Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (3): 411-418.doi: 10.12307/2023.877
Previous Articles Next Articles
Finite element analysis of the influence of scaffold materials on the fixed restoration of edentulous maxillary implants under two designs
Chen Yuanyuan, Wang Wei, Zhao Lu, Annikaer·Aniwaer, Nijati·Turson
- Department of Stomatology, Second Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830063, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2022-11-28Accepted:2023-01-10Online:2024-01-28Published:2023-07-10 -
Contact:Nijati·Turson, Chief physician, Associate professor, Department of Stomatology, Second Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830063, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Chen Yuanyuan, Master candidate, Department of Stomatology, Second Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830063, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:Natural Science Foundation of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, No. 2016D01c192 (to NT)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Yuanyuan, Wang Wei, Zhao Lu, Annikaer·Aniwaer, Nijati·Turson. Finite element analysis of the influence of scaffold materials on the fixed restoration of edentulous maxillary implants under two designs[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 411-418.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
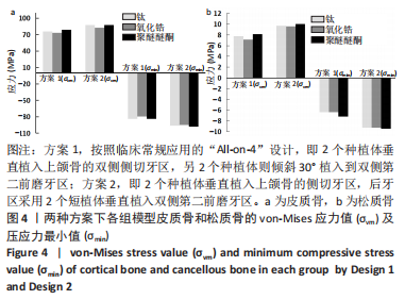
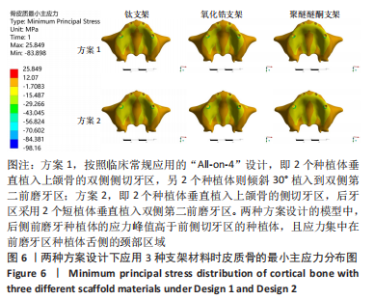
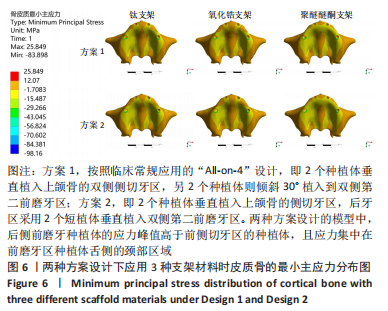
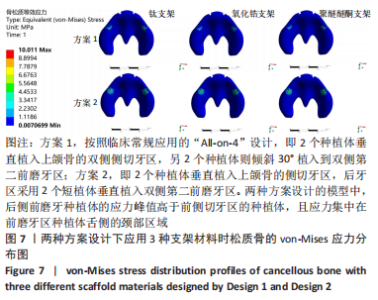
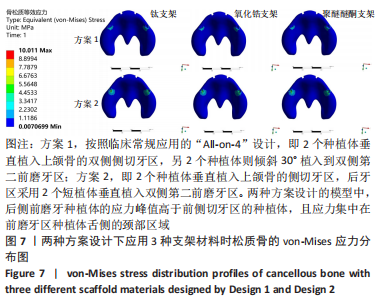
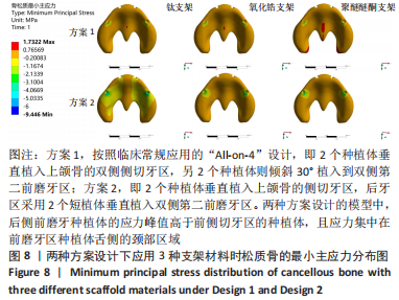
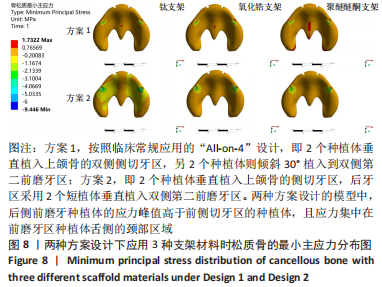
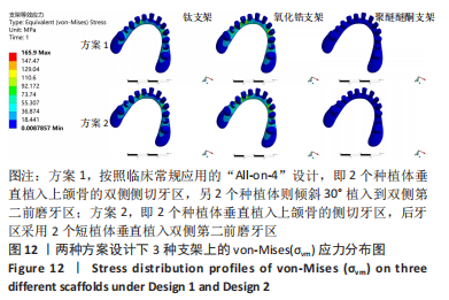
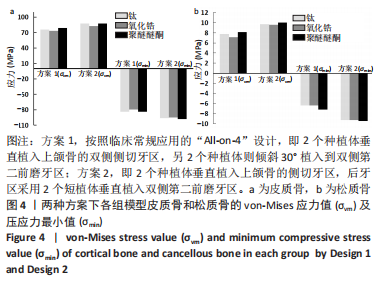
2.1 各组模型种植体周围骨组织的应力分布 两种固定种植方案设计下的3个模型在斜向加载下,由图4a可见,在皮质骨上的应力峰值差别不大,其中应用聚醚醚酮支架下的模型的应力峰值最大,其次是钛支架、氧化锆支架。所有模型均显示出相似的σvm 和σmin 应力分布模式,前磨牙区植入物周围皮质骨的σvm和 σmin均高于侧切牙区,应力特别集中在前磨牙区种植体舌侧皮质骨的颈部区域,靠近载荷施加部位,见图5,6。 图4b显示6种模型所选用的3种支架材料在松质骨上的应力峰值均明显低于皮质骨。其中应用聚醚醚酮支架的模型在两种方案设计中的松质骨上都显示出最高的σvm 值(方案1=8.126 MPa,方案2=10.011 MPa)及σmin 值(方案1= -7.175 MPa,方案2=-9.446 MPa),与方案1设计相比较,方案2 设计下的σvm 及σmin 值分别增加了19%及24%。图7,8显示,在松质骨上所有组中均显示出相似的σvm和σmin分布模式。从数据上看,聚醚醚酮支架对骨组织的应力较氧化锆支架最大增加12%,两种方案设计在后侧前磨牙区种植体远中及舌侧的皮质骨/松质骨界面都有着较高的应力值。"
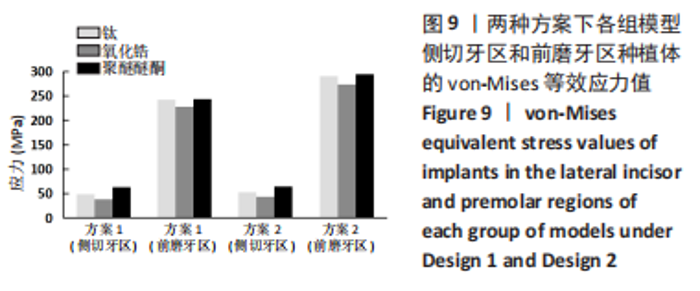
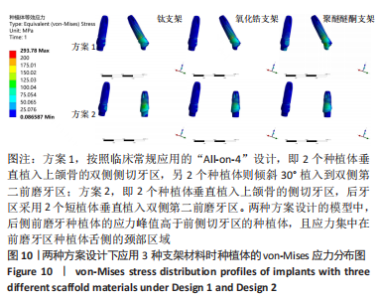
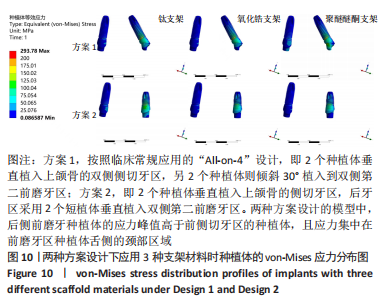
2.2 各组模型种植体的应力分布 图9显示6个模型在方案2设计中后侧前磨牙区种植体上均有着较高的von-Mises应力峰值,远远大于前侧侧切牙区的种植体,应力主要集中前磨牙区种植体的舌侧颈部区域,见图10。从3种支架材料的对比来看,种植体应力的最大值由小到大分别为氧化锆、钛、聚醚醚酮支架模型。与氧化锆支架相比,聚醚醚酮支架对种植体最大应力峰值的增加大于50%,应力主要集中在方案1设计中侧切牙区种植体舌侧近基台的位置,此时种植体会有机械并发症的可能性。同时不管选用哪种支架材料,方案2后侧前磨牙区短直种植体的σvm 值均高于方案1中的长斜标准种植体,相比之下,方案2设计中种植体的σvm 值分别增加了17%,16%,18%。"
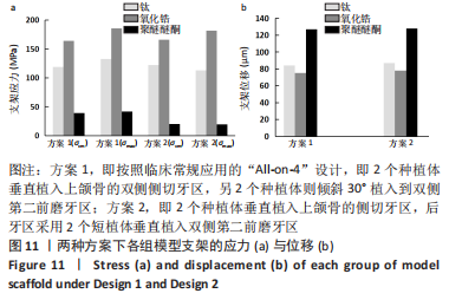
