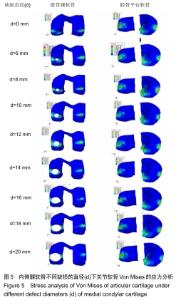
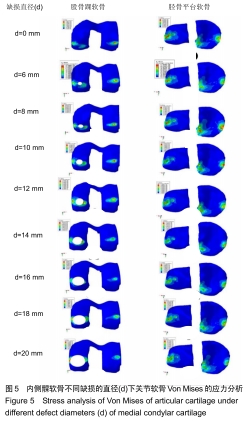
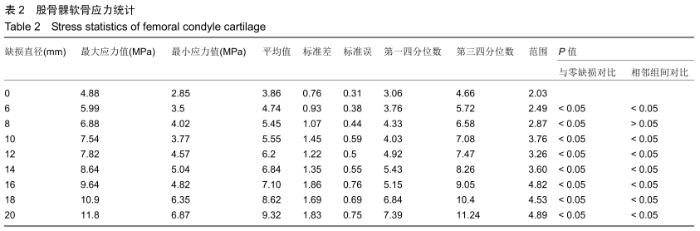
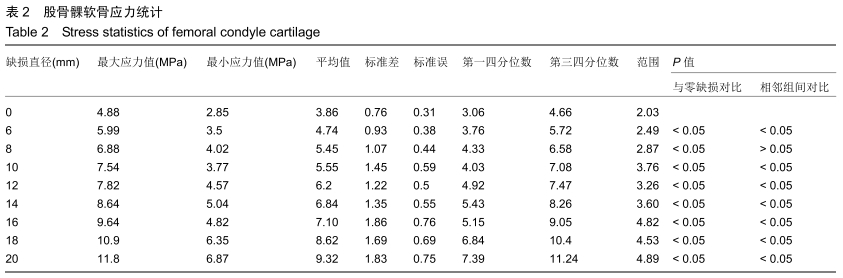
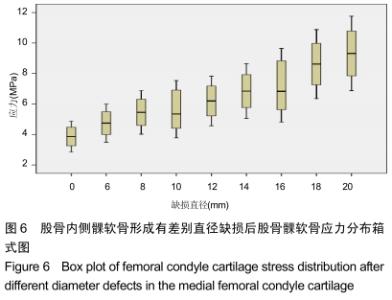
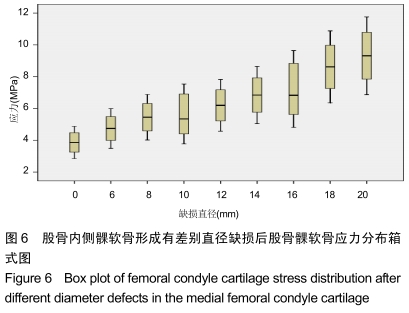
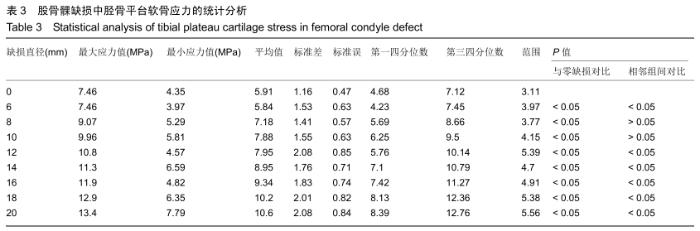
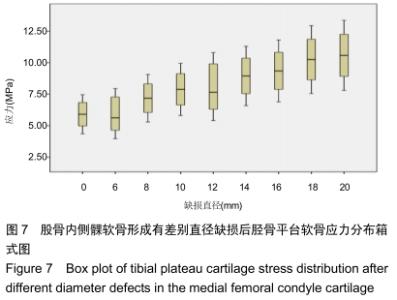
[1] 姜宗来.从生物力学到力学生物学的进展[J].力学进展,2017,47(1): 309-332.
[2] 裴福兴,李箭,陈安民,等.骨科学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2016:308-309
[3] 连芩,庄佩,靳忠民,等.大尺寸关节支架的3D打印及应用[J].中国科学:信息科学,2015,45(2):248-258.
[4] 郑荣宗,吴伟东,林蔚,等.关节镜下自体骨软骨移植治疗膝关节软骨缺损[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2014,29(10):1050-1051.
[5] 吴昊,罗辉耀,梁斌,等.微骨折+原位钻孔缝合法治疗股骨髁骨软骨骨折[J].临床骨科杂志,2016,19(4):466-468.
[6] 张洪美,何名江,荆琳.关节镜下自体骨软骨移植治疗伴局灶性软骨缺损的膝骨关节炎[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2013,28(S1):23-24.
[7] 刘久翔,王青,崔维顶,等.自体骨软骨移植术治疗膝关节软骨损伤的临床疗效[J].江苏医药,2016,42(7):830-832.
[8] 刘祺,郭林,杨柳,等.膝关节半月板及股骨髁软骨损伤关节镜下标准化分区法及其临床应用[J].创伤外科杂志,2007,9(3):203-205.
[9] SHRIRAM D, PRAVEEN KUMAR G, SUBBURAJ K, et al.Evaluating the effects of material properties of artificial meniscal implant in the human knee joint using finite element analysis.Sci Rep.2017,7(1):1-11.
