Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (22): 3460-3466.doi: 10.12307/2022.271
Previous Articles Next Articles
Fabrication and safety evaluation of collagen sponge
Liu Chaoyuan, Gao Tianfang, Huang Wei
- Hangzhou Singclean Medical Products Co., Ltd., Hangzhou 310018, Zhejiang Province, China
-
Received:2020-11-23Revised:2021-01-23Accepted:2021-05-27Online:2022-08-08Published:2022-01-12 -
Contact:Huang Wei, Senior engineer, Hangzhou Singclean Medical Products Co., Ltd., Hangzhou 310018, Zhejiang Province, China -
About author:Liu Chaoyuan, Master, Assistant engineer, Hangzhou Singclean Medical Products Co., Ltd., Hangzhou 310018, Zhejiang Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Chaoyuan, Gao Tianfang, Huang Wei. Fabrication and safety evaluation of collagen sponge[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(22): 3460-3466.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
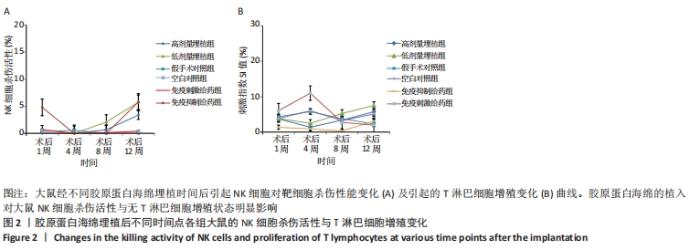
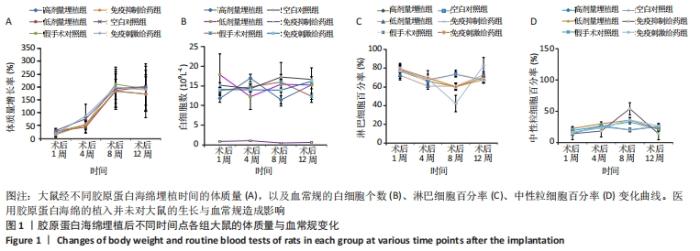
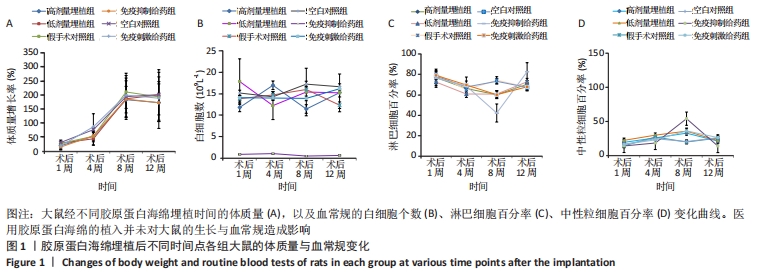
可以看出,各组大鼠体质量都随时间延长呈增加趋势,高剂量埋植组、低剂量埋植组、假手术对照组和空白对照组大鼠的体质量增长趋势一致,同时这4种处理类型的组间比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。结果表明医用胶原蛋白海绵的植入并未对大鼠的饮食、生长造成影响。 2.1.2 大鼠血常规分析 借助血细胞计数仪对大鼠外周血进行了白细胞计数、淋巴细胞百分率、中性粒细胞百分率等进行了结果统计分析,其结果见图1。 外周血白细胞计数:术后1,4,8,12周,医用胶原蛋白海绵高剂量埋植组、低剂量埋植组、假手术对照组和空白对照组的白细胞水平均在正常值范围[对应值为(2.9-20.9)×109 L-1]内,且4组间比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。此外,免疫抑制剂给药组大鼠白细胞数低于正常值范围,且与免疫刺激剂给药组的白细胞计数比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。 淋巴细胞检测:术后1,4,8,12周,医用胶原海绵高剂量埋植组、低剂量埋植组、假手术对照组和空白对照组的淋巴细胞百分率均在正常值范围(56.7%-93.1%),且组间比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。此外,在第8周时,免疫抑制剂给药组较其他各组低,并且低于正常值范围,与免疫刺激剂给药组比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。 外周血的中性粒细胞百分率:术后1,4,8,12周,医用胶原蛋白海绵高剂量埋植组、低剂量埋植组、假手术对照组、空白对照组的中性粒细胞百分率相对稳定,基本都在正常值范围(5.3%-38.1%)内。此外,第8周时,免疫抑制剂给药组的淋巴细胞百分率低于其余各组,并且低于正常值范围,与免疫刺激剂给药组比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。 以上血细胞检测结果表明,医用胶原蛋白海绵埋植大鼠体内后大鼠的外周血白细胞计数、淋巴细胞百分率、中性粒细胞百分率等数据结果同假手术对照组、空白对照组之间无明显差异,基本都维持在正常值范围内,表明了胶原蛋白海绵的植入未对血常规方面产生异常影响。 2.1.3 NK细胞杀伤活性测定 自然杀伤细胞(NK细胞)杀伤活性结果,见图2A。可以看出,在术后1,4,8,12周,医用胶原海绵高剂量埋植组和低剂量埋植组的NK细胞杀伤活性同假手术对照组、空白对照组相近,组间比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。但另一方面从数据的均值上分析发现,第8-12周实验组的NK细胞杀伤活性有上升的趋势。研究表明,胶原蛋白是LAIR-1的高亲和性受体,而LAIR-1在机体中发挥着免疫抑制的作用[23]。将胶原蛋白与LAIR-1结合,对静止NK细胞及活化的NK细胞在行使对靶细胞杀伤时产生明显的抑制作用[24-26]。基于此,作者做出推断:胶原蛋白海绵植入前期对NK细胞活性产生抑制,因而表现为NK细胞杀伤活性较低;随着胶原蛋白在体内的降解(8周前)及胶原蛋白在植入位点的逐渐消失(8-12周),在组织受损部位将重新表现出一定的杀伤活性;同时通过对比低剂量埋植和高剂量埋植组发现,高剂量埋植组在第8,12周的NK细胞杀伤活性较低剂量埋植组低,与其在体内降解仍有残留有关,也有效地支持此推论。 结果表明,埋植医用胶原蛋白海绵的大鼠靶细胞表面自身MHC-I类分子与NK细胞表面抑制性受体之间的平衡仍能保持良好,故而胶原蛋白海绵的植入对大鼠NK细胞杀伤活性无明显影响。 2.1.4 T淋巴细胞增殖实验 T淋巴细胞增殖实验结果如图2B所示。可以看出,在术后第1,4,8,12周,医用胶原海绵高剂量埋植组、低剂量埋植组与假手术对照组、空白对照组的T细胞增殖刺激指数值接近(P > 0.05);而前8周时,免疫抑制给药组的T淋巴细胞增殖刺激指数值同免疫刺激给药组比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。"