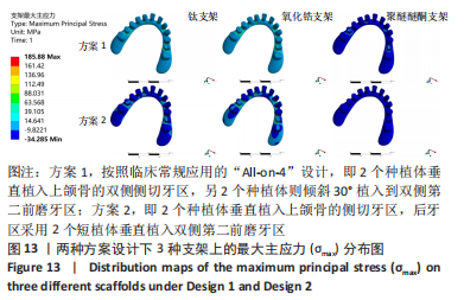
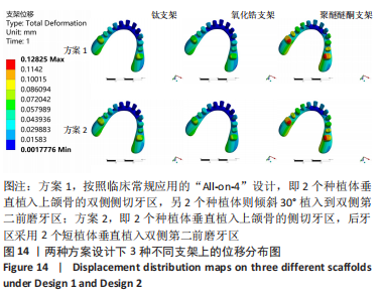
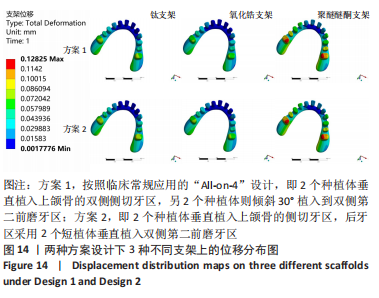
2.3 各组模型上部支架的应力分布及位移分析 与种植体及周围骨组织的应力分布相反,所有设计模型上部支架结构各应力最大值由大到小依次为氧化锆、钛、聚醚醚酮支架。在两种方案设计下,聚醚醚酮支架应力峰值均明显小于氧化锆支架,σvm 值和σmax 值都分别减少了76%,88%和78%,89%,见图11a。由图12,13可观察到,所有组模型应力分布模式相似,主要集中在牙合力加载处,最大值出现在双侧尖牙近中位置近基台处。图11b、图14显示两种方案设计下所有模型的支架位移水平值相差不大,且趋势与载荷方向一致,总体位移都明显发生支架的后侧。在应用聚醚醚酮支架的两种模型具有更高的位移水平(方案1=127 μm,方案2=128 μm),而氧化锆支架与钛支架组位移水平则较一致。"
| [1] RAGHOEBAR GERRY M, PIETER O, CARINA BG, et al. Long-term effectiveness of maxillary sinus floor augmentation:A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Clin Periodontol. 2019;46 Suppl 21(s21):307-318. [2] HENDRIK N, KLAAS L,AYDIN G, et al. Effect of enriched bone-marrow aspirates on the dimensional stability of cortico-cancellous iliac bone grafts in alveolar ridgeaugmentation. Int J Implant Dent. 2022;8(1):34-34. [3] 吴炯睿,高益鸣.上颌窦解剖与上颌窦外提升手术并发症的研究进展[J].中国口腔颌面外科杂志,2022,20(1):93-97. [4] 木志翔,刘婷,陈陶,等.两种上颌无牙颌种植固定修复方案的有限元分析[J].口腔医学研究,2019,35(10):931-935. [5] MALÓ P, RANGERT O, NOBRE M, et al.“All‐on‐Four” Immediate‐Function Concept with Brånemark System Implants for Completely Edentulous Mandibles:A Retrospective Clinical Study. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2003;5 Suppl 1:2-9. [6] 何添荣.两种解决上颌后牙区骨量不足的种植修复方式的临床对照试验[D].上海:上海交通大学,2012. [7] SANTANA LCL, GUASTALDI FPS, IDOGAVA HT, et al. Mechanical Stress Analysis of Different Configurations of the All-on-4 Concept in Atrophic Mandible: A 3D Finite Element Study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2021; 36(1):75-85. [8] VETROMILLA BM, MAZZETTI T, PEREIRA-CENCI T. Short versus standard implants associated with sinus floor elevation:an umbrella review of meta-analyses of multiple outcomes. J Prosthet Dent. 2021;126(4):503-511. [9] CAROSI P, LORENZI C, LAURETI M, et al. Short dental implants(≤6 mm) to rehabilitate severe mandibular atrophy:a systematic review. Int J Oral Maxillofacial Implants. 2021;36(1):30-37. [10] YAN Q, WU X, SU M, et al. Short implants(≤6 mm) versus longer implants with sinus floor elevation in atrophic posterior maxilla:a systematic review and meta analysis. BMJ Open. 2019;9(10):e029826. [11] LOFAJ F, KUCERA J, NÉMETH D, et al. Optimization of Tilted implant geometry for stress reduction in All-on-4 treatment concept:finite element analysis study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2018;33(6):1287-1295. [12] BARBIN T, SILVA LDR, VELOSO DV, et al. Biomechanical behavior of CAD/CAM cobalt-chromium and zirconia full-arch fixed prostheses. J Adv Prosthodont. 