Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (5): 730-735.doi: 10.12307/2022.119
Previous Articles Next Articles
Granulocyte colony-stimulating factors improve myocardial fibrosis in rats with myocardial infarction
Yin Tingting1, Du Dayong2, Jiang Zhixin2, Liu Yang2, Liu Qilin1, Li Yuntian1, 2
- 1The Second School of Clinical Medicine, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510000, Guangdong Province, China; 2The 305th Hospital of Chinese PLA, Beijing 100000, China
-
Received:2021-02-25Revised:2021-02-27Accepted:2021-04-12Online:2022-02-18Published:2021-11-02 -
Contact:Li Yuntian, MD, Chief physician, The Second School of Clinical Medicine, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510000, Guangdong Province, China; The 305th Hospital of Chinese PLA, Beijing 100000, China -
About author:Yin Tingting, Master, The Second School of Clinical Medicine, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510000, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the Military Coronary Heart Disease Diagnosis and Treatment Center Construction Project, No. 09GXB (to LYT); the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 30971235 (to JZX [project participant])
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yin Tingting, Du Dayong, Jiang Zhixin, Liu Yang, Liu Qilin, Li Yuntian. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factors improve myocardial fibrosis in rats with myocardial infarction[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 730-735.
share this article
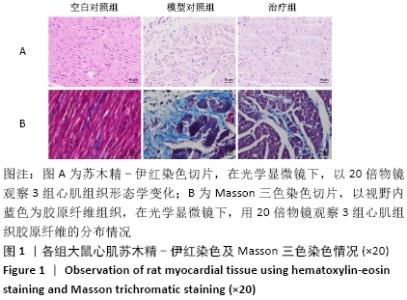
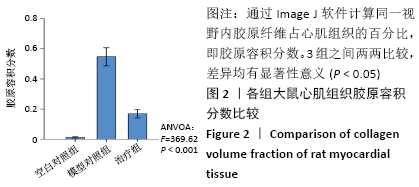
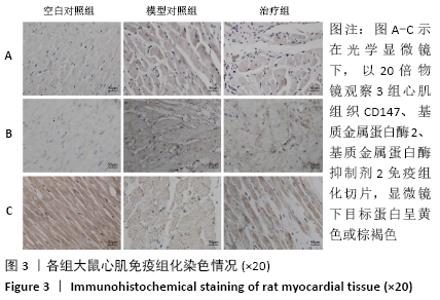
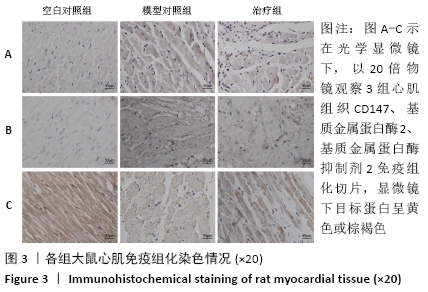
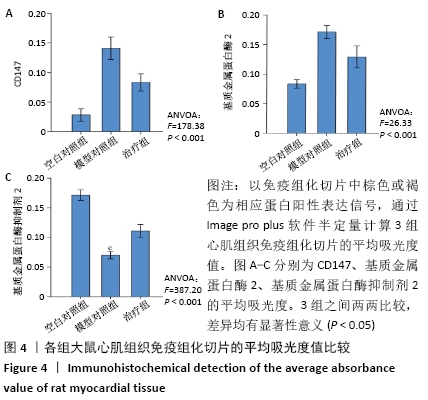
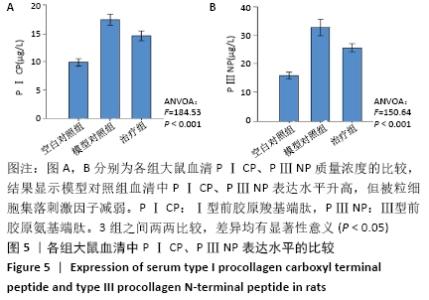
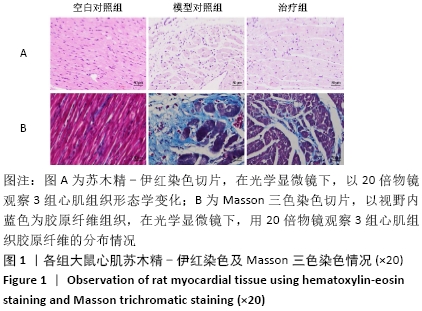
2.1 实验动物数量分析 实验选用大鼠27只,分为3组,造模成功的大鼠有14只,成模率为70%。 2.2 各组大鼠苏木精-伊红染色情况 空白对照组心肌细胞排列规整,心肌肌束完整,染色均一,心肌间质无或少量的炎性细胞浸润;模型对照组心肌细胞排列紊乱,坏死心肌细胞被大量松散的纤维结缔组织替代,大量的单核巨噬细胞、淋巴细胞、浆细胞聚集浸润;治疗组与模型对照组相比,心肌细胞排列相对规整,纤维结缔组织增生情况明显减少,炎症细胞散在分布,见图1A。 2.3 各组大鼠Masson染色及胶原容积分数情况 显微镜下红染的是正常心肌,蓝染的是胶原纤维组织,见图1B。空白对照组以整齐排列的红染心肌细胞为主,仅有少量的蓝染胶原纤维分布于部分血管周围;与空白对照组相比,模型对照组的胶原纤维显著增多(P < 0.001),分布于梗死区延伸至梗死边缘区;治疗组的胶原纤维含量则较模型对照组显著减少(P < 0.001),见图2。 "
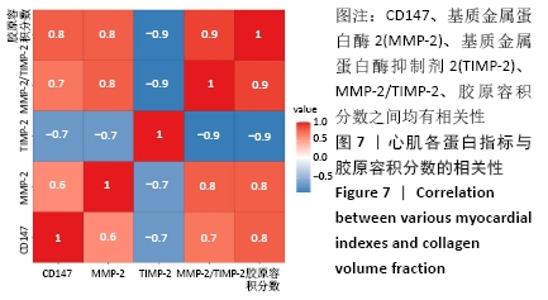
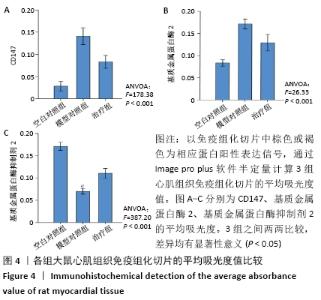
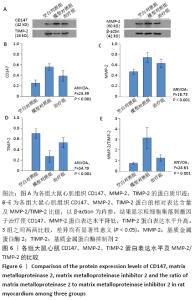
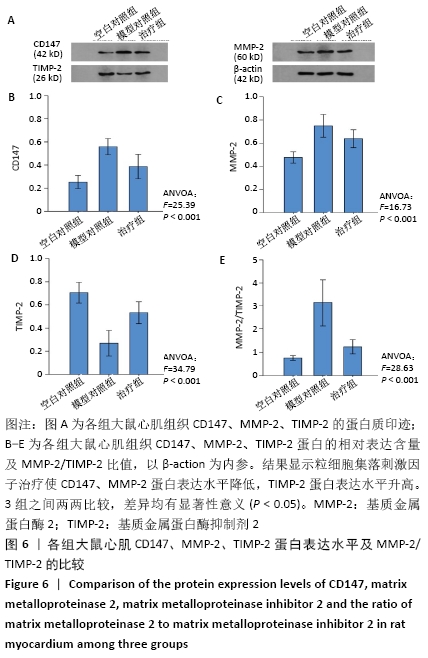
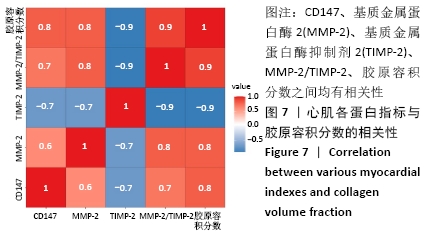
与模型对照组相比,治疗组心肌组织CD147、基质金属蛋白酶2蛋白表达水平显著下降,基质金属蛋白酶抑制剂2蛋白表达水平显著增加,基质金属蛋白酶2/基质金属蛋白酶抑制剂2的比例显著降低(P < 0.001),表明在急性心肌梗死后存在基质金属蛋白酶2/基质金属蛋白酶抑制剂2比例的失衡,可能与CD147/基质金属蛋白酶2信号通路激活相关。 2.7 心肌各蛋白指标与胶原容积分数的相关性 CD147、基质金属蛋白酶2、基质金属蛋白酶2/基质金属蛋白酶抑制剂2与胶原容积分数成正相关(r=0.8,0.8,0.9,P < 0.05),基质金属蛋白酶抑制剂2与胶原容积分数成负相关(r=-0.9, P < 0.05);CD147与基质金属蛋白酶2、基质金属蛋白酶2/基质金属蛋白酶抑制剂2成正相关(r=0.8,0.7,P < 0.05)。这些数据表明,CD147是基质金属蛋白酶2的上游刺激因子,可通过上调基质金属蛋白酶2含量,增加基质金属蛋白酶2/基质金属蛋白酶抑制剂2比值,加剧心肌纤维化,见图7。"
