[1] 原新,金牛.在国家战略体系中积极应对老龄社会问题[J].人口研究,2021,45(2):3-12.
[2] 王志灼,谷莉,周谋望.中国老年人跌倒风险因素识别及评估工具应用的研究进展[J].中国康复医学杂志,2021,36(11):1440-1444.
[3] 陈殿生,申振阳,尹虎.防跌倒步态平衡训练机器人发展现状[J].包装工程,2022,43(12)75-86.
[4] 杨艳林,张红燕,廖婷,等.我国老年人跌倒影响因素研究的可视化分析[J].上海护理,2020,20(4):19-24.
[5] PARK SH. Tools for assessing fall risk in the elderly: a systematic review and meta analysis. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2018;30(1):1-16.
[6] 高茂龙,宋岳涛.中国老年人跌倒发生率meta分析[J].北京医学, 2014,36(10):796-798.
[7] 周剑,华兴一,汤健.骨质疏松性骨折的诊疗与防治[J].临床内科杂志,2020,37(5):331-334.
[8] 丁志宏,杜书然,王明鑫.我国城市老年人跌倒状况及其影响因素研究[J].人口与发展,2018,24(4):120-128.
[9] 于东辉,汤霖,王潮.基于CSI的摔倒检测系统[J].微型电脑应用, 2021,37(7):1-4.
[10] GREENWALD RM, CHU JJ, JESSIMAN AW. Dynamic Wrist Joint Protector for Sports Applications. The Engineering of Sport 6. 2006;3:157-162.
[11] MACHOLD W, KWASNY O, EISENHARDT P, et al. Reduction of severe wrist injuries in snowboarding by an optimized wrist protection device: a prospective randomized trial. J Trauma. 2002;52(3):517-520.
[12] CHANDLER JW, STABILE KJ, PFAEFFLE HJ, et al.Anatomic Parameters for Planning of Interosseous Ligament Reconstruction Using Computer-Assisted Techniques. J Hand Surg(Am). 2003;28(1):111-116.
[13] CHENG HY, LIN CL, LIN YH, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of the modified double-plating fixation for the distal radius fracture. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2007;22(5):510-517.
[14] LEDOUX P, LAMBLIN D, WUILBAUT A, et al. A finite-element analysis of Kienbock’s Disease. J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2008;33(3):286-291.
[15] MAJUMDER S, ROYCHOWDHURY A, PAL S. Effects of trochanteric soft tissue thickness and hip impact velocity on hip fracture in sideways fall through 3D finite element simulations. J Biomech. 2008;41(13):2834-2842.
[16] MAJUMDER S, ROYCHOWDHURY A, PAL S. Simulation of hip fracture in sideways fall using a 3D finite element model of pelvis-femur-soft tissue complex with simplified representation of whole body. Med Eng Phys. 2007;29(10):1167-1178.
[17] 董谢平,王冬梅,何剑颖,等.腕保护器抗冲击载荷的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(30):5531-5535.
[18] 张朝驹,何川,陈洪卫,等.基于有限元模型分析伸直型桡骨远端骨折的生物力学特点[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(12):1898-1902.
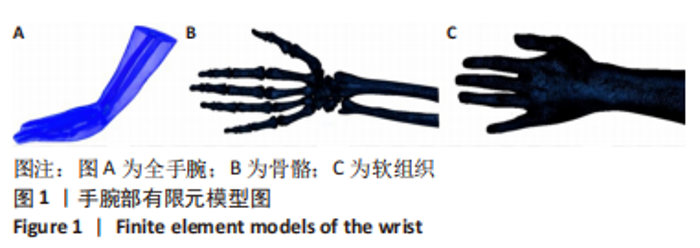
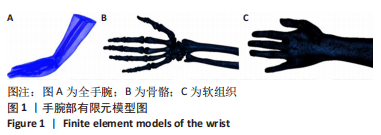
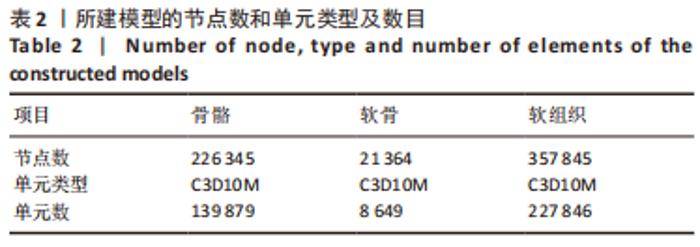
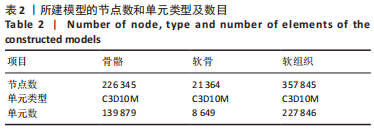
[19] 朱海波,朱建民,马南,等.基于软骨和韧带的全腕关节有限元模型建立和舟状骨生物力学研究[J].上海医学,2014,37(7):602-605+ 541.
[20] WU CH, TU ST, CHANG YF, et al. Fracture liaison services improve outcomes of patients with osteoporosis-related fractures: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis. Bone. 2018;111:92-100.
[21] 梁志昊,梁中星,李世文.太极拳运动训练联合运动管理在老年骨质疏松患者中的应用效果分析[J].反射疗法与康复医学,2022,3(15): 38-41,45.
[22] 邓介超,唐海,刘建泉,等. Otago运动训练对老年骨质疏松症患者平衡能力和跌倒风险的影响[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志, 2022,15(1):31-35.
[23] 朱仁坤.弹力带和24式太极拳训练对预防老年人摔倒的影响[D].北京:北京体育大学,2020.
[24] 王晓雯,陈贵全.传统养生与现代体育运动防治原发性骨质疏松的研究进展[J].国际老年医学杂志,2022,43(6):755-758.
[25] 丁梦龙.24周二十四式简化太极拳对促进老年人功能性体适能与预防再摔倒的实验研究[D].西安:西安体育学院,2021.
[26] 林进龙,魏玥,陈功,等.中国老年人不同严重程度跌倒风险与慢性病和睡眠的关联研究[J].中华疾病控制杂志,2021,25(1):25-31.
[27] 吴跃迪,刘腊梅,王珍珠,等.老年人衰弱和跌倒相关性研究进展[J].全科护理,2021,19(24):3377-3380.
[28] 殷雪娇,徐阳星,徐秀容,等.血清骨膜蛋白和骨硬化蛋白对老年2型糖尿病患者骨质疏松的诊断价值[J].中国现代医学杂志,2023, 33(1):7-12.
[29] 王晓霞.心血管疾病生活方式干预措施[J],临床合理用药杂志,2011, 4(24):110.
[30] 岳跃学,贾玉玲,王秀红.老年人跌倒风险预测模型研究进展[J].护理研究,2022,36(16):2944-2948.
[31] BURKHART TA, ANDREWS DM. The effectiveness of wrist guards for reducing wrist and elbow accelerations resulting from simulated forward falls. J Appl Biomech. 2010;26(3):281-289.
[32] MÜLLER I, VOGIATZIS M, WIESE K, et al. Biomechanical examinations of the efficacy of wrist guards in inline skating. Sportverletz Sportschaden. 2003;17(2):80-83.
[33] FAN YL, XU HY, XIA MY, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of axial-loading simulated experiment in wrist fractures: a finite element analysis. J Int Med Res. 2020;48(10):300060520966884.
[34] VARGA P, SCHEFZIG P, UNGER E, et al. Finite element based estimation of contact areas and pressures of the human scaphoid in various functional positions of the hand. J Biomech. 2013;46(5):984-990.
|