[10] 王俊然,杜玮瑾,陈维毅,等.有限元分析不同屈曲状态下胫-股关节的生物力学变化[J].中国组织工程研究, 2018,22(31):4975-4981.
[11] 何川,李彦林,王国梁,等.不同屈曲状态下膝关节韧带生物力学的有限元分析[J].中国运动医学杂志,2015,34(7):662-669.
[12] 王傲寒,董万鹏,王兵,等.膝关节三维有限元模型的建立和验证[J].计算机辅助工程,2018,27(Z1):68-71+76.
[13] MAROUANE H, SHIRAZI-ADL A, HASHEMI J. Quantification of the role of tibial posterior slope in knee joint mechanics and ACL force in simulated gait.J Biomech. 2015;48(10):1899-905.
[14] 王傲寒,董万鹏,王兵,等.膝关节三维有限元模型的建立和验证[J].计算机辅助工程,2018,27(Z1):68-71+76.
[15] 董跃福,牟志芳,刘旭东,等.膝关节有限元解剖模型的构建及其力学分析[J].临床骨科杂志,2015,18(06):686-692.
[16] 郭俊超.计及半月板的人体膝关节动力学仿真及三维有限元分析[D].洛阳:河南科技大学,2009.
[17] 王光达,张祚福,于娟,等.膝关节三维有限元模型的建立及生物力学分析[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(52):9702-9705.
[18] 陈凯宁.基于三维有限元方法探索ACL断裂后胫股关节轨迹异常对半月板和软骨应力分布的影响[D].重庆:第三军医大学,2013.
[19] 谢井文,张刚,薛水培,等.MRI和关节镜测量膝关节软骨缺损面积的一致性[J]. 中国医学创新, 2017, 14(10):125-128.
[20] WIDUCHOWSKI W, WIDUCHOWSKI J, TRZASKA T.Articular cartilage defects: study of 25,124 knee arthroscopies.The Knee.2007;14(3): 177-182.
[21] BHOSALE AM, RICHARDSON JB. Articular cartilage: structure, injuries and review of management. Br Med Bull. 2008;87:77-95.
[22] 许可,马信龙,张园,等.异常应力条件下关节软骨的变化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011,14(46): 8559-8562.
[23] 张胜 黄昌林,胡蕴玉,等.不同应力载荷模式致牛关节软骨细胞及基质损伤的差异[J]. 第四军医大学学报,2005,24(15):1369-1372.
[24] 张英,崔磊,刘伟,等.力学环境对软骨基质代谢的影响[J].中国生物工程杂志,2003,23(7):80-83.
[25] LINDEN B.Osteochondritis dissecans of the femoral condyles: a long-term follow-up study.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1977;59(6):769-776.
[26] HUGHSTON JC, HERGENROEDER PT, COURTENAY BG. Osteochondritis dissecans of the femoral condyles. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1984;66(9):1340-1348.
[27] 田倩倩.缺损软骨损伤演化过程的研究[D].天津:天津理工大学,2014。
[28] BRITTBERG M, FAXEN E, PETERSON L. Carbon fiber scaffolds in the treatment of early knee arthrosis: a prospective 4-year follow-up of 37 patients. Clin Orthop.1994;307:155-164.
[29] HOMMINGA GN, BULSTRA SK, BOUWMEESTER PS, et al. Perichondral grafting for cartilage lesions of the knee.J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1990;72(6):1003-1007.
[30] LORENTZON R, HILDINGSON C, ALFREDSON H.Treatment of deep cartilage defects in the knee with periosteum transplantation.Swedish Orthopaedic Association Meeting.Karlstad,Sweden.1996.
[31] 陈纪伟.膝关节镜下个体化自体骨软骨移植治疗在股骨软骨损伤中的临床疗效回顾性研究[D].青岛:青岛大学,2017.
[32] JORGE C, ROBERT F, CECILIA P, et al. Biological Therapies for Cartilage Lesions in the Hip: A New Horizon.Orthopedics.2016;39(4): e715-723
[33] RONGA M, STISSI P, CHERUBINO P, et al.Treatment of unstable osteochondritis dissecans in adults with autogenous osteochondral grafts (Mosaicplasty): long-term results.Joints.2015;3(4):173-178.
[34] UEMATSU K, HABATA T, FUJISAWA Y, et al. Osteochondritis dissecans of the knee: long-term results of excision of the osteochondral fragment. Knee.2005;12(3):205-208.
[35] ADACHI N, DEIE M, OCHI M, et al.Functional and radiographic outcomes of unstable juvenile osteochondritis dissecans of the knee treated with lesion fixation using bioabsorbable pins. J Pediatr Orthop. 2015;35(1):82-88.
[36] ROBINSON D,KERSH M,PANDY MG,et al.Mechanical properties of normal and osteoarthritic human articular cartilage. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater.2016;8(61):96-109.
[37] 仝路.股骨内髁虚拟软骨缺损对膝关节软骨、半月板应力的影响[D].昆明:昆明医科大学,2013.
[38] 王俊然.膝关节在屈曲和步态运动下胫—股关节生物力学的有限元分析[D].太原:太原理工大学,2017.
|