| [1] NICHOLS M, TOWNSEND N, SCARBOROUGH P, et al. Cardiovascular disease in Europe 2014: epidemiological update (vol 35, pg 2950, 2014). Eur Heart J. 2014;35(42):2950-2959. [2] YEH RW, SIDNEY S, CHANDRA M, et al. Population trends in the incidence and outcomes of acute myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 2010;362(23):2155-2165. [3] SCALISE R, DE SARRO R, CARACCIOLO A, et al. Fibrosis after Myocardial Infarction: An Overview on Cellular Processes, Molecular Pathways, Clinical Evaluation and Prognostic Value. Med Sci (Basel). 2021;9(1):16. [4] LAI TM, KUO PJ, LIN CY, et al. CD147 self-regulates matrix metalloproteinase-2 release in gingival fibroblasts after coculturing with U937 monocytic cells. J Periodontol. 2020;91(5):651-660. [5] PICCOLI MT, GUPTA SK, VIERECK J, et al. Inhibition of the Cardiac Fibroblast-Enriched lncRNA Meg3 Prevents Cardiac Fibrosis and Diastolic Dysfunction. Circ Res. 2017;121(5):575-583. [6] RAMIREZ-CARRACEDO R, TESORO L, HERNANDEZ I, et al. Ivabradine-Stimulated Microvesicle Release Induces Cardiac Protection against Acute Myocardial Infarction. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(18):6566. [7] GÖMÖRI K, SZABADOS T, KENYERES É, et al. Cardioprotective Effect of Novel Matrix Metalloproteinase Inhibitors. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(19):6990. [8] GUARNER V, NIETO-LIMA B, CANO-MARTÍNEZ A, et al. GCSF Partially Repairs Heart Damage Induced by Repetitive β-adrenergic Stimulation in Mice: Potential Role of the Mobilized Bone Marrow-derived Cells. Int J Pharmacol. 2007;12(7):689-700. [9] POURTAJI A, JAHANI V, MOALLEM S, et al. Application of G-CSF in Congestive Heart Failure Treatment. Curr Cardiol Rev. 2019;15(2):83-90. [10] 龙雨, 邓娟娟, 曹楚珩, 等. 冠状动脉结扎法致大鼠心肌纤维化模型的建立方法探讨[J]. 湖南中医杂志,2018,34(6):158-159. [11] ORLIC D, KAJSTURA J, CHIMENTI S, et al. Mobilized bone marrow cells repair the infarcted heart, improving function and survival. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98(18):10344-10349. [12] YE L, D’AGOSTINO G, LOO SJ, et al. Early Regenerative Capacity in the Porcine Heart. Circulation. 2018;138(24):2798-2808. [13] BO B, LI S, ZHOU K, et al. The Regulatory Role of Oxygen Metabolism in Exercise-Induced Cardiomyocyte Regeneration. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:664527. [14] METES-KOSIK N, LUPTAK I, DIBELLO PM, et al. Both selenium deficiency and modest selenium supplementation lead to myocardial fibrosis in mice via effects on redox-methylation balance. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2012;56(12):1812-1824. [15] KWON SG, PARK I, KWON YW, et al. Role of stem cell mobilization in the treatment of ischemic diseases. Arch Pharm Res. 2019;42(3):224-231. [16] TAO Z, TAN S, CHEN W, et al. Stem Cell Homing: a Potential Therapeutic Strategy Unproven for Treatment of Myocardial Injury. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2018;11(5): 403-411. [17] UEDA K, TAKANO H, HASEGAWA H, et al. Granulocyte colony stimulating factor directly inhibits myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury through Akt-endothelial NO synthase pathway. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2006;26(6):e108-e113. [18] TAVAKOLI F, OSTAD SN, KHORI V, et al. Outcome improvement of cellular cardiomyoplasty using triple therapy: mesenchymal stem cell+erythropoietin+vascular endothelial growth factor. Eur J Pharmacol. 2013; 714(1-3):456-463. [19] WANG W, YE S, ZHANG L, et al. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor attenuates myocardial remodeling and ventricular arrhythmia susceptibility via the JAK2-STAT3 pathway in a rabbit model of coronary microembolization. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2020;20(1):85. [20] FORECHI L, BALDO MP, MEYERFREUND D, et al. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor improves early remodeling in isoproterenol-induced cardiac injury in rats. Pharmacol Rep. 2012;64(3):643-649. [21] DECOUX A, LINDSEY ML, VILLARREAL F, et al. Myocardial matrix metalloproteinase-2: inside out and upside down. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2014;77:64-72. [22] BRIEST W. Significance of matrix metalloproteinases in norepinephrine-induced remodelling of rat hearts. Cardiovasc Res. 2003;57(2):379-387. [23] CRUZ JO, SILVA AO, RIBEIRO JM, et al. Epigenetic Regulation of the N-Terminal Truncated Isoform of Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 (NTT-MMP-2) and Its Presence in Renal and Cardiac Diseases. Front Genet. 2021;12:637148. [24] BELL RM, KUNUTHUR SP, HENDRY C. Matrix metalloproteinase inhibition protects CyPD knockout mice independently of RISK/mPTP signalling: a parallel pathway to protection. Basic Res Cardiol. 2013;108(2):1-12. [25] KRZYWONOS-ZAWADZKA A, FRANCZAK A, SAWICKI G, et al. Mixture of MMP-2, MLC, and NOS Inhibitors Affects NO Metabolism and Protects Heart from Cardiac I/R Injury. Cardiol Res Pract. 2020;2020:1561478. [26] GABISON EE, MOURAH S, STEINFELS E, et al. Differential expression of extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer (CD147) in normal and ulcerated corneas: role in epithelio-stromal interactions and matrix metalloproteinase induction. Am J Pathol. 2005;166(1):209-219. [27] LAI TM, KUO PJ, LIN CY, et al. CD147 self-regulates matrix metalloproteinase-2 release in gingival fibroblasts after coculturing with U937 monocytic cells. J Periodontol. 