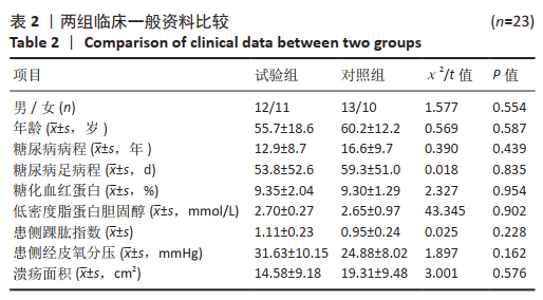
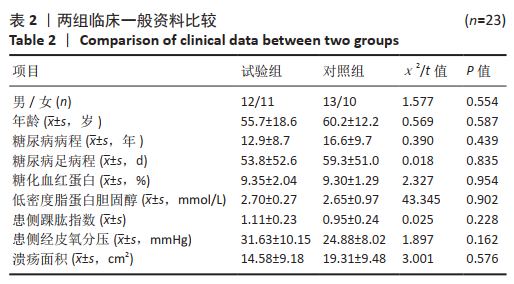
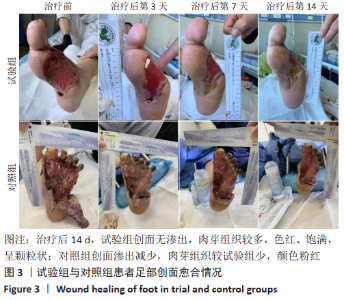
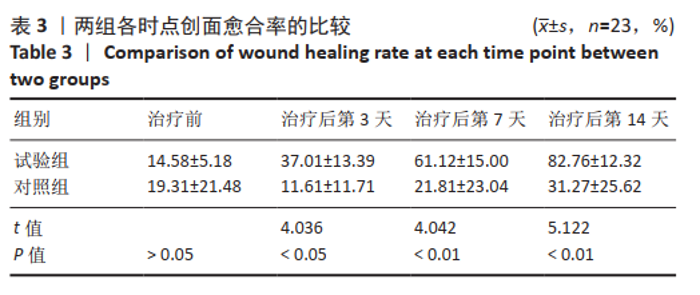
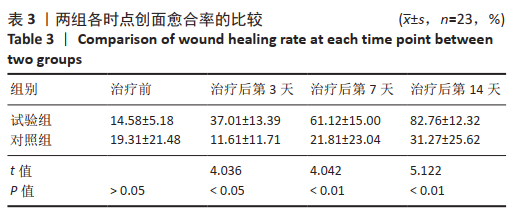
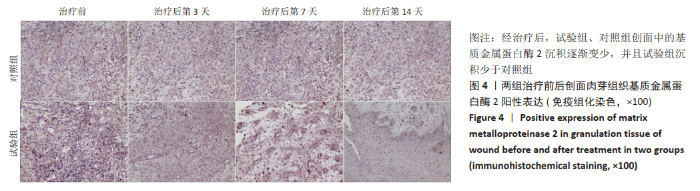
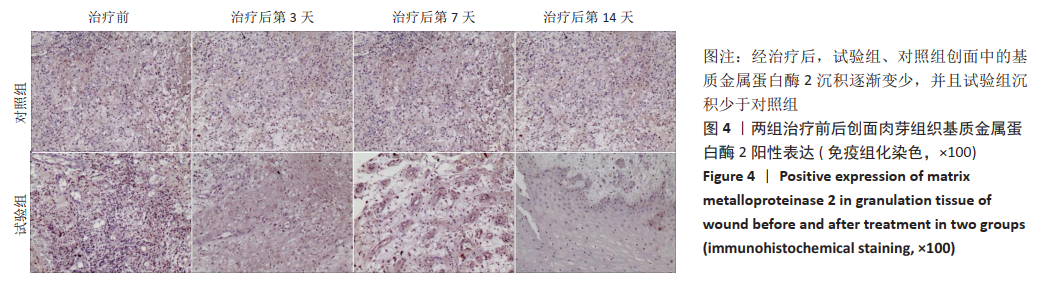
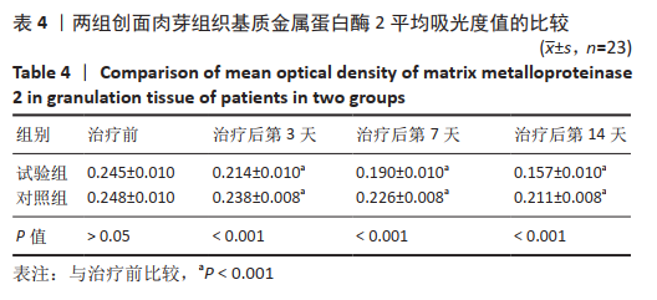
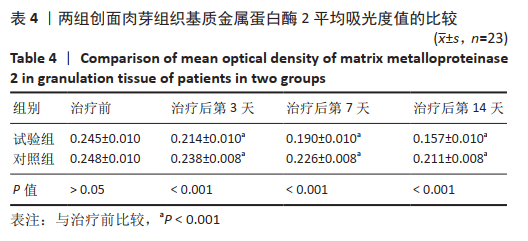
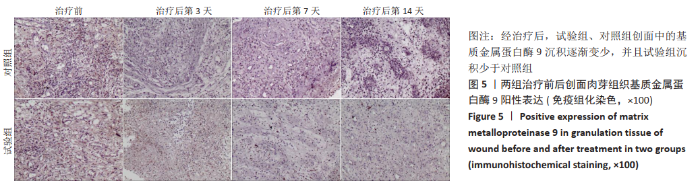
[1] 付小兵.如何在中国建立规范化的体表慢性难愈合创面防控培训与教育体系: 我们的初步实践与体会[J].感染•炎症•修复,2019, 20(1):23-26.
[2] 宁光,毕宇芳.中国成人糖尿病流行与控制现状[A].中国疾病预防控制中心达能营养中心.营养与糖尿病并发症——达能营养中心第十六届学术会议论文集[C].中国疾病预防控制中心达能营养中心:中国疾病预防控制中心达能营养中心,2013:5.
[3] REIBER GE, RAUGI GJ. Preventing foot ulcers and amputations in diabetes. Lancet. 2005;366(9498):1676-1677.
[4] LAVERY LA, ARMSTRONG DG, WUNDERLICH RP, et al. Risk factors for foot infections in individuals with diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2006;29(6): 1288-1293.
[5] MURPHY-LAVOIE HM, BHIMJI SS. Diabetic, Foot Infections. Statpearls. Treasure Island (FL): Statpearls publishingLLC, 2017.
[6] WHITING DR, GUARIGUATA L, WEIL C, et al.IDF diabetes atlas: global estimates of the prevalence of diabetes for 2011 and 2030. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2011;94(3):311-321.
