Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (8): 1264-1271.doi: 10.12307/2023.089
Previous Articles Next Articles
YAP/TAZ, a core factor of the Hippo signaling pathway, is involved in bone formation
Yang Zhishan1, 2, Tang Zhenglong1, 2
- 1School of Stomatology of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550001, Guizhou Province, China; 2Hospital of Stomatology of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550001, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2022-03-17Accepted:2022-05-06Online:2023-03-18Published:2022-07-28 -
Contact:Tang Zhenglong, MD, Professor, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, School/Hospital of Stomatology of Guizhou Medical University,Guiyang 550001, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Yang Zhishan, Master candidate, Physician, School/Hospital of Stomatology of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550001, Guizhou Province, China. -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Regional Program), No. 82060197 (to TZL)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yang Zhishan, Tang Zhenglong. YAP/TAZ, a core factor of the Hippo signaling pathway, is involved in bone formation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1264-1271.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
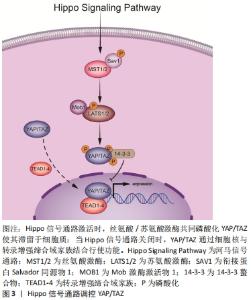
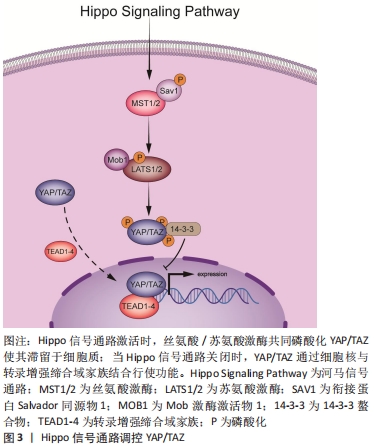