2020;12(6):329-337. [13] BAGEGNI A, ABOU-AYASH S, RÜCKER G, et al. The influence of prosthetic materialon implant and prosthetic survival of implant-supported fixed complete dentures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Prosthodont Res. 2019;63(3):251-265. [14] WONG C, NARVEKAR U, PETRIDIS H. Prosthodontic complications of metal‑ceramic and all‑ceramic,complete‑arch fixed implant prostheses with minimum 5years mean follow‑up period.A systematic review and meta‑analysis. J Prosthodont. 2019;28(2):e722-e735. [15] BIDRA AS, TISCHLER M, PATCH C. Survival of 2039 complete arch fixed implant-supported zirconia prostheses:a retrospective study. J Prosthet Dent. 2018;119(2):220-224. [16] WAGNER F, SEEMANN R, MARINCOLA M, et al. Fiber-reinforced resin fixed prostheses on 4 short implants in severely atrophic maxillas:1-year results of a prospective cohort study. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2018;76(6):1194-1199. [17] MOUNIR M, ATEF M, ABOU-ELFETOUH A, et al. Titanium and polyether ether ketone (PEEK) patient-specific sub-periosteal implants:two novel approaches for rehabilitation of the severely atrophic anterior maxillary ridge. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2018;47(5):658-664. [18] MALÓ P, DE ARAÚJO NOBRE M, LOPES A, et al. All-on-4 treatment concept for the rehabilitation of the completely edentulous mandible: a 7-year clinical and 5-year radiographic retrospective case series with risk assessment for implant failure and marginal bone level. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2015;17 Suppl 2:e531-e541. [19] KIM WH, HONG K, LIM D, et al. Optimal position of attachment for removable thermoplastic aligner on the lower canine using finite element analysis. Materials. 2020;13:3369. [20] SIRANDONI D, LEAL E, WEBER B, et al. Effect of different framework materials in implant-supported fixed mandibular prostheses:a finite element analysis. Int J Oral Max Implant. 2019;34(6):e107-e114. [21] HA SR. Biomechanical three‑dimensional finite element analysis of monolithic zirconia crown with different cement type. J Adv Prosthodont. 2015;7:475-483. [22] CHANG CH, CHEN CS, HSU ML, et al. Biomechanical effect of platform switching in implant dentistry:A three-dimensional finite element analysis. Int J Oral Max Implant. 2010;25:295-304. [23] DÍEZ-PASCUAL AM, NAFFAKH M, GONZÁLEZ-DOMÍNGUEZ JM, et al. High performance PEEK/carbon nanotube composites compatibilized with polysulfones-Ⅱ.Mechanical and electrical properties. Carbon. 2010; 48(12):3500-3511. [24] RADI IA, ELMAHROUKY N. Effect of two different soft liners and thicknesses mediating stress transfer for immediately loaded 2-implant supported mandibular overdentures: a finite element analysis study. J Prosthet Dent. 2016;116(3):356-361. [25] FERREIRA MB, BARAO VA, DELBEN JA, et al. Non-linear 3D finite element analysis of full-arch implant-supported fixed dentures. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2014;38:306-314. [26] SKIRBUTIS G, DZINGUTE A, MASILIUNAITE V, et al. A review of PEEK polymer’s properties and its use in prosthodontics. Stomatologija. 2017;19(1):19-23. [27] DESTE G, DURKAN R. Effects of all-on-four implant designs in mandible on implants and the surrounding bone: A 3-D finite element analysis. Niger J Clin Pract. 2020;23(4):456-463. [28] DAYAN SC, GECKILI O. The influence of framework material on stress distribution in maxillary complete-arch fixed prostheses supported by four dental implants: a three-dimensional finite element analysis. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2021;24(14):1606-1617. [29] 董泽文,张小军,李彦生,等.不同牙合方式下人体下颌骨膜下种植体的生物力学特性[J].医用生物力学,2012,27(6):655-660. [30] 于文倩,李晓茜,陈思艺,等.上部结构材料对无牙下颌种植固定修复影响的三维有限元分析[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2021,56(2):190-195. [31] HAROUN F, OZAN O. Evaluation of Stresses on Implant, Bone, and Restorative Materials Caused by Different Opposing Arch Materials in Hybrid Prosthetic Restorations Using the All-on-4 Technique. Materials (Basel). 2021;14(15):4308. [32] 温颖,郑东翔,张振庭,等.全口无牙领应用种植固定修复后的咬合力分布研究[J].北京口腔医学,2008,16(6):325-328. [33] FERREIRA MB, BARÃO VA, FAVERANI LP, et al. The role of superstructure material on the stress distribution in mandibular full-arch implant-supported fixed dentures. A CT-based 3D-FEA.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2014;35:92-99. [34] DAS NEVES FD, FONES D, BERNARDES SR, et al. Short implants--an analysis of longitudinal studies. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2006;21(1):86-93. [35] OZAN O, KURTULMUS-YILMAZ S. Biomechanical Comparison of Different Implant Inclinations and Cantilever Lengths in All-on-4 Treatment Concept by Three-Dimensional Finite Element Analysis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2018;33(1):64-71. [36] 唐庭,张磊,侯永福,等.All-on-4种植即刻修复对口腔健康相关生活质量的影响[J].上海口腔医学,2018,27(1):52-55. [37] LIU T, MU Z, YU T, et al. Biomechanical comparison of implant inclinations and load times with the all-on-4 treatment concept: a three-dimensional finite element analysis. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2019;22(6):585-594. [38] 范震,刘月,王佐林.牙列缺失倾斜种植设计[J].华西口腔医学杂志, 2021,39(4):377-385. [39] ASAWA N, BULBULE N, KAKADE D, et al. Angulated implants: an alternative to bone augmentation and sinus lift procedure: systematic review. J Clin Diagn Res. 2015;9(3):ZE10-ZE13. [40] ERCAL P, TAYSI AE, AYVALIOGLU DC, et al. Impact of peri-implant bone resorption,prosthetic material,and crown to implant ratio on the stress distribution of short implants:a finite element analysis. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2021;59(4):813-824. [41] 施斌,廖一林,晏奇.短种植体在上颌后牙区的应用与风险[J].