Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (9): 1459-1466.doi: 10.12307/2022.446
Previous Articles Next Articles
Mechanism and prospects of regulating lymphatic reflux function in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
Zhang Lichuang1, 2, 3, 4, Xu Hao2, 3, 4, Ma Yinghui1, Xiong Mengting2, 3, 4, Han Haihui1, Bao Jiamin2, 3, 4, Zhai Weitao1, Liang Qianqian1, 2, 3, 4
- ¹Guanghua Hospital, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200052, China; 2Longhua Hospital, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200030, China; 3Institute of Spondylosis, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200030, China; 4Key Laboratory of Theory and Therapy of Muscles and Bones, Ministry of Education, Shanghai 200030, China
-
Received:2021-03-15Revised:2021-03-30Accepted:2021-07-28Online:2022-03-28Published:2021-12-10 -
Contact:Zhai Weitao, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Guanghua Hospital, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200052, China Liang Qianqian, Researcher, Doctoral supervisor, Guanghua Hospital, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200052, China; Longhua Hospital, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200030, China; Institute of Spondylosis, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200030, China; Key Laboratory of Theory and Therapy of Muscles and Bones, Ministry of Education, Shanghai 200030, China -
About author:Zhang Lichuang, Master, Guanghua Hospital, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200052, China; Longhua Hospital, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200030, China; Institute of Spondylosis, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200030, China; Key Laboratory of Theory and Therapy of Muscles and Bones, Ministry of Education, Shanghai 200030, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China (General Program), No. 81873321 (to XH); Excellent Youth Science Fund Project of National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81822050 (to LQQ); Key International Cooperation and Exchange Project of National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81920108032 (to LQQ); Shanghai Medical Leading Talents, No. 2019LJ02; Shanghai Shuguang Project, No. 19SG39 (to LQQ); Ministry of Education Innovation Team Development Project, No. IRT1270 (to LQQ); Ministry of Science and Technology Key Field Innovative Team Planning Project, No. 2015RA4002 (to LQQ); Shanghai “Top Priority” Clinical Medicine Center, No. 2017ZZ01010 (to LQQ); Shanghai Three-Year Action Plan Project, No. ZY(2018-2020)-CCCX-3003, ZY2018-2020-FWTX-7005 (to LQQ); Changning District “Guanghua Excellence PI Project”, No. 2016-01, 2016-06 (to LQQ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Lichuang, Xu Hao, Ma Yinghui, Xiong Mengting, Han Haihui, Bao Jiamin, Zhai Weitao, Liang Qianqian. Mechanism and prospects of regulating lymphatic reflux function in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1459-1466.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