2.1 介导YAP/TAZ激活的因素 YAP/TAZ的调控依赖于Hippo信号通路,但也由其他条件控制,需要考虑细胞微环境。因为细胞微环境的改变可以抑制或促进YAP/TAZ进入细胞核或细胞质,从而完全改变YAP/TAZ的功能状态,所以说明YAP/TAZ的调控具有特殊性。 2.1.1 经典Hippo信号通路介导YAP/TAZ功能 Hippo信号通路最早在2003年由HARVEY等[4]学者在果蝇体内发现。经典的Hippo信号通路由以下几个效应因子组成:丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶、YAP/TAZ。当Hippo信号通路激活时,丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶同时激活,YAP/TAZ在衔接蛋白Salvador同源物1和Mob激酶激活物1的协助下被磷酸化,并与细胞质中的14-3-3螯合物结合[5],在细胞质中隔离使功能抑制,导致泛素化和蛋白降解[6]。 当Hippo信号通路关闭时,YAP/TAZ去磷酸化并易位到细胞核中行使功能。由于YAP和TAZ是不包含DNA结合域的转录共激活剂,因此需要与分子伴侣相互作用,主要是转录增强缔合域家族的成员[7]。如果敲除转录增强缔合域则显著降低了YAP靶基因的表达,而转录增强的缔合结构域的缺失导致了YAP/TAZ定位于细胞质内,即使YAP/TAZ没有被磷酸化,也无法位移至细胞核内,在细胞核的YAP/TAZ与转录增强缔合域转录因子结合,诱导细胞进行增殖、存活和迁移等转录程序[8-9],见图3。 "
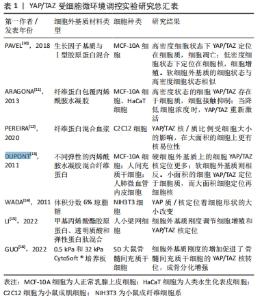
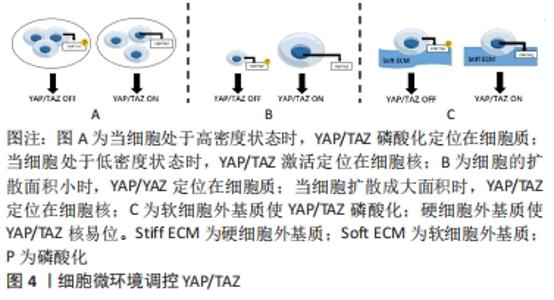
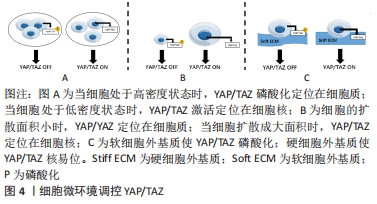
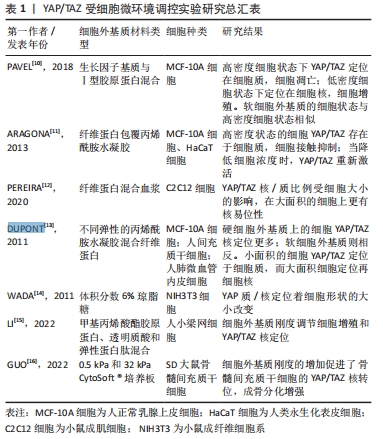
2.1.2 细胞微环境调控YAP/TAZ 细胞浓度调控YAP/TAZ核易位[10]。研究发现,YAP/TAZ在细胞的定位和磷酸化除了受Hippo通路调节外也受细胞浓度的调节。当细胞培养呈低密度时,YAP/TAZ主要位于细胞核内,并驱动细胞增殖;细胞培养呈高密度时,则迁移至细胞质。当高密度的细胞状态被“破坏”后,YAP/TAZ又可重新定位到细胞核内进行增殖[11]。说明YAP/YAZ磷酸化与高密度的细胞状态存在关系。 YAP/TAZ可以感知细胞形状变化[12],改变其在细胞中的定位。研究证实YAP在小表面积的细胞中主要定位在细胞质[13],但在大表面积的细胞中明显定位于细胞核[14]。有学者发现,通过将细胞种植在微图案细胞黏附基质[14],“拉伸”细胞,使紧凑的细胞重新伸展,迅速激活了YAP/TAZ核易位,并重新进入DNA合成期;而未“拉伸”的细胞呈圆形、YAP/TAZ活性被抑制和细胞增殖受限、表明细胞形状改变后传递力学信号,并以YAP/TAZ作为调节细胞增殖的决定因子。 细胞外基质刚度介导YAP/TAZ的调控。此类研究将Hippo通路的活性与细胞微环境联系起来,并解释了机械信号的改变对细胞和组织的表型效应有影响。研究发现,在硬水凝胶上生长的细胞中YAP/TAZ的活性与在塑料基质上生长的细胞相似,而在软基质水凝胶上生长的细胞抑制YAP/TAZ活性的水平与消耗YAP/TAZ的活性水平相当[13,15],此结果在三维的细胞外基质培养细胞中同样符合,在三维软细胞外基质上,YAP/TAZ定位于细胞质中;相反,当细胞培养在三维硬细胞外基质上,YAP定位于细胞核[11,16]。总之,YAP/TAZ的功能激活与细胞外基质刚度性质紧密相关。 因此,除了从分子层面上可以影响YAP/TAZ的细胞核易位以外,低细胞浓度、大面积的细胞形态和机械信号传导也会导致YAP/TAZ的核易位使其功能激活,从而能够行使控制细胞增殖、分化的功能。细胞可以从微环境中感知刺激,表现为YAP/TAZ活性水平,YAP/TAZ激活与否可以决定细胞行为,可以作为促进组织再生的新研究方向,利用YAP/TAZ的特性模拟组织再生的修复机制,将其运用到大型的骨骼缺损或组织损伤中,通过治疗来激活修复、预防或逆转受损组织,见表1,图4。 "
