建的贡献,结果表明,肌源干细胞的植入率明显高于其他两组,后两组的植入率相近。此外,骨髓间充质干细胞移植后未见明确的周围神经支持细胞形成或整合到血管内,而肌源干细胞和坐骨神经细胞表现出典型的向全部支持细胞分化。此外,植入的肌源干细胞有助于增加血管形成,有利于血液供应和废物排泄,这一趋势似乎是肌源干细胞移植的典型特征。神经营养因子和神经/血管生长因子mRNA的表达也得到了证实,尤其是神经生长因子、脑源性神经营养因子、胶质细胞源性神经营养因子、重组人半乳糖凝集素1、细胞黏附分子、睫状神经营养因子、白血病抑制因子、转录因子Sox10、碱性成纤维细胞生长因子和胰岛素样生长因子1对神经再生很重要,而生长因子诱导蛋白和肝细胞生长因子对血管再生很重要。肌源干细胞移植后这些因子的表达至少保留了4周,这些因子在受损/移植部位的充分表达可能会对受体细胞和供体细胞产生旁分泌效应,促进经再生,还证明了与健康神经移植相比,肌源干细胞具有更大的治疗潜力。 美国学者JOHNNY HUARD在一项研究中证明了在特定培养条件下,人肌源干细胞可分化为表型成熟的神经细胞和神经胶质细胞[75]。在NeuroCult增殖液中培养2 d后,人肌源干细胞形成神经球,人肌源干细胞来源神经球表达神经和神经胶质特异性蛋白,例如β-tubulin和GFAP,人肌源干细胞来源神经球共表达Tuj1和S100,而其他神经球仅表达Tuj1。 将人肌源干细胞植入小鼠临界大小的坐骨神经缺损中,通过分化为许旺细胞产生髓鞘来再生神经,恢复了神经功能,在近端神经残端的生长锥处出现了人类特异性的PCNA+供体细胞,这表明人肌源干细胞包围在再生轴突周围,以促进髓鞘形成和轴突生长。近年发现,人肌源干细胞在体内主要通过旁分泌细胞因子来发挥其再生功能[83],诱导内源性轴突生长而发挥治疗作用。因此,人肌源干细胞促进神经再生至少部分是通过旁分泌/内分泌机制介导的。人肌源干细胞在正常和重症联合免疫缺陷小鼠中表现出免疫特权特性[80],包括它们以相似的方式存活、分裂和参与伤口愈合的能力[84]。此外,在移植后18个月内没有观察到损伤部位有肿瘤形成的迹象。 人肌源干细胞可以通过流式细胞术被进一步分离获得Sk-dN/29+细胞和Sk34+细胞[70],培养2周后,这两种细胞分别表现出高肌源性(Sk-dN/29+)和多潜能(Sk-34+)特性。体内分析显示,Sk-dN/29+细胞促进肌肉再生,而Sk34+细胞表现出旺盛的间质植入性,并分化为许旺细胞、神经周围/神经内膜细胞、血管内皮细胞和周细胞;此外,对于长间隙损伤,Sk34+细胞移植组在电刺激坐骨神经后,下游肌肉的强直性张力显著恢复(超过90%);SK-dN/29+细胞移植组的功能恢复也好于对照组。因此,在细胞生物学、组织形态学和生理学方面,人Sk34+细胞显示出与小鼠肌源干细胞相似的治疗能力。有趣的是,在Sk-dN/29+细胞中也观察到了显著的轴突/髓鞘数量的恢复,而Sk-dN/29+细胞在移植后2-4周内被完全消除。此外,血管数量增加也很明显(四五倍),与适度的功能恢复相关。因此,移植的Sk-dN/29+细胞在最初2-4周的旁分泌效应可能对整体恢复有积极影响,对受损神经组织的修复起到辅助作用。Sk34+细胞和Sk-dN/29+细胞联合移植将是神经修复的最佳方法[70]。作者还发现,与单独培养相比,移植前将SK-dN/29+和Sk-34+细胞共培养后的植入率和分化能力显著降低。因此,他们建议分别培养这2个群体,然后进行联合移植,以获得最佳的神经修复效果。尽管如此,SK-dN/29+细胞和Sk-34+细胞的进一步鉴定,以及它们在功能恢复中的协同作用还需要进一步的研究。 以上研究不仅证明了鼠和人骨骼肌源性干细胞移植到横断坐骨神经后可以通过分化为许旺细胞、神经束膜/神经内膜细胞、血管周细胞、内皮细胞和平滑肌细胞等展现出显著的治疗能力,还可以通过分泌作用促进坐骨神经再生。 尽管大多数研究验证了肌源干细胞的巨大潜力,肌源干细胞移植治疗仍有致瘤风险。在一项研究中,将肌源干/祖细胞移植到小鼠临界大小的坐骨神经缺损后,受损的周围神经在移植后6周显示完全再生,受损的周围神经功能完全恢复[85]。然而,坐骨神经再生11-13周之间,观察到肿瘤生长,由此产生的肿瘤是具有横纹肌母细胞分化的恶性周围神经鞘瘤,表达肌源性、神经源性和胶质标记物。肌源干细胞参与了损伤周围神经的再生,当它们接收到神经源性和肌源性分化信号时,将以微环境和时间依赖方式转化。 2.3.5 肌源干细胞与神经导管等联合移植研究 目前,装载细胞等活性成分的神经导管等逐渐成为神经移植治疗长间隙神经缺损的替代方法。仅用无细胞导管需要两三个月才能修复1 cm的间隙,这可能导致肌肉退化和功能障碍[86]。与单纯空神经导管相比,植入神经导管的干细胞和许旺细胞表现出更好的功能修复效果[87-88],可控释放的再生神经营养因子也被证明有利于轴突生长[89]。但是许旺细胞的大量获取仍然很困难[90],因此研究人员将重点放在了用干细胞增强的神经导管的发展上。 TAMAKI等[82]证明小鼠肌源干细胞能够在脱细胞导管连接的长间隙坐骨神经缺损模型中重建肌肉-神经-血管单位。随着临床应用的进一步深入,该小组随后研究了人肌源干细胞在这种神经损伤模型中的治疗潜力。他们发现,将人类Sk-34+细胞移植到由食管黏膜下层构建的脱细胞神经导管中,有利于轴突生长和髓鞘形成,并在导管中分化为周围神经血管支持细胞。 在最近发表的一项研究中,研究人员制备了一种带管腔的肌管,桥接C57野生型小鼠坐骨神经5 mm长的缺损,然后将绿色荧光蛋白标记的肌源干细胞和基质胶混悬液移植到管内[25]。术后4周和8周进行组织学和功能评估,结果显示肌肉组织工程化修复神经缺损效果显著,新生神经高表达绿色荧光蛋白。 除了移植到损伤的坐骨神经,肌源干细胞移植到其他周围神经也表现出了显著的治疗效果。对于多神经分支损伤如面神经损伤,很难找到匹配的神经移植物,也未见报道有合适的神经导管被开发出来,有学者研制出的一种干细胞补片显示出良好的治疗效果[91]。该研究人员开发了一种使用凝胶状肌源干细胞片状颗粒的三维补片移植系统[92],将由肌源干细胞组成的三维贴片移植系统应用于严重手术切除后的面神经-血管网络的再生,显著促进了功能恢复,并证明了骨骼肌来源多能干细胞补片治疗神经血管大缺损方面的潜在应用价值。 对于横断喉返神经,研究人员建立了一种新的治疗方法,利用小鼠肌源干细胞和生物可吸收聚糖酸酯联合移植获得横断喉返神经的形态和功能再生[93]。分离小鼠肌源干细胞,扩增后接种聚糖酸酯进行联合移植,以单纯培养基移植和聚糖酸酯+培养基移植(聚糖酸酯组)为对照,8周后,经喉镜检查显示联合移植组呼吸时自发声带运动恢复了80%,而培养基移植组和聚糖酸酯组则完全没有恢复。肌源干细胞定植在受损的横断喉返神经,表现出良好的阻止细胞在聚糖酸酯上扩散的作用,神经生长因子mRNA表达增强。免疫组织化学分析显示,肌源干细胞向许旺细胞、神经束膜/神经内膜细胞分化,轴突恢复率达86%以上。 此外,也有研究报道了自主运动对人骨骼肌源性干细胞结合脱细胞导管桥接治疗长间隙神经损伤具有明显的促进作用[94]。 虽然出现了各种神经导管及新型干细胞移植手段,但鲜有报道治疗效果超过自体神经移植。目前仍受到范围小 (≤3 cm)和功能恢复率低的限制[95]。3D打印是一种增材制造技术,它是以一种数字模型文件为基础,运用粉末状金属或塑料等可粘合材料,通过逐层堆叠累积的方式来构造3D结构物体的技术,这项技术的兴起使人们能够更精确地复制天然周围神经的特征,也能够个性化地将细胞或材料组合来克服神经再生的一些挑战。