中国口腔种植学杂志,2021,26(4):213-218. [42] LOMBARDO G, SIGNORIELLO A, SIMAN CAS-PALLARES M, et al. Survival of short and ultra-short locking-taper implants supporting single crowns in the posterior mandible: a 3-year retrospective study. J Oral Implantol. 2020;46(4):396-406. [43] LIN ZZ, JIAO YQ, YE ZY, et al. The survival rate of transcrestal sinus floor elevation combined with short implants:a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Int J lmplant Dent. 2021;7(1):41. [44] KUL E, KORKMAZ IH. Effect of different design of abutment and implant on stress distribution in 2 implants and peripheral bone:a finite element analysis study. J Prosthet Dent. 2021;126(5):664.e1-664.e9. [45] NIELSEN HB, SCHOU S, BRUUN NH, et al. Single-crown restorations supported by short implants(6 mm)compared with standard length implants(13mm)in conjunction with maxillary sinus floor augmentation:a randomized,controlled clinical trial. Int J Implant Dent. 2021;7(1):66. [46] AYNA M, WESSING B, GUTWALD R, et al. A 5-year prospective clinical trial on short implants (6mm)for single tooth re-placement in the posterior maxilla:immediate versus delayed loading. Odontology. 2019;107(2):244-253. [47] CAROSI P, LORENZI C, LIO F, et al. Short implants (≤6mm) as an alternative treatment option to maxillary sinus lift. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2021; 50(11):1502-1510. [48] LOPEZ C, VASCO M, RUALES E, et al. Three‑dimensional finite element analysis of stress distribution in zirconia and titanium dental implants. J Oral Implantol. 2018;44(6):409-415. [49] SEEMANN R, WAGNER F, MARINCOLA M, et al. Fixed,fiber-reinforced resin bridges on 5.0-mm implants in severely atrophic mandibles: up to 5 years′ follow-up of a prospective cohort study. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2018;76(5): 956-962. [50] 皮昕.口腔解剖生理学[M]. 6版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2007:294. [51] VERRI FR, CRUZ RS, DE SOUZA BATISTA VE, et al. Can the modeling for simplification of a dental implant surface affect the accuracy of 3D finite element analysis. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2016;19(15):1665-1672. [52] DOGANAY O, KILIC E. Comparative finite element analysis of short implants with different treatment approaches in the atrophic mandible. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2020;35(4):e69-76. [53] BHERING CLB, MESQUITA MF, KEMMOKU DT, et al. Comparison between all-on-four and all-on-six treatment concepts and framework material on stressdistribution in atrophic maxilla: A prototyping guided 3D-FEA study. Mat Sci Eng C-Mater. 