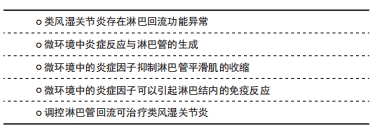
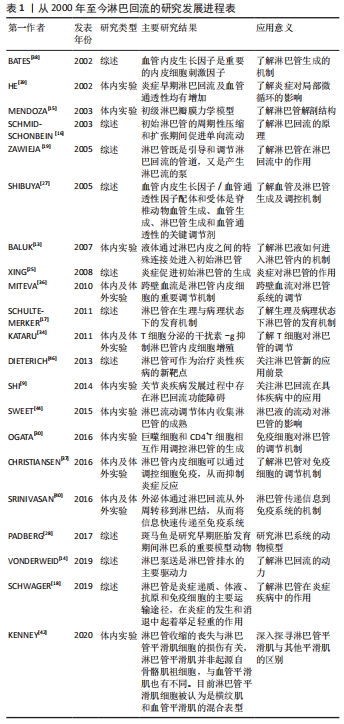
2.1.1 类风湿关节炎存在淋巴回流功能异常 淋巴管包括毛细淋巴管和集合淋巴管,两者具有不同的形态、细胞结构和功能。毛细淋巴管由单层淋巴管内皮细胞组成。邻近的内皮细胞由淋巴管内皮细胞-钙黏蛋白与紧密连接蛋白内皮细胞选择性黏附分子和连接黏附分子等紧密连接蛋白组成的纽扣状连接,这些连接只在离散的位置将相邻细胞紧密连接在一起[13-14]。内皮细胞未连接的瓣片形成原始的初级瓣膜系统,打开时会产生直径2.0-3.0 μm的小孔,允许间质液体进入血管腔,并防止淋巴向相反方向渗漏[14-17]。集合淋巴管外围覆盖有淋巴管平滑肌,管内有管瓣,淋巴管系统与心血管系统不同,其缺少中心泵,所以淋巴管收缩的主要机制是由淋巴平滑肌的内在收缩活动提供的,它短暂而独立地收缩每个淋巴管[14]。这种收缩和松弛的阶段性循环允许淋巴通过下游阀门被推入下一个腔室,同时产生的流体压力关闭上游阀门,限制淋巴回流[14]。淋巴管呈现这种节律性相性收缩的能力被称为淋巴泵,也是该淋巴管系统发挥其基本功能的机制,最终参与静脉循环。 在炎症发生时,淋巴系统可以通过影响组织间液、炎症递质、免疫反应来调节炎症反应[18]。而关节炎中免疫细胞需要依靠淋巴管进行运输,研究表明淋巴管可以从间质空间中吸收液体、大分子和细胞,最终循环至血液循环系统;而关节周围炎症反应的加剧可能是淋巴回流受阻造成,最终形成关节水肿和基质破坏[19]。类风湿关节炎存在淋巴回流功能异常。临床研究发现新诊断类风湿关节患者的淋巴结呈增大趋势,相比之下慢性类风湿关节炎患者的淋巴结则相对较小[20];另外,与健康人相比类风湿关节炎患者的淋巴回流功能明显降低[21]。动物实验结果同样表明,在类风湿关节炎急性进展期,关节旁淋巴回流功能增强,淋巴结增大;而慢性期则呈现相反趋势[22]。此外长期的类风湿关节炎,会使得淋巴结内B细胞移位至淋巴窦,使得淋巴管腔堵塞,最终导致下肢淋巴回流减少[23]。 2.1.2 微环境中炎症反应与淋巴管的生成 微环境中的炎症反应使得淋巴管内皮细胞增殖进而促进淋巴管生成[24]。关节炎发作时,炎性滑膜会招募炎症细胞,如巨噬细胞等,巨噬细胞则可参与淋巴管的生成[25],其机制可能与巨噬细胞分泌的肿瘤坏死因子α刺激淋巴管内皮细胞产生内皮生长因子有关[26],而血管内皮生长因子内皮生长因子C是已知的最重要和最具体的淋巴管生长因子之一[25,27-28]。而关节腔内注射内皮生长因子C腺相关病毒可增加关节部位的淋巴管生成,改善淋巴回流功能,减少关节损伤[29]。OGATA等[30]研究发现巨噬细胞与CD4+T细胞相互作用,促进淋巴管生成,巨噬细胞减少模型鼠、淋巴细胞缺乏核基因重组激活基因2的基因鼠和CD4+T细胞缺乏小鼠的淋巴管生成和水肿都明显减少;这可能是Th1和Th17细胞刺激病灶处的巨噬细胞活化,进而产生内皮生长因子C,内皮生长因子C促进了淋巴管的生成,抑制这一机制不仅会抑制早期淋巴管生成,也抑制后续的淋巴管水肿的产生;尽管炎症过程如何导致淋巴水肿的病理改变仍不清楚,但是这些发现足以表明淋巴水肿与其他慢性炎性疾病有相似之处;此外实验结果还显示他汀类药物明显抑制新淋巴管的形成和水肿,服用他汀类药物1个月可出现抑制与淋巴水肿相关的组织学改变,3个月后组织中的γ-干扰素+和白细胞介素17+CD4T细胞组分;虽然他汀类药物对单独培养的CD11b+细胞中内皮生长因子C的产生没有影响,但是他汀类药物可以降低CD11b+细胞与CD4+T细胞共培养的损伤性细胞中内皮生长因子C的表达和内皮生长因子C的分泌;同时他汀类药物也降低了CD4+T细胞中γ-干扰素和白细胞介素17α的水平;这些结果表明,他汀类药物可通过干扰病变Th1/Th17细胞与巨噬细胞之间的相互作用来抑制病理淋巴管的生成。研究发现抑制淋巴管生成及阻断淋巴回流,类风湿性关节炎的症状可明显加重[31]。 T细胞负调控淋巴管的生成,其中1型辅助型T细胞分泌一种多效性细胞因子γ-干扰素,在启动细胞介导的适应性免疫反应以及调节细胞生长和分化中起重要作用[32]。γ-干扰素具有较强的抗血管及淋巴管生成作用[33-34]。对于血管而言,LBE等[35]研究表明γ-干扰素具有较强的抗血管作用,可抑制血管生成,此外在肿瘤免疫治疗过程中观察到了血管退化,主要是由位于肿瘤微环境及其周围T细胞分泌的γ-干扰素引起。而对于淋巴管而言,KATARU等[34]发现γ-干扰素对促淋巴管生成造血细胞的干扰并不是抑制淋巴结内淋巴管,而是负调控淋巴管内皮细胞的基因转录因子(prospero homeobox protein 1,Prox-1)的表达,即T细胞主要通过γ-干扰素负调控淋巴结内淋巴管,而不是直接地抑制。巨噬细胞识别炎症信号,召集T细胞,T细胞分泌γ-干扰素对淋巴管的生长具有负调控作用。此外,淋巴管内皮细胞具有递呈内源性抗原功能,并参与调节外周免疫耐受,这可能是T细胞通过调节淋巴结内淋巴管来协调整个免疫系统的生物调节机制之一。 树突状细胞是参与调节淋巴回流的重要细胞[36-37]。炎症状态下,血管通透性增大,跨壁血流增加,使淋巴管内皮细胞表达和分泌趋化因子21的功能增强,促进了树突状细胞向淋巴结的输送[36];同时,血管通透性的增加,会导致液体和蛋白质流入细胞间质,间质液体压力升高,淋巴回流代偿性增加[36,38-39]。 另有研究显示,正常的淋巴管内皮细胞条件培养液能显著抑制树突状细胞的成熟,这或许是淋巴管内皮细胞调节细胞免疫反应,限制炎症的新机制[37]。更有研究表明,组织损伤后淋巴流量几乎是立即增加[36],而炎症细胞因子的表达增加过程可能需要几个小时[36,38-39],造成这种情况的原因,可能与外泌体的信息传递相关。SRINIVASAN等[40]研究发现,局部微环境中的外泌体可快速通过淋巴管转运到淋巴结,在淋巴结启动有效的免疫反应之前,提供了一种在迁移细胞到达之前快速交换感染特异性信息的机制。 2.1.3 微环境中的炎症因子抑制淋巴管平滑肌的收缩 淋巴管系统由毛细淋巴管、预收集淋巴管及集合淋巴管构成,其中集合淋巴管主要依靠淋巴管平滑肌的收缩来推动淋巴液回流[41]。谱系追踪显示淋巴管平滑肌与骨骼肌和血管平滑肌是不同的,KENNEY等[42]研究显示淋巴管平滑肌并不是起源于骨骼肌祖细胞,而是与血管平滑肌起源相同,但是发育后期淋巴管平滑肌又区别于血管平滑肌,更有趣的是淋巴管发育后期又表达出了部分骨骼肌表型,但其发育机制至今未明。2016年,LIANG等[31]研究发现在炎症状态下淋巴管内皮细胞产生的大量诱导型一氧化氮合酶,可能是抑制淋巴管平滑肌细胞收缩的关键因子,进一步研究显示淋巴管平滑肌细胞的收缩受限可能与一氧化氮有关,最终使得淋巴回流减少[43]。