3D打印的优点:①3D打印可以根据不同部位的神经以及损伤大小来定制支架的形状。与3D成像相结合,能够获取3D拓扑数据来设计与损伤微环境相匹配的支架,且具有高度的解剖学保真度[96];②3D打印方法允许将合适的细胞类型或生物分子直接打印到所需的支架上,以实现原位重建和再生[97];③3D打印允许在一台打印机中集成不同类别的多种材料,包括细胞、生物材料、纤维、聚合物、纳米材料、陶瓷和金属。这种选择不同材料的灵活性可以精确高效地制备出不同需求的个性化产品[98];④3D打印提供了器官级别的体外神经系统平台的快速成型,可以更加清楚地展示出人体中复杂的神经网络系统。总之,3D打印这些功能在重建复杂结构(如神经系统)方面比其他方法具有更强大的优势[99]。 尽管3D打印神经再生装置及其应用已取得重大进展,但仍有许多问题需要克服:①到目前为止,只有有限的几种神经细胞被研究过,因此有必要对特定细胞类型赋予所需功能;②除了细胞、生物材料等,还需要将血管网络结合到支架中;③生物材料和细胞的最佳组合仍有待进一步研究。在选择和设计生物材料时,应仔细考虑以下方面:①生物材料的机械性能;②打印分辨率要求小于50 μm,以便在结构上与天然组织网络相匹配;③完整性、低毒性和适合多层通道构建;④生物降解性;⑤细胞相容性或包含神经细胞增殖和黏附所需的生物成分[100]。"
| [1] ZHANG X, QU W, LI D, et al. Functional Polymer‐Based Nerve Guide Conduits to Promote Peripheral Nerve Regeneration. Advanced Materials Interfaces. 2020;7(14):2000225. [2] RELAIX F, BENCZE M, BOROK MJ, et al. Perspectives on skeletal muscle stem cells. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):692. [3] SCHMIDT CE, LEACH JB. Neural tissue engineering: strategies for repair and regeneration. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2003;5:293-347. [4] PINHO AC, FONSECA AC, SERRA AC, et al. Peripheral Nerve Regeneration: Current Status and New Strategies Using Polymeric Materials. Adv Healthc Mater. 2016;5(21):2732-2744. [5] PETCU EB, MIDHA R, MCCOLL E, et al. 3D printing strategies for peripheral nerve regeneration. Biofabrication. 2018;10(3):032001. [6] TOS P, PIANA R, BOUX E, et al. Index Finger Pollicization for Functional Preservation of the Hand After Giant Liposarcoma Resection of the Thenar Eminence. J Hand Microsurg. 2015;7(1):216-219. [7] FARONI A, MOBASSERI SA, KINGHAM PJ, et al. Peripheral nerve regeneration: experimental strategies and future perspectives. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015;82-83:160-167. [8] MARTÍNEZ DE ALBORNOZ P, DELGADO PJ, Forriol F, et al. Non-surgical therapies for peripheral nerve injury. Br Med Bull. 2011;100:73-100. [9] HAASTERT-TALINI K, SCHMITTE R, KORTE N, et al. Electrical stimulation accelerates axonal and functional peripheral nerve regeneration across long gaps. J Neurotrauma. 2011;28(4):661-674. [10] BANNAGA A, GUO T, OUYANG X, et al. Magnetic stimulation accelerating rehabilitation of peripheral nerve injury. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2002;22(2):135-139. [11] BUCHAIM DV, ANDREO JC, FERREIRA JUNIOR RS, et al. Efficacy of Laser Photobiomodulation on Morphological and Functional Repair of the Facial Nerve. Photomed Laser Surg. 2017;35(8):442-449. [12] JOUNG I, YOO M, WOO JH, et al. Secretion of EGF-like domain of heregulinβ promotes axonal growth and functional recovery of injured sciatic nerve. Mol Cells. 2010;30(5):477-484. [13] SHARMA N, MARZO SJ, JONES KJ, et al. Electrical stimulation and testosterone differentially enhance expression of regeneration-associated genes. Exp Neurol. 2010;223(1):183-191. [14] LI R, LIU Z, PAN Y, et al. Peripheral nerve injuries treatment: a systematic review. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2014;68(3):449-454. [15] JOHNSON EO, SOUCACOS PN. Nerve repair: experimental and clinical evaluation of biodegradable artificial nerve guides. Injury. 