Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (6): 840-845.doi: 10.12307/2023.243
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of M2 macrophage-derived exosomes on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
Liu Wentao1, Feng Xingchao2, Yang Yi2, Bai Shengbin1
- 1School of Basic Medicine, Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 2First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830011, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2022-02-08Accepted:2022-04-18Online:2023-02-28Published:2022-08-09 -
Contact:Bai Shengbin, MD, Professor, School of Basic Medicine, Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China Yang Yi, Master, Associate chief physician, First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830011, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Liu Wentao, Master candidate, School of Basic Medicine, Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the Autonomous Region Science and Technology Support Project: Bone Mechanobiology Collaborative Innovation Platform, No. 2020E0285 (to YY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Wentao, Feng Xingchao, Yang Yi, Bai Shengbin. Effect of M2 macrophage-derived exosomes on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 840-845.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
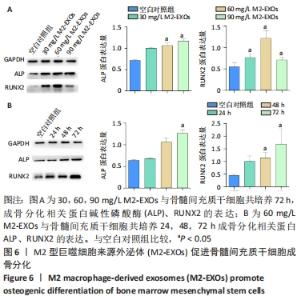
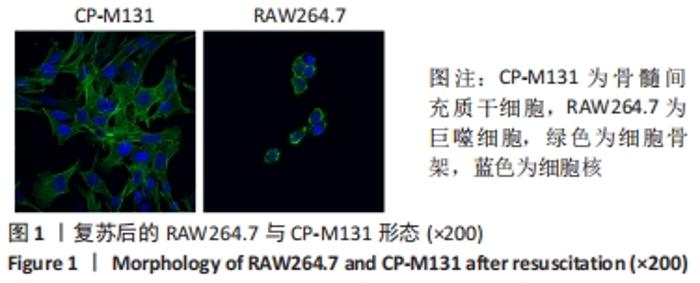
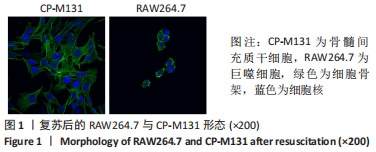
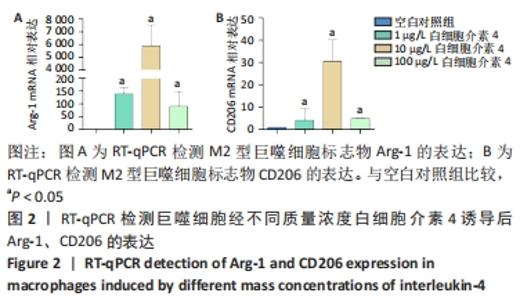
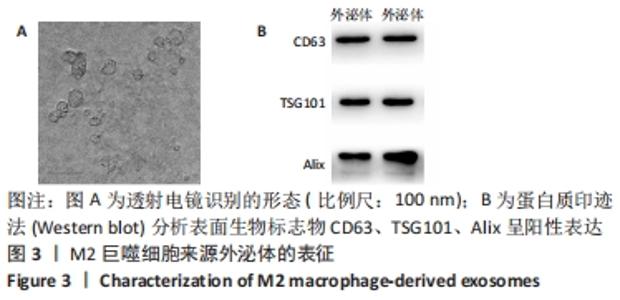
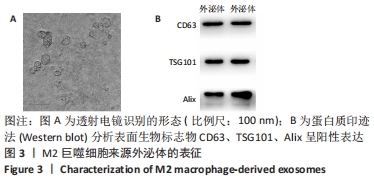
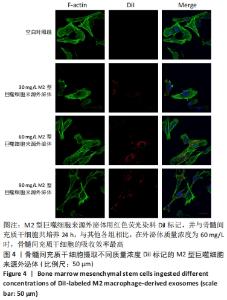
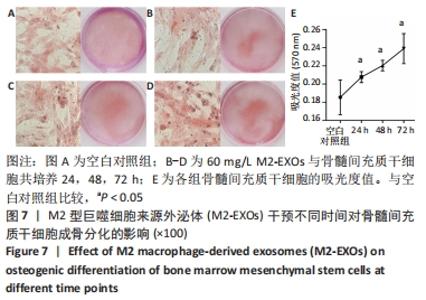
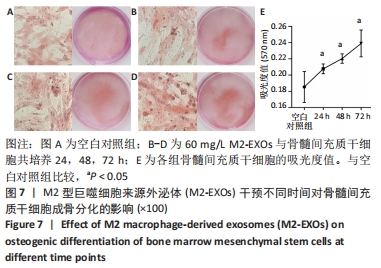
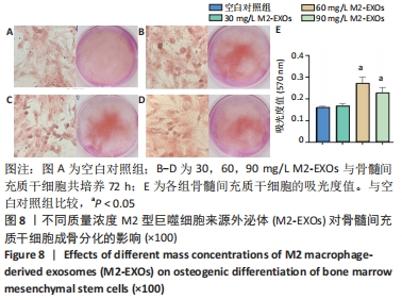
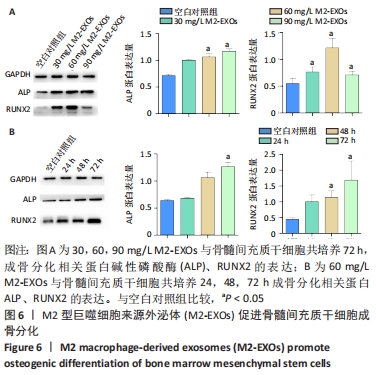
2.5 M2型巨噬细胞来源外泌体促进骨髓间充质干细胞成骨 骨髓间充质干细胞与30,60,90 mg/L M2型巨噬细胞来源外泌体共培养72 h后,其中60 mg/L M2型巨噬细胞来源外泌体组成骨分化相关蛋白RUNX2最高(P < 0.05),与M2型巨噬细胞来源外泌体摄取效率结果一致,见图6A。而且发现骨髓间充质干细胞与60 mg/L M2型巨噬细胞来源外泌体共培养24,48,72 h,成骨分化相关蛋白RUNX2、碱性磷酸酶表达随时间变化逐渐上调(P < 0.05),见图6B。茜素红染色结果显示,随着共培养时间增加,矿物质沉积染色逐渐增强,表明骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨分化,见图7。此外,60 mg/L M2型巨噬细胞来源外泌体组矿物质沉积染色显著大于其余组(P < 0.05),与M2型巨噬细胞来源外泌体摄取效率及蛋白质印迹结果一致,见图8。这些结果均表明M2型巨噬细胞来源外泌体可以促进骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化。"
| [1] RAHMAN M, PENG XL, ZHAO XH, et al. 3D bioactive cell-free-scaffolds for in-vitro/in-vivo capture and directed osteoinduction of stem cells for bone tissue regeneration. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(11):4083-4095. [2] SEEHERMAN HJ, WILSON CG, VANDERPLOEG EJ, et al. A BMP/Activin A Chimera Induces Posterolateral Spine Fusion in Nonhuman Primates at Lower Concentrations Than BMP-2. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2021;103(16):e64. [3] LIN Z, XIONG Y, MENG W, et al. Exosomal PD-L1 induces osteogenic differentiation and promotes fracture healing by acting as an immunosuppressant. Bioact Mater. 2021;13:300-311. [4] MATA R, YAO Y, CAO W, et al. The Dynamic Inflammatory Tissue Microenvironment: Signality and Disease Therapy by Biomaterials. Research (Wash D C). 2021;2021:4189516. [5] ALLAVENA P, SICA A, SOLINAS G, et al. The inflammatory micro-environment in tumor progression: the role of tumor-associated macrophages. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2008;66(1):1-9. [6] RIHAWI K, RICCI AD, RIZZO A, et al. Tumor-Associated Macrophages and Inflammatory Microenvironment in Gastric Cancer: Novel Translational Implications. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(8):3805. [7] 蓝春花,孟玲,陈成英,等.绿原酸抑制糖酵解及脂肪酸代谢调控M1型巨噬细胞极化[J].中国免疫学杂志,2021,37(20):2440-2444. [8] WITHEREL CE, SAO K, BRISSON BK, et al. Regulation of extracellular matrix assembly and structure by hybrid M1/M2 macrophages. Biomaterials. 2021;269:120667. [9] COTZOMI-ORTEGA I, NIETO-YAÑEZ O, JUÁREZ-AVELAR I, et al. Autophagy inhibition in breast cancer cells induces ROS-mediated MIF expression and M1 macrophage polarization. Cell Signal. 2021;86:110075. [10] TIAN H, LIN S, WU J, et al. Kaempferol alleviates corneal transplantation rejection by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation and macrophage M1 polarization via promoting autophagy. Exp Eye Res. 2021;208:108627. [11] LUO Q, LI X, ZHONG W, et al. Dicalcium silicate-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and autophagy-mediated macrophagic inflammation promotes osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs. Regen Biomater. 2021;8: rbab075. [12] ZHANG H, WANG SQ, HANG L, et al. GRP78 facilitates M2 macrophage polarization and tumour progression. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021;78(23): 7709-7732. [13] HWANG SM, CHUNG G, KIM YH, et al. The Role of Maresins in Inflammatory Pain: Function of Macrophages in Wound Regeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(23):5849. [14] WU J, ZHANG L, SHI J, et al. Macrophage phenotypic switch orchestrates the inflammation and repair/regeneration following acute pancreatitis injury. EBioMedicine. 2020;58:102920. [15] RAMON S, DALLI J, SANGER JM, et al. The Protectin PCTR1 Is Produced by Human M2 Macrophages and Enhances Resolution of Infectious Inflammation. Am J Pathol. 2016;186(4):962-973. [16] WANG GF, XIE GL, ZHU B, et al. Identification and characterization of the Enterobacter complex causing mulberry (Morus alba) wilt disease in China. Eur J Plant Pathol. 2010;126(4):465-478. [17] LI Z, XU F, WANG Z, et al. Macrophages Undergo M1-to-M2 Transition in Adipose Tissue Regeneration in a Rat Tissue Engineering Model. Artif Organs. 2016;40(10):E167-E178. [18] XIA Y, HE XT, XU XY, et al. Exosomes derived from M0, M1 and M2 macrophages exert distinct influences on the proliferation and differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. PeerJ. 2020;8:e8970. [19] DUNBAR H, WEISS DJ, ROLANDSSON ENES S, et al. The Inflammatory Lung Microenvironment; a Key Mediator in MSC Licensing. Cells. 2021; 10(11):2982. [20] KISHIMOTO K, TERABE K, TAKAHASHI N, et al. Metabolic changes in synovial cells in early inflammation: Involvement of CREB phosphorylation in the anti-inflammatory effect of 2-deoxyglucose. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2021;708:108962. [21] WANG Q, CAI J, CAI XH, et al. miR-346 regulates osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells by targeting the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. PLoS One. 2013;8(9):e72266. [22] ZAMINY A, RAGERDI KASHANI I, BARBARESTANI M, et al. Osteogenic differentiation of rat mesenchymal stem cells from adipose tissue in comparison with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells: melatonin as a differentiation factor. Iran Biomed J. 2008;12(3):133-141. [23] CHEN L, WU C, WEI D, et al. Biomimetic mineralized microenvironment stiffness regulated BMSCs osteogenic differentiation through cytoskeleton mediated mechanical signaling transduction. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;119:111613. [24] LI M, XING X, HUANG H, et al. The Role of Apoptotic Bodies From Different Stages of Apoptosis in Maintaining the Vitality of BMSCs. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-643891/v1[2021-01-08]. [25] MURRAY PJ, ALLEN JE, BISWAS SK, et al. Macrophage Activation and Polarization: Nomenclature and Experimental Guidelines. Immunity. 2014;41(2):339-340. [26] CINTI S, MITCHELL G, BARBATELLI G, et al. Adipocyte death defines macrophage localization and function in adipose tissue of obese mice and humans. J Lipid Res. 2005;46(11):2347-2355. [27] MOSSER DM, EDWARDS JP. Exploring the full spectrum of macrophage activation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8(12):958-969. [28] MARTIN KE, GARCÍA AJ. Macrophage phenotypes in tissue repair and the foreign body response: Implications for biomaterial-based regenerative medicine strategies. Acta Biomater. 2021;133:4-16. [29] CHAMPAGNE CM, TAKEBE J, OFFENBACHER S, et al. Macrophage cell lines produce osteoinductive signals that include bone morphogenetic protein-2. Bone. 2002;30(1):26-31. [30] PIRRACO RP, REIS RL, MARQUES AP. Effect of monocytes/macrophages on the early osteogenic differentiation of hBMSCs. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2013;7(5):392-400. [31] LUO M, ZHAO F, LIU L, et al. IFN-γ/SrBG composite scaffolds promote osteogenesis by sequential regulation of macrophages from M1 to M2. J Mater Chem B. 2021;9(7):1867-1876. [32] ELASHIRY M, ELSAYED R, CUTLER CW. Exogenous and Endogenous Dendritic Cell-Derived Exosomes: Lessons Learned for Immunotherapy and Disease Pathogenesis. Cells. 2021;11(1):115. [33] YOU LN, TAI QW, XU L, et al. Exosomal LINC00161 promotes angiogenesis and metastasis via regulating miR-590-3p/ROCK axis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Gene Ther. 2021;28(6):719-736. [34] BRANSCOME H, PAUL S, KHATKAR P, et al. Stem Cell Extracellular Vesicles and their Potential to Contribute to the Repair of Damaged CNS Cells. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2020;15(3):520-537. [35] BOMMANAVAR S, HOSMANI J, TOGOO RA, et al. Role of matrix vesicles and crystal ghosts in bio-mineralization. J Bone Miner Metab. 2020;38(6):759-764. [36] YING W, GAO H, DOS REIS FCG, et al. MiR-690, an exosomal-derived miRNA from M2-polarized macrophages, improves insulin sensitivity in obese mice. Cell Metab. 2021;33(4):781-790.e5. [37] 张程,包丽荣,杨于桃,等.M2巨噬细胞外泌体对高糖高胰岛素条件下小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的影响[J].四川大学学报(医学版),2022,53(1):63-70. [38] XIONG Y, CHEN L, YAN C, et al. M2 Macrophagy-derived exosomal miRNA-5106 induces bone mesenchymal stem cells towards osteoblastic fate by targeting salt-inducible kinase 2 and 3. J Nanobiotechnology. 2020;18(1):66. |
| [1] | Pan Zhongjie, Qin Zhihong, Zheng Tiejun, Ding Xiaofei, Liao Shijie. Targeting of non-coding RNAs in the pathogenesis of the osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1441-1447. |