微环境中的炎症反应损伤了淋巴回流功能,使得淋巴回流较少,然而淋巴回流的减少又会调节淋巴管的发育[44],但是淋巴液的流动是如何调控淋巴管的成熟,其机制尚未被阐述清楚。 2.1.4 微环境中的炎症因子可以引起淋巴结内的免疫反应 富含大量炎症因子的淋巴液,会引起淋巴结的免疫反应[10]。BELL等[45]研究发现当关节滑膜持续处于炎症时,巨噬细胞及淋巴管内皮细胞会高表达一氧化氮合成酶,促使免疫细胞转运至淋巴结,使得淋巴结体积增大。然而SCHWAGER等[18]认为在关节炎早期为“扩张”阶段,淋巴管生成增加和淋巴结增大或不伴淋巴管收缩,限制了炎症反应;而接下来的“塌陷”阶段,淋巴结缩小和淋巴管收缩障碍,引起淋巴回流功能显著下降,最终导致关节破坏。在另一项研究中发现“塌陷”的淋巴结可能是B细胞移位至淋巴窦所致[23]。 2.1.5 调控淋巴管回流可治疗类风湿关节炎 长期的研究显示淋巴回流障碍加重了关节炎的发作及进展,靶向淋巴回流功能可能是治疗关节炎的新选择[46-47]。已经有实验证明,使用一氧化氮合酶抑制剂处理,可以改善淋巴回流功能[31];而硼替佐米可以抑制巨噬细胞的炎症反应,降低了淋巴管内皮细胞的一氧化氮合酶表达,使得滑膜淋巴功能改善,关节组织损伤减轻[48]。此外,研究发现清除B细胞可以治疗淋巴结阻塞的炎症性关节炎[23]。 临床上用于调控淋巴回流治疗关节炎的药物极其缺乏,然而中医药对疾病病理过程中的淋巴管生成有一定的调节作用,有助于疾病的治疗[49]。HAN等[50]研究显示防己黄芪汤可以促进早期关节炎的淋巴管生长,改善淋巴管回流功能,维持软骨结构,最终延缓了关节炎的进展;而另一项研究结果显示独活寄生汤同样可以促进淋巴管生长,改善淋巴管回流,继而抑制关节炎的严重程度[51]。不仅中药复方对淋巴管生成具有促进作用,中药单体成分也可促进淋巴管的生成,且中药单体更具有成为新药的潜质,有深入研究的价值。 HOU等[52]研究表明人参皂苷Rg1具有显著改善淋巴引流功能,减少了滑膜炎症和骨侵蚀,降低了血清白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α的浓度,并增加了过表达肿瘤坏死因子基因的模型小鼠足部皮肤上淋巴管的平滑肌覆盖率的功能。此外,人参皂苷Rg1治疗12周对肝和肾组织没有造成任何损害。以上研究表明,一些具有除痹功能的中药复方,例如独活寄生汤等都具有促进淋巴回流功能治疗类风湿关节炎的作用。它们的有效成分或抑制炎症因子的释放,或减轻炎症因子刺激下淋巴管内皮细胞释放一氧化氮,防止淋巴管平滑肌细胞“泵”的功能受损或下降,或刺激淋巴管生成或成熟,保护淋巴管的结构,多方位改善淋巴回流功能,减轻类风湿关节炎的损伤。有关淋巴结对关节炎的调控机制,至今仍有很多值得去研究的内容。2000年至今淋巴回流的研究进程,见表1。 "
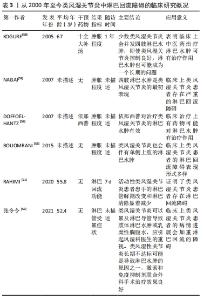
2.2 类风湿关节炎中淋巴回流障碍的临床研究 2.2.1 改善淋巴回流有利于缓解类风湿关节炎的临床症状 在关节炎发病过程中,关节周围淋巴回流障碍和中医的痹症理论非常相似,并且经过研究证明传统治疗痹症的中草药可直接调控淋巴的回流功能[55]。最新的临床研究发现活动期的类风湿关节炎患者手部的淋巴管数量呈减少趋势,相应的淋巴回流功能降低[21],研究还发现与正常人相比,活动期类风湿关节炎患者手背上吲哚菁绿荧光染料的近红外成像的总长度较短,该发现为解释类风湿关节炎患者局部滑膜炎症及组织损伤提供了合理的机制;具体而言,由于淋巴回流功能受损,炎症因子在关节局部积累,而关节局部的炎症因子则会直接损伤局部组织;此外,该项研究提示类风湿关节炎手部的吲哚菁绿荧光染料的近红外成像检查是可行的,可作为未来临床研究类风湿关节炎疾病严重程度或类风湿关节炎发作期的评价指标。临床数据似乎与实验室客观数据并不相符,动物研究显示炎症反应促进了淋巴管生成[24],这与临床数据相悖,但却支持了促进淋巴管生成、改善淋巴回流功能治疗关节炎的观点。 类风湿关节炎作为关节炎中的重要组成,其病理改变有其显著特点,有报道显示类风湿关节炎的患者可伴有四肢的淋巴水肿[53],但是单纯的四肢局部水肿较为罕见,临床病例也可见单侧肢体的淋巴水肿[56],报道中认为四肢的局部继发性淋巴水肿是较为罕见的类风湿关节炎的并发症,它们影响下肢及上肢的功能,其中上肢肿胀最为常见。 目前诊断淋巴水肿,多基于受累上肢的侵润性肿胀、疼痛等临床症状;此外可通过引流区的淋巴活检、淋巴造影或淋巴闪烁扫描等进行确诊;影像学通常显示淋巴管阻塞,很少观察到淋巴管扩张。此外,这种类风湿关节炎并发的四肢水肿,很少观察到消退,这种肿胀多为慢性症状。因此这种水肿会导致一些严重的、有时甚至致残的并发症,特别是细菌感染、关节受限及慢性皮肤溃疡。另外报道中还认为目前针对淋巴水肿治疗的争议很多,而改善类风湿关节炎的治疗,并不能改善淋巴水肿的症状,物理治疗似乎成为了最有效的治疗方式,除此之外还可以增加利尿剂来改善淋巴回流的效果,近旁淋巴关节注射皮质类固醇激素也是较为有效的治疗方法。而在生物制剂方面,肿瘤坏死因子α抑制剂也较为有效,但是也有使用肿瘤坏死因子α抑制剂后并发淋巴水肿的可能,这似乎又相互矛盾。 在临床治疗上,靶向淋巴水肿的药物较为匮乏,有临床研究报道依那西普可以治疗类风湿关节炎并发的淋巴水肿[54],但是目前仅有1例报道,具体作用尚未可知。另外据文献报道十全大补汤对淋巴水肿也有明显效果[58],很多传统除痹的中药对促进淋巴回流都具有良好的效果,动物实验早已证明了该类中药的作用及其作用机制,但是临床实践情况具体如何,目前还未有大量的临床报道。这可能是以往没有评估淋巴回流的有效方法,现在的吲哚菁绿荧光染料的近红外成像可能将成为变革性的评估淋巴回流功能的检测方式,或许未来将会有大量的相关文献报道。较为明显的淋巴水肿是类风湿关节炎的罕见并发症,其实临床上最为多见的应当是类风湿关节炎合并的淋巴功能受损或者更轻微的淋巴回流障碍[57],因为初期的淋巴回流障碍并没有引起临床症状,可能会经常被忽视。 淋巴系统作为重要的“水道”系统,其参与了关节液的回流。生理状态下,关节旁的淋巴系统将局部微环境中的“垃圾”带走。在类风湿关节炎状态下,这种“水道”系统,可将免疫细胞及炎症因子等产物转运至淋巴结和回流入血,从而减轻局部关节的炎症反应,延缓了关节的损伤。当这种回流液体的“水道”系统发生障碍甚至堵塞,则会加剧局部关节的损伤。而类风湿关节炎存在淋巴回流功能障碍,所以调控淋巴回流是可以治疗类风湿关节炎,但是目前相关的临床研究仍然较少。长期以来大多数的临床医生很少关注关节炎过程中的淋巴回流问题,此外淋巴回流障碍可能起病较为隐秘,临床症状较轻,临床也缺少靶向淋巴回流的药物,诸多的原因造成了淋巴回流障碍被忽视,以至于在淋巴水肿时,甚至出现严重并发症才会被关注。 调控淋巴回流不仅在保守治疗过程中有价值,在改善关节置换后的并发症方面同样具有很好的前景。研究者们应该重视淋巴管系统在类风湿关节炎发生发展过程中的作用,寻找更多更好的药物,为类风湿关节炎的治疗提供更多的手段。类风湿关节炎中淋巴回流障碍的临床研究,见表3。 "