2008;39 Suppl 3:S30-36. [16] MIDHA R. Emerging techniques for nerve repair: nerve transfers and nerve guidance tubes. Clin Neurosurg. 2006;53:185-190. [17] RAY WZ, MACKINNON SE. Management of nerve gaps: autografts, allografts, nerve transfers, and end-to-side neurorrhaphy. Exp Neurol. 2010;223(1):77-85. [18] NORKUS T, NORKUS M, RAMANAUSKAS T. Donor, recipient and nerve grafts in brachial plexus reconstruction: anatomical and technical features for facilitating the exposure. Surg Radiol Anat. 2005;27(6): 524-530. [19] GRINSELL D, KEATING CP. Peripheral nerve reconstruction after injury: a review of clinical and experimental therapies. Biomed Res Int. 2014; 2014:698256. [20] PARK S, KOPPES RA, FRORIEP UP, et al. Optogenetic control of nerve growth. Sci Rep. 2015;5:9669. [21] DEISSEROTH K, FENG G, MAJEWSKA AK, et al. Next-generation optical technologies for illuminating genetically targeted brain circuits. J Neurosci. 2006;26(41):10380-10386. [22] DEISSEROTH K. Optogenetics: 10 years of microbial opsins in neuroscience. Nat Neurosci. 2015;18(9):1213-1225. [23] WARD PJ, JONES LN, MULLIGAN A, et al. Optically-Induced Neuronal Activity Is Sufficient to Promote Functional Motor Axon Regeneration In Vivo. PLoS One. 2016;11(5):e0154243. [24] KARACAOGLU E, YÜKSEL F, PEKER F, et al. Nerve regeneration through an epineurial sheath: its functional aspect compared with nerve and vein grafts. Microsurgery. 2001;21(5):196-201. [25] XU Z, CHEN Z, FENG W, et al. Grafted muscle-derived stem cells promote the therapeutic efficiency of epimysium conduits in mice with peripheral nerve gap injury. Artif Organs. 2020;44(5):E214-E225. [26] RINKER B, VYAS KS. Clinical applications of autografts, conduits, and allografts in repair of nerve defects in the hand: current guidelines. Clin Plast Surg. 2014;41(3):533-550. [27] HOUSCHYAR KS, MOMENI A, PYLES MN, et al. The Role of Current Techniques and Concepts in Peripheral Nerve Repair. Plast Surg Int. 2016;2016:4175293. [28] VIJAYAVENKATARAMAN S, ZHANG S, THAHARAH S, et al. Electrohydrodynamic Jet 3D Printed Nerve Guide Conduits (NGCs) for Peripheral Nerve Injury Repair. Polymers (Basel). 2018;10(7):753. [29] WU X, WANG S, CHEN B, et al. Muscle-derived stem cells: isolation, characterization, differentiation, and application in cell and gene therapy. Cell Tissue Res. 2010;340(3):549-567. [30] LONG X, OLSZEWSKI M, HUANG W, et al. Neural cell differentiation in vitro from adult human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2005;14(1):65-69. [31] SYPECKA J, ZIEMKA-NALECZ M, DRAGUN-SZYMCZAK P, et al. A simple, xeno-free method for oligodendrocyte generation from human neural stem cells derived from umbilical cord: engagement of gelatinases in cell commitment and differentiation. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2017; 11(5):1442-1455. [32] KRAUSE MP, DWORSKI S, FEINBERG K, et al. Direct genesis of functional rodent and human schwann cells from skin mesenchymal precursors. Stem Cell Reports. 