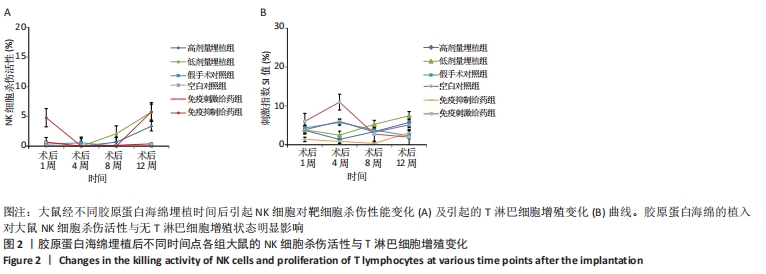
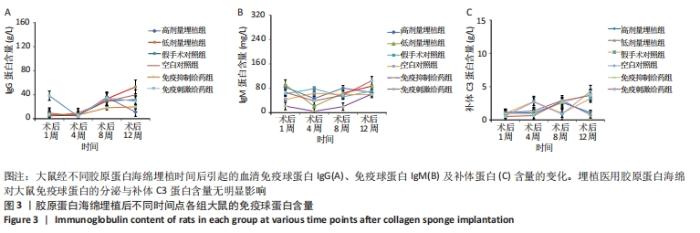
这些结果表明,医用胶原海绵高剂量埋植组、低剂量埋植组、假手术对照组和空白对照组的淋巴细胞对刺激的反应性及功能状态相一致,即胶原蛋白海绵的埋植对大鼠T淋巴细胞增殖状态无明显影响。 2.1.5 免疫球蛋白含量检测 免疫球蛋白含量变化的结果如图3A,B所示。可以看出,在术后第1,4,8,12周,医用胶原海绵高剂量埋植组、低剂量埋植组与假手术对照组、空白对照组的血清IgG蛋白含量接近(P > 0.05)。同样,对IgM蛋白进行含量分析,亦显示出埋植组与对照组无明显差异。此外,对免疫刺激和免疫抑制组对比发现,免疫抑制给药组的血清IgM含量在前8周时显著低于免疫刺激给药组(P < 0.05)。以上血清免疫球蛋白含量统计结果表明,埋植医用胶原蛋白海绵对大鼠免疫球蛋白的分泌无明显影响。 2.1.6 补体C3蛋白含量检测 从图3C中可以看出,术后第1,4,8,12周,医用胶原海绵高剂量埋植组、低剂量埋植组、假手术对照组及空白对照组的血清补体蛋白含量变化趋势较为一致。在4个时间点,6种不同大鼠处理方式的大鼠补体C3蛋白含量无明显差异。这样的结果表明,医用胶原蛋白海绵的埋植对大鼠体内补体C3蛋白含量无明显影响。"

| [1] BEHRENS AM, SIKORSKI MJ, KOFINAS P. Hemostatic strategies for traumatic and surgical bleeding. Journal of Biomed Mater Res Part A. 2014;102(11):4182-4194. [2] SHEN W, ZHENG Z, RAN J, et al. Long-term effects of knitted silk-collagen sponge scaffold on anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction and osteoarthritis prevention. Biomaterials. 2014;35(28):8154-8163. [3] BARNARD J, MILLNER R. A review of topical hemostatic agents for use in cardiac surgery. Ann Surg. 2009;88(4):1377-1383. [4] TOMPECK A, GAJDHAR AUR, DOWLING M, et al. A comprehensive review of topical hemostatic agents: the good, the bad, and the novel. J Trauma Acute Care. 2019;88(1):e1-e21. [5] 孙国飞,刘建恒,张里程,等.院前创伤急救止血敷料:优势与问题及应用前景[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(22):3575-3582. [6] SLEZAK P, MONFORTE X, FERGUSON J, et al. Properties of collagen-based hemostatic patch compared to oxidized cellulose-based patch. J Mater Sci Mater M. 2018;29(6):71. [7] JIN J, JI Z, XU M, et al. Microspheres of carboxymethyl chitosan, sodium alginate, and collagen as a hemostatic agent in vivo. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2018;4(7):2541-2551. [8] CHENG X, SHAO Z, LI C, et al. Isolation, Characterization and evaluation of collagen from jellyfish rhopilema esculentum kishinouye for use in hemostatic applications. Plos One. 2017;12(1):e0169731. [9] 景沛.胶原蛋白质(Ⅰ-XⅫ型)[J].生命的化学,1995,15(6):30-31. [10] FRIESS W. Collagen–biomaterial for drug delivery. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 1998;45:113-136. [11] ACHNECK HE, SILESHI B, JAMIOLKOWSKI RM, et al. A comprehensive review of topical hemostatic agents: efficacy and recommendations for use. Ann Surg. 2010;251(2):217-228. [12] PALLASKE F, PALLASKE A, HERKLOTZ K, et al. The significance of collagen dressings in wound management: a review. J Wound Care. 2018;27(10):692-702. [13] SILESHI B, ACHNECK HE, LAWSON JH. Management of surgical hemostasis: topical agents. Vascular. 