Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (8): 1260-1265.doi: 10.12307/2022.233
Previous Articles Next Articles
Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism
Wang Jing1, Xiong Shan1, Cao Jin1, Feng Linwei2, Wang Xin1
- 1Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563003, Guizhou Province, China; 2Nanchuan District Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chongqing 408400, China
-
Received:2021-06-17Revised:2021-06-21Accepted:2021-07-09Online:2022-03-18Published:2021-11-02 -
Contact:Wang Xin, MD, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563003, Guizhou Province, China Feng Linwei, Attending physician, Nanchuan District Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chongqing 408400, China -
About author:Wang Jing, Master candidate, Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563003, Guizhou Province, China Xiong Shan, Master candidate, Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563003, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 31960209 and 31760266 (both to WX); Basic Research Program of Guizhou Science and Technology Department, No. [2020]1Y093 (to WX)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
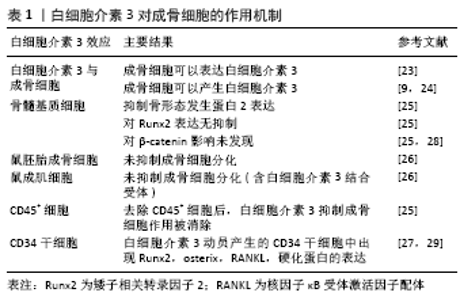
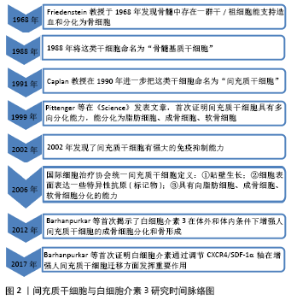
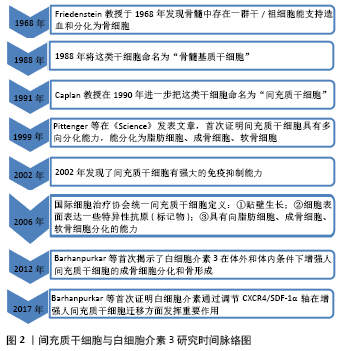
间充质干细胞具有分化为脂肪细胞、成骨细胞、软骨细胞的能力,参与损伤后的骨再生过程[11]。骨缺损后,趋化因子从骨髓、骨膜、血管壁、肌肉、循环及其他组织招募间充质干细胞,使之迁移至骨损伤部位[12]。间充质干细胞在骨初始阶段形成和维持中起关键作用。软骨内骨化是一种骨愈合机制:间充质干细胞分化为软骨细胞沉积软骨,其钙化后再重塑成骨。膜内骨化是另一种骨愈合机制:间充质干细胞或未分化的成骨细胞直接分化为成骨细胞[13]。成骨细胞在骨骼初始形成、维持骨量和骨折修复中发挥作用。间充质干细胞分泌的多种生物活性分子为成骨细胞发挥作用而创造出良好的骨再生微环境[14]。 白细胞介素3主要由CD4+ T淋巴细胞分泌,通过与造血细胞和其他细胞类型上的特定高亲和力受体结合而发挥其生物学活性[15]。研究发现人类间充质干细胞和成骨细胞在mRNA和蛋白质水平上均表达白细胞介素3受体α(IL-3Rα)。故白细胞介素3会上调成骨细胞特异性基因和转录因子的表达并增强间充质干细胞中的成骨细胞分化[9]。骨形态发生蛋白参与间充质细胞分化为软骨细胞和成骨细胞,及骨祖细胞分化为成骨细胞的过程[13]。骨形态发生蛋白来自骨祖细胞、间充质细胞、成骨细胞和软骨细胞,主要存在于骨细胞外基质中。BARHANPURKAR等[9]使用白细胞介素3中和抗体处理添加白细胞介素3(100 μg/L)的间充质干细胞培养基和对照组,发现抗白细胞介素3中和抗体消除了白细胞介素3对骨形态发生蛋白2合成的刺激作用,表明白细胞介素3通过刺激骨形态发生蛋白2促进成骨细胞分化。Smad1/5/8是骨形态发生蛋白受体的直接下游分子,在骨形态发生蛋白信号转导中起着核心作用,研究发现骨形态发生蛋白2信号激活Smad1/5/8复合物,进而控制成骨细胞基因的转录[16],而白细胞介素3通过激活Smad1/5/8复合物诱导间充质干细胞中的骨形态发生蛋白2的信号传导。白细胞介素3可以通过JAK2激活STAT途径,而JAK2抑制剂AG490可以显著抑制白细胞介素3对成骨细胞分化的刺激作用,这表明JAK/STAT途径可能参与了白细胞介素3介导的成骨作用[17]。此外,BARHANPURKAR等[9]将羟基磷灰石/磷酸三钙生物移植物植入间充质干细胞中(106 细胞/生物移植物),并在不存在或存在白细胞介素3(100 μg/L)的情况下在成骨培养基中孵育10 d,然后将这些生物移植物从皮下植入免疫缺损小鼠体内,10周后发现有白细胞介素3移植物小鼠骨基质的合成明显增加且骨钙素沉积增多,这表明白细胞介素3有增强间充质干细胞体内骨增殖的能力。 2.2 白细胞介素3对成骨细胞的作用 骨稳态是由成骨性成骨细胞和吸收骨的破骨细胞之间的相互串扰严格控制的。骨重塑是一个动态过程,其中破骨细胞吸收旧的或受损的骨骼,并用成骨细胞形成的新生骨骼代替。作为骨形成细胞,成骨细胞通过一系列细胞因子的连续作用从间充质前体骨髓系到终末分化为成熟的成骨细胞[18-20]。成骨细胞可以产生细胞外蛋白(如骨钙蛋白、碱性磷酸酶和Ⅰ型胶原蛋白等)参与骨基质的形成,其中Ⅰ型胶原蛋白占骨基质蛋白的90%以上[21]。