2014;3(1):85-100. [33] YAMAZAKI A, YASHIRO M, MII S, et al. Isoproterenol directs hair follicle-associated pluripotent (HAP) stem cells to differentiate in vitro to cardiac muscle cells which can be induced to form beating heart-muscle tissue sheets. Cell Cycle. 2016;15(5):760-765. [34] SUN F, ZHOU K, MI WJ, et al. Combined use of decellularized allogeneic artery conduits with autologous transdifferentiated adipose-derived stem cells for facial nerve regeneration in rats. Biomaterials. 2011;32(32):8118-8128. [35] ERBA P, MANTOVANI C, KALBERMATTEN DF, et al. Regeneration potential and survival of transplanted undifferentiated adipose tissue-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve conduits. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2010;63(12):e811-817. [36] HUANG JI, KAZMI N, DURBHAKULA MM, et al. Chondrogenic potential of progenitor cells derived from human bone marrow and adipose tissue: a patient-matched comparison. J Orthop Res. 2005;23(6): 1383-1389. [37] PARKER MA, ANDERSON JK, CORLISS DA, et al. Expression profile of an operationally-defined neural stem cell clone. Exp Neurol. 2005; 194(2):320-332. [38] BELKIND-GERSON J, HOTTA R, WHALEN M, et al. Engraftment of enteric neural progenitor cells into the injured adult brain. BMC Neurosci. 2016;17:5. [39] SUN D, GUGLIOTTA M, ROLFE A, et al. Sustained survival and maturation of adult neural stem/progenitor cells after transplantation into the injured brain. J Neurotrauma. 2011;28(6):961-972. [40] COSTAMAGNA D, BERARDI E, CECCARELLI G, et al. Adult Stem Cells and Skeletal Muscle Regeneration. Curr Gene Ther. 2015;15(4):348-363. [41] TAMAKI T, OKADA Y, UCHIYAMA Y, et al. Clonal multipotency of skeletal muscle-derived stem cells between mesodermal and ectodermal lineage. Stem Cells. 2007;25(9):2283-2290. [42] 姚致雅.肛门直肠畸形大鼠盆底肌发育异常的分子机制及其宫内移植干细胞修复作用的研究[D].沈阳:中国医科大学,2020. [43] JANKOWSKI RJ, DEASY BM, HUARD J. Muscle-derived stem cells. Gene Ther. 2002;9(10):642-647. [44] CEUSTERS J, LEJEUNE JP, SANDERSEN C, et al. From skeletal muscle to stem cells: an innovative and minimally-invasive process for multiple species. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):696. [45] URISH KL, VELLA JB, OKADA M, et al. Antioxidant levels represent a major determinant in the regenerative capacity of muscle stem cells. Mol Biol Cell. 2009;20(1):509-520. [46] VELLA JB, THOMPSON SD, BUCSEK MJ, et al. Murine and human myogenic cells identified by elevated aldehyde dehydrogenase activity: implications for muscle regeneration and repair. PLoS One. 2011;6(12): e29226. [47] DEASY BM, GHARAIBEH BM, POLLETT JB, et al. Long-term self-renewal of postnatal muscle-derived stem cells. Mol Biol Cell. 2005;16(7): 3323-3333. [48] NEEF K, TRESKES P, XU G, et al. Dynamic Support Culture of Murine Skeletal Muscle-Derived Stem Cells Improves Their Cardiogenic Potential In Vitro. Stem Cells Int. 2015;2015:247091. [49] AGUIARI P, LEO S, ZAVAN B, et al. High glucose induces adipogenic differentiation of muscle-derived stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(4):1226-1231. [50] KIM KS, LEE JH, AHN HH, et al. The osteogenic differentiation of rat muscle-derived stem cells in vivo within in situ-forming chitosan scaffolds. Biomaterials. 