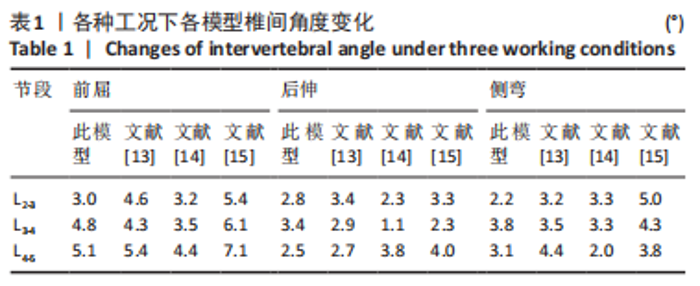
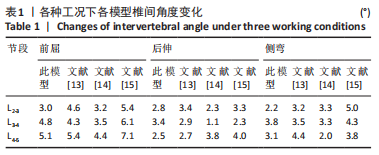
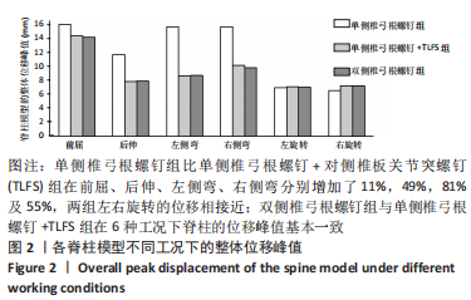
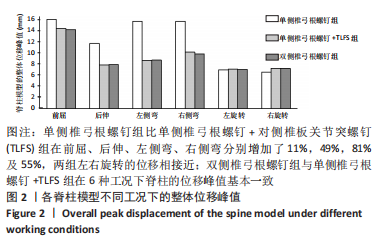
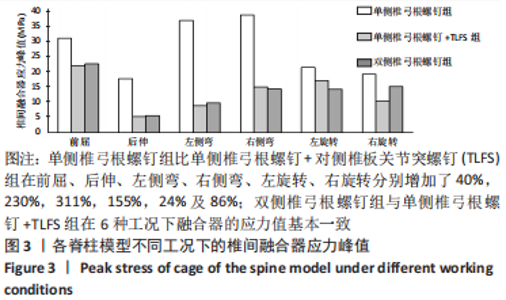
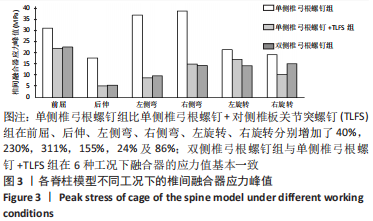
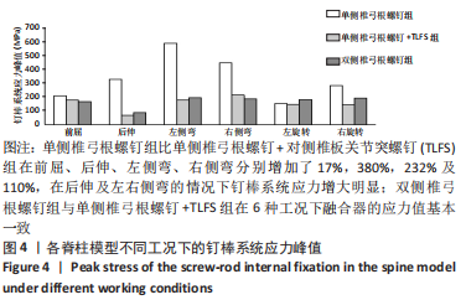
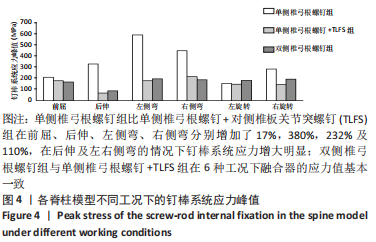
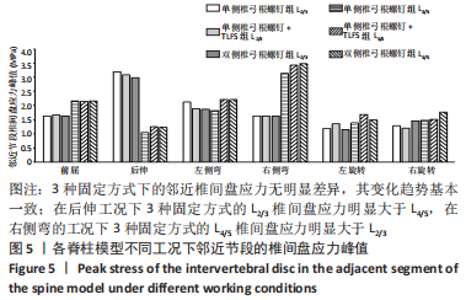
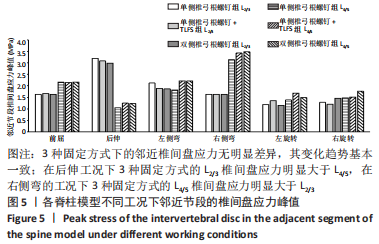
[1] 张骏, 金梦然, 赵廷潇, 等. 经皮脊柱内镜辅助下腰椎椎体间融合术及其临床应用[J].中国骨伤,2019,32(12):1138-1143.
[2] YUAN C, WANG J, ZHOU Y, et al. Endoscopic lumbar discectomy and minimally invasive lumbar interbody fusion: a contrastive review. Wideochir Inne Tech Maloinwazyjne. 2018;13(4):429-434.