2008;16 Suppl 1:S22-S28. [14] MANON-JENSEN T, KJELD NG, KARSDAL MA. Collagen-mediated hemostasis. J Thromb Haemost. 2016;14:438-448. [15] FLECK CA, SIMMAN R. Modern collagen wound dressings: function and purpose. J Am Coll Cert Wound Spec. 2010;2(3):50-54. [16] AN B, LIN Y, BRODSKY B. Collagen interactions: drug design and delivery. Adv Drug Deliver Rev. 2016;97:69-84. [17] SHEEHY EJ, CUNNIFFE GM, O’BRIEN FJ. 5-Collagen-based biomaterials for tissue regeneration and repair. Peptides and Proteins as Biomaterials for Tissue Regeneration and Repair. 2018:27-150. [18] GELSE K, PÖSCHL E, AIGNER T. Collagens--structure, function, and biosynthesis. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2003;55(12):1531-1546. [19] 陆美娇.动物源性修复材料的病毒灭活与免疫原的观察[D].烟台:烟台大学,2015. [20] No. 97D-0411, Guidance for Industry: The sourcing and processing of gelatin to reduce the potential risk by bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE) in FDA-regulated products for human.1997. [21] 史新立,谭芳奕,王召旭,等疯牛病病原体研究及动物源性医疗器械产品安全性思考[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2006,20(20):1138-1144. [22] 国家食品药品监督管理局.血液制品去除/灭活病毒技术方法及验证指导原则[S].2002. [23] LEBBINK RJ. Collagens are functional, high affinity ligands for the inhibitory immune receptor LAIR-1. J Exp Med. 2006;203(6):1419-1425. [24] MEYAARD L, ADEMA G, CHANG C, et al. LAIR-1, a novel inhibitory receptor expressed on human mononuclear leukocytes. Immunity. 1997;7:283-290. [25] POGGI A, TOMASELLO E, REVELLO V, et al. p40 molecule regulates NK cell activation mediated by NK receptors for HLA class I antigens and TCR-mediated triggering of T lymphocytes.Int Immunol. 1997;9:1271-1279. [26] 付强.LAIRs和胶原分子调节人早孕蜕膜NK细胞功能的分子机制[D].上海:复旦大学,2014. [27] 国家药品监督管理局.动物源性医疗器械注册技术审查指导原则(2017年版)[S]. 2017. [28] NAGHSHINEH N, TAHVILDARI K, NOZARI M. Preparation of chitosan, sodium alginate, gelatin and collagen biodegradable sponge composites and their application in wound healing and curcumin delivery. J Polym Environ. 2019;27:2819-2830. [29] FUKUSHIMA SI,YONETSU M, YASUI T. Polarization-resolved second-harmonic-generation imaging of dermal collagen fiber in prewrinkled and wrinkled skins of ultraviolet-B-exposed mouse. J Biomed Opt. 2018;24(3):1-8. [30] ARAGONA F. Is bovine collagen safe? J Duro. 1991;97(6):279-281. [31] LYNN AK, YANNAS IV, BONFIELD W. Antigenicity and immunogenicity of collagen. J Biomed Mater Res Part B. 2010;71B(2):343-354. [32] BONDIOLI E, FINI M, VERONESI F, et al. Development and evaluation of a decellularized membrane from human dermis. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2014;8(4):325-336. [33] INABA S, NAGAHARA S, MAKITA N, et al. Atelocollagen-mediated systemic delivery prevents immunostimulatory adverse effects of siRNA in mammals. Mol Ther. 2012;20(2):356-366. [34] ZHAO W, CHI C, ZHAO Y, et al. Preparation, physicochemical and antioxidant properties of acid- and pepsin-soluble collagens from the swim bladders of miiuycroaker (miichthysmiiuy). Mar Drugs. 2018; 16(5):161. [35] BAE JE, KIM CK, KIM S, et al. Virus inactivation during the manufacture of a collagen type I from bovine hides. Korean J Microbio. 2012;48(4): 314-318. [36] LI L, ZHAO Y,HE Y, et al. Physicochemical and antioxidant properties of acid- and pepsin-soluble collagens from the scales of miiuycroaker (miichthysmiiuy). Mar Drugs. 2018;16(10): 394. [37] BLANCO M, SOTELO CG, RICARDO I, et al. New strategy to cope with common fishery policy landing obligation: collagen extraction from skins and bones of undersized hake (merlucciusmerluccius). Polymers. 2019;11(9):1485. [38] MONIRUZZAMAN SM, TAKAHASHI K, NESA NU, et al. Characterization of acid- and pepsin-soluble collagens extracted from scales of carp and lizardfish caught in Japan, Bangladesh and Vietnam with a focus on thermostability. Food Sci and Tech Res. 2019;25(2):331-340. [39] CALIGIURI MA. Human natural killer cells. Blood. 2008;112(3):461-469. [40] MELISSA, A, GELLER, JEFFREY J, et al. Use of allogeneic NK cells for cancer immunotherapy. Immunotherapy. 2011;3(12):1445-1459. [41] SNYDER MR, WEYAND CM, GORONZY JJ. The double life of NK receptors: stimulation or co-stimulation? Trends Immunol. 2004; 25(1):25-32. [42] ALI RI, KUMAR S, ALI RA, et al. B and T cell epitope mapping and study the humoral and cell mediated immune response to B-T constructs of YscF antigen of Yersinia pestis. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 2013;36(4):365-378. |
| [1] | He Guanyu, Xu Baoshan, Du Lilong, Zhang Tongxing, Huo Zhenxin, Shen Li. Biomimetic orientated microchannel annulus fibrosus scaffold constructed by silk fibroin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 560-566. |
| [2] | Han Zhi, Wang Zhimiao, Gaxi Sijia, Lu Qingling, Guo Tao. Tissue engineered cartilage constructed by polyurethane composite chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(22): 3455-3459. |
| [3] | Meng Lulu, Liu Hao, Liu Han, Zhang Jun, Li Ruixin, Gao Lilan. Mechanical properties of silk fibroin/type I collagen/hydroxyapatite scaffolds based on low-temperature 3D printing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(22): 3550-3555. |
| [4] | Wang Kun, He Benxiang. Asperosaponin VI therapy for Achilles tendinopathy in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 211-217. |
