Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (17): 2630-2636.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1716
Previous Articles Next Articles
Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells promote myocardial repair after myocardial infarction under hypoxia
Zhang Pin1, Guo Ying1, Gao Yajie1, Wang Zhendong1, Li Baiyi1, Zhang Xiaomin1, Niu Yuhu1, Liu Zhizhen1, Ma Lihui2, Niu Bo3, Guo Rui1
- 1Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China; 2People’s Hospital of Sanya City, Sanya 572000, Hainan Province, China; 3Department of Biotechnology, Capital Institute of Pediatrics, Beijing 100020, China
-
Revised:2019-01-14Online:2019-06-18Published:2019-06-18 -
Contact:Guo Rui, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China; Niu Bo, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Biotechnology, Capital Institute of Pediatrics, Beijing 100020, China -
About author:Zhang Pin, Master candidate, Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81370312 (to NB); Research Funding Project for Returned Overseas Students in Shanxi Province, No. 2016-051 (to LZZ); the Medical and Health Science and Technology Innovation Project of Sanya, No. 2014 YW01 (to MLH)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Pin, Guo Ying, Gao Yajie, Wang Zhendong, Li Baiyi, Zhang Xiaomin, Niu Yuhu, Liu Zhizhen, Ma Lihui, Niu Bo, Guo Rui. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells promote myocardial repair after myocardial infarction under hypoxia[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(17): 2630-2636.
share this article
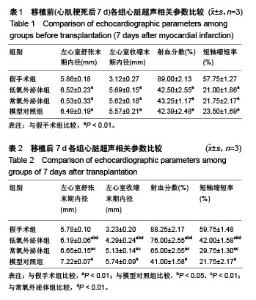
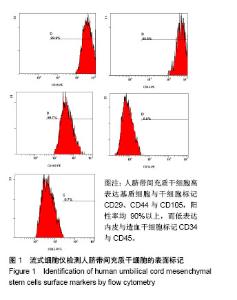
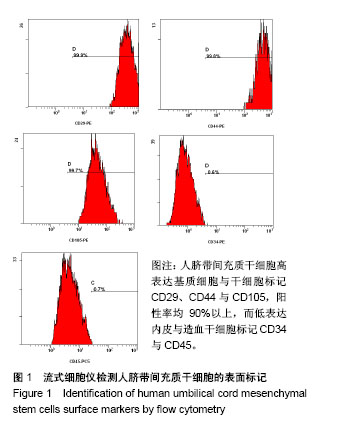
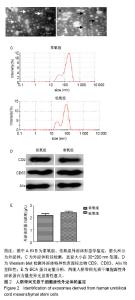
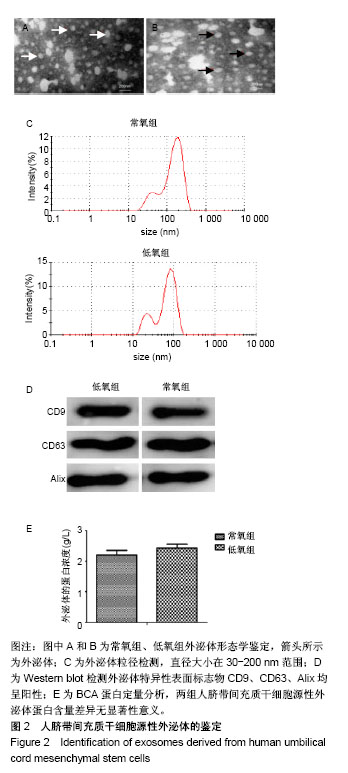
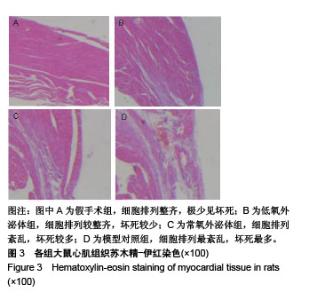
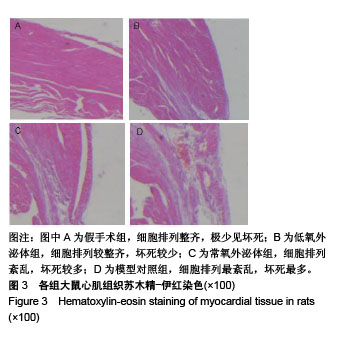
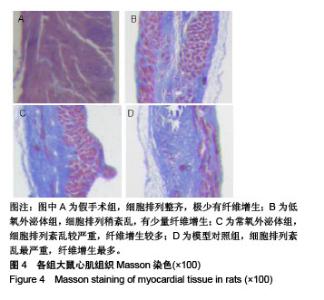
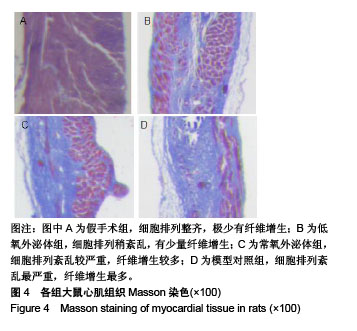
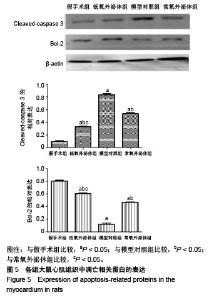
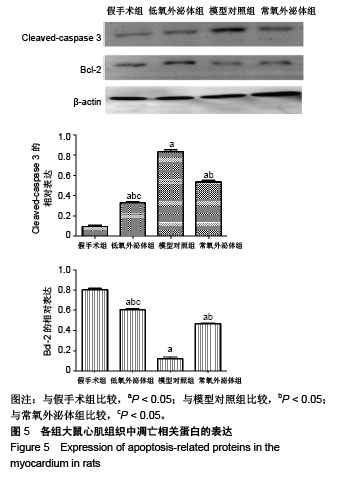
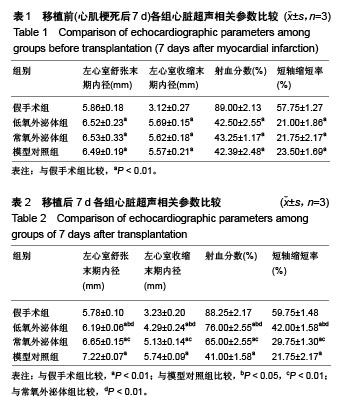
2.3 心肌梗死模型的建立 SD大鼠麻醉后,结扎心脏冠状动脉左前降支,大体观察见结扎部位以下变为青紫色或变苍白,心电图示ST段明显抬高。术中因结扎冠脉后发生室颤死亡1只,术后因心力衰竭死亡2只,气胸死亡1只,共计4只。假手术大鼠术后第1天精神状态无明显变化;心肌梗死模型大鼠术后第1天精神萎靡,3 d左右开始活跃,1周左右进食量和活动量基本正常。 2.4 各组大鼠心功能比较 所有实验大鼠移植前(心肌梗死后7 d),各模型组与假手术组相比,左心室舒张末期内径、左心室收缩末期内径、射血分数、短轴缩短率差异有显著性意义(P < 0.01),见表1,各模型组之间上述指标差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。移植治疗7 d后,假手术组一切正常,低氧外泌体组、常氧外泌体组大鼠心功能均有明显改善,主要表现在射血分数、短轴缩短率增加,左心室舒张末期内径、左心室收缩末期内径减小。模型对照组的射血分数、短轴缩短率显著低于低氧外泌体组、常氧外泌体组(P < 0.01),见表2;常氧外泌体组的射血分数、短轴缩短率显著低于低氧外泌体组(P < 0.01)。同时,模型对照组的左心室舒张末期内径、左心室收缩末期内径显著大于低氧外泌体组、常氧外泌体组(P < 0.01);常氧外泌体组的左心室舒张末期内径、左心室收缩末期内径显著大于低氧外泌体组(P < 0.01)。"
