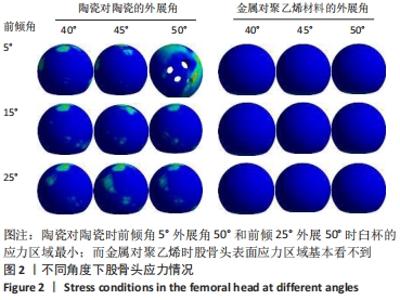
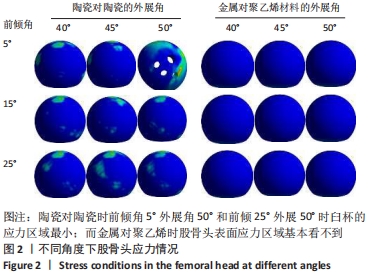
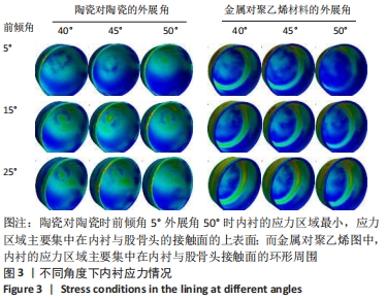
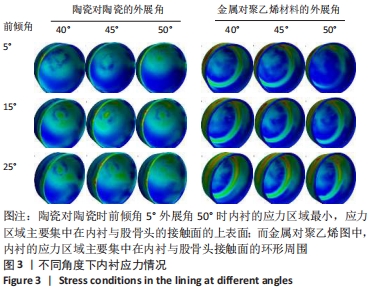
[1] 黄和涛, 潘建科, 杨伟毅, 等. 全髋关节置换过程中使用保留股骨颈假体有效和安全性的系统评价[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2020,24(6):962-967.
[2] GOH S, CHUA K, CHONG D, et al. The quest for longevity in the total hip replacement: a concept study of design elements using finite element analysis. Orthopaedic Proceedings. 2016;98B(SUPP_1).
[3] LEARMONTH ID, YOUNG C, RORABECK C. The operation of the century: total hip replacement.Lancet. 2007;370(9597):1508-1519.
[4] 邢金锋, 宋科官, 彭锂,等. 全关节成形术中假体周围骨溶解的 概述:本体因素与未来发展方向[J]. 现代生物医学进展,2016,16(2):386-389+316.
[5] 戚大春, 安新荣.全髋关节置换假体位置的确定方法及生物力学特性[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(26):3811-3816.
[6] 刘庆, 殷建华, 周乙雄, 等. 陶瓷对陶瓷人工髋关节置换手术技巧及相关研究[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,15(14):1062-1064.
[7] 刘嘉, 邓江.髋臼假体定位准确性的研究进展[J].中国骨伤,2016,29(8):770-773.
[8] ABDEL MP, VON ROTH P, JENNINGS MT, et al. What safe zone? The vast majority of dislocated THAs are within the Lewinnek safe zone for acetabular component position. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016;474(2):386-391.
[9] BEVERLAND DE, O’NEILL CK, RUTHERFORD M, et al. Placement of the acetabular component. Bone Joint J. 2016;98-B(1 Suppl A):37-43.
[10] TRIPURANENI KR, MUNSON NR, ARCHIBECK MJ, et al. Acetabular Abduction and Dislocations in Direct Anterior vs Posterior Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Retrospective, Matched Cohort Study. J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(10):2299-2302.
[11] LEWINNEK GE, LEWIS JL,TARR R, et al. Dislocations after total hip-replacement arthroplasties. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1978;60(2):217-220.
[12] BEREND KR, SPORER SM, SIERRA RJ, et al. Achieving stability and lower-limb length in total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;92(16):2737-2752.
[13] Seagrave KG, Troelsen A, Malchau H, et al. “Acetabular cup position and risk of dislocation in primary total hip arthroplasty: a systematic review of the literature.Acta Orthop. 2017;88(1):10-17.
[14] Abu-Amer Y, Darwech I, Clohisy JC. Aseptic loosening of total joint replacements: mechanisms underlying osteolysis and potential therapies. Arthritis Res Ther. 2007;9 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S6.
