Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (3): 456-460.doi: 10.12307/2022.075
Previous Articles Next Articles
Pathogenesis of femoral head necrosis after internal fixation of femoral neck fractures in young adults
Liang Haoran, Zhou Xin, Yang Yanfei, Niu Wenjie, Song Wenjie, Ren Zhiyuan, Wang Xueding, Liu Yang, Duan Wangping
- Department of Orthopedics, Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Key Laboratory of Bone and Soft Tissue Injury Repair, Taiyuan 030000, Shanxi Province, China
-
Received:2021-03-04Revised:2021-03-06Accepted:2021-05-07Online:2022-01-28Published:2021-10-29 -
Contact:Duan Wangping, MD, Associate professor, Master’s supervisor, Department of Orthopedics, Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Key Laboratory of Bone and Soft Tissue Injury Repair, Taiyuan 030000, Shanxi Province, China -
About author:Liang Haoran, Master candidate, Department of Orthopedics, Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Key Laboratory of Bone and Soft Tissue Injury Repair, Taiyuan 030000, Shanxi Province, China -
Supported by:Key Research & Development Program of Shanxi Province, No. 201903D421019 (to DWP)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liang Haoran, Zhou Xin, Yang Yanfei, Niu Wenjie, Song Wenjie, Ren Zhiyuan, Wang Xueding, Liu Yang, Duan Wangping. Pathogenesis of femoral head necrosis after internal fixation of femoral neck fractures in young adults[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 456-460.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
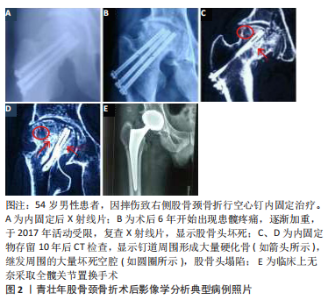
2.1 股骨颈骨折对股骨头血供的影响 股骨颈骨折的治疗应尽早保证股骨头血供的恢复,强调早期手术和解剖复位。但青壮年股骨颈骨折多由高能量的损伤引起,骨折多为移位或粉碎性骨折,骨折移位破坏了股骨颈的关节囊外基底动脉 环[11],经内固定治疗后虽达到了解剖复位,但致使股骨头的主要血供受损,造成了股骨头发生缺血坏死[12]。ZHAO等[13]的研究表明,股骨头从上、前、下支持动脉和圆韧带动脉接收其主要血液供应,3个支持动脉组(上、下和前组)的分支在进入股骨后构成骨骺和干骺端动脉分支的主干,并在骨骺上方形成骨骺动脉网和骨骺下方的干骺端动脉网,圆韧带动脉组的动脉丛通过中央凹进入股骨头,然后加入骨骺动脉网结构,因此骨骺动脉网结构是股骨头中分布最广、最主要的网结构;骺动脉网和下支持动脉系统是股骨颈骨折后维持股骨头血供的2个重要结构;在骨内血管系统中,股骨头周围的骨骺动脉主干的吻合比位于中心区域的少,该研究证实,通用的股骨头外周区域倒金字塔方式在距软骨下骨5 mm处置钉,有很大的风险损伤上、下、前骺主干动脉,对骨折后股骨头的主要血供骺动脉网造成二次医源性损伤。因此股骨颈骨折内固定治疗,不仅要达到解剖复位,内固定物还应尽可能靠近股骨头中部,以减少骨内血管系统的破坏。但多螺钉的置入致使股骨头骨内血供的受损不可避免,极大可能造成股骨头发生缺血坏死。作者认为早期手术及解剖复位,及时挽回股骨头囊外血供,多微孔、高机械强度和与骨修复相容的新型材料与技术的研发应得到开展,或者采用高机械强度及良好组织相容性的单金属螺钉中心固定方式用以解决股骨颈骨折术后骨内血供的破坏。 2.2 股骨颈骨折后股骨头坏死的生物力学因素 2.2.1 骨折后骨小梁重建与生物力学的关系 Wolff 定律为生物力学的基本理论,认为长期的外部应力刺激会造成骨骺内外部结构发生改变,以适应外界的刺激。机械载荷对骨小梁连续重塑的动态过程进行双重调控。在股骨颈骨折愈合的早期,适量的机械载荷有利于促进骨小梁的生长,并逐渐趋于平衡保持一定的性能[14];但当机械载荷超过骨小梁所能承受的临界点就会造成骨小梁的变形与断裂,最终会导致骨小梁坏死塌陷,导致股骨头坏死的发生[15]。 2.2.2 内置物存留及取出股骨头颈的生物力学 临床上青壮年股骨颈骨折患者,主要采用闭合复位空心螺钉内固定手术治疗[4]。随着内固定技术的发展,股骨颈骨折内固定后骨折愈合率有了明显的提高,可达90%以上,极大改善了患者预后。