| [1] Ankrum JA, Ong JF, Karp JM. Mesenchymal stem cells: immune evasive, not immune privileged. Nat Biotechnol. 2014;32(3):252-260.[2] Yu B, Zhang X, Li X. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(3):4142-4157. [3] Sahoo S, Klychko E, Thorne T, et al. Exosomes from human CD34(+) stem cells mediate their proangiogenic paracrine activity. Circ Res. 2011;109(7):724-728.[4] Sun L, Xu R, Sun X, et al. Safety evaluation of exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stromal cell. Cytotherapy. 2016;18(3):413-422.[5] Taverna S, Amodeo V, Saieva L, et al. Exosomal shuttling of miR-126 in endothelial cells modulates adhesive and migratory abilities of chronic myelogenous leukemia cells. Mol Cancer. 2014;13:169. [6] Xiao J, Pan Y, Li XH, et al. Cardiac progenitor cell-derived exosomes prevent cardiomyocytes apoptosis through exosomal miR-21 by targeting PDCD4. Cell Death Dis. 2016;7(6):e2277.[7] Hu X, Xu Y, Zhong Z, et al. A Large-Scale Investigation of Hypoxia-Preconditioned Allogeneic Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Myocardial Repair in Nonhuman Primates: Paracrine Activity Without Remuscularization. Circ Res. 2016;118(6): 970-983.[8] Wang X, Yin X, Sun W, et al. Intravenous infusion umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell in primary immune thrombocytopenia: A two-year follow-up. Exp Ther Med. 2017;13(5):2255-2258.[9] Wang Y, Han ZB, Ma J, et al. A toxicity study of multiple-administration human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in cynomolgus monkeys. Stem Cells Dev. 2012; 21(9):1401-1408.[10] Majore I, Moretti P, Stahl F, et al. Growth and differentiation properties of mesenchymal stromal cell populations derived from whole human umbilical cord. Stem Cell Rev. 2011;7(1): 17-31. [11] 雷鑫,陈彦,张建林,等.评价脐带间充质干细胞移植前细胞活性的指标[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(32):5847-5854.[12] 崔蕾,雷鑫,牛玉虎,等.人脐带间充质干细胞移植治疗大鼠急性肺损伤[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(14):2563-2569.[13] 郭莹,王秀伟,牛玉虎,等.人脐带间充质干细胞来源外泌体提取方法的比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(9):1382-1388.[14] Khong SML, Lee M, Kosaric N, et al. Single-Cell Transcriptomics of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Reveal Age-Related Cellular Subpopulation Depletion and Impaired Regenerative Function. Stem Cells. 2018. doi: 10.1002/stem.2934. [Epub ahead of print][15] Hendijani F, Sadeghi-Aliabadi H, Haghjooy Javanmard S. Comparison of human mesenchymal stem cells isolated by explant culture method from entire umbilical cord and Wharton's jelly matrix. Cell Tissue Bank. 2014;15(4):555-565.[16] Taghizadeh RR, Cetrulo KJ, Cetrulo CL. Wharton's Jelly stem cells: future clinical applications. Placenta. 2011;32 Suppl 4:S311-315. [17] Prabhu SD, Frangogiannis NG. The Biological Basis for Cardiac Repair After Myocardial Infarction: From Inflammation to Fibrosis. Circ Res. 2016;119(1):91-112.[18] Carreau A, El Hafny-Rahbi B, Matejuk A, et al. Why is the partial oxygen pressure of human tissues a crucial parameter? Small molecules and hypoxia. J Cell Mol Med. 2011;15(6): 1239-1253.[19] Zhou P, Tan YZ, Wang HJ, et al. Hypoxic preconditioning-induced autophagy enhances survival of engrafted endothelial progenitor cells in ischaemic limb. J Cell Mol Med. 2017;21(10):2452-2464.