Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (6): 862-867.doi: 10.12307/2023.909
Previous Articles Next Articles
Finite element analysis of osteoporosis in proximal femur after cannulated screw fixation for femoral neck fracture
Xue Xiaofeng1, Wei Yongkang2, Qiao Xiaohong1, Du Yuyong1, Niu Jianjun1, Ren Lixin1, Yang Huifeng1, Zhang Zhimin1, Guo Yuan2, Chen Weiyi2
- 1Lvliang People’s Hospital, Lvliang 033000, Shanxi Province, China; 2College of Biomedical Engineering, Taiyuan University of Technology, Taiyuan 030000, Shanxi Province, China
-
Received:2022-11-23Accepted:2023-01-29Online:2024-02-28Published:2023-07-11 -
Contact:Qiao Xiaohong, MD, Chief physician, Lvliang People’s Hospital, Lvliang 033000, Shanxi Province, China -
About author:Xue Xiaofeng, Master, Associate chief physician, Lvliang People’s Hospital, Lvliang 033000, Shanxi Province, China Wei Yongkang, Master candidate, College of Biomedical Engineering, Taiyuan University of Technology, Taiyuan 030000, Shanxi Province, China -
Supported by:a grant from Shanxi Provincial Department of Science and Technology, No. 201903D321150 (to QXH)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xue Xiaofeng, Wei Yongkang, Qiao Xiaohong, Du Yuyong, Niu Jianjun, Ren Lixin, Yang Huifeng, Zhang Zhimin, Guo Yuan, Chen Weiyi. Finite element analysis of osteoporosis in proximal femur after cannulated screw fixation for femoral neck fracture[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 862-867.
share this article
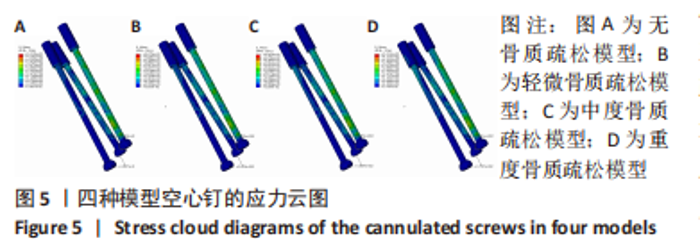
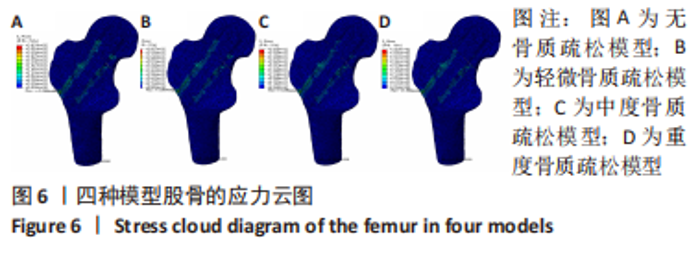
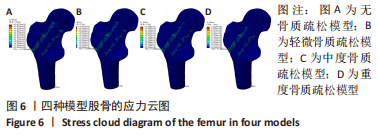
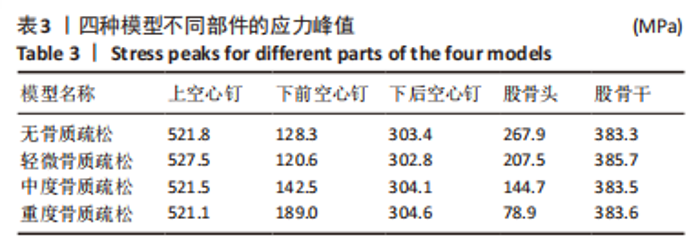
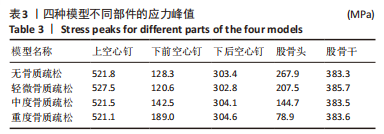
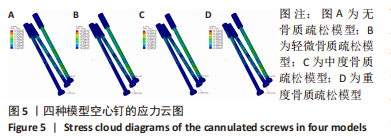
2.2 不同模型计算结果的对比分析 4种不同模型的有限元计算结果(1种股骨颈骨折空心钉内固定术后股骨近端无骨质疏松模型、3种股骨颈骨折空心钉内固定术后股骨近端骨质疏松模型),其应力都主要分布在空心钉附近,当不同刚度的材料共同承担外部载荷时,刚度大的材料将会承载较高的载荷,刚度低的材料承担较小的载荷,该应力结果符合应力遮挡效应。 股骨近端无骨质疏松模型与骨质疏松模型的等效应力分析:随着股骨近端骨质疏松程度不断加重,其股骨头上所承担的载荷越来越小,应力峰值从267.9 MPa降低到78.9 MPa。而相对于下前空心钉,当股骨近端发生轻微骨质疏松时,其应力峰值相对股骨近端无骨质疏松模型略微减小,随着股骨近端骨质疏松程度不断加重,其等效应力峰值发生较大的增高,从120.6 MPa增高到189.0 MPa,而4种有限元模型的其他部件:上空心钉、下后空心钉、股骨干的应力峰值变化不太明显。4种模型的应力云图,见图5和图6,不同部件的应力峰值见表3。"
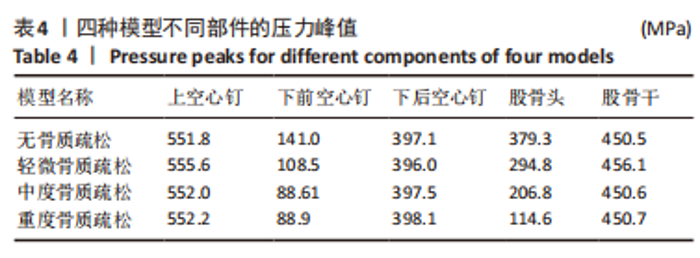
股骨近端无骨质疏松模型与骨质疏松模型的接触压力分析:随着股骨近端骨质疏松程度不断加重,其股骨头及下前空心钉上的接触压力峰值越来越小,股骨头接触压力峰值从379.3 MPa降低至114.6 MPa,下前空心钉接触压力峰值从141.0 MPa降低至88.9 MPa。4种有限元模型的其他部件:上空心钉、下后空心钉、股骨干接触压力峰值仅有细微的变化,见表4。随着股骨近端骨质疏松程度的不断加重,其最大位移也在不断增大。股骨颈骨折空心钉内固定术后股骨近端无骨质疏松模型与轻微骨质疏松、中度骨质疏松、重度骨质疏松模型的最大位移发生在股骨头处,分别为0.80,0.81,0.83,0.88 mm。3枚空心钉的最大位移也略有增长,而股骨干的位移基本没有变化。利用单因素方差分析法对数据进行处理分析,在显著性水平α=0.05条件下,骨质疏松程度对不同部件的应力、接触压力、位移峰值无显著性影响,其F值分别为F=0.03,F=0.12,F=0.14均小于F0.05(3,16)=3.24。"

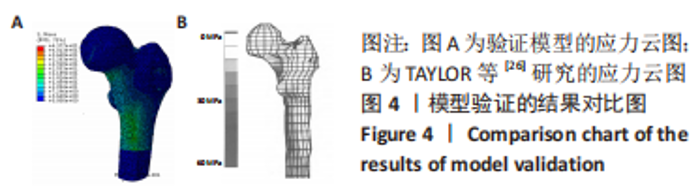
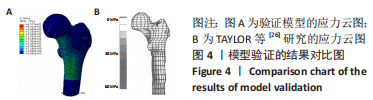
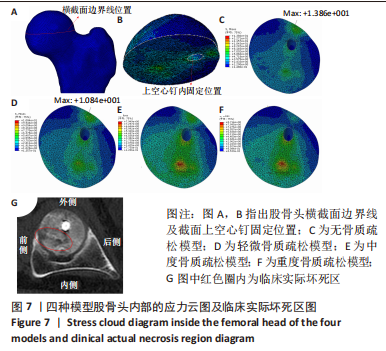
该研究还重点分析了股骨头内部的应力分布情况,探究了股骨近端生物力学环境变化对股骨头坏死的影响。随着股骨近端骨质疏松程度的加重,股骨头内部应力分布也发生相应变化。股骨近端无骨质疏松模型在股骨头上外侧区域附近的应力峰值为13.8 MPa,轻微骨质疏松时,该区域应力峰值降低为10.8 MPa,随着骨质疏松程度的进一步加重,应力峰值位置发生改变,转移至股骨前上内侧附近,中度骨质疏松时该区域应力峰值为7.9 MPa,重度骨质疏松时该区域应力峰值增长至8.7 MPa,并与临床实际坏死区做对比,该病例的CT片示:股骨头坏死区域位于股骨头的前上内侧,与该研究中的有限元模型发生骨质疏松后股骨头内部应力峰值转移位置基本相符,见图7。研究表明,股骨颈骨折空心钉内固定术后股骨近端发生骨质疏松,会改变股骨头内部应力分布,应力峰值位置的转移可能是该位置坏死的生物力学因素之一。"