[7] APELQVIST J, BAKKER K, VAN HOUTUM WH, et al. International consensus and practical guidelines on the management and the prevention of the diabetic foot. International Working Group on the Diabetic Foot. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2000;16 Suppl 1:S84-92.
[8] HUSSAIN Z, THU HE, SHUID AN, et al. Recent Advances in Polymer-based Wound Dressings for the Treatment of Diabetic Foot Ulcer: An Overview of State-of-the-art. Curr Drug Targets. 2018;19(5):527-550.
[9] KOZLOWSKA J, SIONKOWSKA A, SKOPINSKA-WISNIEWSKA J, et al. Northern pike (Esox lucius) collagen: Extraction, characterization and potential application. Int J Biol Macromol. 2015;81:220-227.
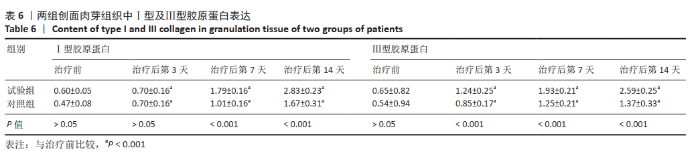
[10] An B, Lin YS, Brodsky B. Collagen interactions: Drug design and delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2016;97:69-84.
[11] 刘慧玲,王栋,章金刚.胶原蛋白在临床医学中的应用[J].北京生物医学工程,2005,24(3):239-241.
[12] CALVI EN, NAHAS FX, BARBOSA MV, et al. Collagen fibers in the rectus abdominis muscle of cadavers of different age. Hernia. 2014;18: 527-533.