| [5] | Shan Zhengming, Tao Shuchun, Hu Chunmei, Zhang Zhiyuan, Ding Yinan, He Mengcheng, Tang Qiusha. Extraction, identification and proteomic analysis of exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(19): 3036-3042. |
| [6] | Kong Lingyue, Hu Yongcheng, Han Changxu. Echinops latifolius, a Mongolian medicine, for treating cartilage injury in a rabbit model of knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(17): 2649-2653. |
| [7] | Wang Quanzhen, Xiao Yingfeng, Wan Shengxiang, Zhang Jian, Zhou Bo, Meng Fanbin, Yu Longbiao, Yu Fei. Effect of connective tissue growth factor on the secretion of type I and III collagen in tenocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(17): 2673-2677. |
| [8] | Zhang Hongmei, Sun Xirao, Wang Chengyue. Effect of polymethyl methacrylate/mineralized collagen/Mg-Ca composite material on osteogenic differentiation of mouse preosteoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(16): 2498-2503. |
| [9] | Yuan Yihang, Xu Menghan, Niu Xufeng. Gelatin collagen composite hydrogel and inducible factor regulate differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into hepatocyte-like cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(16): 2510-2515. |
| [10] | Xu Xiang, Wu Yimin, Li Shuwen, Ma Libo, Wang Yupeng, Yu Yingnan, Sun Tao, Zhang Yuan, Ren Wei, Yin Heping. Histological comparison between goat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and adhesive fibrin for the repair of annulus fibrosus defect of intervertebral discs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(13): 1974-1978. |
| [11] | Hu Kai, Chen Weiming, Luo Jingwan, Li Miao, Wang Jingjing, Li Mao, Shen Yajun, Chen Jinfa, Bai Yulong. Effect of peracetic acid/ethanol on the properties of allogeneic skin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(10): 1537-1543. |
| [12] | Zhao Zixi, Xu Jun, Ding Min, Li Xiwen, Zhang Jinghang, Wang Penghua. Changes of type I and III collagen and matrix metalloproteinase 2 and 9 on the wound of diabetic foot ulcer with external application of medical collagen dressing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(10): 1544-1550. |
| [13] | Yang Tengyun, Li Yanlin, Liu Dejian, Wang Guoliang, Zheng Zhujun. Chondrogenic differentiation of peripheral blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells induced by transforming growth factor beta 3: a dose-effect relationship [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(1): 45-51. |
| [14] | Shen Jinbo, Zhang Lin. Micro-injury of the Achilles tendon caused by acute exhaustive exercise in rats: ultrastructural changes and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1190-1195. |
| [15] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||