而成骨细胞分泌有机基质是致密的胶原蛋白层,通过平行和正交方式交汇于应力负荷轴,随后通过主动和被动运输以及pH值控制,将极致密的羟基磷灰石基矿物沉积到该基质中使之矿化[22]。 BIRCH等[23]使用反转录聚合酶链反应(PCR)发现成骨细胞可以表达白细胞介素3。此外,骨质疏松症骨折患者外植骨的类似研究也观察到成骨细胞产生白细胞介素3[24]。另一方面,EHRLICH等[25]用白细胞介素3(0.01-10 μg/L)处理原代小鼠和人类骨髓基质细胞,发现白细胞介素3以剂量依赖性方式抑制基础和骨形态发生蛋白2刺激的成骨细胞形成;但白细胞介素3不会抑制成骨细胞分化所需关键转录因子Runx2的表达,并且在加入白细胞介素3后β-catenin途径(Wnt经典信号途径)下游的效应蛋白水平不变。这些表明白细胞介素3通过基础和骨形态发生蛋白2的抑制产生对骨髓基质成骨细胞的影响,而未发现白细胞介素3对Runx2和β-catenin途径的效应。有趣的是,虽然小鼠胚胎成骨细胞前体细胞和小鼠成肌细胞上有白细胞介素3的结合受体IL-3Rα,但是研究发现白细胞介素3不能抑制它们的成骨细胞分化[26]。由于白细胞介素3是重要的调节造血作用的细胞因子,研究者去除人骨髓基质细胞和鼠基质细胞中的CD45+细胞,观察其与白细胞介素3的反应,发现去除CD45+细胞消除了白细胞介素3对成骨细胞的抑制作用,表明白细胞介素3对成骨细胞分化的抑制作用是通过单核细胞/巨噬细胞(CD45造血细胞)间接起作用[25]。此外,研究者将白细胞介素3动员产生的CD34+干细胞放入刺激成骨培养基中,实时定量基因扩增荧光检测系统表达分析发现了早期和成熟的成骨细胞标记物,如Runx2、Osterix、RANKL以及骨细胞标记物SPARC、硬化蛋白的表达[27]。白细胞介素3对成骨细胞的作用机制总结,见表1。"
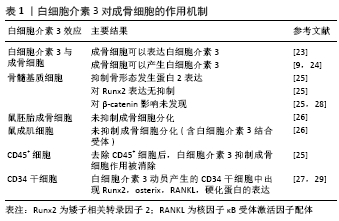

2.3 白细胞介素3对破骨细胞的作用 破骨细胞是一种大型多核细胞,通过巨噬细胞集落刺激因子和RANKL从单核/巨噬细胞系细胞分化而来。RANKL通过信号受体RANK传递信号。RANKL/RANK信号刺激活化T细胞核因子1调节破骨细胞的形成,并诱导破骨基因表达[4]。破骨细胞代谢失调会导致骨质疏松症的发生。早期的研究表明白细胞介素3刺激破骨细胞生成。HATTERSLEY等[30]将鼠造血细胞与白细胞介素3孵育于塑料盖和骨片上,并检测其对破骨细胞形成的影响,发现白细胞介素3仅诱导破骨细胞的部分成熟,进一步发育则通过其他因子如1,25(OH)2D3增强或完成。MYINT 等[31]使用白细胞介素3(100 ng/d)注射到骨硬化小鼠体内,发现2周后骨髓腔明显扩大,并检测到耐酒石酸酸性磷酸酶(一种破骨细胞的标记酶)阳性细胞与骨髓巨噬细胞数量明显增加,这表明白细胞介素3可以诱导破骨细胞的发育,纠正小鼠骨硬化。此外,在多发性骨髓瘤中,白细胞介素3与巨噬细胞炎性蛋白1α(MIP-1α)或RANKL的联合比单独巨噬细胞炎性蛋白1α或RANKL增强人破骨细胞的形成和骨吸收效果更强[32]。新近研究发现,小鼠钙化骨细胞表达白细胞介素3,进而增加膜结合RANKL表达和产生耐酒石酸磷酸酶阳性单核细胞[33]。 也有研究发现,白细胞介素3对破骨细胞会产生抑制作用。白细胞介素3不仅可以调节培养的胚胎小鼠长骨中新近复制的前体细胞中破骨细胞的发育[34],也会有效抑制在小鼠骨髓培养中产生的含有酒石酸抗性酸性磷酸酶多核细胞的产生(半数效应浓度为每毫升3集落)[35]。KHAPLI等[36]发现白细胞介素3在破骨细胞前体中通过抑制核因子κB的磷酸化和降解来阻止RANKL诱导的核因子κB核易位,从而抑制RANKL诱导的破骨细胞分化。而抗白细胞介素3抗体中和了白细胞介素3对破骨细胞分化的抑制作用,并且白细胞介素3对破骨细胞分化的抑制作用是不可逆的,这表明白细胞介素3抑制破骨细胞主要是通过RANKL来进行的[8]。此外,在小鼠炎性关节炎模型中,白细胞介素3能有效抑制单核/巨噬细胞谱系造血前体中肿瘤坏死因子α诱导的骨吸收,并且白细胞介素3在肿瘤坏死因子α、转化生长因子、转化生长因子β3、白细胞介素6和前列腺素E2等促炎细胞因子存在的情况下,对肿瘤坏死因子α诱导的骨吸收仍然有抑制作用。此外,白细胞介素3阻止了肿瘤坏死因子α诱导的c-fos核易位和AP-1 DNA结合活性,且白细胞介素3预处理可预防由抗Ⅱ型胶原蛋白和脂多糖的混合物诱发的小鼠炎症性关节炎的发展[37]。这些表明白细胞介素3在抑制肿瘤坏死因子α诱导的骨吸收和预防小鼠关节炎症中也起着重要作用。GUPTA等[38]研究了白细胞介素3对健康捐献者和骨质疏松症患者外周血单核细胞培养物中RANKL诱导的人破骨细胞分化和骨吸收的作用和机制,使用外周血单核细胞在巨噬细胞集落刺激因子和RANKL的作用下分化成功能性破骨细胞,并通过αV/β3抗体(23c6)表达和骨吸收来评估其作用强度,结果发现白细胞介素3剂量依赖性地抑制23c6阳性破骨细胞的形成、骨吸收和Ⅰ型胶原的c端末端肽(一种胶原降解产物)的生成。研究者随后分析了白细胞介素3对破骨细胞形成所必需的核因子κB受体激活因子和c-Fms受体以及c-Fos、PU.1、活化T细胞核因子1蛋白和RelB转录因子的影响,发现白细胞介素3在mRNA和蛋白水平上显著抑制c-Fms,并下调PU.1和c-Fos表达。此外,白细胞介素3还抑制了来自骨质疏松个体骨髓细胞的破骨细胞的形成,这或许为骨质疏松提供新的治疗靶点。此外,在一项对人骨髓源性巨噬细胞的研究中,发现白细胞介素3诱导人骨髓源性巨噬细胞中DNA结合/分化抑制剂(Id1),而Id2在白细胞介素3处理后的骨髓来源巨噬细胞破骨细胞分化过程中持续存在,且活化T细胞核因子1蛋白在Id2缺陷的骨髓来源巨噬细胞中的异位表达完全逆转了白细胞介素3对破骨细胞分化的抑制作用[39]。所以白细胞介素3通过调节c-Fos和Ids抑制破骨细胞分化,并具有抗骨侵蚀的作用。