[15] Nakashima Y, Hirata M, Akiyama M, et al. Combined anteversion technique reduced the dislocation in cementless total hip arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 2014;38(1): 27-32.
[16] Rutherford M, O’Connor JD, Hill JC, et al. Patient positioning and cup orientation during total hip arthroplasty: assessment of current UK practice. Hip Int. 2019;29(1):89-95.
[17] Bosker BH, Verheyen CC, Horstmann WG, et al. Poor accuracy of freehand cup positioning during total hip arthroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2007;127(5): 375-379.
[18] 宋新新,董黎敏,张春秋,等.髋关节置换的有限元分析及实验验证[J].天津理工大学学报,2016,32(5):1-5.
[19] Zhang X, Sun X, Shi G. Monitoring the Stability of Artificial Prosthesis Performance for Hip Replacement. J Biomater Tissue Eng. 2019;9(10):1395-1397.
[20] 李军,荆珏华,史占军,等.利伐沙班对全髋关节置换术隐性出血影响的病例对照研究[J].中国骨伤,2014,27(1):34-37.
[21] 张晓强,高菲菲,王战朝,等.膝伤活血灵口服配合低分子肝素钙皮下注射对全膝关节置换术后隐性失血的影响[J].中医正骨,2014,26(4):23-25.
[22] 斯海波,曾羿,兰平文,等.有限元分析应用于全髋关节置换中的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2014,22(24):2256-2260.
[23] 李苏皖,付国建,谢洋,等.骨质疏松患者全髋关节置换术后股骨应力变化的有限元分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2017,25(3):260-263.
[24] Lee JS, Lee KB.New Modulation Techniques for a Leakage Current Reduction and a Neutral -Point Voltage Balance in Transformerless Photovoltaic Systems Using a Three-Level Inverter.IEEE Trans Power Electron. 2014;29 (4):1720-2732.
[25] 郑肖. 初次人工髋关节置换术后行翻修术的原因分析[D]. 泰安:泰山医学院, 2014.
[26] 何斌,章淼锋,沈跃,等.人工髋关节置换术后初次翻修的原因分析及翻修术疗效评估[J].中华骨科杂志,2019,39(15):909-917.
[27] 李强.陶瓷对陶瓷人工髋关节的磨擦界面特征[J].中国组织工程研究,2013, 17(17):3184-3191.
[28] 王俏杰,张先龙.人工髋关节置换术的现状与热点[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2015,9(6):718-724.
[29] 汪群,隋福革,李恒,等.陶瓷对陶瓷人工全髋关节置换术治疗股骨头坏死[J].齐齐哈尔医学院学报,2014,35(9):1323.
[30] 吴立忠,詹洋,吴星,等.大直径股骨头陶瓷对陶瓷人工全髋关节置换术125例疗效分析[J].福建医药杂志,2015,37(3):34-37.
[31] 沈阳,黄环宇,万宗文.全陶界面与金属-聚乙烯界面在人工全髋关节置换术后的早期临床效果比较[J].实用临床医药杂志,2018,22(19):39-42.
[32] ESPOSITO CI, GLADNICK BP, LEE YY,et al. Cup position alone does not predict risk of dislocation after hip arthroplasty.J Arthroplasty. 2015;30(1):109-113.
[33] ALJURAYYAN A, TANZER D, TANZER M.Acute revision hip arthroplasty: a previously unrecognized risk factor for heterotopic ossification. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2016;26(2):183-188.
[34] SHAH SM, WALTER WL, TAI SM,et al. Late Dislocations After Total Hip Arthroplasty: Is the Bearing a Factor? J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(9):2852-2856.
[35] 王春成,李明哲.全髋关节置换假体不同角度的生物力学特点[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(11):1652-1657.
[36] 赵以甦. 以电脑三维骨骼肌肉模型作生物力学分析在运动科学及医学上的意义与应用[J].医用生物力学,2008,23(3):177-192.
[37] 王国伟. 三种不同内固定方式作用于髋关节假体周围 B1 型骨折的有限元分析及新型假体周围板的设计与改良[D].济南:山东大学,2016.
[38] WHITE PB, MEFTAH M, RANAWAT AS,et al. A Comparison of Blood Metal Ions in Total Hip Arthroplasty Using Metal and Ceramic Heads. J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(10):2215-2220.
|