[13] 卫秀洋,王万明,陈勇忠,等.胶原蛋白海绵复合bFGF 促进兔胫骨外露创面愈合的实验研究[J].中国医药指南,2012,10(23):399-401.
[14] SIGNORELLI SS, MALAPONTE G, LIBRA M, et al. Plasma levels and zymograhic activities of matrix metalloproteinases 2and 9 in type 2 diabetics with pedpheral arterial disease. Vase Med. 2005;10:1-6.
[15] 宋飞,简华刚.糖尿病足溃疡创面床准备及清创处理[J].创伤外科杂志,2011,13(2):180-182.
[16] SOOD A, GRANICK MS, TOMASELLI NL. Wound Dressings and Comparative Effectiveness Data. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2014;3(8):511-529.
[17] 林源,王润秀,农庆文,等.糖尿病创面愈合过程的动态组织学特征[J].中国临床康复,2005,9(3):118-120,273.
[18] GARY SIBBALD R, WOO KY. The biology of chronic foot ulcers in persons with diabetes. Diabetes/metabolism research and reviews. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2008;24 Suppl 1:S25-30.
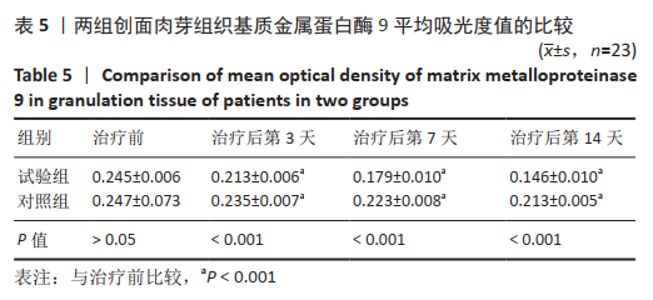
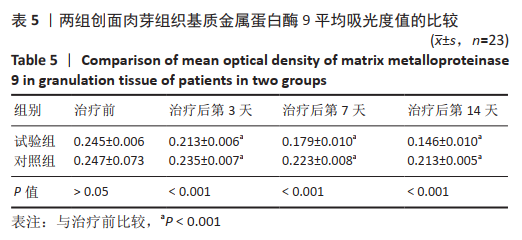
[19] 陈端凯,岑小宁,包崇婵,等.MEBT/MEBO通过PTEN/AKT通路对慢性难愈合创面中基质金属蛋白酶表达的影响[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2020,40(4):459-464.
[20] 陈运起,郑伟民.老年冠状动脉不同病变程度患者治疗后斑块稳定性的临床分析[J].中华老年心脑血管病杂志,2020,22(11): 1209-1211.
[21] 韩隆胤,钱凯,杜彦仪,等.断藤益母汤对胶原诱导性关节炎大鼠软骨破坏的作用及机制研究[J/OL].中华中医药学刊:1-14[2020-11-12].http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/21.1546.R.20201020.0927.034.html.
[22] LIU Y, MIN D, BOLTON T, et al. Increased Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 Predicts Poor Wound Healing in Diabetic Foot Ulcers. Diabetes Care. 2009;32(1): 117-119.
[23] 任国强,李炳辉,李恭驰,等.糖尿病创面基质金属蛋白酶9 对血管内皮生长因子表达的影响[J].中华损伤与修复杂志(电子版), 2017,12(2):123-127.
[24] YANG K, LIU X, LIU Y, et al. DC-SING and Toll-like receptor 4 mediate oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced inflammatory responses in macrophages. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):3296.
[25] REISS MJ, HAN YP, GARCIA E, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 delays wound healing in a murine wound model. Surgery. 2009;147(2): 295-302.
[26] 冯洁,农晓琳.基质金属蛋白酶及其抑制剂在糖尿病皮肤创面愈合中作用的研究进展[J].山东医药,2018,58(38):106-109.
[27] SHARMA AC, SRIVASTAVA RN, SRIVASTAVA SR, et al. Evaluation of the association between a single-nucleotide polymorphism of bone morphogenetic proteins 5 gene and risk of knee osteoarthritis. J Postgrad Med. 2017;63(3):151-156. |