LEE等[8]通过实验进一步发现,白细胞介素3激活信号转导和转录激活因子5(signal transducer and activator of transcription,STAT5),通过诱导Id基因的表达,抑制RANKL诱导的破骨形成。STAT5缺乏抑制白细胞介素3介导的破骨细胞形成抑制,提示STAT5在白细胞介素3介导破骨细胞分化抑制中发挥关键作用。此外,白细胞介素3诱导的STAT5激活上调了Id1和Id2的表达,这是破骨形成的负调控因子,在STAT5缺陷细胞中Id1或Id2的过表达会逆转被白细胞介素3介导所抑制的破骨细胞发育。所以,STAT5通过激活Id基因及其相关通路,参与了白细胞介素3介导的RANKL诱导所抑制的破骨细胞形成。而在HONG等[40]的研究中,认为白细胞介素3通过促进破骨细胞祖细胞的发育但抑制破骨细胞形成过程而在破骨细胞形成中发挥双重作用,这为白细胞介素3在破骨细胞形成中的作用提供了更好的理解。白细胞介素3对破骨细胞的作用机制总结,见表2。"

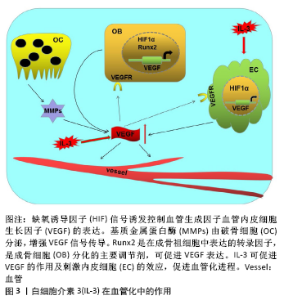
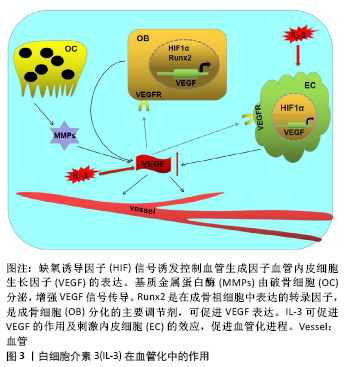
2.4 白细胞介素3对血管化的作用 在哺乳动物骨骼系统中,成骨和血管生成在骨生长、骨再生及骨重塑中的骨稳态中密切相关[46]。大多数哺乳动物的骨骼是通过软骨内骨化而发育的,该过程取决于各种细胞类型的协调增殖、分化和相互作用,但最终依赖于成骨细胞谱系细胞进行骨基质的实际合成和矿化[47]。而软骨内骨形成需要新生血管的帮助,而血管生成主要由内皮细胞释放的血管内皮生长因子进行调 控[48]。白细胞介素3是一种造血生长因子,刺激骨髓祖细胞增殖并分化为不同类型的血细胞,这一特性表明其可用于疾病后的骨髓重建以及骨折后的血管再生。通过在无血清限定条件下使用高通量筛选方法,证明造血干细胞因子如白细胞介素3是人类血管形成和成熟所必需的。通过使用来自胚胎鹌鹑血管的不同来源内皮细胞也证实了这一结论,这些内皮细胞同样在造血细胞因子的作用下萌发并形成血管;相反,使用已知的促血管生成因子如血管内皮细胞生长因子、纤维母细胞生长因子和血管生成素却未能出现上述结果。并且,在处理的人类内皮细胞条件下,形态发生试验中添加血管内皮细胞生长因子和纤维母细胞生长因子时,在3D矩阵中单独或联合使用时,都不会刺激管的形态发生或发芽;然而,在形态发生前添加血管内皮细胞生长因子、纤维母细胞生长因子或两者联合作为内皮细胞启动步骤,可显著增强人或胚胎鹌鹑内皮细胞的形态发生,来响应造血干细胞因子白细胞介素3的效应[49]。因此,血管内皮细胞生长因子和纤维母细胞生长因子影响内皮细胞管的形态发生主要是通过上调造血细胞因子受体IL-3Rα的上游作用,进而控制下游血管形态发生。此外,DENTELLI等[50]向严重免疫缺陷(SCID)小鼠注射含有平滑肌细胞和白细胞介素3或碱性成纤维细胞生长因子的人工基底膜凝胶,发现白细胞介素3处理的平滑肌细胞中条件培养基刺激了内皮细胞的迁移,而平滑肌细胞的迁移不受白细胞介素3刺激的内皮细胞条件培养基影响,但它阻止转化生长因子β活性显著增强,因此,白细胞介素3通过增加转化生长因子β活性影响内皮细胞介导的平滑肌细胞募集。 研究发现血小板生成素可以刺激造血干细胞中的血管内皮细胞生长因子的产生[51]。HATTORI等[52]发现血管内皮生长因子和血管生成素通过募集造血干细胞来发挥作用。研究表明白细胞介素3参与造血祖细胞/干细胞以及成熟造血细胞的存活,增殖和分化[15,29]。此外,白细胞介素3支持在体外多次分裂后的干细胞长期多系再生活性的维持[53]。而在干细胞研究中,白细胞介素3可以促进造血干细胞种群(包括CD34+ c-kit+)的存活,并且体外培养和表型研究发现白细胞介素3可增加CD34+ c-kit+和Ly6A-GFP+ c-kit+等造血干细胞的增殖[54]。这些都表明白细胞介素3可以通过影响造血干细胞,进而促进其对血管内皮细胞生长因子的释放,促进成骨过程中的血管化进程。 白细胞介素3在血管化中的作用,见图3。"
| [1] DOUGAN M, DRANOFF G, DOUGAN SK. GM-CSF, IL-3, and IL-5 Family of Cytokines: Regulators of Inflammation. Immunity. 2019;50(4):796-811. [2] BOOR PPC, DE RUITERPE, ASMAWIDJAJA PS, et al. JAK-inhibitor tofacitinib suppresses interferon alfa production by plasmacytoid dendritic cells and inhibits arthrogenic and antiviral effects of interferon alfa. Transl Res. 2017;188:67-79. [3] DEEM TL, COLLINS JB, DEVOST MH, et al. Assessment of faithful interleukin-3 production by novel bicistronic interleukin-3 reporter mice. Immunol Lett. 2020;221:18-26. [4] ONO T, NAKASHIMA T. Recent advances in osteoclast biology. Histochem Cell Biol. 2018;149(4):325-341. [5] CHEN PC, LIU JF, FONG YC, et al. CCN3 Facilitates Runx2 and Osterix Expression by Inhibiting miR-608 through PI3K/Akt Signaling in Osteoblasts. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(13):3300 [6] CHAI S, WAN L, WANG JL, et al. Gushukang inhibits osteocyte apoptosis and enhances BMP-2/Smads signaling pathway in ovariectomized rats. Phytomedicine. 