Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (7): 985-991.doi: 10.12307/2023.035
Biomechanical analysis of All-on-Four and pterygomaxillary implants under different maxillary bone conditions
Zhu Lin1, 2, 3, Gu Weiping1, 2, 3, Wang Can4, Chen Gang1, 2, 3
- 1Department of General Dentistry, The Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210029, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Jiangsu Province Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases, Nanjing 210029, Jiangsu Province, China; 3Jiangsu Province Engineering Research Center of Stomatological Translational Medicine, Nanjing 210029, Jiangsu Province, China; 4Hefei Stomatological Hospital, Hefei 230000, Anhui Province, China
-
Received:2021-12-25Accepted:2022-01-28Online:2023-03-08Published:2022-07-18 -
Contact:Gu Weiping, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Department of General Dentistry, The Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210029, Jiangsu Province, China; Jiangsu Province Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases, Nanjing 210029, Jiangsu Province, China; Jiangsu Province Engineering Research Center of Stomatological Translational Medicine, Nanjing 210029, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Zhu Lin, Master candidate, Department of General Dentistry, The Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210029, Jiangsu Province, China; Jiangsu Province Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases, Nanjing 210029, Jiangsu Province, China; Jiangsu Province Engineering Research Center of Stomatological Translational Medicine, Nanjing 210029, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:the Advantage Discipline Construction Project in Jiangsu Universities, No. 2018-87 (to GWP); Special Foundation for Health Science Development of Nanjing, No. YKK20246 (to GWP)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhu Lin, Gu Weiping, Wang Can, Chen Gang. Biomechanical analysis of All-on-Four and pterygomaxillary implants under different maxillary bone conditions[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 985-991.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
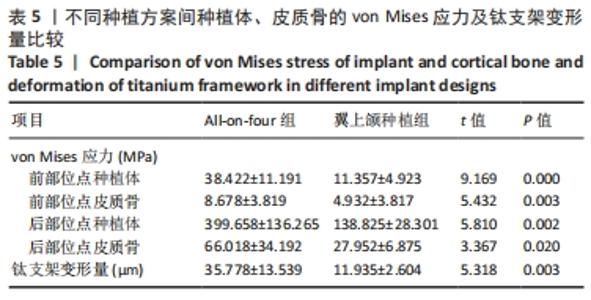
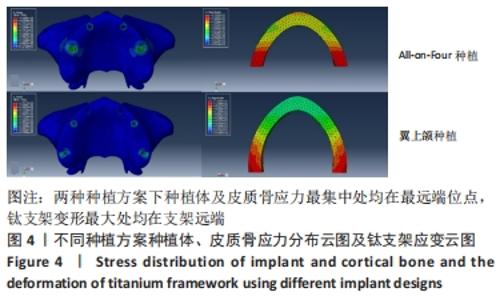
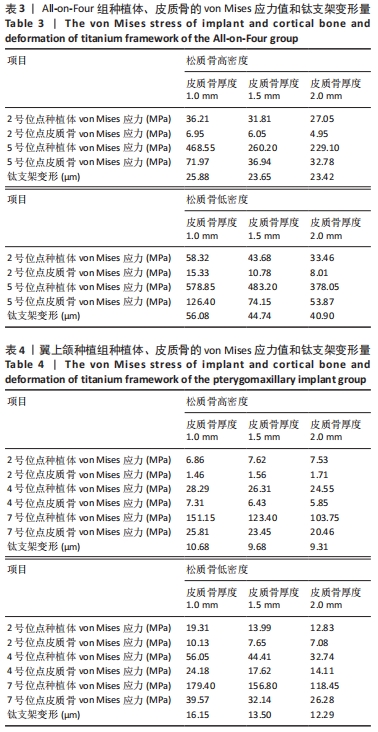
All-on-Four种植方案中,5号位点种植体及皮质骨von Mises值最大;相同松质骨密度下,对比3种不同皮质骨厚度下的模型数据,发现随着皮质骨厚度的增加,种植体、皮质骨的von Mises应力值及钛支架的变形量均呈降低趋势。当皮质骨厚度从1 mm增加到2 mm时,综合两种骨密度比较,5号位点种植体及皮质骨von Mises应力值分别下降了42.04%,56.31%,钛支架变形量下降了21.52%。高密度组5号位点种植体、皮质骨von Mises应力值及钛支架变形量分别比低密度组降低33.90%,44.31%,48.53%。 翼上颌种植方案中,7号位点种植体及皮质骨von Mises值最大,相同松质骨密度下,对比3种不同骨厚度下的模型数据,发现随着皮质骨厚度的增加,种植体、皮质骨von Mises应力值及钛支架的变形量整体呈降低趋势。当皮质骨厚度从1 mm增加到2 mm时,综合两种骨密度比较,7号位点种植体及皮质骨von Mises应力值分别下降了32.78%,28.51%,钛支架变形量下降了19.51%。高密度组7号位点种植体、皮质骨von Mises应力值及钛支架变形量分别比低密度组降低16.79%,28.85%,29.26%。 以上结果提示,厚层皮质骨及高密度松质骨有利于种植体及上部修复体的整体应力分散,且皮质骨厚度及松质骨密度改变对All-on-Four种植方案的影响相较于翼上颌种植方案更为显著。 2.3 不同种植方案的应力分布 将两组种植方案下前部位点及后部位点的种植体、皮质骨von Mises应力值及钛支架变形量进行比较分析,All-on-Four组前部位点及后部位点下种植体、皮质骨的von Mises应力值及钛支架变形量均大于翼上颌种植组(P < 0.05),见表5。 "