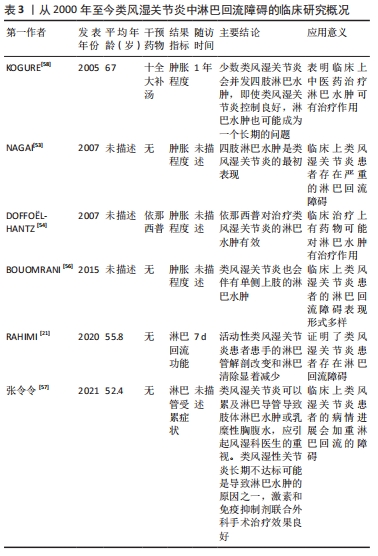

2.2.2 淋巴回流障碍是影响关节置换效果的重要因素 关节置换是晚期关节炎的重要治疗手段,据统计关节置换数量正在逐年增加[59]。然而关节置换必不可少的会破坏一些组织,有继发淋巴水肿的可能[60],淋巴水肿或淋巴回流障碍影响术后伤口的愈合[61],甚至影响关节置换后的疗效。彭志平等[62]研究表明关节置换后并发肿胀的发生率约为70%,其中静脉性水肿约占51.3%、淋巴水肿约占24%。PICHONNAZ等[63]认为关节置换后的肿胀会使得关节活动度受限,影响骨骼肌的收缩及术后功能恢复,甚至决定了关节置换的疗效。此外有研究表明关节置换前存在淋巴水肿会增加关节假体取出率,而提前治疗淋巴水肿则会降低该事件的发生率[64]。众所周知感染是决定关节置换成败的决定因素之一,最新研究显示淋巴水肿本身就是关节置换后感染的危险因素[65],所以处理关节置换手术前后淋巴水肿及肢体肿胀已经是极其迫切的事情。然而处理淋巴水肿及术后肿胀的方法有限,治疗效果欠佳,因此治疗淋巴水肿的新方法逐渐成为该领域的研究热点。有研究认为增加淋巴回流可以改善术后肿胀,但是手动淋巴引流术未能减轻术后肿胀[63],而更新颖的分子治疗却仍处于动物实验阶段,如内皮生长因子C可促进淋巴管生成,改善淋巴回流[66-67]。"

| [1] CHAUHAN K, JANDU JS, GOYAL A, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis. 2021 Jun 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. 2021. [2] YICHENG K, BAO LG, WEIDE VC, et al. High prevalence of comorbid autoimmune diseases in adults with type 1 diabetes from the HealthFacts database. J Diabetes. 2019;11(4):273-279. [3] TUNCER T, GILGIL E, KACAR C, et al. Prevalence of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Spondyloarthritis in Turkey: a nationwide study. Arch Rheumatol. 2017;33(2):128-136. [4] 陶庆文,王金平,徐愿,等.类风湿关节炎中西医结合医疗质量控制指标专家共识(2021年版)[J].中日友好医院学报,2021,35(1):12-15. [5] HAMMER HB, MICHELSEN B, SEXTON J, et al. Swollen, but not tender joints, are independently associated with ultrasound synovitis: results from a longitudinal observational study of patients with established rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78(9):1179-1185. [6] BABAEI M, JAVADIAN Y, NARIMANI H, et al. Correlation between systemic markers of inflammation and local synovitis in knee osteoarthritis. Caspian J Intern Med. 2019;10(4):383-387. [7] LI GS, CUI L, WANG GD. miR-155-5p regulates macrophage M1 polarization and apoptosis in the synovial fluid of patients with knee osteoarthritis. Exp Ther Med. 2021;21(1):68. [8] WOODELL-MAY JE, SOMMERFELD SD. Role of Inflammation and the Immune System in the Progression of Osteoarthritis. J Orthop Res. 2020;38(2):253-257. [9] SHI J, LIANG Q, ZUSCIK M, et al. Distribution and alteration of lymphatic vessels in knee joints of normal and osteoarthritic mice. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014;66(3):657-666. [10] JALKANEN S, SALMI M. Lymphatic endothelial cells of the lymph node. Nat Rev Immunol. 2020;20(9):566-578. [11] ZEDDOU M. Osteoarthritis Is a Low-grade inflammatory disease: obesity’s involvement and herbal treatment. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019;2019:2037484. [12] HUBER-LANG M, KOVTUN A, LGNATIUS A. The role of complement in trauma and fracture healing. Semin Immunol. 2013;25(1):73-78. [13] BALUK P, FUXE J, HASHIZUME H, et al. Functionally specialized junctions between endothelial cells of lymphatic vessels. J Exp Med. 2007;204 (10):2349-2362. [14] VONDERWEID PY. Lymphatic Vessel Pumping. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019; 1124:357-377. [15] MENDOZA E, SCHMID-SCHONBEIN GW. A model for mechanics of primary lymphatic valves. J Biomech Eng. 2003;125(3):407-414. [16] SCHMID-SCHONBEIN GW. The second valve system in lymphatics. Lymphat Res Biol. 2003;1(1):25-31. [17] SCHULTE-MERKER S, SABINE A, PETROVA TV. Lymphatic vascular morphogenesis in development, physiology, and disease. J Cell Biol. 2011;193(4):607-618. [18] SCHWAGER S, DETMAR M. Inflammation and lymphatic function. Front Immunol. 2019;10:308. [19] ZAWIEJA D. Lymphatic biology and the microcirculation: past, present and future. Microcirculation. 2005;12(1):141-150. [20] RAHIMI H, BELL R, BOUTA EM, et al. Lymphatic imaging to assess rheumatoid flare: mechanistic insights and biomarker potential. Arthritis Res Ther. 2016;18:194. [21] RAHIMI H, BELL R, BOUTA EM, et al. Altered lymphatic vessel anatomy and markedly diminished lymph clearance in affected hands of patients with active rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020;72(9):1447-1455. [22] ZHOU Q, WOOD R, SCHWARZ EM, et al. Near-infrared lymphatic imaging demonstrates the dynamics of lymph flow and lymphangiogenesis during the acute versus chronic phases of arthritis in mice. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62(7):1881-1889. [23] LI J, ZHOU Q, WOOD RW, et al. CD23(+)/CD21(hi) B-cell translocation and ipsilateral lymph node collapse is associated with asymmetric arthritic flare in TNF-Tg mice. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011;13(4):R138. [24] MOUTA C, HEROULT M. Inflammatory triggers of lymphangiogenesis. Lymphat Res Biol. 2003;1(3):201-218. [25] XING L, JI RC. Lymphangiogenesis myeloid cells and inflammation. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2008;4(5):599-613. [26] BISOENDIAL R, TABET F, TAK PP, et al. Apolipoprotein A-I limits the negative effect of tumor necrosis factor on lymphangiogenesis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2015;35(11):2443-2450. [27] SHIBUYA M, CLAESSON-WELSH L. Signal transduction by VEGF receptors in regulation of angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Exp Cell Res. 2006;312(5):549-560. [28] PADBERG Y, SCHULTE-MERKER S, VANLMPEL A. The lymphatic vasculature revisited-new developments in the zebrafish. Methods Cell Biol. 2017;138:221-238. [29] ZHOU Q, GUO R, WOOD R, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor C attenuates joint damage in chronic inflammatory arthritis by accelerating local lymphatic drainage in mice. Arthritis Rheum. 2011; 63(8):2318-2328. [30] OGATA F, FUJIU K, MATSUMOTO S, et al. Excess lymphangiogenesis cooperatively induced by macrophages and CD4(+) T cells drives the pathogenesis of lymphedema. J Invest Dermatol. 2016;136(3):706-714. [31] LIANG Q, JU Y, CHEN Y, et al. Lymphatic endothelial cells efferent to inflamed joints produce iNOS and inhibit lymphatic vessel contraction and drainage in TNF-induced arthritis in mice. Arthritis Res Ther. 2016;18:62. [32] VARMA TK, LIN CY, TOLIVER-KINSKY TE, et al. Endotoxin-induced gamma interferon production: contributing cell types and key regulatory factors. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2002;9(3):530-543. [33] FATHALLAH-SHAYKH HM, ZHAO LJ, KAFROUNI AI, et al. Gene transfer of IFN-gamma into established brain tumors represses growth by antiangiogenesis. J Immunol. 2000;164(1):217-222. [34] KATARU RP, KIM H, JANG C, et al. T lymphocytes negatively regulate lymph node lymphatic vessel formation. Immunity. 2011;34(1):96-107. [35] LBE S, QIN Z, SCHULER T et al. Tumor rejection by disturbing tumor stroma cell interactions. J Exp Med. 2001;194(11):1549-1559. [36] MITEVA DO, RUTKOWSKI JM, DIXON JB, et al. Transmural flow modulates cell and fluid transport functions of lymphatic endothelium. Circ Res. 2010;106(5):920-931. [37] CHRISTIANSEN AJ, DIETERICH LC, OHS L, et al. Lymphatic endothelial cells attenuate inflammation via suppression of dendritic cell maturation. Oncotarget. 2016;7(26):39421-39435. [38] BATES DO, HILLMAN NJ, WILLIAMS B, et al. Regulation of microvascular permeability by vascular endothelial growth factors. J Anat. 2002; 200(6):581-597. [39] HE C, YOUNG AJ, WEST CA, et al. Stimulation of regional lymphatic and blood flow by epicutaneous oxazolone. J Appl Physiol. 2002;93(3):966-973. [40] SRINIVASAN S, VANNBERG FO, DIXON JB. Lymphatic transport of exosomes as a rapid route of information dissemination to the lymph node. Sci Rep. 2016;6:24436. [41] 张武强,石继祥.骨性关节炎中淋巴管的研究进展[J].世界最新医学信息文摘,2019,19(66):106-107. [42] KENNEY HM, BELL RD, MASTERS EA. et al. Lineage tracing reveals evidence of a popliteal lymphatic muscle progenitor cell that is distinct from skeletal and vascular muscle progenitors. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):18088. [43] LIANG Q, ZHANG L, XU H, et al. Lymphatic muscle cells contribute to dysfunction of the synovial lymphatic system in inflammatory arthritis in mice. Arthritis Res Ther. 2021;23(1):58. [44] SWEET DT, JIMENEZ JM, CHANG J, et al. Lymph flow regulates collecting lymphatic vessel maturation in vivo. J Clin Invest. 2015;125(8):2995-3007. [45] BELL RD, SLATTERY PN, WU EK, et al. iNOS dependent and independent phases of lymph node expansion in mice with TNF-induced inflammatory-erosive arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2019;21(1):240. [46] DIETERICH LC, SEIDEL CD, DETMAR M. Lymphatic vessels: new targets for the treatment of inflammatory diseases. Angiogenesis. 2014;17(2):359-371. [47] BOUTA EM, BELL RD, RAHIMI H, et al. Targeting lymphatic function as a novel therapeutic intervention for rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2018;14(2):94-106. [48] WANG W, LIN X, XU H, et al. Attenuated joint tissue damage associated with improved synovial lymphatic function following treatment with bortezomib in a mouse model of experimental posttraumatic osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019;71(2):244-257. [49] PENG L, DONG Y, FAN H, et al. Traditional Chinese medicine regulating lymphangiogenesis: a literature review. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:1259. [50] HAN H, MA Y, WANG X, et al. Fang-Ji-Huang-Qi-Tang attenuates degeneration of early-stage KOA mice related to promoting joint lymphatic drainage function. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020;2020:3471681. [51] CHEN Y, LI J, LI Q, et al. Du-Huo-Ji-Sheng-Tang attenuates inflammation of TNF-Tg mice related to promoting lymphatic drainage function. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016;2016:7067691. [52] HOU T, LIU Y, WANG X, et al. Ginsenoside Rg1 promotes lymphatic drainage and improves chronic inflammatory arthritis. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2020;20(4):526-534. [53] NAGAI Y, AOYAMA K, ENDO Y, et al. Lymphedema of the extremities developed as the initial manifestation of rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Dermatol. 2007;17(2):175-176. [54] DOFFOEL-HANTZ V, SPARSA A, VERBEKE S, et al. Lymphoedema: a rare complication of inflammatory rheumatism. Successful treatment with etanercept. Eur J Dermatol. 2007;17(4):337-338. [55] LIANG Q, SHI Q, WOOD RW, et al. Peri-articular lymphatic system and “Bi” theory of Chinese medicine in the pathogenesis and treatment of arthritis. Chin J Integr Med. 2015;21(9):648-655. [56] BOUOMRANI S, NOUMA H, SLAMA A, et al. Unilateral lymphedema of the upper limb in a rheumatoid arthritis. Pan Afr Med J. 2015;21:214. [57] 张令令,高兰,张国华,等.类风湿关节炎合并淋巴管受累的临床特征[J].中华临床免疫和变态反应杂志,2021,15(1):33-38. [58] KOGURE T, HOSHINO A, LTO K, et al. Beneficial effect of complementary alternative medicine on lymphedema with rheumatoid arthritis. Mod Rheumatol. 2005;15(6):445-449. [59] 边焱焱,程开源,常晓,等.2011至2019年中国人工髋膝关节置换手术量的初步统计与分析[J].中华骨科杂志,2020,40(21):1453-1460. [60] 靳松,孙自强,金星,等.继发性淋巴水肿的诊治进展[J].中国血管外科杂志,2017,9(4):316-320. [61] JONES RE, RUSSELL RD, HUO MH. Wound healing in total joint replacement. Bone Joint J. 2013;95-B(11 Suppl A):144-147. [62] 彭志平,林云.彩超对人工关节置换术后下肢肿胀原因的诊断价值[J].中国超声医学杂志,2017,33(1):57-59. [63] PICHONNAZ C, BASSIN JP, LECUREUX E, et al. Effect of manual lymphatic drainage after total knee arthroplasty: a randomized controlled trial. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2016;97(5):674-682. [64] VORAVITVET TY, CHEN C, LIN CY, et al. Lymphedema microsurgery reduces the rate of implant removal for patients who have pre-existing lymphedema and total knee arthroplasty for knee osteoarthritis. J Surg Oncol. 2020;121(1):57-66. [65] KOLZ JM, RAINER WG, WYLES CC, et al. Lymphedema: a significant risk factor for infection and implant failure after total knee arthroplasty. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2020;28(23):996-1002. [66] SAITO Y, NAKAGAMI H, KANEDA Y, et al. Lymphedema and therapeutic lymphangiogenesis. Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:804675. [67] YOSHIDA S, HAMUY R, HAMADA Y, et al. Adipose-derived stem cell transplantation for therapeutic lymphangiogenesis in a mouse secondary lymphedema model. Regen Med. 2015;10(5):549-562. |