2019;64:153063. [7] GYŐRI DS, MÓCSAI A. Osteoclast Signal Transduction During Bone Metastasis Formation. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:507. [8] LEE J, SEONG S, KIM JH, et al. STAT5 is a key transcription factor for IL-3-mediated inhibition of RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis. Sci Rep. 2016;6:30977. [9] BARHANPURKAR AP, GUPTA N, SRIVASTAVA RK, et al. IL-3 promotes osteoblast differentiation and bone formation in human mesenchymal stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012;418(4):669-675. [10] AMARASEKARA DS, YUN H, KIM S, et al. Regulation of Osteoclast Differentiation by Cytokine Networks. Immune Netw. 2018;18(1):e8. [11] PAJARINEN J, LIN T, GIBON E, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-macrophage crosstalk and bone healing. Biomaterials. 2019;196:80-89. [12] TAKEUCHI R, KATAGIRI W, ENDO S, et al. Exosomes from conditioned media of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells promote bone regeneration by enhancing angiogenesis. PLoS One. 2019; 14(11):e0225472. [13] GARG P, MAZUR MM, BUCK AC, et al. Prospective Review of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Differentiation into Osteoblasts. Orthop Surg. 2017;9(1):13-19. [14] GÖTHERSTRÖM C, WALTHER-JALLOW L. Stem Cell Therapy as a Treatment for Osteogenesis Imperfecta. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2020; 18(4):337-343. [15] KLEPPE M, SPITZER MH, LI S, et al. Jak1 Integrates Cytokine Sensing to Regulate Hematopoietic Stem Cell Function and Stress Hematopoiesis. Cell Stem Cell. 2017;21(4):489-501.e7. [16] WANG S, HU S, WANG J, et al. Conditioned medium from bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells inhibits vascular calcification through blockade of the BMP2-Smad1/5/8 signaling pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):160. [17] REDDY EP, KORAPATI A, CHATURVEDI P, et al. IL-3 signaling and the role of Src kinases, JAKs and STATs: a covert liaison unveiled. Oncogene. 2000;19(21):2532-2547. [18] LEE WC, GUNTUR AR, LONG F, et al. Energy Metabolism of the Osteoblast: Implications for Osteoporosis. Endocr Rev. 2017;38(3): 255-266. [19] THIEL A, REUMANN MK, BOSKEY A, et al. Osteoblast migration in vertebrate bone. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2018;93(1):350-363. [20] HOU Z, WANG Z, TAO Y, et al. KLF2 regulates osteoblast differentiation by targeting of Runx2. Lab Invest. 2019;99(2):271-280. [21] KIM JM, LIN C, STAVRE Z, et al. Osteoblast-Osteoclast Communication and Bone Homeostasis. Cells. 