但是,股骨颈骨折术后股骨头坏死率迄今仍无明显的下降趋势[16],对青壮年股骨颈骨折患者,空心钉内固定后内植物长期存留与股骨头坏死的关系、内植物是否应该取出,以及合理的内植物取出方式与时机等,尚存在争议。 股骨颈是连接股骨头与股骨干之间的重要桥梁。在股骨颈与股骨干之间形成了2个重要的角度:颈干角与前倾角。由于颈干角与前倾角的存在使股骨颈内侧产生应压力、外侧产生张应力,同时还承受一定的剪切力。LAMBERS等[14]研究表明在股骨颈骨折置入内固定物,股骨头处于各种生物力学环境时,股骨头颈所承受的压应力、张应力及剪切力主要由内固定物承担,骨小梁处于恢复阶段。当内固定物取出后,所有的张应力、压应力和剪切力都作用于原骨折部位,股骨颈不能完全承受全部受力,导致其生物应力及承载功能发生紊乱,产生大体不可见的的形态学改变,导致骨小梁的调整,很容易导致股骨颈的微骨折甚至再骨折[17]。同时,由于内固定物取出对股骨头周围血运的破坏,引起股骨头局部缺血,进而影响骨小梁的重建,致使股骨头形态学发生改变,当骨小梁的调整不适应髋臼对股骨头的应力需要时,就会发生变性、吸收、塌陷,最终导致股骨头坏死。 内固定物不取出时,由于各种生物应力主要集中作用于内固定材料上,应力负载的增加会导致骨量和显微结构的变化,使骨的体积分数、骨小梁数量、骨小梁直径增大,而对杆状小梁的显微结构没有显著影响[18]。由于各种生物应力的作用,内固定周围会出现大量硬化骨,见图2。而正常股骨头主要由海绵质骨小粱组成,具有一定弹性[19]。有研究表明,股骨颈骨折术后骨小梁受外部应力的影响重新排列,以适应股骨头所处的各种生物应力环境;同时,应力传递的方向决定着重建骨小梁的排列方向[18]。但内固定置入后破坏了股骨头的力学及弹性结构,在步行周期中压力值总是在变化,伴随着长期周期性高负荷应力作用,致使骨小梁发生形变、断裂以便获得最大接触面积,降低单位面积的负荷,但骨小梁形变与断裂超过临界点可导致微细骨折和骨小梁僵硬[20]。伴随长期周期性极限应力作用于股骨头,致使钉道周围的松质骨骨小梁坏死塌陷,形成硬化骨,内固定物及其周围形成的硬化骨进而破坏了股骨头正常的弹性功能,致使股骨头长期在应力作用下发生骨小梁结构的破坏,硬化骨及废用性骨量的增多,预示着股骨头坏死的不可逆性发展[21]。由此可见,内固定取出与否对股骨头坏死的进展均没有积极作用。"
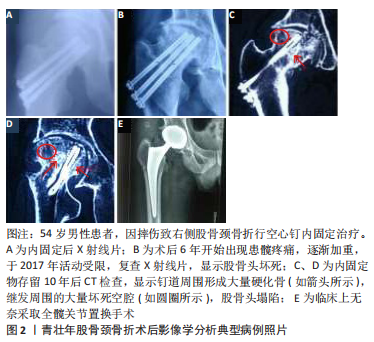
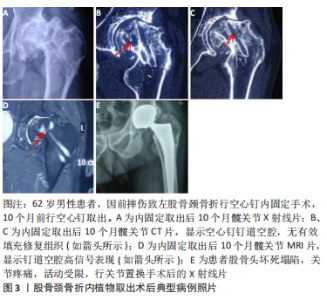
2.2.3 骨折模型中倒三角结构与其他结构的力学 目前,对于治疗青壮年股骨颈骨折内置物包括空心螺钉、动力髋螺钉、髓内钉、锁定钢板等,然而目前对于青壮年股骨颈骨折治疗时内置物的选取及构型仍存在争议。大多数对内置物的研究多集中在内置物的稳定性及强度等的研究,而忽略了内置物置入后对股骨头整体力学结构的影响。 LI等[22]通过有限元分析不同构型(三角形、倒三角形、前三角形、后三角形和垂直模型)空心加压螺钉固定Pauwels Ⅲ型股骨颈骨折的力学结果显示,倒三角形螺钉比其他结构承受更大的应力,倒三角模型每个螺钉都分散了一些应力,但至少有一个螺钉承受了峰值应力,且倒三角形结构的螺钉在增加载荷下承受最高的应力值;但与其他结构相比,倒三角形骨结构表现出最小的屈服应变。li等[23]评估了单独置入部分螺纹螺钉或由部分螺纹螺钉和全螺纹螺钉组成的组合螺钉,在治疗不稳定股骨颈骨折中形成的不同构型的力学结果显示,每组中的全螺纹螺钉承受的压力最大,而部分螺纹螺钉承受的压力较小。因此,认为虽然倒三角结构为股骨颈骨折提供了较高的稳定性,但螺钉所承受的应力载荷比其他结构的较大,容易导致应力集中,虽然采用螺纹螺钉降低了螺钉周围的应力,但螺纹结构对股骨头内部骨骺动脉的破坏更大,易导致股骨头坏死的发生。 BLIVEN等[24]应用动态循环压缩实验比较3个倒三角形空心螺钉、一个滑动髋骨螺钉和防旋转螺钉,或者一个带弹簧伸缩螺钉的锁定板系统在Pauwels Ⅲ型股骨颈骨折中的力学分布显示,使用加压螺纹钉系统提供了与当前金标准方法(空心螺钉)相似或更好的生物力学性能。li 等[25]设计了一种结合了股骨髁螺钉和滑动髋螺钉强度的钢板,进行有限元分析比较该钢板与动力髋螺钉+去旋转螺钉的组合和单独使用空心螺钉在股骨颈骨折中的力学分布,结果表明在股骨的应力分布、应力峰值和旋转角度方面,钢板能产生更稳定的固定,钢板可能保持空心螺钉和动力髋螺钉+去旋转螺钉的强度,并在抗剪切力和旋转力方面表现出更好的性能,在最小位移和旋转角度方面获得最佳的稳定性。 由此可知,加压螺钉或强度更佳的钢板系统都可提供与空心螺钉相似或者更好地生物力学性能。在加压螺钉系统中施加3 000 N的应力,螺钉仍能提供稳定的力学稳定性,但螺钉承受的最大应力也比空心螺钉大,长期处于高应力环境中易导致内置物周围形成硬化骨,而最终导致股骨头坏死的发生。LINDE等[26]通过闪烁扫描法研究不同内固定手术前后股骨头的血供,发现动力髋螺钉固定后对血供的破坏可达35%。因此可见,动力髋螺钉对延缓骨折后股骨头坏死的发生没有积极作用。 2.2.4 新型内置物的发展及优势 SHEN等[27]在动物模型中比较空心骨移植动力髋螺钉和标准动力髋螺钉治疗股骨颈骨折的骨愈合情况,表明空心骨移植动力髋螺装置可促进股骨颈骨折愈合、刺激骨小梁形成、增加骨密度,在股骨颈骨折内固定方面比标准动力髋螺钉有优势。HUANG等[28]研究发现,一种新型的可生物降解高纯度镁承重螺钉具有足够的机械强度和与骨修复相容的降解速率;此外,在股骨头和股骨颈骨组织和血液供应的降解过程和重建过程中实现了良好的骨形成。由此可见,新型内置物不仅考虑了内置物的强度及稳定性,更加注重对股骨头骨内血供的恢复,以刺激骨小梁的形成。 2.2.5 针对内置物周围应力集中及硬化骨形成的设想 作者的前期临床研究发现,股骨颈骨折术后内置物长期存留,CT或核磁等影像学检查可发现钉道周围可形成明显硬化带,且长期存留内置物取出后,在长达1年左右时间股骨头钉道内无明显再生组织填充,见图3。 而且在步行周期中压力值总是在变化[29],因此无论采取何种结构,内置物螺纹的选择和内置物置入时是否加压,在应力负载的长期作用下都不可避免地导致内置物周围形成硬化骨,从而导致股骨头坏死的发生。