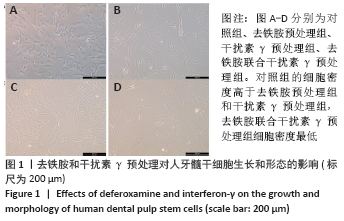
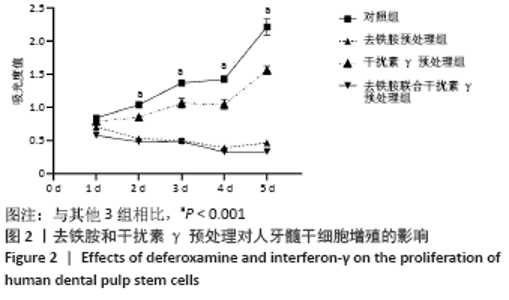
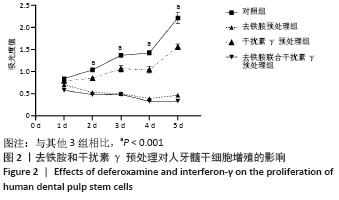
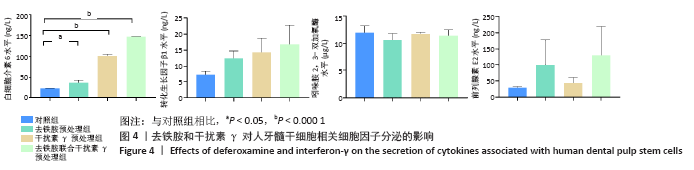
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (7): 1012-1019.doi: 10.12307/2022.137
Previous Articles Next Articles
Immunomodulatory effects of deferoxamine and interferon gamma on human dental pulp stem cells
Zhou Ying1, Zhang Huan2, Liao Song3, Hu Fanqi3, Yi Jing1, Liu Yubin1, Jin Jide1
- 1Institute of Radiation Medicine, Academy of Military Medical Science, Academy of military Sciences, Beijing 100850, China; 2Department of Breast and Bone and Soft Tissue Oncology, Affiliated Tumor Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 3General Hospital of Chinese PLA, Beijing 100853, China
-
Received:2021-03-30Revised:2021-04-01Accepted:2021-04-19Online:2022-03-08Published:2021-10-29 -
Contact:Jin Jide, MD, Associate researcher, Institute of Radiation Medicine, Academy of Military Medical Science, Academy of military Sciences, Beijing 100850, China -
About author:Zhou Ying, Master, Institute of Radiation Medicine, Academy of Military Medical Science, Academy of military Sciences, Beijing 100850, China -
Supported by:Key Military Logistics Project, No. BWS17J021 (to ZY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhou Ying, Zhang Huan, Liao Song, Hu Fanqi, Yi Jing, Liu Yubin, Jin Jide. Immunomodulatory effects of deferoxamine and interferon gamma on human dental pulp stem cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1012-1019.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
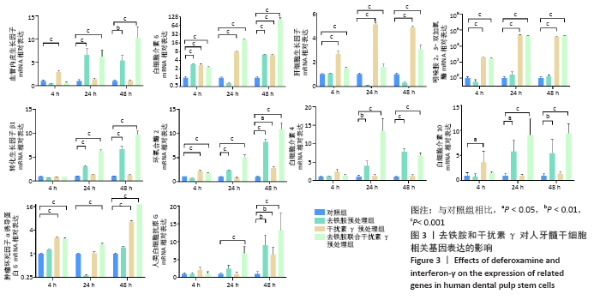
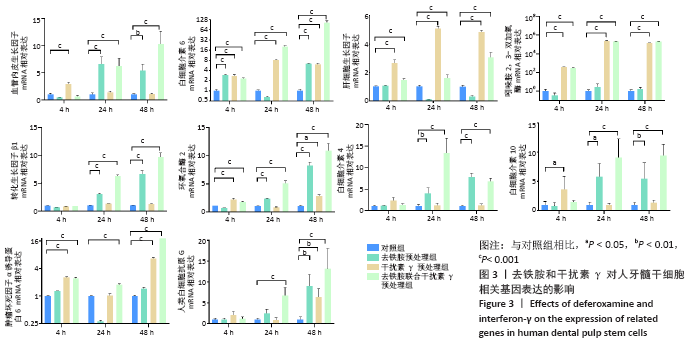
2.3 去铁胺和干扰素γ对人牙髓干细胞相关基因表达的影响 由图3可知,血管内皮生长因子在去铁胺处理后24 h表达开始升高,并持续到48 h;在干扰素γ处理后仅在4 h时表达高于对照组;而联合处理后24 h表达明显高于对照组,并持续到48 h。白细胞介素6的表达在4 h时各预处理组均高于对照组,并持续到48 h(但在24 h去铁胺组显著降低)。肝细胞生长因子和吲哚胺2,3-双加氧酶的表达只有干扰素γ预处理组和联合预处理组高于对照组,由4 h持续到48 h。转化生长因子β1、环氧合酶2、白细胞介素4和白细胞介素10的表达则只有去铁胺预处理组和联合预处理组在24 h和48 h高于对照组。肿瘤坏死因子α诱导蛋白6的表达在处理后4 h和48 h高于对照组(但在24 h去铁胺预处理组显著降低),而联合预处理组在3个时间段均高于对照组。人类白细胞抗原G的表达在24 h只有联合预处理组高于对照组,48 h 3个预处理组均高于对照组。 相比其他组,去铁胺预处理组对血管内皮生长因子、白细胞介素6、转化生长因子β1、环氧合酶2、人类白细胞抗原G、白细胞介素4和白细胞介素10等基因的表达上调作用较显著;干扰素γ预处理组对白细胞介素6、肝细胞生长因子、吲哚胺2,3-双加氧酶和肿瘤坏死因子α诱导蛋白6等基因的表达上调较显著,而二者联合预处理后血管内皮生长因子、白细胞介素6、转化生长因子β1、环氧合酶2、白细胞介素10、肿瘤坏死因子α诱导蛋白6、人类白细胞抗原G等基因的表达均出现显著上调,但肝细胞生长因子与吲哚胺2,3-双加氧酶基因的表达在干扰素γ预处理组上调更显著。"
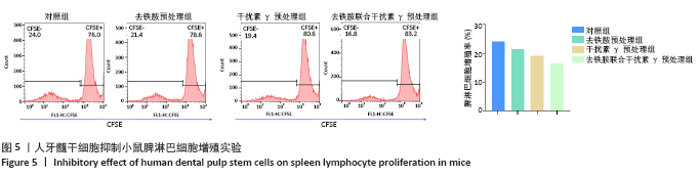
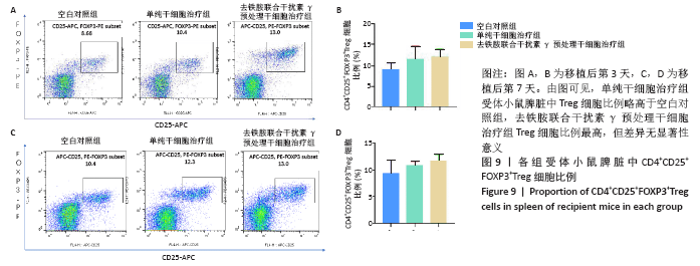
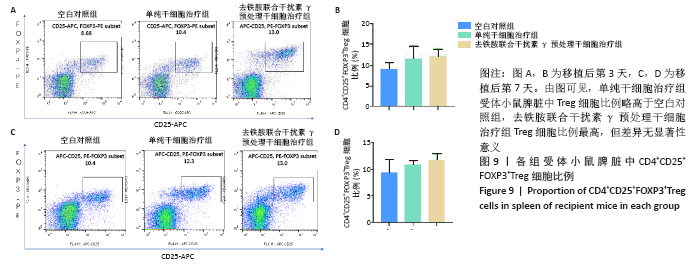