| [2] | Dang Yi, Du Chengyan, Yao Honglin, Yuan Nenghua, Cao Jin, Xiong Shan, Zhang Dingmei, Wang Xin. Hormonal osteonecrosis and oxidative stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1469-1476. |
| [3] | Yang Zhishan, Tang Zhenglong. YAP/TAZ, a core factor of the Hippo signaling pathway, is involved in bone formation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1264-1271. |
| [4] | Liu Xiaolin, Mu Xinyue, Ma Ziyu, Liu Shutai, Wang Wenlong, Han Xiaoqian, Dong Zhiheng. Effect of hydrogel-loaded simvastatin microspheres on osteoblast proliferation and differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 998-1003. |
| [5] | Yuan Wei, Liu Jingdong, Xu Guanghui, Kang Jian, Li Fuping, Wang Yingjie, Zhi Zhongzheng, Li Guanwu. Osteogenic differentiation of human perivascular stem cells and its regulation based on Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 866-871. |
| [6] | Qiao Luhui, Ma Ziyu, Guo Haoyu, Hou Yudong. Comparison of puerarin and icariin on the biological properties of mouse preosteoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 872-877. |
| [7] | Yuan Bo, Xie Lide, Fu Xiumei. Schwann cell-derived exosomes promote the repair and regeneration of injured peripheral nerves [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 935-940. |
| [8] | Xu Qijing, Yang Yichun, Lei Wei, Yang Ying, Yu Jiang, Xia Tingting, Zhang Meng, Zhang Tao, Zhang Qian. Advances and problems in cell-free treatment of diabetic skin chronic wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 962-969. |
| [9] | Chen Guanting, Zhang Linqi, Li Qingru. Meta-analysis of the value of exosomal miRNA for the diagnosis of chronic kidney disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 970-976. |
| [10] | Long Yanming, Xie Mengsheng, Huang Jiajie, Xue Wenli, Rong Hui, Li Xiaojie. Casein kinase 2-interaction protein-1 regulates the osteogenic ability of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in osteoporosis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 878-882. |
| [11] | Li Xinyue, Li Xiheng, Mao Tianjiao, Tang Liang, Li Jiang. Three-dimensional culture affects morphology, activity and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 846-852. |
| [12] | Li Qicheng, Deng Jin, Fu Xiaoyang, Han Na. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes on hypoxia-treated myoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 853-859. |
| [13] | Wang Min, Yin Xiushan, Wang Yingxi, Zhang Yan, Zhao Long, Xia Shuyue. Inhalation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes alleviates inflammatory injury in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 827-834. |
| [14] | Zhang Houjun, Deng Bowen, Jiang Shengyuan, Zhao Yi, Ren Jingpei, Xu Lin, Mu Xiaohong. Proteomic analysis of cerebrospinal fluid exosomes derived from cerebral palsy children [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 903-908. |
| [15] | Gao Ting, Ma Xiaohong, Li Xiaorong. Extraction and identification of exosomes from three different sources of ovarian granulosa cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 860-865. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||