| [1] SWART E, ROULETTE P, LEAS D, et al. ORIF or Arthroplasty for Displaced Femoral Neck Fractures in Patients Younger Than 65 Years Old: An Economic Decision Analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2017;99(1):65-75. [2] TIAN FM, ZHANG L, ZHAO HY, et al. An increase in the incidence of hip fractures in Tangshan, China. Osteoporos Int. 2014;25(4):1321-1325. [3] 张长青,张英泽,余斌,等.成人股骨颈骨折诊治指南[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2018,20(11):921-928. [4] 徐凯航,纪方.青壮年股骨颈骨折的治疗进展[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2020,22(6):549-552. [5] SLOBOGEAN GP, SPRAGUE SA, SCOTT T, et al. Complications following young femoral neck fractures. Injury. 2015;46(3):484-491. [6] STOCKTON DJ, O’HARA LM, O’HARA NN, et al. High rate of reoperation and conversion to total hip arthroplasty after internal fixation of young femoral neck fractures: a population-based study of 796 patients. Acta Orthop. 2019;90(1):21-25. [7] PATTERSON JT, ISHII K, TORNETTA P 3RD, et al. Open Reduction Is Associated With Greater Hazard of Early Reoperation After Internal Fixation of Displaced Femoral Neck Fractures in Adults 18-65 Years. J Orthop Trauma. 2020;34(6):294-301. [8] SLOBOGEAN GP, STOCKTON DJ, ZENG B, et al. Femoral Neck Fractures in Adults Treated With Internal Fixation: A Prospective Multicenter Chinese Cohort. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2017;25(4):297-303. [9] LI M, COLE PA. Anatomical considerations in adult femoral neck fractures: how anatomy influences the treatment issues? Injury. 2015; 46(3):453-458. [10] UEO T, TSUTSUMI S, YAMAMURO T, et al. Biomechanical aspects of the development of aseptic necrosis of the femoral head. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg (1978). 1985;104(3):145-149. [11] 张永飞,张义修.股骨颈骨折术后股骨头坏死的力学因素[J].骨与关节损伤杂志,2001,16(4):270-272. [12] KIM YM, LEE SH, LEE FY, et al. Morphologic and biomechanical study of avascular necrosis of the femoral head. Orthopedics. 1991;14(10): 1111-1116. [13] WANG Y, MA JX, YIN T, et al. Correlation Between Reduction Quality of Femoral Neck Fracture and Femoral Head Necrosis Based on Biomechanics. Orthop Surg. 2019;11(2):318-324. [14] SUN W, WANG BL, LI ZR, et al. Chinese specialist consensus on diagnosis and treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Orthop Surg. 2011;3(2):131-137. [15] YUE Y, YANG H, LI Y, et al. Combining ultrasonic and computed tomography scanning to characterize mechanical properties of cancellous bone in necrotic human femoral heads. Med Eng Phys. 2019;66:12-17. [16] MA JX, HE WW, ZHAO J, et al. Bone Microarchitecture and Biomechanics of the Necrotic Femoral Head. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):13345. [17] CIARELLI MJ, GOLDSTEIN SA, KUHN JL, et al. Evaluation of orthogonal mechanical properties and density of human trabecular bone from the major metaphyseal regions with materials testing and computed tomography. J Orthop Res. 1991;9(5):674-682. [18] HARP JH, ARONSON J, HOLLIS M. Noninvasive determination of bone stiffness for distraction osteogenesis by quantitative computed tomography scans. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994;(301):42-48. [19] HOBATHO MC, RHO JY, ASHMAN RB. Anatomical variation of human cancellous bone mechanical properties in vitro. Stud Health Technol Inform. 1997;40:157-173. [20] RHO JY, HOBATHO MC, ASHMAN RB. Relations of mechanical properties to density and CT numbers in human bone. Med Eng Phys. 1995;17(5): 347-355. [21] 张国栋,廖维靖,陶圣祥,等.股骨有限元分析赋材料属性的方法[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(43):8436-8441. [22] LENGSFELD M, SCHMITT J, ALTER P, et al. Comparison of geometry-based and CT voxel-based finite element modelling and experimental validation. Med Eng Phys. 1998;20(7):515-522. [23] MEI J, LIU S, JIA G, et al. Finite element analysis of the effect of cannulated screw placement and drilling frequency on femoral neck fracture fixation. Injury. 2014;45(12):2045-2050. [24] ZENG W, LIU Y, HOU X. Biomechanical evaluation of internal fixation implants for femoral neck fractures: A comparative finite element analysis. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2020;196:105714. [25] EBERLE S, GERBER C, VON OLDENBURG G, et al. A biomechanical evaluation of orthopaedic implants for hip fractures by finite element analysis and in-vitro tests. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2010;224(10):1141-1152. [26] TAYLOR ME, TANNER KE, FREEMAN MA, et al. Stress and strain distribution within the intact femur: compression or bending? Med Eng Phys. 1996;18(2):122-131. [27] TIANYE L, PENG Y, JINGLI X, et al. Finite element analysis of different internal fixation methods for the treatment of Pauwels type III femoral neck fracture. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;112:108658. [28] LI J, ZHAO Z, YIN P, et al. Comparison of three different internal fixation implants in treatment of femoral neck fracture-a finite element analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):76. [29] FREITAS A, TOLEDO JÚNIOR JV, FERREIRA DOS SANTOS A, et al. Biomechanical study of different internal fixations in Pauwels type III femoral neck fracture - A finite elements analysis. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2020 ;14:145-150. [30] 赵耀,许新忠,程文丹,等.股骨颈动力交叉钉系统内固定治疗股骨颈骨折的早期疗效分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2022,37(4): 389-391. [31] 孙玉生.不同数量空心螺钉内固定治疗股骨颈骨折的有限元分析及生物力学测定[D].蚌埠:蚌埠医学院,2020. [32] JIANG D, ZHAN S, WANG L, et al. Biomechanical comparison of five cannulated screw fixation strategies for young vertical femoral neck fractures. J Orthop Res. 2021;39(8):1669-1680. [33] 梁跃闯,李艳军,于鹤童,等.正三角构型, 倒三角构型空心螺钉内固定及股骨颈动力交叉钉系统固定治疗股骨颈骨折的有效性分析[J].创伤外科杂志,2022,24(9):659-664. [34] 刘俊俊,付建国,柳威,等.三角稳定固定系统对股骨颈骨折生物力学特性的有限元分析[J].中国医学物理学杂志,2021,38(7):893-897. [35] BHANDARI M, TORNETTA P 3RD, HANSON B, et al. Optimal internal fixation for femoral neck fractures: multiple screws or sliding hip screws? J Orthop Trauma. 