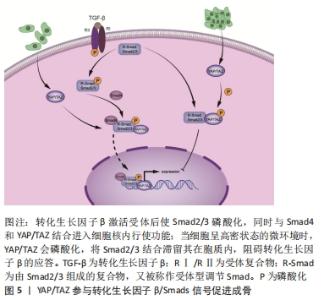
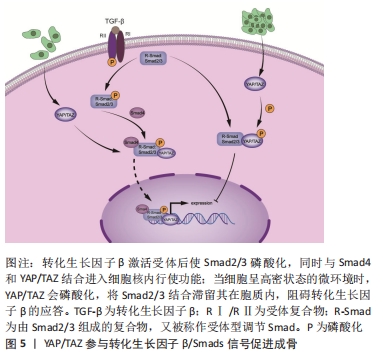
2.2 Yap/Taz参与成骨信号传递 2.2.1 Yap/Taz与转化生长因子β和Smads家族交叉对话 现有研究证明YAP/TAZ参与转化生长因子β/Smads信号传导相互作用,并参与骨形成。Smad蛋白家族是一种中介分子,将转化生长因子β及其受体结合产生的信号从细胞质传递到细胞核,从而在信号传递和调节下游靶基因转录中发挥重要作用,其中Smad2和Smad3是转化生长因子β的特异性介质[17]。在转化生长因子β通路中,转化生长因子β激活受体激酶,并磷酸化Smad2/3构成的受体型调节Smads(Receptor-regulatory Smads,R-Smads),磷酸化的R-Smads与Smad4形成复合物[18]。这些通过转化生长因子β通路形成的复合物被转移到细胞核中,它们的核积累多少会影响靶基因的表达[19]。而YAP/TAZ调节Smad2/3和Smad4的核积累,YAP/TAZ的缺失将直接导致其复合物在细胞核中积累失败,从而抑制转化生长因子β信号传导[20]。 转化生长因子β的激活需要YAP/TAZ参与,通过与磷酸化的Smad2/3相互作用而转移到细胞核中[21]。在细胞浓度较高的情况下,磷酸化的YAP/TAZ可与Smad 2/3一起保留在细胞质中,并抑制转化生长因子β的应答[22]。当抑制YAP活性后,Smad2/3表达水平显著减少,从而抑制了转化生长因子β的应答[23],即使再使用转化生长因子β刺激细胞,也没有升高Smad2/3的表达,此外该研究还发现转化生长因子β/Smad也受细胞外基质刚度的调控。说明YAP/TAZ与转化生长因子β/Smad功能相辅相成。Smad家族还通过转化生长因子β途径促进骨细胞的形成。LIU等[24]发现间隙连接蛋白43的表达与Smad依赖的转化生长因子β信号通路相关。Smad2/3与Smad4结合形成的复合物可以上调靶基因连接蛋白的表达,从而参与骨细胞的活动。而YAP/TAZ可以与其他转录辅助因子相互作用调节转化生长因子β/Smad靶基因的表达[25-26]。这些观察结果可得出,YAP和TAZ可认为是骨细胞中转化生长因子β介导的骨重塑的潜在介导因子,见图5。 "
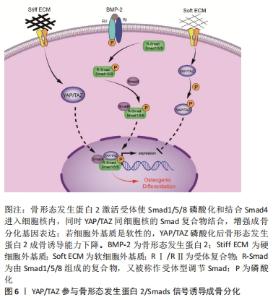
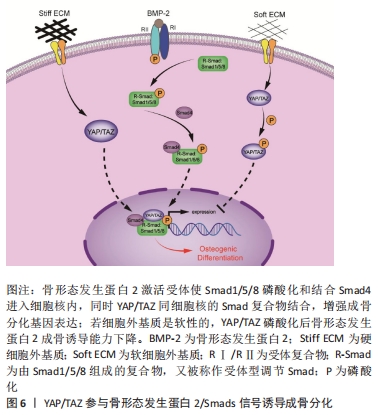
2.2.2 Yap/Taz与骨形态发生蛋白2和Smads家族交叉对话 骨形态发生蛋白是众所周知的成骨因子并能促进Runx2表达。Uemura等[27]使用骨形态发生蛋白受体抑制剂后显著降低了斑马鱼胚胎鳃盖中Runx2的表达水平,说明骨形态发生蛋白的表达对Runx2表达至关重要,而在斑马鱼细胞中过度表达YAP和YAZ后发现Runx2表达也有升高,表明YAP/TAZ转录激活是前成骨细胞中表达Runx2的前提。研究发现TAZ通过结合Smad4共激活Runx2以驱动间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化并抑制脂肪生成[28]。 在骨形态发生蛋白家族中,骨形态发生蛋白2被认为是最有效的成骨分化诱导剂。