[1] VAN OSTBRWYCK H, DUYCK J, VANDER S, et al. The influence of bone mechanical properties and jimplanu fxsaton upon bone loading around oral implants. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1998;9(6):407-412.
[2] GENGJ, TANKB C, LIU G. Application of finite element analysis in implant dentistty: A reriew of xche literature. Prosthet Dent. 2001;85(6):585-598.
[3] GROSS U, STRUNZ V. The interface of various glasses and glass ceramics with a bony implantation bed. Biomed Mater Res. 1985;19(3):251-271.
[4] MARTIN JY, SCHWARTZ Z, HUMMERT TW, et al. Effect of titanium sufface toughness on proliferation differentiation and protein synthesis of human osteoblast-like cells(MG63). Biomed Mater Res. 1995;29(3): 389-401.
[5] MARTIN DC, O’RYAN FS, INDRESANO AT, et al. Characte ristics of implant failures in patients with a history of oralbisphosphonate therapy. Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010;68(3):508-514.
[6] HUISKES R. Validation of adaptive bone-remodeling simulation models. Stud Health Technol Inform. 1997;40:33-48.
[7] HUISKES R, WEINANS H, VAN RIETBERGEN B. The relationship between stress shielding and bone resorption around total hip stems and the effects of flexible materials. Clin Orthop Relat R. 1992;274(274):124-134.
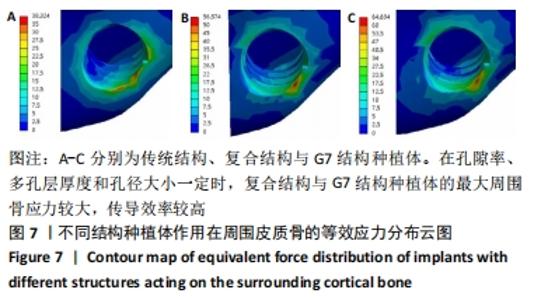
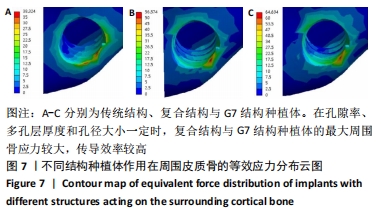
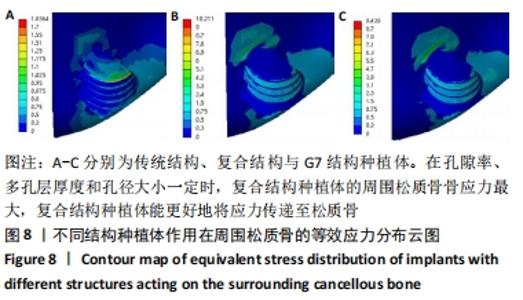
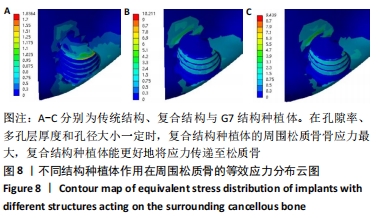
[8] 刘亭松,高荣,魏霆,等.多孔结构钛种植体对周围骨组织应力分布影响的三维有限元分析[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2019,54(1):35-40.
[9] KITAMURA E, STEGAROIU R, NOMURA S, et al. Biomechanical aspects of marginal bone resorption around osseointegrated implants:considerations based on a three-dimensional finite element analysis. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2004;15(4):401-412.
[10] LI SJ, XU QS, WANG Z, et al. Inflfluence of cell shape on mechanical properties of Ti-6Al-4V meshes fabricated by electron beam melting method. Acta Biomater. 2014;10:4537-4547.
[11] WOESZ A, STAMPFLFL J, FRATZL P. Cellular solids beyond the apparent density – an experimental assessment of mechanical properties. Adv Eng Mater. 2004;6(3):134-138.
[12] MEIJER HJ, STARMANS FJ, STEEN WH, et al. Loading conditions of endosseous implants in an edentulous human mandible.A three-dimensional flnite element study. J Oral Rehabil. 1996;23:757-763.
[13] 黄宇文.有限元分析在口腔生物力学中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(13):2423-2426.
[14] 游嘉,方利华,张青,等.基于SLM技术的表面多孔钛金属多根牙种植体的骨结合研究[J].中国生物医学工程学报,2015,34(3):315-322.
[15] 黄美慧,姜闻博,张翁,等.牙种植体表面多孔层厚度对骨界面应力分布的影响[J].口腔材料器械杂志,2016,25(2):61-65.
[16] DEMENKO V, LINETSKIY I, NESVIT K, et al. Ultimate masticatory force as a criterion in implant selection. J Dent Res. 2011;90(10):1211.
[17] 陈霞云,陈松龄,张美超.下颌后牙区不同骨质内种植体即刻负载的三维有限元分析[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2011,46(4):233-236.
[18] PARK CH, LEE CS, KIM YJ, et al. Improved pre-osteoblast response and mechanical compatibility of ultrafine-grained Ti-13Nb-13Zr alloy. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2011;22(7):735-742.
[19] FROST HM. A 2003 update of bone physiology and Wolff’s Law for clinicians. Angle Orthod. 2004;74(1):3-15.
[20] WANG K, LI DH, GUO JF, et al. Effects of buccal bi-cortical anchorages on primary stability of dental implants:a numerical approach of natural frequency analysis. J Oral Rehabil. 2009;36(4):284-291.
[21] BOZKAYA D, MUFTU S, MUFTU A. Evaluation of load transfer characteristics of five different implants in compact bone at different load levels by finite elements analysis. J Prosthet Dent. 2004;92(6): 523-530.
[22] STEIGENGA JT, AL-SHAMMARI KF, NOCITI FH, et al. Dental implant design and itsrelationship to long-term implant success. Implant Dent. 2003;12(4):306-317.
|