针对这种现象,作者认为在内固定周围形成硬化骨之前,适时的取钉并置入一种新型高强度、可降解、多微孔结构及又可促进成骨血管化的内置物,用以抑制硬化骨的形成,从而可终止股骨头坏死的发生;或者可研发设计一种与股骨骨组织强度等生物学功能相仿的生物骨,用以股骨颈骨折的治疗,从而避免内置物周围的应力集中,用以消除股骨头坏死的发生。 2.3 股骨颈骨折内固定术后股骨头坏死的分子生物学 2.3.1 miRNAs与股骨头坏死的关系 miRNAs是真核生物体内是一类内生的、具有调控作用的、长度为20-24个核苷酸的小RNA,其在细胞的生长发育过程中具有多种重要调节作用[30-31]。大量研究表明,血液中miRNA表达的变化与疾病的发生发展有着密切关系[32-33]。由于临床上血液样品易于获取且稳定不易降解,使得miRNA成为众多疾病研究、药物毒性、机体损伤研究筛选生物标记的重要对象[34-35]。近几十年来,许多微小核糖核酸在人类疾病中得到证实和表征,有许多研究证明miRNA与非创伤股骨头坏死的发展有关,如miR-708和miR-27a[36-37]。作为微小核糖核酸之一,miR-26a与多种人类疾病有关,如骨肉瘤[38-39]、骨创伤和骨转移[40-41]。张颖等[42]的研究表明,hsa-miR-93-5p、hsa-let-7i-5p、hsa-miR-320a、hsa-miR-25-3p等特异性miRNA为创伤性股骨头坏死特异表达的miRNA,为创伤性股骨头坏死的发病机制提供了数据保障。HAN等[43]通过对比股骨头坏死组和对照组之间的miRNA发现,lncRNA H19- hsa-miR-519b-3p / hsa-miR-296-5p-ANKH和lncRNA c9orf163- hsa-miR-424-5p-CCNT1的ceRNA可能在股骨头坏死的发展中发挥重要作用。 2.3.2 动静脉瘘与股骨头坏死的关系 NAIK等[44]的研究表明,临床上动静脉瘘与股骨头软骨下骨的血管供应减少有关,这会导致关节面坏死和塌陷,最终导致髋关节的退化。动静脉内瘘的次要原因包括血红蛋白病、储存障碍、系统性红斑狼疮、减压病等。酒精、类固醇、创伤、凝血病,许多其他因素,如遗传因素、环境因素、怀孕等生理过程、吸烟、药物滥用等生活方式、血色病等疾病也是动静脉内瘘的危险因素。研究分析表明,高半胱氨酸、缺氧、凝血、破骨细胞分化和软骨内骨化是与疾病相关的主要途径。 2.3.3 不同基因与股骨头坏死的关系 HUANG等[45]的研究表明,碱性成纤维生长因子2和FAM201A与股骨头坏死的发生有关。此外,胰岛素样生长因子、SOX9和Ⅱ型胶原纤维α1基因也可能影响股骨头坏死的发病机制。LEE等[46]的研究表明,mtDNA-CN(线粒体DNA)可能是预测股骨头坏死临床特征的重要标志。mtDNA-CN与年龄呈正相关,与红细胞沉降率呈负相关。 长的非编码RNA(lncRNA)对于多种疾病的发生和发展至关重要。尽管lncRNAs参与干细胞的生物学活性并在干细胞分化中起关键作用,但是在人骨髓源性间充质干细胞成骨分化中,股骨头坏死及其过程中特定lncRNA的表达监管作用尚未完全阐明。LI等[47]研究发现,lncRNA与脂肪酸代谢、细胞凋亡和转化生长因子β信号通路密切相关,MAPT反义RNA 1(MAPTAS1)的过度表达可在细胞和mRNA水平上促进成骨并抑制人骨髓源性间充质干细胞的脂肪形成。 "
| [1] BRODERICK JM, BRUCE-BRAND R, STANLEY E, et al. Osteoporotic hip fractures:the burden of fifixation failure. Sci World J. 2013;2013:515197 [2] TIAN FM, ZHANG L, ZHAO HY, et al. An increase in the incidence of hip fractures in Tangshan,China. Osteoporos Int. 2014;25:1321-1325. [3] 中华医学会骨科学分会创伤骨科学组,中国医师协会骨科医师分会创伤专家工作委员会.成人股骨颈骨折诊治指南[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2018,20(11):921-928. [4] 徐凯航,纪方.青壮年股骨颈骨折的治疗进展[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2020,22(6):549-552. [5] SLOBOGEAN GP, SPRAGUE SA, SCOTT T, et al. Complications following young femoral neck fractures. Injury. 2015;46(3):484-491. [6] STOCKTON DJ, O’HARA LM, O’HARA NN, et al. High rate of reoperation and conversion to total hip arthroplasty after internal fixation of young femoral neck fractures: a population-based study of 796 patients. Acta Orthop. 2019;90(1):21-25. [7] PATTERSON JT, ISHII K, TORNETTA P 3RD, et al. Open reduction is associated with greater hazard of early reoperation after internal fixation of displaced femoral neck fractures in adults 18-65 Years. J Orthop Trauma. 2020;34(6):294-301. [8] SLOBOGEAN GP, STOCKTON DJ, ZENG B. Femoral neck fractures in adults treated with internal fixation:a prospective multicenter Chinese cohort. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2017;25:297-303. [9] SHAH SN, KAPOOR CS, JHAVERI MR, et al. Analysis of outcome of avascular necrosis of femoral head treated by core decompression and bone grafting. Clin Orthop Trauma. 2015;6(3):160-166. [10] LI MN, COLE PA. Anatomical considerations in adult femoral neck fractures:how anatomy influences the treatment issues. Injury. 2015; 46:453-458. [11] LARGE TM, ADAMS MR, LOEFFLER BJ, et al. Posttraumatic Avascular Necrosis After Proximal Femur, Proximal Humerus,Talar Neck,and Scaphoid Fractures. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2019;27(21):794-805. [12] PAPAPIETRO N, DIMARTINO A, NICCOLI G, et al. Trabecular metal screw implanted for avascular necrosis of the femoral head may complicate subsequent arthroplasty surgery. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2014; 24(6):931-938. [13] ZHAO D, QIU X, WANG B, et al. Epiphyseal Arterial Network and Inferior Retinacular Artery Seem Critical to Femoral Head Perfusion in Adults With Femoral Neck Fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2017;475(8): 2011-2023. [14] LAMBERS FM, KOCH K, KUHN G, et al. Trabecular bone adapts to long-term cyclic loading by increasing stiffness and normalization of dynamic morphometric rates. Bone. 2013;55(2):325-334. [15] ZWAHLEN A, CHRISTEN D, RUFFONI D, et al. Image -guided failure as-sessment of human trabecular bone - inverse finite element mod-elling for characterization of elastic properties. Biomed Tech (Berl). 2013;Suppl 1:/j/bmte.2013.58.issue-s1-D/bmt-2013-4114/bmt-2013-4114.xml. [16] DUFFIN M, PILSON HT. Technologies for Young Femoral Neck Fracture Fixation. J Orthop Trauma. 2019;33Suppl1:S20-S26. [17] SHAH SN, KAPOOR CS, JHAVERI MR, et al. Analysis of outcome of avascular necrosis of femoral head treated by core decompression and bone grafting. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2015;6(3):160-166. [18] WANG H, JI B, LIU XS, et al. Analysis of microstructural and me-chanical alterations of trabecular bone in a simulated three-dimen-sional remodeling process. J Biomech. 2012;45(14):2417-2425. [19] GODA I, ASSIDI M, GANGHOFFER JF. Cosserat 3D anisotropic models of trabecular bone from the homogenisation of the trabecular structure. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2012;15(1):288-290. [20] MARTELLI S, PERILLI E. Time-elapsed synchrotron-light microstructural imaging of femoral neck fracture. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2018; 84:265-272. [21] TING BL, HENG M, VRAHAS MS, et al. Is disuse osteopenia a favorable prognostic sign after femoral neck fracture? J Orthop Trauma. 