| [1] LEUNG M, ALGHAMDI R, GUALLART I F, et al. Patient-Related Risk Factors for Maxillary Sinus Augmentation Procedures: A Systematic Literature Review. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2021;41(3): e121-e128. [2] KIM J, LIM Y, KIM B, et al. How Do Parameters of Implant Primary Stability Correspond with CT-Evaluated Bone Quality in the Posterior Maxilla? A Correlation Analysis. Materials. 2021;14(2):270. [3] TESTORI T, WEINSTEIN T, TASCHIERI S, et al. Risk factors in lateral window sinus elevation surgery. Periodontology 2000. 2019;81(1):91-123. [4] RAGUCCI GM, ELNAYEF B, SUÁREZ-LÓPEZ DEL AMO F, et al. Influence of exposing dental implants into the sinus cavity on survival and complications rate: a systematic review. Int J Implant Dent. 2019;5(1):6. [5] DEL FABBRO M, TESTORI T, KEKOVIC V, et al. A Systematic Review of Survival Rates of Osseointegrated Implants in Fully and Partially Edentulous Patients Following Immediate Loading. J Clin Med. 2019; 8(12):2142. [6] GUTIÉRREZ MUÑOZ D, OBRADOR ALDOVER C, ZUBIZARRETA-MACHO Á, et al. Survival Rate and Prosthetic and Sinus Complications of Zygomatic Dental Implants for the Rehabilitation of the Atrophic Edentulous Maxilla: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Biology. 2021;10(7):601. [7] SIGNORINI L, FAUSTINI F, SAMARANI R, et al. Immediate fixed rehabilitation supported by pterygoid implants for participants with severe maxillary atrophy: 1-Year postloading results from a prospective cohort study. J Prosthet Dent. 2021;126(1):67-75. [8] MALÓ P, DE ARAÚJO NOBRE M, LOPES A, et al. The All-on-4 concept for full-arch rehabilitation of the edentulous maxillae: A longitudinal study with 5-13 years of follow-up. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2019;21(4): 538-549. [9] STELLA JP, WARNER MR. Sinus slot technique for simplification and improved orientation of zygomaticus dental implants: a technical note. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2000;15(6):889-893. [10] MALÓ P, RANGERT B, NOBRE M. All-on-4 immediate-function concept with Brånemark System implants for completely edentulous maxillae: a 1-year retrospective clinical study. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2005; 7 Suppl 1:S88-S94. [11] 周磊,岳新新.All-on-Four技术在口腔种植领域中的应用进展[J].口腔疾病防治,2017,25(1):1-7. [12] KWON T, BAIN PA, LEVIN L. Systematic review of short- (5-10 years) and long-term (10 years or more) survival and success of full-arch fixed dental hybrid prostheses and supporting implants. J Dent. 2014; 42(10):1228-1241. [13] BALSHI TJ, WOLFINGER GJ, BALSHI SF. Analysis of 356 pterygomaxillary implants in edentulous arches for fixed prosthesis anchorage. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1999;14(3):398-406. [14] ZHONG J, GUAZZATO M, CHEN J, et al. Effect of different implant configurations on biomechanical behavior of full-arch implant-supported mandibular monolithic zirconia fixed prostheses. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2020;102:103490. [15] MALÓ P, NOBRE MD, LOPES A. The rehabilitation of completely edentulous maxillae with different degrees of resorption with four or more immediately loaded implants: a 5-year retrospective study and a new classification. Eur J Oral Implantol. 2011;4(3):227-243. [16] DI STEFANO DA, AROSIO P, PERROTTI V, et al. Correlation between Implant Geometry, Bone Density, and the Insertion Torque/Depth Integral: A Study on Bovine Ribs. Dent J (Basel). 