2008;29(33):4420-4428. [51] LI H, JOHNSON NR, USAS A, et al. Sustained release of bone morphogenetic protein 2 via coacervate improves the osteogenic potential of muscle-derived stem cells. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2013; 2(9):667-677. [52] PARK HS, HAHN S, CHOI GH, et al. Muscle-derived stem cells promote angiogenesis and attenuate intimal hyperplasia in different murine vascular disease models. Stem Cells Dev. 2013;22(6):866-877. [53] BELLAYR IH, GHARAIBEH B, HUARD J, et al. Skeletal muscle-derived stem cells differentiate into hepatocyte-like cells and aid in liver regeneration. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2010;3(7):681-690. [54] FARACE F, PRESTOZ L, BADAOUI S, et al. Evaluation of hematopoietic potential generated by transplantation of muscle-derived stem cells in mice. Stem Cells Dev. 2004;13(1):83-92. [55] TANG Y, HE H, CHENG N, et al. PDGF, NT-3 and IGF-2 in combination induced transdifferentiation of muscle-derived stem cells into Schwann cell-like cells. PLoS One. 2014;9(1):e73402. [56] KIM ES, KIM GH, KANG ML, et al. Potential induction of rat muscle-derived stem cells to neural-like cells by retinoic acid. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2011;5(5):410-414. [57] KWON JS, KIM GH, KIM DY, et al. Chitosan-based hydrogels to induce neuronal differentiation of rat muscle-derived stem cells. Int J Biol Macromol. 2012;51(5):974-979. [58] VOJNITS K, PAN H, MU X, et al. Characterization of an Injury Induced Population of Muscle-Derived Stem Cell-Like Cells. Sci Rep. 2015;5: 17355. [59] KIM HS, LEE BN, CHOI S, et al. Behavior of Muscle-Derived Stem Cells on Silica Nanostructured Substrates. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020;10(9):1651. [60] TAMAKI T, UCHIYAMA Y, HIRATA M, et al. Therapeutic isolation and expansion of human skeletal muscle-derived stem cells for the use of muscle-nerve-blood vessel reconstitution. Front Physiol. 2015;6:165. [61] GHARAIBEH B, LU A, TEBBETS J, et al. Isolation of a slowly adhering cell fraction containing stem cells from murine skeletal muscle by the preplate technique. Nat Protoc. 2008;3(9):1501-1509. [62] 刘志强,李妍,杨小娟,等.小鼠肌源性干细胞在3种不同培养基中的增殖特征[J].基础医学与临床,2019,39(12):1669-1674. [63] ROMERO-RAMOS M, VOURC’H P, YOUNG HE, et al. Neuronal differentiation of stem cells isolated from adult muscle. J Neurosci Res. 2002;69(6):894-907. [64] TAMAKI T, UCHIYAMA Y, OKADA Y, et al. Functional recovery of damaged skeletal muscle through synchronized vasculogenesis, myogenesis, and neurogenesis by muscle-derived stem cells. Circulation. 2005; 112(18):2857-2866. [65] PARK JS, KIM S, HAN DK, et al. Isolation of neural precursor cells from skeletal muscle tissues and their differentiation into neuron-like cells. Exp Mol Med. 2007;39(4):483-490. [66] XU Z, YU L, LU H, et al. A modified preplate technique for efficient isolation and proliferation of mice muscle-derived stem cells. Cytotechnology. 2018;70(6):1671-1683. [67] SEALE P, SABOURIN LA, GIRGIS-GABARDO A, et al. Pax7 is required for the specification of myogenic satellite cells. Cell. 2000;102(6):777-786. [68] COTTLE BJ, LEWIS FC, SHONE V, et al. Skeletal muscle-derived interstitial progenitor cells (PICs) display stem cell properties, being clonogenic, self-renewing, and multi-potent in vitro and in vivo. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):158. [69] LEE JY, QU-PETERSEN Z, CAO B, et al. Clonal isolation of muscle-derived cells capable of enhancing muscle regeneration and bone healing. J Cell Biol. 2000;150(5):1085-1100. [70] TAMAKI T, HIRATA M, NAKAJIMA N, et al. A Long-Gap Peripheral Nerve Injury Therapy Using Human Skeletal Muscle-Derived Stem Cells (Sk-SCs): An Achievement of Significant Morphological, Numerical and Functional Recovery. PLoS One. 2016;11(11):e0166639. [71] ALESSANDRI G, PAGANO S, BEZ A, et al. Isolation and culture of human muscle-derived stem cells able to differentiate into myogenic and neurogenic cell lineages. Lancet. 2004;364(9448):1872-1883. [72] LADAK A, OLSON J, TREDGET EE, et al. Differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells to support peripheral nerve regeneration in a rat model. Exp Neurol. 2011;228(2):242-252. [73] TERENGHI G. Peripheral nerve regeneration and neurotrophic factors. J Anat. 1999;194(Pt 1):1-14. [74] RODRÍGUEZ FJ, VERDÚ E, CEBALLOS D, et al. Nerve guides seeded with autologous schwann cells improve nerve regeneration. Exp Neurol. 2000;161(2):571-584. [75] LAVASANI M, THOMPSON SD, POLLETT JB, et al. Human muscle-derived stem/progenitor cells promote functional murine peripheral nerve regeneration. J Clin Invest. 2014;124(4):1745-1756. [76] YANG J, WANG X, WANG Y, et al. Dopaminergic neuronal conversion from adult rat skeletal muscle-derived stem cells in vitro. Neurochem Res. 2012;37(9):1982-1992. [77] ZENG X, ZHANG L, SUN L, et al. Recovery from rat sciatic nerve injury in vivo through the use of differentiated MDSCs in vitro. Exp Ther Med. 2013;5(1):193-196. [78] KONDO T, CASE J, SROUR EF, et al. Skeletal muscle-derived progenitor cells exhibit neural competence. Neuroreport. 2006;17(1):1-4. [79] VOURC’H P, ROMERO-RAMOS M, CHIVATAKARN O, et al. Isolation and characterization of cells with neurogenic potential from adult skeletal muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004;317(3):893-901. [80] QU-PETERSEN Z, DEASY B, JANKOWSKI R, et al. Identification of a novel population of muscle stem cells in mice: potential for muscle regeneration. J Cell Biol. 2002;157(5):851-864. [81] LAVASANI M, LU A, PENG H, et al. Nerve growth factor improves the muscle regeneration capacity of muscle stem cells in dystrophic muscle. Hum Gene Ther. 2006;17(2):180-192. [82] TAMAKI T, HIRATA M, SOEDA S, et al. Preferential and comprehensive reconstitution of severely damaged sciatic nerve using murine skeletal muscle-derived multipotent stem cells. PLoS One. 2014;9(3):e91257. [83] LAVASANI M, ROBINSON AR, LU A, et al. Muscle-derived stem/progenitor cell dysfunction limits healthspan and lifespan in a murine progeria model. Nat Commun. 2012;3:608. [84] RADFAR AJ, ROBBINS PD, HUARD J, et al. Transplantation of virally transduced cells into the dermis of immunocompetent and immunodeficient (SCID) mice to determine gene expression profile and differential donor cell survival. Wound Repair Regen. 