[3] DIPAOLA CP, MOLINARI RW. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2008;16(3):130-139.
[4] PARK P, GARTON HJ, GALA VC, et al. Adjacent segment disease after lumbar or lumbosacral fusion: review of the literature. Spine. 2004; 29(17):1938-1944.
[5] CHEN HH, CHEUNG HH, LI KC. Biomechanical Analysis of Unilateral Fixation With Interbody Cages. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30(4):E92-96.
[6] 陈伟, 黄明光, 冯杰荣, 等. UPS固定对TILF术后邻近节段生物力学影响的有限元分析[J]. 中南医学科学杂志,2019,47(4):341-345.
[7] FERNÁNDEZ-FAIREN M, SALA P, RAMÍREZ H, et al. A prospective randomized study of unilateral versus bilateral instrumented posterolateral lumbar fusion in degenerative spondylolisthesis. Spine. 2007;32(4):395-401.
[8] 周跃, 王健, 初同伟, 等. 内窥镜下经X-Tube单侧和双侧腰椎椎弓根螺钉固定的疗效评价[J]. 中华创伤杂志,2007,23(9):654-658.
[9] 董健文, 邱奕雁, 赵卫东, 等. 单侧椎弓根钉棒固定单节段腰椎及其邻近节段生物力学研究 [J]. 中国临床解剖学杂志,2010,28(1):85-89.
[10] 侯继春, 何人可, 曹杨. 单侧椎弓根螺钉固定系统在腰椎退行性疾病治疗中的研究进展[J]. 中国骨与关节外科,2020,13(1):67-72.
[11] 马亮, 许永涛, 佘远举. 腰椎融合联合上一节段棘突间动态固定的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2018,22(23):3647-3653.
[12] 闫家智, 吴志宏, 徐日新, 等. 腰椎后路单节段椎弓根螺钉内固定的三维有限元分析[J]. 中华医学杂志,2009,89(1):7-11.
[13] SHIM CS, PARK SW, LEE SH, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of an interspinous stabilizing device, Locker. Spine. 2008;33(22):E820.
[14] SHIRAZI-ADL SA, SHRIVASTAVA SC, AHMED AM. Stress analysis of the lumbar disc-body unit in compression. A three-dimensional nonlinear finite element study. Spine. 1984;9(2):120-134.
[15] YAMAMOTO I, PANJABI MM, CRISCO T, et al. Three-dimensional movements of the whole lumbar spine and lumbosacral joint. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1989;14(11):1256-1260.
[16] OSMAN SG. Endoscopic transforaminal decompression, interbody fusion, and percutaneous pedicle screw implantation of the lumbar spine: A case series report. Int J Spine Surg. 2012;6(1):157-166.
[17] MAGERL FP. Stabilization of the lower thoracic and lumbar spine with external skeletal fixation. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1984;(189):125-41.
[18] GROB D, HUMKE T. Translaminar screw fixation in the lumbar spine: technique, indications, results. Eur Spine J. 1998;7(3):178-186.
[19] 毛克亚, 王岩, 肖嵩华, 等. 单侧微创经椎间孔腰椎体间融合术采用椎弓根螺钉结合经椎板关节突螺钉混合内固定可行性研究[J]. 中华外科杂志,2011,49(12):1067-1070.
[20] 曾忠友, 张建乔, 严卫锋, 等. 单节段腰椎病变通道下肌间隙入路三种固定方式的对比研究 [J]. 中华骨科杂志,2017,37(8):480-491.
[21] HUANG P, WANG Y, XU J, et al. Minimally invasive unilateral pedicle screws and a translaminar facet screw fixation and interbody fusion for treatment of single-segment lower lumbar vertebral disease: surgical technique and preliminary clinical results. J Orthop Surg Res. 2017;12(1):117.
[22] 孙凤龙, 梁庆晨, 王宏庆, 等. 脊柱内镜下经椎间孔腰椎椎间融合术治疗腰椎间盘突出症伴腰椎不稳的早期临床研究[J]. 中华骨与关节外科杂志,2019,12(10):754-760.
[23] DEGUCHI M. Biomechanical evaluation of translaminar facet joint fixation. A comparative study of poly-L-lactide pins, screws, and pedicle fixation. Spine. 1998;23(12):1307-1312; discussion 1313.
[24] 薛剑, 靳安民, 孙小平, 等. 单侧腰椎弓根螺钉及经椎板关节突螺钉固定与双侧固定的比较[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2013,17(9): 1571-1578.
|