2019;7(1):25. [17] VAN STEENBERGHE D, JACOBS R, DESNYDER M, et al. The relative impact of local and endogenous patient-related factors on implant failure up to the abutment stage. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2002;13(6):617-622. [18] OZAN O, KURTULMUS-YILMAZ S. Biomechanical Comparison of Different Implant Inclinations and Cantilever Lengths in All-on-4 Treatment Concept by Three-Dimensional Finite Element Analysis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2018;33(1):64-71. [19] LIU X, PANG F, LI Y, et al. Effects of Different Positions and Angles of Implants in Maxillary Edentulous Jaw on Surrounding Bone Stress under Dynamic Loading: A Three-Dimensional Finite Element Analysis. Comput Math Methods Med. 2019;2019:8074096. [20] WANG X, ZHANG T, YANG E, et al. Biomechanical Analysis of Grafted and Nongrafted Maxillary Sinus Augmentation in the Atrophic Posterior Maxilla with Three-Dimensional Finite Element Method. Scanning. 2020;2020:8419319. [21] YALÇıN M, KAYA B, LACIN N, et al. Three-Dimensional Finite Element Analysis of the Effect of Endosteal Implants with Different Macro Designs on Stress Distribution in Different Bone Qualities. Int J Oral Max Impl. 2019;34(3):E43-E50. [22] RODRÍGUEZ X, RAMBLA F, DE MARCOS LOPEZ L, et al. Anatomical study of the pterygomaxillary area for implant placement: cone beam computed tomographic scanning in 100 patients. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2014;29(5):1049-1052. [23] ARAUJO RZ, SANTIAGO JÚNIOR JF, CARDOSO CL, et al. Clinical outcomes of pterygoid implants: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2019;47(4):651-660. [24] IHDE S, PAKA U, JARZB S, et al. Three-Dimensional Determination of the Fusion Zone between the Distal Maxilla and the Pterygoid Plate of the Sphenoid Bone and Considerations for Implant Treatment Procedure. Appl Sci. 2021;11(1):30. [25] 王璨,顾卫平,蒋煜彬,等.不同种植设计对下颌无牙颌应力影响的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(4):573-578. [26] MERICSKE-STERN R, ASSAL P, MERICSKE E, et al. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1995;10(3):345-353. [27] 董海东,汤春波,周储伟,等.6颗种植体支持的上颌无牙颌固定义齿应力分布研究[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2016,32(5):659-663. [28] LISIAK-MYSZKE M, MARCINIAK D, BIELIŃSKI M, et al. Application of Finite Element Analysis in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery-A Literature Review. Materials (Basel, Switzerland). 2020;13(14):3063. [29] CICCIÙ M. Bioengineering Methods of Analysis and Medical Devices: A Current Trends and State of the Art. Materials (Basel, Switzerland). 2020;13(3):797. [30] SCHULLER-GÖTZBURG P, ENTACHER K, PETUTSCHNIGG A, et al. Sinus elevation with a cortical bone graft block: a patient-specific three-dimensional finite element study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2012; 27(2):359-368. [31] OLIVEIRA H, BRIZUELA VELASCO A, RÍOS-SANTOS J, et al. Effect of Different Implant Designs on Strain and Stress Distribution under Non-Axial Loading: A Three-Dimensional Finite Element Analysis. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(13):4738. [32] MIYAMOTO I, TSUBOI Y, WADA E, et al. Influence of cortical bone thickness and implant length on implant stability at the time of surgery--clinical, prospective, biomechanical, and imaging study. Bone. 2005;37(6):776-780. [33] LEKHOLM U, ZARB GA. Patient selection and preparation. Tissue Integrated Prostheses. Chicago: Quintessence Publishing Co. Inc., 1985: 199-209. [34] OKUMURA N, STEGAROIU R, KITAMURA E, et al. Influence of maxillary cortical bone thickness, implant design and implant diameter on stress around implants: a three-dimensional finite element analysis. J Prosthodont Res. 2010;54(3):133-142. [35] SUGIURA T, YAMAMOTO K, HORITA S, et al. The effects of bone density and crestal cortical bone thickness on micromotion and peri-implant bone strain distribution in an immediately loaded implant: a nonlinear finite element analysis. J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2016;46(3):152-165. [36] AYALI A, ALTAGAR M, OZAN O, et al. Biomechanical comparison of the All-on-4, M-4, and V-4 techniques in an atrophic maxilla: A 3D finite element analysis. Comput Biol Med. 2020;123:103880. [37] BECKER W, HUJOEL PP, BECKER BE, et al. Osteoporosis and implant failure: an exploratory case-control study. J Periodontol. 2000;71(4): 625-631. [38] HAKIM SG, GLANZ J, OFER M, et al. Correlation of cone beam CT-derived bone density parameters with primary implant stability assessed by peak insertion torque and periotest in the maxilla. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2019;47(3):461-467. [39] DRAGO C, HOWELL K. Concepts for Designing and Fabricating Metal Implant Frameworks for Hybrid Implant Prostheses. J Prosthodont. 2012;21(5):413-424. [40] 王稚英,李瑞飘.无牙颌即刻负重种植义齿风险因素的研究进展[J].口腔医学研究,2019,35(9):821-826. [41] FISCHER K, STENBERG T. Prospective 10-year cohort study based on a randomized, controlled trial (RCT) on implant-supported full-arch maxillary prostheses. part II: prosthetic outcomes and maintenance. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2013;15(4):498-508. [42] RASMUSSEN EJ. Alternative prosthodontic technique for tissue-integrated prostheses. J Prosthet Dent. 1987;57(2):198-204. [43] TAYLOR TD. Prosthodontic Complications Associated with Implant Therapy. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am. 1991;3(4):979-991. [44] GHERLONE E, CAPPARÉ P, VINCI R, et al. Conventional Versus Digital Impressions for “All-on-Four” Restorations. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2016;31(2):324-330. [45] SIGNORINI L, FAUSTINI F, SAMARANI R, et al. Immediate fixed rehabilitation supported by pterygoid implants for participants with severe maxillary atrophy: 1-Year postloading results from a prospective cohort study. J Prosthet Dent. 2021;126(1):67-75. [46] SANTIAGO JUNIOR JF, VERRI FR, ALMEIDA DADF, et al. Finite element analysis on influence of implant surface treatments, connection and bone types. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016;63:292-300. [47] SCHNEIDER D, MARQUARDT P, ZWAHLEN M, et al. A systematic review on the accuracy and the clinical outcome of computer-guided template-based implant dentistry. Clin Oral Implan Res. 2009;20( Suppl 4):73-86. [48] BRÅNEMARK PI, SVENSSON B, VAN STEENBERGHE D. Ten-year survival rates of fixed prostheses on four or six implants ad modum Brånemark in full edentulism. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1995;6(4):227-231. [49] BALAJI VR, LAMBODHARAN R, MANIKANDAN D, et al. Pterygoid Implant for Atrophic Posterior Maxilla. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2017;9(Suppl 1): S261-S263. |