[20] Santos Nascimento D, Mosqueira D, Sousa LM, et al. Human umbilical cord tissue-derived mesenchymal stromal cells attenuate remodeling after myocardial infarction by proangiogenic, antiapoptotic, and endogenous cell-activation mechanisms. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014;5(1):5.[21] Ohnuki M, Takahashi K. Present and future challenges of induced pluripotent stem cells. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2015;370(1680):20140367.[22] Zhang Y, Hu YW, Zheng L, et al. Characteristics and Roles of Exosomes in Cardiovascular Disease. DNA Cell Biol. 2017; 36(3):202-211.[23] Charoenviriyakul C, Takahashi Y, Nishikawa M, et al. Preservation of exosomes at room temperature using lyophilization. Int J Pharm. 2018;553(1-2):1-7.[24] Li RC, Tao J, Guo YB, et al. In vivo suppression of microRNA-24 prevents the transition toward decompensated hypertrophy in aortic-constricted mice. Circ Res. 2013;112(4): 601-605.[25] Bernardo BC, Gao XM, Winbanks CE, et al. Therapeutic inhibition of the miR-34 family attenuates pathological cardiac remodeling and improves heart function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109(43):17615-17620.[26] Ibrahim AG, Cheng K, Marbán E. Exosomes as critical agents of cardiac regeneration triggered by cell therapy. Stem Cell Reports. 2014;2(5):606-619.[27] Feng Y, Huang W, Meng W, et al. Heat shock improves Sca-1+ stem cell survival and directs ischemic cardiomyocytes toward a prosurvival phenotype via exosomal transfer: a critical role for HSF1/miR-34a/HSP70 pathway. Stem Cells. 2014;32(2):462-472.[28] Hu GW, Li Q, Niu X, et al. Exosomes secreted by human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells attenuate limb ischemia by promoting angiogenesis in mice. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015;6:10.[29] Kogure T, Yan IK, Lin WL, et al. Extracellular Vesicle-Mediated Transfer of a Novel Long Noncoding RNA TUC339: A Mechanism of Intercellular Signaling in Human Hepatocellular Cancer. Genes Cancer. 2013;4(7-8):261-272.[30] Mohankumar S, Patel T. Extracellular vesicle long noncoding RNA as potential biomarkers of liver cancer. Brief Funct Genomics. 2016;15(3):249-256.[31] Xu LF, Wu ZP, Chen Y, et al. MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) regulates cellular proliferation, invasion, migration, and apoptosis by targeting PTEN, RECK and Bcl-2 in lung squamous carcinoma, Gejiu City, China. PLoS One. 2014;9(8):e103698.[32] Lin J, Li J, Huang B, et al. Exosomes: novel biomarkers for clinical diagnosis. Scientific World Journal. 2015;2015: 657086.[33] Diaz G, Wolfe LM, Kruh-Garcia NA, et al. Changes in the Membrane-Associated Proteins of Exosomes Released from Human Macrophages after Mycobacterium tuberculosis Infection. Sci Rep. 2016;6:37975.[34] Zhang J, Ma J, Long K, et al. Overexpression of Exosomal Cardioprotective miRNAs Mitigates Hypoxia-Induced H9c2 Cells Apoptosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(4): E711. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [3] | Zhao Min, Feng Liuxiang, Chen Yao, Gu Xia, Wang Pingyi, Li Yimei, Li Wenhua. Exosomes as a disease marker under hypoxic conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1104-1108. |