2.5 去铁胺联合干扰素γ对人牙髓干细胞抑制淋巴细胞增殖的影响 不同预处理的人牙髓干细胞与CFSE预染的小鼠脾淋巴细胞共培养3 d后,通过流式细胞术检测脾淋巴细胞的增殖。如图5所示,与抗CD3抗体活化的脾细胞共培养后,去铁胺或干扰素γ预处理人牙髓干细胞均抑制了脾淋巴细胞的增殖,且去铁胺联合干扰素γ预处理人牙髓干细胞抑制脾淋巴细胞的增殖作用最强。 2.6 小鼠异体移植皮片的存活时间 空白对照组小鼠移植皮片在术后7 d即开始有动物出现脱落,至观察期14 d结束所有小鼠的移植皮肤均发生脱落,平均存活时间仅为(9.25±3.20) d;单纯干细胞治疗组移植皮片的存活时间较空白对照组有所延长,平均存活时间为(11.75±2.21) d;去铁胺联合干扰素γ预处理干细胞治疗组至观察期14 d结束,仅有1只小鼠的移植皮肤在第14天发生脱落。结果表明,人牙髓干细胞可以延长小鼠异体移植皮肤的存活时间,但去铁胺联合干扰素γ预处理人牙髓干细胞的作用更为明显。"
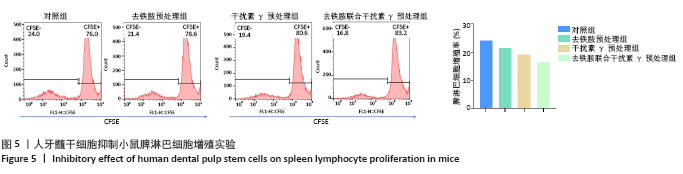
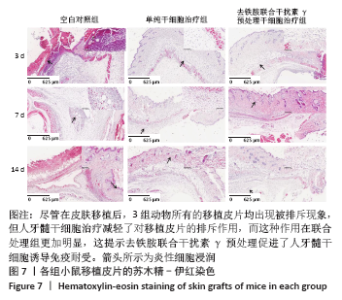
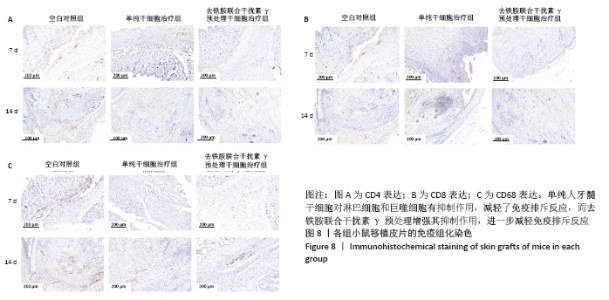
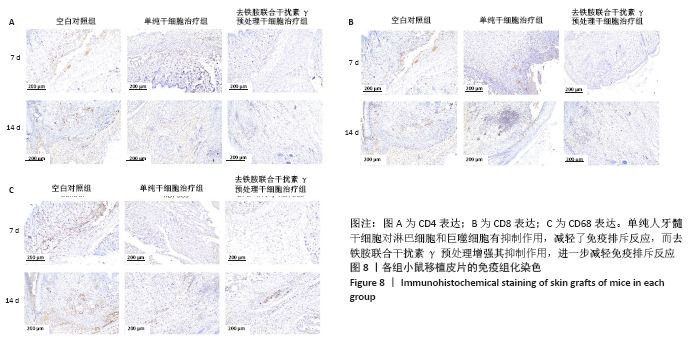
2.8 移植皮片苏木精-伊红染色结果 如图7所示,移植后第3天,空白对照组小鼠移植皮片出现大量炎细胞浸润,出现急性脓肿,炎症反应显著,表皮和真皮均出现坏死,评分为4级;单纯干细胞治疗组移植皮片可见局灶性炎细胞浸润,有轻微表皮变性,评分为2级;去铁胺联合干扰素γ预处理干细胞治疗组移植皮片的皮肤附属器尚存完好,仅有少量炎细胞浸润,评分为1级。移植后第7天,空白对照组皮片仍显示大量炎细胞浸润,组织水肿,表皮、真皮坏死,出现慢性肉芽肿,评分为3级;单纯干细胞治疗组移植皮片可见局灶性炎性细胞浸润,有轻微表皮变性,评分为2级:去铁胺联合干扰素γ预处理干细胞治疗组移植皮片没有发现表皮变性,但可见局灶炎症细胞浸润,皮肤附属器尚存完好,评分为1级。移植后第14天,空白对照组和单纯干细胞治疗组小鼠移植皮片已完全脱落;去铁胺联合干扰素γ预处理干细胞治疗组移植皮片仅有少许炎细胞浸润,表皮、真皮结构完整,附属器尚存完好,瘢痕修复好,评分为1级。尽管在皮肤移植后,3组动物所有的移植皮片均出现被排斥现象,但人牙髓干细胞治疗减轻了对移植皮片的排斥作用,而这种作用在联合处理组更加明显,这提示去铁胺联合干扰素γ预处理促进了人牙髓干细胞诱导免疫耐受。"
| [1] KITTLESON MM, KOBASHIGAWA JA. Cardiac Transplantation: Current Outcomes and Contemporary Controversies. JACC Heart Fail. 2017;5(12): 857-868. [2] STEHLIK J, KOBASHIGAWA J, HUNT SA, et al. Honoring 50 Years of Clinical Heart Transplantation in Circulation: In-Depth State-of-the-Art Review. Circulation. 2018;137(1):71-87. [3] YANG H, APRECIO RM, ZHOU X, et al. Therapeutic effect of TSG-6 engineered iPSC-derived MSCs on experimental periodontitis in rats: a pilot study. PLoS One. 2014;9(6):e100285. [4] GRONTHOS S, MANKANI M, BRAHIM J, et al. Postnatal human dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) in vitro and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000; 97(25):13625-13630. [5] JI L, BAO L, GU Z, et al. Comparison of immunomodulatory properties of exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and dental pulp stem cells. Immunol Res. 2019;67(4-5):432-442. [6] DUIJVESTEIN M, WILDENBERG ME, WELLING MM, et al. Pretreatment with interferon-γ enhances the therapeutic activity of mesenchymal stromal cells in animal models of colitis. Stem Cells. 2011;29(10):1549-1558. [7] OSES C, OLIVARES B, EZQUER M, et al. Preconditioning of adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells with deferoxamine increases the production of pro-angiogenic, neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory factors: Potential application in the treatment of diabetic neuropathy. PLoS One. 2017;12(5):e0178011. [8] 孙卫民,王惠琴.