| [1] | Ye Linqiang, Lu Guoliang, Jiang Xiaobing, Li Zhen, Weng Rui, Liang De, Huang Xuecheng, Feng Yonghong. Biomechanical effects of cement filling location on osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture: a three-dimensional finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(28): 4435-4440. |
| [2] | Wang Yuan, Zhang Yang. Finite element biomechanical analysis of various bone mineral densities on edentulous mandibular four-implant-supported overdentures fixed using Locator attachments [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(22): 3492-3497. |
| [3] | Li Yuan, Song Liang, Zhang Jianguo, Hu Fengling. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of stress distributions in osteoporosis and normal mandibular dental implant-supported overdentures with flat-type and cushion-type magnetic attachments [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(16): 2540-2544. |
| [4] | Wu Chao, Gao Mingjie, Wang Jianzhong, Zhang Yunfeng, Yu Jinghong, Cai Yongqiang, Wang Haiyan, He Yujie, Tong Ling, Li Jiawei, Gao Shang, Wang Xing, Wu Min, Li Zhijun, Li Xiaohe. Finite element analysis of stress and displacement of Lenke 3 adolescent idiopathic scoliosis thoracolumbar spine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(33): 5273-5280. |
| [5] | Shu Qihang, Liao Yijia, Xue Jingbo, Yan Yiguo, Wang Cheng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of a new three-dimensional printed porous fusion cage for cervical vertebra [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3810-3815. |
| [6] | Liu Fushenghua, Xu Jian, Zhao Bingcheng, Wei Gehan, Qin Wenbao. Three-dimensional finite element biomechanical analysis of stage II adult acquired flatfoot deformity after medial column stabilization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(18): 2805-2810. |
| [7] | Zhang Yeming, Wu Di, Zhang Ling, Liu Min, Yu Yong, Cui Jiewen, Yuan Bingqian, Li Qing. Effect of different defect areas of medial femoral condyle cartilage on peripheral cartilage stress: three-dimensional finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(12): 1911-1916. |
| [8] | Chen Junliang, Li Mingxia, Lü Dongmei, He Yun. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of mini implants supported mandibular overdentures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(10): 1491-1495. |
| [9] | Chen Zhen-qiu, Zhang Qiu-xia, Zhou Guang-quan, Pang Zhi-hui, Wei Qiu-shi. Three-dimensional parametric modeling during unicompartmental knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(4): 588-593. |
| [10] | Li Yun-gang, Chen Wei-jian, Li Gui-tao, Sun Hong-tao, Yan Jian-hao, Wang Xiong-chang, Wang Jing. Finite element analysis of different tibial shaft fracture fixed by Locking compression plate under different movement gait [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(4): 612-619. |
| [11] | Li Xiao-lin, Ren Bo-xu, Xu Zi-sheng. Finite element model of rabbit tibial fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(4): 620-624. |
| [12] | Zhang Jia-yu, Cui Jie, Liu Qin, He Hui-yu. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of buccal-lingual mandibular width [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(28): 5164-5170. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||