2016; 30(9):496-502. [22] LI J, WANG M, ZHOU J, et al. Optimum Configuration of Cannulated Compression Screws for the Fixation of Unstable Femoral Neck Fractures: Finite Element Analysis Evaluation. Biomed Res Int. 2018; 2018:1271762. [23] LI J, WANG M, ZHOU J, et al. Finite element analysis of different screw constructs in the treatment of unstable femoral neck fractures. Injury. 2020;51(4):995-1003. [24] BLIVEN E, SANDRIESSER S, AUGAT P, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of locked plating fixation for unstable femoral neck fractures. Bone Joint Res. 2020;9(6):314-321. [25] LI J, ZHAO Z, YIN P, et al. Comparison of three different internal fixation implants in treatment of femoral neck fracture-a finite element analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;12;14(1):76. [26] LINDE F, ANDERSEN E, HVASS I, et al. Avascular femoral head necrosis following fracture fixation. injury. 1986;17(3):159-164. [27] SHEN JZ, YAO JF, LIN DS, et al. Hollow-bone-graft dynamic hip screw can fix and promote bone union after femoral neck fracture: an experimental research. Int J Med Sci. 2012;9(10):916-22. [28] HUANG S, WANG B, ZHANG X, et al. High-purity weight-bearing magnesium screw: Translational application in the healing of femoral neck fracture. Biomaterials. 2020;238:119829. [29] NODA M, NAKAMURA Y, ADACHI K, et al. Dynamic finite element analysis of implants for femoral neck fractures simulating walking. J Orthop Surg(Hong Kong). 2018;26(2):2309499018777899. [30] WU F, HUANG W, YANG Y, et al. miR-155-5p regulates mesenchymal stem cell osteogenesis and proliferation by targeting GSK3B in steroid-associated osteonecrosis. Cell Biol Int. 2021;45(1):83-91. [31] CHEN N, XIAO B, WANG S. Bioinformatics analysis of microRNA linked to ubiquitin proteasome system in traumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Medicine. 2020;99(33):e21706. [32] HENN D, ABU-HALIMA M, KAHRAMAN M, et al. A multivariable miRNA signature delineates the systemic hemodynamic impact of arteriovenous shunt placement in a pilot study. Sci Rep.2020;10(1):21809. [33] CUI S, ZHOU Z, LIU X, et al. Identification and Characterization of Serum microRNAs as Biomarkers for Human Disc Degeneration: An RNA Sequencing Analysis. Diagnostics (Basel). 2020;10(12):E1063. [34] MEYER A, HERKT S, KUNZE-SCHUMACHER H, et al. The transcription factor TAL1 and miR-17-92 create a regulatory loop in hematopoiesis. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):21438. [35] UMEZU T, TSUNEYAMA K, KANEKURA K, et al. Comprehensive analysis of liver and blood miRNA in precancerous conditions. Sci Rep. 2020; 10(1):21766. [36] HAO C, YANG S, XU W, et al. MiR-708 promotes steroid-induced osteonecrosis of femoral head, sup-presses osteogenic differentiation by targeting SMAD3. Sci Rep. 2016;6:22599. [37] GU C, XU Y, ZHANG S, et al. miR-27a attenuates adipo-genesis and promotes osteogenesis in steroid-induced rat BMSCs by targeting PPARgamma and GREM1. Sci Rep. 2016;6:38491. [38] WANG Z, WANG Z, LIU J, et al. Long non-coding RNA SNHG5 sponges miR-26a to promote the tumorigen-esis of osteosarcoma by targeting ROCK1. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;107:598-605. [39] LIU J, MI B, WANG Y, et al. miR-26a suppresses osteo-sarcoma migration and invasion by directly targeting HMGA1. Oncol Lett. 2018;15(6): 8303-8310. [40] LI Z, NI J. Role of microRNA-26a in the diagnosis of lower extremity deep vein thrombosis in patients with bone trauma. Exp Ther Med. 2017;14(5):5069-5074. [41] ZHAO Z, DAI XS, WANG ZY, et al. MicroRNA-26a reduces synovial inflammation and cartilage injury in osteoarthritis of knee joints through impairing the NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Biosci Rep. 2019; 39:4. [42] 张颖,张蕾蕾,柴玉娜,等.创伤性股骨头坏死中差异miRNA的筛选与验证[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2017,19(11):978-985. [43] HAN N, LI Z. Non-coding RNA Identification in Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head Using Competitive Endogenous RNA Network Analysis. Orthop Surg. 2021;21. doi: 10.1111/os.12834. [44] NAIK AA, NARAYANAN A, KHANCHANDANI P, et al. Systems analysis of avascular necrosis of femoral head using integrative data analysis and literature mining delineates pathways associated with disease. Sci Rep. 2020;22;10(1):18099. [45] HUANG G, ZHAO G, XIA J, et al. FGF2 and FAM201A affect the development of osteonecrosis of the femoral head after femoral neck fracture. Gene. 2018;652:39-47. [46] LEE SW, LEE KJ, KIM BS, et al. Clinical Characteristics of Mitochondrial DNA Copy Number in Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head. Medicina (Kaunas). 2020;56(5):239. [47] LI T, XIAO K, XU Y, et al. Identification of long non coding RNAs expressed during the osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells obtained from patients with ONFH. Int J Mol Med. 2020;46(5):1721-1732. [48] 刘光波,梅玉倩,马海洋,等.股骨头坏死骨吸收区对股骨头内应力分布及疾病进展的影响[J].中华骨科志,2020,40(7):408-416. |
| [1] | Xu Xinzhong, Wu Zhonghan, Yu Shuisheng, Zhao Yao, Xu Chungui, Zhang Xin, Zheng Meige, Jing Juehua. Biomechanical analysis of different ways of inserting Steinmann Pins into the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1313-1317. |
