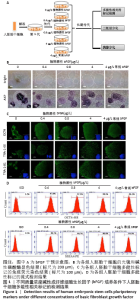
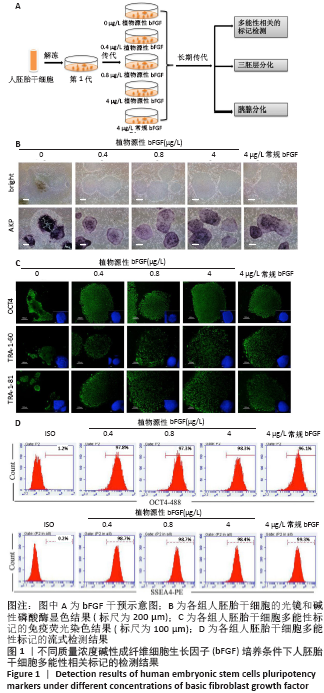
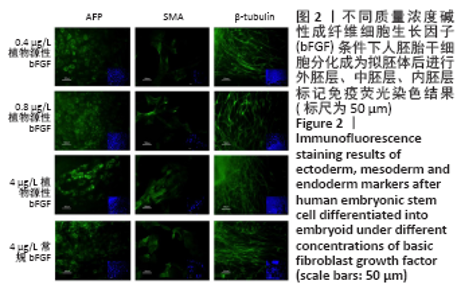
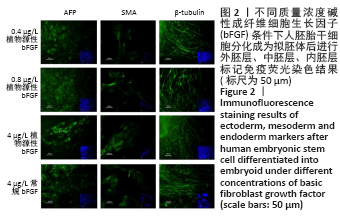
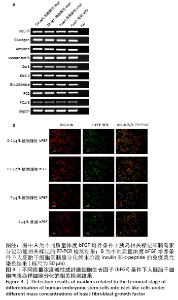
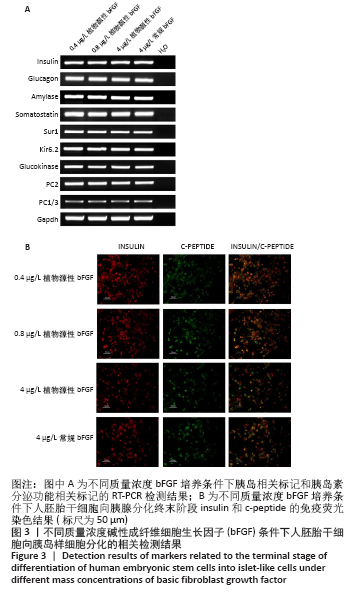
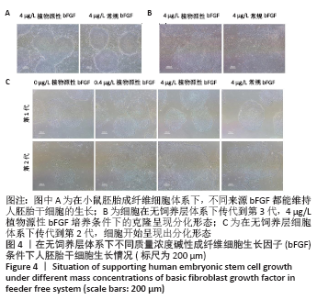
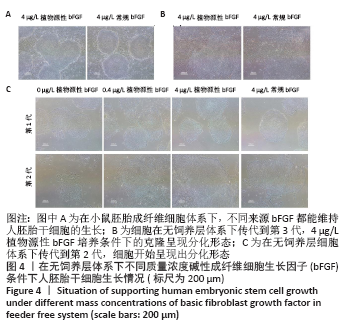
[1] EISELLEOVA L, MATULKA K, KRIZ V, et al. A complex role for FGF-2 in self-renewal, survival, and adhesion of human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells. 2009;27(8):1847-1857.
[2] DING VM, BOERSEMA PJ, FOONG LY, et al. Tyrosine phosphorylation profiling in FGF-2 stimulated human embryonic stem cells. PLoS One. 2011;6(3):e17538.
[3] DING VM, LING L, NATARAJAN S, et al. FGF-2 modulates Wnt signaling in undifferentiated hESC and iPS cells through activated PI3-K/GSK3beta signaling. J Cell Physiol. 2010;225(2):417-428.