| [1] | Zhuang Zhikun, Wu Rongkai, Lin Hanghui, Gong Zhibing, Zhang Qianjin, Wei Qiushi, Zhang Qingwen, Wu Zhaoke. Application of stable and enhanced lined hip joint system in total hip arthroplasty in elderly patients with femoral neck fractures complicated with hemiplegia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1429-1433. |
| [2] | Zhu Chan, Han Xuke, Yao Chengjiao, Zhou Qian, Zhang Qiang, Chen Qiu. Human salivary components and osteoporosis/osteopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1439-1444. |
| [3] | Jin Tao, Liu Lin, Zhu Xiaoyan, Shi Yucong, Niu Jianxiong, Zhang Tongtong, Wu Shujin, Yang Qingshan. Osteoarthritis and mitochondrial abnormalities [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1452-1458. |
| [4] | Zhu Chan, Han Xuke, Yao Chengjiao, Zhang Qiang, Liu Jing, Shao Ming. Acupuncture for Parkinson’s disease: an insight into the action mechanism in animal experiments [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1272-1277. |
| [5] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [6] | Zhou Hongqin, Wu Dandan, Yang Kun, Liu Qi. Exosomes that deliver specific miRNAs can regulate osteogenesis and promote angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1107-1112. |
| [7] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [8] | Huang Chenwei, Fei Yankang, Zhu Mengmei, Li Penghao, Yu Bing. Important role of glutathione in stemness and regulation of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1119-1124. |
| [9] | Hui Xiaoshan, Bai Jing, Zhou Siyuan, Wang Jie, Zhang Jinsheng, He Qingyong, Meng Peipei. Theoretical mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine theory on stem cell induced differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1125-1129. |
| [10] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [11] | Fan Yiming, Liu Fangyu, Zhang Hongyu, Li Shuai, Wang Yansong. Serial questions about endogenous neural stem cell response in the ependymal zone after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1137-1142. |
| [12] | Guo Jia, Ding Qionghua, Liu Ze, Lü Siyi, Zhou Quancheng, Gao Yuhua, Bai Chunyu. Biological characteristics and immunoregulation of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1093-1101. |
| [13] | Wu Weiyue, Guo Xiaodong, Bao Chongyun. Application of engineered exosomes in bone repair and regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1102-1106. |
| [14] | Huang Hao, Hong Song, Wa Qingde. Finite element analysis of the effect of femoral component rotation on patellofemoral joint contact pressure in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 848-852. |
| [15] | Yuan Jing, Sun Xiaohu, Chen Hui, Qiao Yongjie, Wang Lixin. Digital measurement and analysis of the distal femur in adults with secondary knee valgus deformity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 881-885. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||