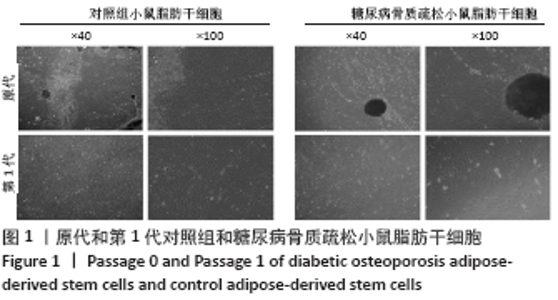
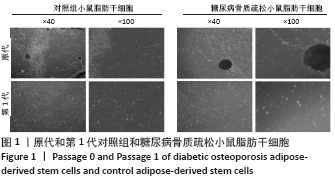
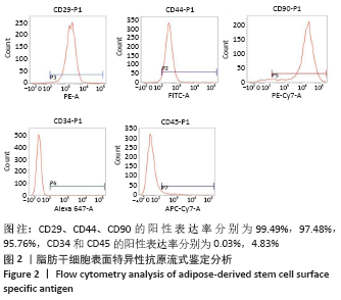
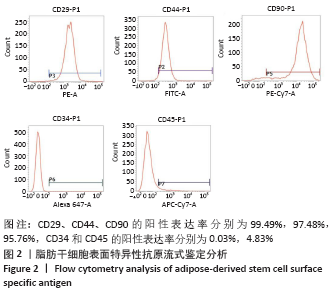
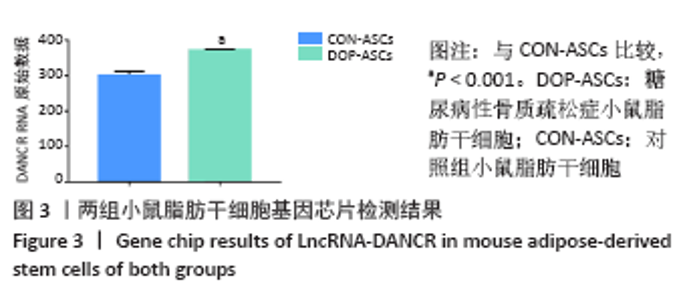
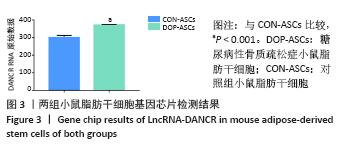
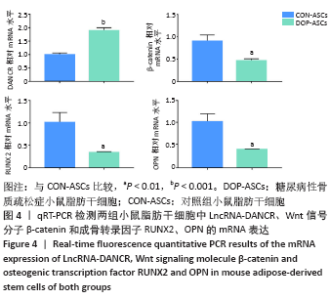
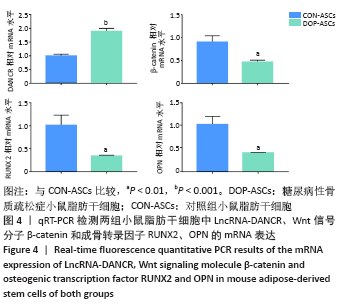
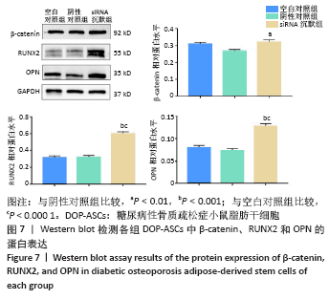
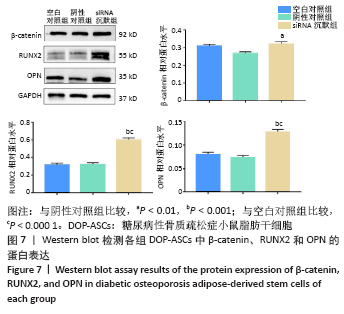
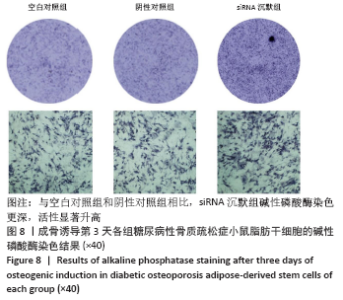
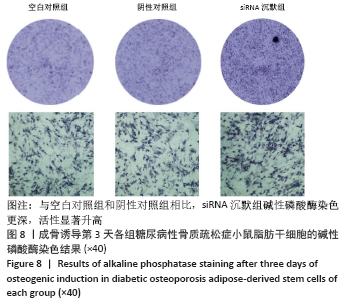
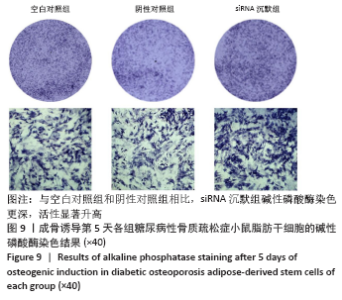
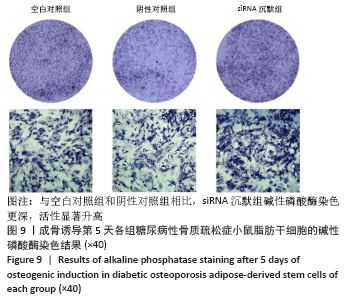
[1] 唐辉,姚志浩,罗道文,等.高脂高糖饮食结合链脲佐菌素建立2型糖尿病性骨质疏松症大鼠模型[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(8): 1207-1211.