| [4] | Nie Huijuan, Huang Zhichun. The role of Hedgehog signaling pathway in transforming growth factor beta1-induced myofibroblast transdifferentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 754-760. |
| [5] | Chen Ziyang, Pu Rui, Deng Shuang, Yuan Lingyan. Regulatory effect of exosomes on exercise-mediated insulin resistance diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4089-4094. |
| [6] | Ruan Guangping, Yao Xiang, Liu-Gao Miyang, Cai Xuemin, Li Zian, Pang Rongqing, Wang Jinxiang, Pan Xinghua. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for traumatic systemic inflammatory response syndrome in tree shrews [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3994-4000. |
| [7] | Gao Kun, Chen Dayu, Zhang Yong, Liu Weidong, Sun Shufen, Lai Wenqiang, Ma Dujun, Wu Yihong, Lin Zhanpeng, Jiang Yinglu, Yu Weiji. Achyranthes bidentata alcohol extract inhibits extracellular matrix degradation of the cartilage by regulating synovial fibroblast exosomes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3636-3640. |
| [8] | Lang Limin, He Sheng, Jiang Zengyu, Hu Yiyi, Zhang Zhixing, Liang Minqian. Application progress of conductive composite materials in the field of tissue engineering treatment of myocardial infarction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3584-3590. |
| [9] | Wang Kang, Zhi Xiaodong, Wang Wei. Effect of stem cell derived exosomes on repairing peripheral nerve injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3083-3089. |
| [10] | Zhao Shuangdan, Zheng Jiahua, Qi Wenbo, Huang Xianghua. Role and mechanism of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells in reproductive system diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3097-3102. |
| [11] | Sun Weixing, Zhao Yongchao, Zhao Ranzun. Mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in the treatment of myocardial infarction: problems, crux and new breakthrough [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3103-3109. |
| [12] | Chen Siyu, Li Yannan, Xie Liying, Liu Siqi, Fan Yurong, Fang Changxing, Zhang Xin, Quan Jiayu, Zuo Lin. Thermosensitive chitosan-collagen composite hydrogel loaded with basic fibroblast growth factor retards ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2472-2478. |
| [13] | Liu Feng, Zhang Yu, Wang Yanli, Luo Wei, Han Chaoshan, Li Yangxin. Application of temperature-sensitive chitosan hydrogel encapsulated exosomes in ischemic diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2479-2487. |
| [14] | Cai Yuan, Deng Chengliang. Therapeutic application of adipose stem cell-free liquid extracts: skin aging, wound healing, scar recovery and nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(13): 2097-2102. |
| [15] | Liu Tao, Zhang Nini, Huang Guilin . Relationship between extracellular vesicles and radiation-induced tissue injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(13): 2121-2126. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||