[4] ONUMA Y, HIGUCHI K, AIKI Y, et al. A stable chimeric fibroblast growth factor (FGF) can successfully replace basic FGF in human pluripotent stem cell culture. PLoS One. 2015;10(4):e0118931.
[5] KROON E, MARTINSON LA, KADOYA K, et al. Pancreatic endoderm derived from human embryonic stem cells generates glucose-responsive insulin-secreting cells in vivo. Nat Biotechnol. 2008;26(4): 443-452.
[6] KUNISADA Y, TSUBOOKA-YAMAZOE N, SHOJI M, et al. Small molecules induce efficient differentiation into insulin-producing cells from human induced pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cell Res. 2012;8(2):274-284.
[7] THOMSON JA, ITSKOVITZ-ELDOR J, SHAPIRO SS, et al. Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts. Science. 1998;282(5391): 1145-1147.
[8] DVORAK P, DVORAKOVA D, KOSKOVA S, et al. Expression and potential role of fibroblast growth factor 2 and its receptors in human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells. 2005;23(8):1200-1211.
[9] VALLIER L, ALEXANDER M, PEDERSEN RA. Activin/Nodal and FGF pathways cooperate to maintain pluripotency of human embryonic stem cells. J Cell Sci. 2005;118(Pt 19):4495-4509.
[10] XU X, BROWNING VL, ODORICO JS. Activin, BMP and FGF pathways cooperate to promote endoderm and pancreatic lineage cell differentiation from human embryonic stem cells. Mech Dev. 2011; 128(7-10):412-427.
[11] 曾湘晖,杨华.饲养层分泌碱性成纤维生长因子与支持人胚胎干细胞生长[J].生殖医学杂志,2012,21(3):247-251.
[12] GREBER B, LEHRACH H, ADJAYE J. Fibroblast growth factor 2 modulates transforming growth factor beta signaling in mouse embryonic fibroblasts and human ESCs (hESCs) to support hESC self-renewal. Stem Cells. 2007;25(2):455-464.
[13] WANG G, ZHANG H, ZHAO Y, et al. Noggin and bFGF cooperate to maintain the pluripotency of human embryonic stem cells in the absence of feeder layers. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;330(3): 934-942.
[14] ZHOU J, OU-YANG Q, LI J, et al. Human feeder cells support establishment and definitive endoderm differentiation of human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2008;17(4):737-749.
[15] 何丽娟,习佳飞.一种新的人胚胎干细胞无饲养层培养方法的建立[J].生物技术通讯,2010,21(5):660-665.
[16] 周轶平, ROCHAT ANNE, HATZFELD ANTOINETTE,等. bFGF诱导MEF生成的条件培养基对人胚胎干细胞生长的影响[J].分子细胞生物学报,2009,42(3):193-199.
[17] LEVENSTEIN ME, LUDWIG TE, XU RH, et al. Basic fibroblast growth factor support of human embryonic stem cell self-renewal. Stem Cells. 2006;24(3):568-574.
[18] XU RH, PECK RM, LI DS, et al. Basic FGF and suppression of BMP signaling sustain undifferentiated proliferation of human ES cells. Nat Methods. 2005;2(3):185-190.
[19] ZHANG D, MAI Q, LI T, et al. Comparison of a xeno-free and serum-free culture system for human embryonic stem cells with conventional culture systems. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;7(1):101.
[20] EISELLEOVA L, PETERKOVA I, NERADIL J, et al. Comparative study of mouse and human feeder cells for human embryonic stem cells. Int J Dev Biol. 2008;52(4):353-363.
[21] PARK Y, CHOI IY, LEE SJ, et al. Undifferentiated propagation of the human embryonic stem cell lines, H1 and HSF6, on human placenta-derived feeder cells without basic fibroblast growth factor supplementation. Stem Cells Dev. 2010;19(11):1713-1722.
[22] SÁNCHEZ L, GUTIERREZ-ARANDA I, LIGERO G, et al. Maintenance of human embryonic stem cells in media conditioned by human mesenchymal stem cells obviates the requirement of exogenous basic fibroblast growth factor supplementation. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2012;18(5):387-396. |