2020;9(9):2073. [22] BLAIR HC, LARROUTURE QC, LI Y, et al. Osteoblast Differentiation and Bone Matrix Formation In Vivo and In Vitro. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2017;23(3):268-280. [23] BIRCH MA, GINTY AF, WALSH CA, et al. PCR detection of cytokines in normal human and pagetic osteoblast-like cells. J Bone Miner Res. 1993;8(10):1155-1162. [24] WALSH CA, BIRCH MA, FRASER WD, et al. Cytokine expression by cultured osteoblasts from patients with osteoporotic fractures. Int J Exp Pathol. 2000; 81(2):159-163. [25] EHRLICH LA, CHUNG HY, GHOBRIAL I, et al. IL-3 is a potential inhibitor of osteoblast differentiation in multiple myeloma. Blood. 2005;106(4):1407-1414. [26] HARIRI H, PELLICELLI M, ST-ARNAUD R. Nfil3, a target of the NACA transcriptional coregulator, affects osteoblast and osteocyte gene expression differentially. Bone. 2020;141:115624. [27] SRIKANTH L, SUNITHA MM, KUMAR PS, et al. Gel based in vitro 3D model exploring the osteocytic potentiality of human CD34(+) stem cells. Mol Biol Rep. 2016;43(11):1233-1242. [28] ROODMAN GD. New potential targets for treating myeloma bone disease. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12(20 Pt 2):6270s-6273s. [29] KNAPP DJ, HAMMOND CA, AGHAEEPOUR N, et al. Distinct signaling programs control human hematopoietic stem cell survival and proliferation. Blood. 2017;129(3):307-318. [30] HATTERSLEY G, CHAMBERS TJ. Effects of interleukin 3 and of granulocyte-macrophage and macrophage colony stimulating factors on osteoclast differentiation from mouse hemopoietic tissue. J Cell Physiol. 1990;142(1):201-209. [31] MYINT YY, MIYAKAWA K, NAITO M, et al. Granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor and interleukin-3 correct osteopetrosis in mice with osteopetrosis mutation. Am J Pathol. 1999; 154(2):553-566. [32] LEE JW, CHUNG HY, EHRLICH LA, et al. IL-3 expression by myeloma cells increases both osteoclast formation and growth of myeloma cells. Blood. 2004;103(6):2308-2315. [33] SINGH K, PIPRODE V, MHASKE ST, et al. IL-3 Differentially Regulates Membrane and Soluble RANKL in Osteoblasts through Metalloproteases and the JAK2/STAT5 Pathway and Improves the RANKL/OPG Ratio in Adult Mice. J Immunol. 2018;200(2):595-606. [34] LORENZO JA, SOUSA SL, FONSECA JM, et al. Colony-stimulating factors regulate the development of multinucleated osteoclasts from recently replicated cells in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1987;80(1):160-164. [35] SHINAR DM, SATO M, RODAN GA. The effect of hemopoietic growth factors on the generation of osteoclast-like cells in mouse bone marrow cultures. Endocrinology. 