2020;91(5):651-660. [28] AOKI M, KOGA K, HAMASAKI M, et al. Emmprin, released as a microvesicle in epithelioid sarcoma, interacts with fibroblasts. Int J Oncol. 2017;50(6):2229-2235. [29] LOYER X, ZLATANOVA I, DEVUE C, et al. Intra-Cardiac Release of Extracellular Vesicles Shapes Inflammation Following Myocardial Infarction. Circ Res. 2018; 123(1):100-106. [30] RAMIREZ-CARRACEDO R, TESORO L, HERNANDEZ I, et al. Ivabradine-Stimulated Microvesicle Release Induces Cardiac Protection against Acute Myocardial Infarction. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(18). [31] HASANEEN NA, CAO J, PULKOSKI-GROSS A, et al. Extracellular Matrix Metalloproteinase Inducer (EMMPRIN) promotes lung fibroblast proliferation, survival and differentiation to myofibroblasts. Respir Res. 2016;17:17. [32] GYÖRFI AH, MATEI AE, DISTLER J. Targeting TGF-β signaling for the treatment of fibrosis. Matrix Biol. 2018;68-69:8-27. [33] LI X, CHU G, ZHU F, et al. Epoxyeicosatrienoic acid prevents maladaptive remodeling in pressure overload by targeting calcineurin/NFAT and Smad-7. Exp Cell Res. 2020;386(1):111716. [34] GONZÁLEZ MN, DEY N, GARG NJ, et al. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor partially repairs the damage provoked by Trypanosoma cruzi in murine myocardium. Int J Cardiol. 2013;168(3):2567-2574. [35] GUO Y, SU L, LI Y, et al. The synergistic therapeutic effect of hepatocyte growth factor and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor on pulmonary hypertension in rats. Heart Vessels. 2014;29(4):520-531. |
| [1] | Chen Xianghe, Liu Bo, Yang Kang, Lu Pengcheng, Yu Huilin. Treadmill exercise improves the myocardial fibrosis of spontaneous type 2 diabetic mice: an exploration on the functional pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1210-1215. |
| [2] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [3] | Nie Huijuan, Huang Zhichun. The role of Hedgehog signaling pathway in transforming growth factor beta1-induced myofibroblast transdifferentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 754-760. |
| [4] | Lang Limin, He Sheng, Jiang Zengyu, Hu Yiyi, Zhang Zhixing, Liang Minqian. Application progress of conductive composite materials in the field of tissue engineering treatment of myocardial infarction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3584-3590. |
| [5] | Sun Weixing, Zhao Yongchao, Zhao Ranzun. Mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in the treatment of myocardial infarction: problems, crux and new breakthrough [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3103-3109. |