细胞因子研究方法学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社, 1998:165-175. [9] 赵洁. TGF-β对骨髓间充质干细胞免疫抑制作用的影响及机制研究[D].济南:山东大学,2019. [10] HOLDEN P, NAIR LS. Deferoxamine: An Angiogenic and Antioxidant Molecule for Tissue Regeneration. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2019;25(6):461-470. [11] BEEREPOOT LV, SHIMA DT, KUROKI M, et al. Up-regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor production by iron chelators. Cancer Res. 1996; 56(16):3747-3751. [12] SHEN X, WAN C, RAMASWAMY G, et al. Prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors increase neoangiogenesis and callus formation following femur fracture in mice. J Orthop Res. 2009;27(10):1298-1305. [13] IKEDA Y, TAJIMA S, YOSHIDA S, et al. Deferoxamine promotes angiogenesis via the activation of vascular endothelial cell function. Atherosclerosis. 2011;215(2):339-347. [14] CHEKANOV VS, NIKOLAYCHIK V, MATERNOWSKI MA, et al. Deferoxamine enhances neovascularization and recovery of ischemic skeletal muscle in an experimental sheep model. Ann Thorac Surg. 2003;75(1):184-189. [15] HOFFBRAND AV, GANESHAGURU K, HOOTON JW, et al. Effect of iron deficiency and desferrioxamine on DNA synthesis in human cells. Br J Haematol. 1976;33(4):517-526. [16] LEDERMAN HM, COHEN A, LEE JW, et al. Deferoxamine: a reversible S-phase inhibitor of human lymphocyte proliferation. Blood. 1984;64(3):748-753. [17] HU K, OLSEN BR. The roles of vascular endothelial growth factor in bone repair and regeneration. Bone. 2016;91:30-38. [18] PRICOLA KL, KUHN NZ, HALEEM-SMITH H, et al. Interleukin-6 maintains bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell stemness by an ERK1/2-dependent mechanism. J Cell Biochem. 2009;108(3):577-588. [19] HOOGDUIJN MJ, POPP F, VERBEEK R, et al. The immunomodulatory properties of mesenchymal stem cells and their use for immunotherapy. Int Immunopharmacol. 2010;10(12):1496-1500. [20] DE MIGUEL MP, FUENTES-JULIAN S, BLAZQUEZ-MARTINEZ A, et al. Immunosuppressive properties of mesenchymal stem cells: advances and applications. Curr Mol Med. 2012;12(5):574-591. [21] YOU S, THIEBLEMONT N, ALYANAKIAN MA, et al. Transforming growth factor-beta and T-cell-mediated immunoregulation in the control of autoimmune diabetes. Immunol Rev. 2006;212:185-202. [22] KEHRL JH. Transforming growth factor-beta: an important mediator of immunoregulation. Int J Cell Cloning. 