2009;23(6):403-407. [36] TSAO AK, ROBERSON JR, CHRISTIE MJ, et al. Biomechanical and clinical evaluations of a porous tantalum implant for the treatment of early-stage osteonecrosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87 Suppl 2:22-27. [37] 邱士超,刘利,吴迪.股骨头坏死的生物力学及有限元分析相关研究[J].临床医药文献电子杂志,2019,6(28):43-44. [38] XIAO D, YE M, LI X, et al. Biomechanics analysis for the treatment of ischemic necrosis of the femoral head by using an interior supporting system. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(3):4551-4556. [39] ZHANG Y, TIAN L, YAN Y, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of the expansive cannulated screw for fixation of femoral neck fractures. Injury. 2011;42(11):1372-1376. [40] 赵春伶,贾少薇,李剑,等.基于 3D 打印多孔支架和植入体的结构设计研究进展[J].医用生物力学,2019,34(4):446-452. [41] 褚楷,张兴琳,鲁兴,等.股骨颈骨折内固定物取出后股骨头内部微骨折发生风险研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2020,34(9):1091-1095. [42] 潘显明,胡修德,谭映军,等.82 例青壮年股骨颈骨折治疗结果的评价[J].中华创伤杂志,2000,16(3):145-147. [43] 王荣升,韩雪,王静,等.股骨颈骨折行闭合复位空心钉内固定后股骨头坏死[J].中国老年学杂志,2020,40(23):4984-4986. [44] 马剑雄,何伟伟,赵杰,等.股骨头坏死发病机制研究的最新进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(27):4397. [45] SEBESTYÉN A, MESTER S, VOKÓ Z, et al. Wintertime surgery increases the risk of conversion to hip arthroplasty after internal fixation of femoral neck fracture. Osteoporos Int. 2015;26(3):1109-1117. [46] 王义生,李劲峰.股骨头坏死发病机制的研究现状与展望[J].中华实验外科杂志,2020,37(6):1001-1010. [47] 申洪全,陆慧,张孝华,等.计算机辅助 2 枚空心钉置入内固定治疗股骨颈骨折的生物力学分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(6): 882-887. [48] 余霄,张迪峰,宋蒙胜,等.骨质疏松性股骨颈骨折空心钉内固定术后股骨颈短缩对髋关节生物力学影响的有限元分析[J].中华医学杂志,2020,100(33):2628-2632. [49] PEDERSEN DR, BRAND RA, DAVY DT. Pelvic muscle and acetabular contact forces during gait. J Biomech. 1997;30(9):959-965. |
| [1] | Kang Zhijie, Cao Zhenhua, Xu Yangyang, Zhang Yunfeng, Jin Feng, Su Baoke, Wang Lidong, Tong Ling, Liu Qinghua, Fang Yuan, Sha Lirong, Liang Liang, Li Mengmeng, Du Yifei, Lin Lin, Wang Haiyan, Li Xiaohe, Li Zhijun. Finite element model establishment and stress analysis of lumbar-sacral intervertebral disc in ankylosing spondylitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 840-846. |
| [2] | Zhang Min, Peng Jing, Zhang Qiang, Chen Dewang. Mechanical properties of L3/4 laminar decompression and intervertebral fusion in elderly osteoporosis patients analyzed by finite element method [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 847-851. |
| [3] | Huang Peizhen, Dong Hang, Cai Qunbin, Lin Ziling, Huang Feng. Finite element analysis of anterograde and retrograde intramedullary nail for different areas of femoral shaft fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 868-872. |
| [4] | Tan Nengxian, Wu Wenzheng, Zheng Churong, Luo Lieliang, Gu Peng, Ouyang Chongzhi, Zheng Xiaohui. Finite element analysis of different fixation methods of partially threaded cannulated screws for treating vertical femoral neck fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 873-878. |