| [2] | Zhuang Zhikun, Wu Rongkai, Lin Hanghui, Gong Zhibing, Zhang Qianjin, Wei Qiushi, Zhang Qingwen, Wu Zhaoke. Application of stable and enhanced lined hip joint system in total hip arthroplasty in elderly patients with femoral neck fractures complicated with hemiplegia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1429-1433. |
| [3] | Zhu Chan, Han Xuke, Yao Chengjiao, Zhou Qian, Zhang Qiang, Chen Qiu. Human salivary components and osteoporosis/osteopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1439-1444. |
| [4] | Jin Tao, Liu Lin, Zhu Xiaoyan, Shi Yucong, Niu Jianxiong, Zhang Tongtong, Wu Shujin, Yang Qingshan. Osteoarthritis and mitochondrial abnormalities [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1452-1458. |
| [5] | Zhang Lichuang, Xu Hao, Ma Yinghui, Xiong Mengting, Han Haihui, Bao Jiamin, Zhai Weitao, Liang Qianqian. Mechanism and prospects of regulating lymphatic reflux function in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1459-1466. |
| [6] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [7] | Zhu Chan, Han Xuke, Yao Chengjiao, Zhang Qiang, Liu Jing, Shao Ming. Acupuncture for Parkinson’s disease: an insight into the action mechanism in animal experiments [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1272-1277. |
| [8] | Wang Xinmin, Liu Fei, Xu Jie, Bai Yuxi, Lü Jian. Core decompression combined with dental pulp stem cells in the treatment of steroid-associated femoral head necrosis in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1074-1079. |
| [9] | Guo Jia, Ding Qionghua, Liu Ze, Lü Siyi, Zhou Quancheng, Gao Yuhua, Bai Chunyu. Biological characteristics and immunoregulation of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1093-1101. |
| [10] | Wu Weiyue, Guo Xiaodong, Bao Chongyun. Application of engineered exosomes in bone repair and regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1102-1106. |
| [11] | Zhou Hongqin, Wu Dandan, Yang Kun, Liu Qi. Exosomes that deliver specific miRNAs can regulate osteogenesis and promote angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1107-1112. |
| [12] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [13] | Huang Chenwei, Fei Yankang, Zhu Mengmei, Li Penghao, Yu Bing. Important role of glutathione in stemness and regulation of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1119-1124. |
| [14] | Hui Xiaoshan, Bai Jing, Zhou Siyuan, Wang Jie, Zhang Jinsheng, He Qingyong, Meng Peipei. Theoretical mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine theory on stem cell induced differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1125-1129. |
| [15] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||