1990;126(3):1728-1735. [36] KHAPLI SM, MANGASHETTI LS, YOGESHA SD, et al. IL-3 acts directly on osteoclast precursors and irreversibly inhibits receptor activator of NF-kappa B ligand-induced osteoclast differentiation by diverting the cells to macrophage lineage. J Immunol. 2003;171(1):142-151. [37] YOGESHA SD, KHAPLI SM, SRIVASTAVA RK, et al. IL-3 inhibits TNF-alpha-induced bone resorption and prevents inflammatory arthritis. J Immunol. 2009;182(1):361-370. [38] GUPTA N, BARHANPURKAR AP, TOMAR GB, et al. IL-3 inhibits human osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption through downregulation of c-Fms and diverts the cells to dendritic cell lineage. J Immunol. 2010;185(4):2261-2272. [39] OH J, LEE MS, YEON JT, et al. Inhibitory regulation of osteoclast differentiation by interleukin-3 via regulation of c-Fos and Id protein expression. J Cell Physiol. 2012;227(5):1851-1860. [40] HONG H, SHI Z, QIAO P, et al. Interleukin-3 plays dual roles in osteoclastogenesis by promoting the development of osteoclast progenitors but inhibiting the osteoclastogenic process. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;440(4):545-550. [41] BRITO C, STAVROULLAKIS AT, FERREIRA AC, et al. Extract of acai-berry inhibits osteoclast differentiation and activity. Arch Oral Biol. 2016;68:29-34. [42] PIPRODE V, SINGH K, KUMAR A, et al. IL-3 inhibits rat osteoclast differentiation induced by TNF-α and other pro-osteoclastogenic cytokines. J Biosci. 2021;46:63. [43] KELLY EA, ESNAULT S, JOHNSON SH, et al. Human eosinophil activin A synthesis and mRNA stabilization are induced by the combination of IL-3 plus TNF. Immunol Cell Biol. 2016;94(7):701-708. [44] BORRIELLO F, IANNONE R, DI SOMMA S, et al. GM-CSF and IL-3 Modulate Human Monocyte TNF-α Production and Renewal in In Vitro Models of Trained Immunity. Front Immunol. 2016;7:680. [45] WANG JM, LAI MZ, YANG-YEN HF. Interleukin-3 stimulation of mcl-1 gene transcription involves activation of the PU.1 transcription factor through a p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent pathway. Mol Cell Biol. 2003;23(6):1896-909. [46] PENG Y, WU S, LI Y, et al. Type H blood vessels in bone modeling and remodeling. Theranostics. 2020; 10(1):426-436. [47] WANG X, ZHANG Y, CHOUKROUN J, et al. Effects of an injectable platelet-rich fibrin on osteoblast behavior and bone tissue formation in comparison to platelet-rich plasma. Platelets. 