2000;8(6):503-510. [85] LAVASANI M, POLLETT JB, USAS A, et al. The microenvironment-specific transformation of adult stem cells models malignant triton tumors. PLoS One. 2013;8(12):e82173. [86] HUANG CW, HUANG WC, QIU X, et al. The Differentiation Stage of Transplanted Stem Cells Modulates Nerve Regeneration. Sci Rep. 2017; 7(1):17401. [87] GEORGIOU M, GOLDING JP, LOUGHLIN AJ, et al. Engineered neural tissue with aligned, differentiated adipose-derived stem cells promotes peripheral nerve regeneration across a critical sized defect in rat sciatic nerve. Biomaterials. 2015;37:242-251. [88] COSTA HJ, BENTO RF, SALOMONE R, et al. Mesenchymal bone marrow stem cells within polyglycolic acid tube observed in vivo after six weeks enhance facial nerve regeneration. Brain Res. 2013;1510:10-21. [89] CUI Q. Actions of neurotrophic factors and their signaling pathways in neuronal survival and axonal regeneration. Mol Neurobiol. 2006;33(2): 155-179. [90] SUN XH, CHE YQ, TONG XJ, et al. Improving nerve regeneration of acellular nerve allografts seeded with SCs bridging the sciatic nerve defects of rat. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2009;29(3):347-353. [91] SAITO K, TAMAKI T, HIRATA M, et al. Reconstruction of Multiple Facial Nerve Branches Using Skeletal Muscle-Derived Multipotent Stem Cell Sheet-Pellet Transplantation. PLoS One. 2015;10(9):e0138371. [92] TAMAKI T, SOEDA S, HASHIMOTO H, et al. 3D reconstitution of nerve-blood vessel networks using skeletal muscle-derived multipotent stem cell sheet pellets. Regen Med. 2013;8(4):437-451. [93] KAZUNO A, MAKI D, YAMATO I, et al. Regeneration of Transected Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve Using Hybrid-Transplantation of Skeletal Muscle-Derived Stem Cells and Bioabsorbable Scaffold. J Clin Med. 2018;7(9):276. [94] SETA H, MAKI D, KAZUNO A, et al. Voluntary Exercise Positively Affects the Recovery of Long-Nerve Gap Injury Following Tube-Bridging with Human Skeletal Muscle-Derived Stem Cell Transplantation. J Clin Med. 2018;7(4):67. [95] DALY W, YAO L, ZEUGOLIS D, et al. A biomaterials approach to peripheral nerve regeneration: bridging the peripheral nerve gap and enhancing functional recovery. J R Soc Interface. 2012;9(67):202-221. [96] KADOYA K, LU P, NGUYEN K, et al. Spinal cord reconstitution with homologous neural grafts enables robust corticospinal regeneration. Nat Med. 2016;22(5):479-487. [97] JOHNSON BN, LANCASTER KZ, ZHEN G, et al. 3D Printed Anatomical Nerve Regeneration Pathways. Adv Funct Mater. 2015;25(39):6205-6217. [98] LADD C, SO JH, MUTH J, et al. 3D printing of free standing liquid metal microstructures. Adv Mater. 2013;25(36):5081-5085. [99] JOHNSON BN, LANCASTER KZ, HOGUE IB, et al. 3D printed nervous system on a chip. Lab Chip. 2016;16(8):1393-1400. [100] JOUNG D, LAVOIE NS, GUO SZ, et al. 3D Printed Neural Regeneration Devices. Adv Funct Mater. 2020;30(1):10. |
| [1] | Xiang Xinjian, Liu Fang, Wu Liangliang, Jia Daping, Tao Yue, Zhao Zhengnan, Zhao Yu. High-dose vitamin C promotes the survival of autologous fat transplantation in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1298-1302. |