[2] ALA M, JAFARI RM, DEHPOUR AR. Diabetes Mellitus and Osteoporosis Correlation: Challenges and Hopes. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2020;16(9):984-1001.
[3] MOHSIN S, BANIYAS MM, ALDARMAKI RS, et al. An update on therapies for the treatment of diabetes-induced osteoporosis. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2019;19(9):937-948.
[4] TANIUE K, AKIMITSU N. The Functions and Unique Features of LncRNAs in Cancer Development and Tumorigenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(2): 632.
[5] 李生强,谢冰颖,陈娟,等.绝经后骨质疏松症关联长链非编码RNA uc431+相互作用蛋白质组学分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2021, 25(11):1641-1646.
[6] YANG Y, YUJIAO W, FANG W, et al. The roles of miRNA, lncRNA and circRNA in the development of osteoporosis. Biol Res. 2020;53(1):40.
[7] KUTERBEKOV M, JONAS AM, GLINEL K, et al. Osteogenic Differentiation of Adipose-Derived Stromal Cells: From Bench to Clinics. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2020;26(5):461-474.
[8] PENG S, SHI S, TAO G, et al. JKAMP inhibits the osteogenic capacity of adipose-derived stem cells in diabetic osteoporosis by modulating the Wnt signaling pathway through intragenic DNA methylation. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):120.
[9] WANG CG, HU YH, SU SL, et al. LncRNA DANCR and miR-320a suppressed osteogenic differentiation in osteoporosis by directly inhibiting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Exp Mol Med. 2020; 52(8):1310-1325.
[10] BARON R, KNEISSEL M. WNT signaling in bone homeostasis and disease: from human mutations to treatments. Nat Med. 2013;19(2):179-192.
[11] MOHSIN S, KAIMALA S, SUNNY JJ, et al. Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Increases the Risk to Hip Fracture in Postmenopausal Osteoporosis by Deteriorating the Trabecular Bone Microarchitecture and Bone Mass. J Diabetes Res. 2019;2019:3876957.
[12] SHAO X, YANG Y, TAN Z, et al. Amelioration of bone fragility by pulsed electromagnetic fields in type 2 diabetic KK-Ay mice involving Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2021;320(5): E951-E966.
[13] 刘梅,张君,王旭霞.糖尿病大鼠牙槽骨骨密度与全身骨密度变化的相关实验研究[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2009,27(4):451-454.
[14] TAJIMA S, TOBITA M, MIZUNO H. Current status of bone regeneration using adipose-derived stem cells. Histol Histopathol. 2018;33(7):619-627.
[15] 彭双麟,姚志浩,罗道文,等.多孔双相磷酸钙陶瓷修复骨质疏松症大鼠颅骨极量缺损的实验研究[J].口腔医学研究,2019,35(4): 377-381.
[16] STORTI G, SCIOLI MG, KIM BS, et al. Adipose-Derived Stem Cells in Bone Tissue Engineering: Useful Tools with New Applications. Stem Cells Int. 2019;2019:3673857.
[17] BARBA M, DI TARANTO G, LATTANZI W. Adipose-derived stem cell therapies for bone regeneration. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2017;17(6): 677-689.
[18] MERCER TR, DINGER ME, MATTICK JS. Long non-coding RNAs: insights into functions. Nat Rev Genet. 2009;10(3):155-159.
[19] KO NY, CHEN LR, CHEN KH. The Role of Micro RNA and Long-Non-Coding RNA in Osteoporosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(14):4886.
[20] PENG S, CAO L, HE S, et al. An Overview of Long Noncoding RNAs Involved in Bone Regeneration from Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Stem Cells Int. 2018;2018:8273648.
[21] WANG Y, LI YP, PAULSON C, et al. Wnt and the Wnt signaling pathway in bone development and disease. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2014; 19:379-407.
[22] MAEDA K, KOBAYASHI Y, KOIDE M, et al. The Regulation of Bone Metabolism and Disorders by Wnt Signaling. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(22): 5525.
[23] LI X, YANG J, BAO M, et al. Wnt signaling in bone metastasis: mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. Life Sci. 2018;208:33-45.
[24] CHEN L, SONG Z, HUANG S, et al. lncRNA DANCR suppresses odontoblast-like differentiation of human dental pulp cells by inhibiting wnt/β-catenin pathway. Cell Tissue Res. 2016;364(2):309-318.
[25] JIANG SY, MIAO YX, HIROKAZU T, et al. Effects of lncRNA DANCR on proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts by regulating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(13):5558-5566.
|