2016;69:715-725. [54] AZCARATE-VELAZQUEZ F, CASTILLO-OYAGUE R, OLIVEROS-LOPEZ LG, et al. Influence of bone quality on the mechanical interaction between implant and bone: a finite element analysis. J Dent. 2019;88:103161. [55] OLIVEIRA MR, GONÇALVES A, GABRIELLI MA, et al. Evaluation of alveolar bone quality: correlation between histomorphometric analysis and Lekholm and Zarb classification. J Craniofac Surg. 2021;32(6):2114-2118. [56] SIRANDONI D, LEAL E, WEBER B, et al. Effect of different framework materials in implant-supported fixed mandibular prostheses: a finite element analysis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2018;34:107-114. [57] MUMCU E, DAYAN SC, GENCELI E, et al. Comparison of four-implant-retained overdentures and implant-supported fixed prostheses using the All-on-4 concept in the maxilla in terms of patient satisfaction,quality of life, and marginal bone loss: a 2-year retrospective study. Quintessence Int. 2020; 51:388-396. [58] MALO P, DE ARA UJO NOBRE M, MOURA GUEDES C, et al. Short-term report of an ongoing prospective cohort study evaluating the outcome of full-arch implant-supported fixed hybrid polyetheretherketone-acrylic resin prostheses and the All-on-Four concept. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2018;20(5):692-702. [59] FERREIRA MB, BARÃO VA, DELBEN JA, et al. Non-linear 3D finite element analysis of full-arch implant-supported fixed dentures. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2014;38:306-314. |
| [1] | Zhu Lin, Gu Weiping, Wang Can, Chen Gang. Biomechanical analysis of All-on-Four and pterygomaxillary implants under different maxillary bone conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 985-991. |
| [2] | Reyila·Kuerban, Xiaheida·Yilaerjiang, Chen Xin, Zilala·Julaiti, Baibujiafu·Yellisi, Nijati·Turson. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of different restorative methods for ultrashort implants [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(30): 4824-4829. |
| [3] | Ye Linqiang, Chen Chao, Liu Yuanhui, Li Zhen, Lu Guoliang. Finite element analysis of position effects on reduction of facet joint displacement by cervical rotatory manipulation for cervical spondylotic radiculopathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(29): 4607-4611. |
| [4] | Huang Dingan, Liu Chen. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of a new height adjustable cervical fusion cage [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(18): 2797-2803. |
| [5] | Lai Jieqing, Li Ruoyu, He Mincong, Lan Yun, Yang Xingfu, Zhou Nannan, Jiang Linheng, Lyu Zheng, Yi Chunzhi, Fang Bin. Clinical efficacy and biomechanical analysis of the tripod percutaneous reconstruction technique in periacetabular lesions caused by metastatic cancer [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(13): 1987-1992. |