| [2] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1316-1322. |
| [3] | Zhu Chan, Han Xuke, Yao Chengjiao, Zhang Qiang, Liu Jing, Shao Ming. Acupuncture for Parkinson’s disease: an insight into the action mechanism in animal experiments [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1330-1335. |
| [4] | Fan Yiming, Liu Fangyu, Zhang Hongyu, Li Shuai, Wang Yansong. Serial questions about endogenous neural stem cell response in the ependymal zone after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1137-1142. |
| [5] | Xuan Juanjuan, Bai Hongtai, Zhang Jixiang, Wang Yaoquan, Chen Guoyong, Wei Sidong. Role of regulatory T cell subsets in liver transplantation and progress in clinical application [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1143-1148. |
| [6] | Tian Chuan, Zhu Xiangqing, Yang Zailing, Yan Donghai, Li Ye, Wang Yanying, Yang Yukun, He Jie, Lü Guanke, Cai Xuemin, Shu Liping, He Zhixu, Pan Xinghua. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulate ovarian aging in macaques [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 985-991. |
| [7] | Gao Yujin, Peng Shuanglin, Ma Zhichao, Lu Shi, Cao Huayue, Wang Lang, Xiao Jingang. Osteogenic ability of adipose stem cells in diabetic osteoporosis mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 999-1004. |
| [8] | Zhou Ying, Zhang Huan, Liao Song, Hu Fanqi, Yi Jing, Liu Yubin, Jin Jide. Immunomodulatory effects of deferoxamine and interferon gamma on human dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1012-1019. |
| [9] | Liang Xuezhen, Yang Xi, Li Jiacheng, Luo Di, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Bushen Huoxue capsule regulates osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via Hedgehog signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1020-1026. |
| [10] | Liu Feng, Peng Yuhuan, Luo Liangping, Wu Benqing. Plant-derived basic fibroblast growth factor maintains the growth and differentiation of human embryonic stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1032-1037. |
| [11] | Luo Xiaoling, Zhang Li, Yang Maohua, Xu Jie, Xu Xiaomei. Effect of naringenin on osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1051-1056. |
| [12] | Xiong Tinglin, Ying Menghui, Zhang Lisha, Zhang Xiaogang, Yang Yan. Electrophysiological characteristics of cardiomyocytes differentiated from induced pluripotent stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1063-1067. |
| [13] | Fang Xiaolei, Leng Jun, Zhang Chen, Liu Huimin, Guo Wen. Systematic evaluation of different therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in the treatment of ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1085-1092. |
| [14] | Guo Jia, Ding Qionghua, Liu Ze, Lü Siyi, Zhou Quancheng, Gao Yuhua, Bai Chunyu. Biological characteristics and immunoregulation of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1093-1101. |
| [15] | Wu Weiyue, Guo Xiaodong, Bao Chongyun. Application of engineered exosomes in bone repair and regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1102-1106. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||