2018;29(1):48-55. [48] Apte RS, Chen DS, Ferrara N. VEGF in Signaling and Disease: Beyond Discovery and Development[J]. Cell, 2019, 176(6): p. 1248-1264. [49] STRATMAN AN, DAVIS MJ, DAVIS GE. VEGF and FGF prime vascular tube morphogenesis and sprouting directed by hematopoietic stem cell cytokines. Blood. 2011;117(14):3709-3719. [50] DENTELLI P, ROSSO A, CALVI C, et al. IL-3 affects endothelial cell-mediated smooth muscle cell recruitment by increasing TGF beta activity: potential role in tumor vessel stabilization. Oncogene. 2004; 23(9):1681-1692. [51] KIRITO K, KAUSHANSKY K. Thrombopoietin stimulates vascular endothelial cell growth factor (VEGF) production in hematopoietic stem cells. Cell Cycle. 2005;4(12):1729-1731. [52] HATTORI K, DIAS S, HEISSIG B, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor and angiopoietin-1 stimulate postnatal hematopoiesis by recruitment of vasculogenic and hematopoietic stem cells. J Exp Med. 2001;193(9):1005-1014. [53] BRYDER D, JACOBSEN SE. Interleukin-3 supports expansion of long-term multilineage repopulating activity after multiple stem cell divisions in vitro. Blood. 2000;96(5):1748-1755. [54] ROBIN C, OTTERSBACH K, DURAND C, et al. An unexpected role for IL-3 in the embryonic development of hematopoietic stem cells. Dev Cell. 2006;11(2):171-180. [55] YOGESHA SD, KHAPLI SM, WANI MR. Interleukin-3 and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor inhibits tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha-induced osteoclast differentiation by down-regulation of expression of TNF receptors 1 and 2. J Biol Chem. 2005;280(12): 11759-11769. [56] BARHANPURKAR-NAIK A, MHASKE ST, POTE ST, et al. Interleukin-3 enhances the migration of human mesenchymal stem cells by regulating expression of CXCR4. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):168. |
| [1] | Li Huo, Wang Peng, Gao Jianming, Jiang Haoran, Lu Xiaobo, Peng Jiang. Relationship between revascularization and internal microstructure changes in osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1323-1328. |
| [2] | Zhu Chan, Han Xuke, Yao Chengjiao, Zhou Qian, Zhang Qiang, Chen Qiu. Human salivary components and osteoporosis/osteopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1439-1444. |
| [3] | Jin Tao, Liu Lin, Zhu Xiaoyan, Shi Yucong, Niu Jianxiong, Zhang Tongtong, Wu Shujin, Yang Qingshan. Osteoarthritis and mitochondrial abnormalities [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1452-1458. |
| [4] | Zhang Lichuang, Xu Hao, Ma Yinghui, Xiong Mengting, Han Haihui, Bao Jiamin, Zhai Weitao, Liang Qianqian. Mechanism and prospects of regulating lymphatic reflux function in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1459-1466. |