| [6] | Ye Linqiang, Lu Guoliang, Jiang Xiaobing, Li Zhen, Weng Rui, Liang De, Huang Xuecheng, Feng Yonghong. Biomechanical effects of cement filling location on osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture: a three-dimensional finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(28): 4435-4440. |
| [7] | Chen Xi, Cheng Hui, Chen Jiahui, Li Xiurong. Clinical applicability of cobalt-chromium metal-ceramic crowns with porcelain margin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(27): 4374-4378. |
| [8] | Wang Yuan, Zhang Yang. Finite element biomechanical analysis of various bone mineral densities on edentulous mandibular four-implant-supported overdentures fixed using Locator attachments [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(22): 3492-3497. |
| [9] | Li Yuan, Song Liang, Zhang Jianguo, Hu Fengling. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of stress distributions in osteoporosis and normal mandibular dental implant-supported overdentures with flat-type and cushion-type magnetic attachments [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(16): 2540-2544. |
| [10] | Wu Chao, Gao Mingjie, Wang Jianzhong, Zhang Yunfeng, Yu Jinghong, Cai Yongqiang, Wang Haiyan, He Yujie, Tong Ling, Li Jiawei, Gao Shang, Wang Xing, Wu Min, Li Zhijun, Li Xiaohe. Finite element analysis of stress and displacement of Lenke 3 adolescent idiopathic scoliosis thoracolumbar spine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(33): 5273-5280. |
| [11] | Shu Qihang, Liao Yijia, Xue Jingbo, Yan Yiguo, Wang Cheng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of a new three-dimensional printed porous fusion cage for cervical vertebra [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3810-3815. |
| [12] | Liu Fushenghua, Xu Jian, Zhao Bingcheng, Wei Gehan, Qin Wenbao. Three-dimensional finite element biomechanical analysis of stage II adult acquired flatfoot deformity after medial column stabilization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(18): 2805-2810. |
| [13] | Zhang Yeming, Wu Di, Zhang Ling, Liu Min, Yu Yong, Cui Jiewen, Yuan Bingqian, Li Qing. Effect of different defect areas of medial femoral condyle cartilage on peripheral cartilage stress: three-dimensional finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(12): 1911-1916. |
| [14] | Chen Junliang, Li Mingxia, Lü Dongmei, He Yun. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of mini implants supported mandibular overdentures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(10): 1491-1495. |
| [15] | Chen Zhen-qiu, Zhang Qiu-xia, Zhou Guang-quan, Pang Zhi-hui, Wei Qiu-shi. Three-dimensional parametric modeling during unicompartmental knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(4): 588-593. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||