| [6] | Zhang Lei, Yan Yu, Liu Yin, Xu Long, Yang Xinglei, Liu Yujia. An 8-week aerobic exercise improves obesity-induced myocardial fibrosis: role of nuclear factor-erythroid 2 p45-related factor 2 pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(17): 2650-2656. |
| [7] | Chen Siyu, Li Yannan, Xie Liying, Liu Siqi, Fan Yurong, Fang Changxing, Zhang Xin, Quan Jiayu, Zuo Lin. Thermosensitive chitosan-collagen composite hydrogel loaded with basic fibroblast growth factor retards ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2472-2478. |
| [8] | Shang Qingqing, Zhou Jianye. Combination of hyaluronic acid hydrogel and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promotes cardiac function after myocardial infarction in rats (II) [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(34): 5559-5563. |
| [9] | Yin Lian, Zhao Jin, Lei Xuemei, Li Miaomiao, Wang Kun, Zhang Tingran, Luo Jiong. Effect of exercise-induced irisin on myocardial fibrosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(23): 3730-3736. |
| [10] |
Chen Siyu, Zhang Tao, Yin Wenjuan, Cai Lei, Li Yannan, Xie Liying, Zuo Lin.
Changes of cardiac function in rats with myocardial
infarction after umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation:
a meta-analysis |
| [11] | He Jigang, Xie Qiaoli, Wang Zihao, Yan Dan, Zhang Hongbo. Time-volume variation in miR-330-3p expression in GATA-4-overexpressing bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell exosomes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(29): 4617-4622. |
| [12] | Zhu Xianhua, Chen Feng, Liu Chongdong, Zhou Wei, Tang Xinhua . Dextran/poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) microspheres combined with three growth factors promote neovascularization in ischemic lower limbs of rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(26): 4142-4147. |
| [13] | Zhang Pin, Guo Ying, Gao Yajie, Wang Zhendong, Li Baiyi, Zhang Xiaomin, Niu Yuhu, Liu Zhizhen, Ma Lihui, Niu Bo, Guo Rui. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells promote myocardial repair after myocardial infarction under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(17): 2630-2636. |
| [14] | Zhao Liang, Qiu Xiaona, Li Xiafei. Research progress of myocardial scaffolds in the treatment of myocardial infarction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(14): 2279-2284. |
| [15] | Hu Ji-hong, Zhao Jing-miao, Wang Qiu-ping, Jia Jia, Lu Juan, Jin Hua, Hou Qian. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on voltage-gated K+ channel proteins and cytokines in the infarcted myocardium of rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(9): 1389-1394. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 218
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 461
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||