1991;9(5):438-450. [23] HUANG YH, ZOZULYA AL, WEIDENFELLER C, et al. T cell suppression by naturally occurring HLA-G-expressing regulatory CD4+ T cells is IL-10-dependent and reversible. J Leukoc Biol. 2009;86(2):273-281. [24] GREENHOUGH A, SMARTT HJ, MOORE AE, et al. The COX-2/PGE2 pathway: key roles in the hallmarks of cancer and adaptation to the tumour microenvironment. Carcinogenesis. 2009;30(3):377-386. [25] WILLIAMS CS, MANN M, DUBOIS RN. The role of cyclooxygenases in inflammation, cancer, and development. Oncogene. 1999;18(55):7908-7916. [26] SUBBARAMAIAH K, DANNENBERG AJ. Cyclooxygenase 2: a molecular target for cancer prevention and treatment. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2003;24(2):96-102. [27] NAKANISHI M, ROSENBERG DW. Multifaceted roles of PGE2 in inflammation and cancer. Semin Immunopathol. 2013;35(2):123-137. [28] MOLNARFI N, BENKHOUCHA M, FUNAKOSHI H, et al. Hepatocyte growth factor: A regulator of inflammation and autoimmunity. Autoimmun Rev. 2015;14(4):293-303. [29] SU J, CHEN X, HUANG Y, et al. Phylogenetic distinction of iNOS and IDO function in mesenchymal stem cell-mediated immunosuppression in mammalian species. Cell Death Differ. 2014;21(3):388-396. [30] DAY AJ, MILNER CM. TSG-6: A multifunctional protein with anti-inflammatory and tissue-protective properties. Matrix Biol. 2019;78-79:60-83. [31] ALEXANDER DZ, PEARSON TC, HENDRIX R, et al. Analysis of effector mechanisms in murine cardiac allograft rejection. Transpl Immunol. 1996; 4(1):46-48. [32] YAMAMOTO N, EINAGA-NAITO K, KURIYAMA M, et al. Cellular basis of skin allograft rejection in mice: specific lysis of allogeneic skin components by non-T cells. Transplantation. 1998;65(6):818-825. [33] GERSHON RK. A disquisition on suppressor T cells. Transplant Rev. 1975;26: 170-185. |
| [1] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1316-1322. |
| [2] | Xiao Hao, Liu Jing, Zhou Jun. Research progress of pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1323-1329. |
| [3] | Tian Chuan, Zhu Xiangqing, Yang Zailing, Yan Donghai, Li Ye, Wang Yanying, Yang Yukun, He Jie, Lü Guanke, Cai Xuemin, Shu Liping, He Zhixu, Pan Xinghua. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulate ovarian aging in macaques [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 985-991. |
| [4] | Hou Jingying, Guo Tianzhu, Yu Menglei, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning targets and downregulates miR-195 and promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell survival and pro-angiogenic potential by activating MALAT1 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1005-1011. |