| [5] | Xiao Hao, Liu Jing, Zhou Jun. Research progress of pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1266-1271. |
| [6] | Zhu Chan, Han Xuke, Yao Chengjiao, Zhang Qiang, Liu Jing, Shao Ming. Acupuncture for Parkinson’s disease: an insight into the action mechanism in animal experiments [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1272-1277. |
| [7] | Huang Chenwei, Fei Yankang, Zhu Mengmei, Li Penghao, Yu Bing. Important role of glutathione in stemness and regulation of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1119-1124. |
| [8] | Hui Xiaoshan, Bai Jing, Zhou Siyuan, Wang Jie, Zhang Jinsheng, He Qingyong, Meng Peipei. Theoretical mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine theory on stem cell induced differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1125-1129. |
| [9] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [10] | Fan Yiming, Liu Fangyu, Zhang Hongyu, Li Shuai, Wang Yansong. Serial questions about endogenous neural stem cell response in the ependymal zone after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1137-1142. |
| [11] | Tian Chuan, Zhu Xiangqing, Yang Zailing, Yan Donghai, Li Ye, Wang Yanying, Yang Yukun, He Jie, Lü Guanke, Cai Xuemin, Shu Liping, He Zhixu, Pan Xinghua. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulate ovarian aging in macaques [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 985-991. |
| [12] | Hou Jingying, Guo Tianzhu, Yu Menglei, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning targets and downregulates miR-195 and promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell survival and pro-angiogenic potential by activating MALAT1 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1005-1011. |
| [13] | Liang Xuezhen, Yang Xi, Li Jiacheng, Luo Di, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Bushen Huoxue capsule regulates osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via Hedgehog signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1020-1026. |
| [14] | Wen Dandan, Li Qiang, Shen Caiqi, Ji Zhe, Jin Peisheng. Nocardia rubra cell wall skeleton for extemal use improves the viability of adipogenic mesenchymal stem cells and promotes diabetes wound repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1038-1044. |
| [15] | Fang Xiaolei, Leng Jun, Zhang Chen, Liu Huimin, Guo Wen. Systematic evaluation of different therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in the treatment of ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1085-1092. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||