| [5] | Wang Mingming, Zhang Zhong, Sun Jianhua, Zhao Gang, Song Hua, Yan Huadong, Lyu Bin. Finite element analysis of three different minimally invasive fixation methods for distal tibial fractures with soft tissue injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 879-885. |
| [6] | Hou Zexin, Xu Benke, Dai Yuan, He Chuan, Zhang Chaoju, Li Xiaolin. Finite element analysis of the mechanism of dorsiflexion injury of wrist joint in elderly people after falls [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 886-890. |
| [7] | Ning Tianliang, Wang Kun, Wang Lingbiao, Han Pengfei. Finite element analysis on correction effect of varus foot orthosis based on the three-point force principle [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 891-899. |
| [8] | Zhang Lili, Zhang Xinglai, Zhang Jie, Zheng Jiejiao. Effect of visual feedback on landing biomechanics in chronic ankle instability patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 900-904. |
| [9] | Zheng Jiafa, Song Xiufeng, Li Hongzhi, Zhou Jinming, Guan Shengyi, Yu He. Open reduction and internal fixation via the para-Achilles tendon approach for the treatment of posterior malleolus sandwich fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 934-938. |
| [10] | Kaiyisaier•Abudukelimu, Maimaitimin•Abulimiti, Li Lei, Yang Xiaokai, Zhang Yukun, Liu Shuai. Effect of lumbar CT values in the diagnosis of osteoporosis in women patients with lumbar degenerative diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 945-949. |
| [11] | Wang Liping, Lian Tianxing, Hu Yongrong, Yang Hongsheng, Zeng Zhimou, Liu Hao, Qu Bo. HU value of chest CT vertebral body in the opportunistic screening of type 2 diabetes mellitus osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 950-954. |
| [12] | Wang Qiang, Li Shiyun, Xiong Ying, Li Tiantian. Biomechanical changes of the cervical spine in internal fixation with different anterior cervical interbody fusion systems [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 821-826. |
| [13] | Wei Yuanbiao, Lin Zhan, Chen Yanmei, Yang Tenghui, Zhao Xiao, Chen Yangsheng, Zhou Yanhui, Yang Minchao, Huang Feiqi. Finite element analysis of effects of sagittal cervical manipulation on intervertebral disc and facet joints [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 827-832. |
| [14] | Zhang Rui, Wang Kun, Shen Zicong, Mao Lu, Wu Xiaotao. Effects of endoscopic foraminoplasty and laminoplasty on biomechanical properties of intervertebral disc and isthmus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 833-839. |
| [15] | Zhang Qianlong, Maihemuti•Yakufu, Song Chenhui, Liu Xiuxin, Ren Zheng, Liu Yuzhe, Muyashaer•Abudushalamu, Sajidan•Aikebaier, Ran Jian. Finite element analysis of the effect of the distribution position and content of bone cement on the stress and displacement of reverse femoral intertrochanteric fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 336-340. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 31
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 289
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||