| [5] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [6] | Fan Yiming, Liu Fangyu, Zhang Hongyu, Li Shuai, Wang Yansong. Serial questions about endogenous neural stem cell response in the ependymal zone after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1137-1142. |
| [7] | Liang Xuezhen, Yang Xi, Li Jiacheng, Luo Di, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Bushen Huoxue capsule regulates osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via Hedgehog signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1020-1026. |
| [8] | Wang Jifang, Bao Zhen, Qiao Yahong. miR-206 regulates EVI1 gene expression and cell biological behavior in stem cells of small cell lung cancer [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1027-1031. |
| [9] | Liu Feng, Peng Yuhuan, Luo Liangping, Wu Benqing. Plant-derived basic fibroblast growth factor maintains the growth and differentiation of human embryonic stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1032-1037. |
| [10] | Wen Dandan, Li Qiang, Shen Caiqi, Ji Zhe, Jin Peisheng. Nocardia rubra cell wall skeleton for extemal use improves the viability of adipogenic mesenchymal stem cells and promotes diabetes wound repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1038-1044. |
| [11] | Zhu Bingbing, Deng Jianghua, Chen Jingjing, Mu Xiaoling. Interleukin-8 receptor enhances the migration and adhesion of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells to injured endothelium [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1045-1050. |
| [12] | Luo Xiaoling, Zhang Li, Yang Maohua, Xu Jie, Xu Xiaomei. Effect of naringenin on osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1051-1056. |
| [13] | Wang Xinmin, Liu Fei, Xu Jie, Bai Yuxi, Lü Jian. Core decompression combined with dental pulp stem cells in the treatment of steroid-associated femoral head necrosis in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1074-1079. |
| [14] | Fang Xiaolei, Leng Jun, Zhang Chen, Liu Huimin, Guo Wen. Systematic evaluation of different therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in the treatment of ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1085-1092. |
| [15] | Guo Jia, Ding Qionghua, Liu Ze, Lü Siyi, Zhou Quancheng, Gao Yuhua, Bai Chunyu. Biological characteristics and immunoregulation of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1093-1101. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||