骨形态发生蛋白2已被证明可以极大地提高人骨髓干细胞和脂肪干细胞的成骨能力[29]。现有研究报道,机械信号可通过快速上调体外内源性的骨形态发生蛋白2而整合到骨形态发生蛋白2信号传导中,并增强细胞内骨形态发生蛋白2的有效性[30]。通过骨形态发生蛋白2信号和生物力学信号的整合,从而使骨形态发生蛋白2促进骨的愈合[31-32]。WEI等[33]发现,在聚乙二醇水凝胶作为软型细胞外基质培养C2C12细胞时使用骨形态发生蛋白2诱导成骨会失败,检测YAP/TAZ主要定位在细胞质;用聚苯乙烯作为硬型细胞外基质培养细胞时成骨分化成功,YAP/TAZ集中在细胞核。当单独敲除YAP或TAZ会导致骨形态发生蛋白2诱导的碱性磷酸酶活性降低,同时敲除YAP和TAZ导致碱性磷酸酶活性更加降低;而过表达YAP或TAZ则加强了碱性磷酸酶的活性,即便细胞培养在软基质上,在骨形态发生蛋白2刺激下过表达YAP/TAZ仍可使细胞成骨分化。 YAP和TAZ从细胞质到细胞核的易位不依赖于骨形态发生蛋白2信号通路,但这种生物学行为会增强骨形态发生蛋白2诱导成骨功能[34]。同时,Smad信号的启动是独立于机械信号的,在Smad家族中,Smad1/5/8与成骨细胞分化密切相关[35]。骨形态发生蛋白2与其受体结合,诱导 Smad1,5和8的磷酸化并于Smad4构成复合物,与YAP/TAZ共同进入细胞核,随后将Runx2转录并诱导骨祖细胞分化为成骨细胞[33]。这2种信号通路之间的串扰协同增强了成骨基因的表达,表明骨形态发生蛋白2信号转导和机械信号转导协同作用促进成骨分化。 上述研究结果表明,YAP/TAZ可以参与成骨过程中的信号传递并且相互关联,因此,YAP/TAZ可能是成骨分化中机械信号传导和成骨信号传导之间的关键点。而且也有研究发现成骨细胞分化除了受分子水平调控以外亦受到细胞微环境调控,见图6。 "

2.3 YAP/TAZ参与骨组织细胞成骨分化 2.3.1 参与间充质干细胞成骨分化 研究发现,YAP/TAZ可以诱导间充质干细胞向成骨细胞系分化,同时抑制脂肪生成和软骨形成[36-37]。YAP/TAZ参与成骨分化过程受细胞外基质刚度、细胞形态和F-肌动蛋白等多项机制调节。 有研究发现,当间充质干细胞在硬质的细胞外基质上培养时YAP/TAZ活性激活,成骨分化基因增加[13];当过表达YAP时,可以促进间充质干细胞在软细胞外基质向成骨分化。另有研究发现扩散形态的骨髓间充质干细胞可以激活YAP/TAZ并促进成骨,而受限制形态的细胞则抑制 YAP/TAZ活性并诱导骨髓间充质干细胞向脂肪生成[16]。 KOMATSU等[36]发现三维浮动培养的间充质干细胞/外基质复合物培育过程中F-肌动蛋白耗损,YAP/TAZ活性降低,更倾向于脂肪和软骨分化;而经过骨诱导后YAP/TAZ活性上升,向成骨方向分化,并且发现经过骨诱导的干细胞/外基质复合物的F-肌动蛋白增加,与YAP/TAZ呈正向调节,促进干细胞/外基质复合物成骨,说明YAP/TAZ在促进间充质干细胞的成骨分化中扮演重要角色。 2.3.2 YAP/TAZ介导骨细胞重塑 有研究通过使用DMP1-Cre的小鼠敲除了YAP或TAZ基因,研究YAP/TAZ在骨细胞介导的骨重塑中的作用[38],发现敲除YAP或TAZ的小鼠股骨成骨细胞数量减少,骨皮质面积减小,骨的力学性能降低。YAP/TAZ缺失降低了骨细胞腔隙的百分比并且软骨基质Ⅱ型胶原纤维的表达降低。YAP/TAZ缺失显著降低了其下游靶基因血管生成诱导剂61和结缔组织生长因子的基因表达。成骨/破骨细胞协调的骨重塑功能有一部分是通过基质细胞蛋白的细胞通信网络(Cellular Communication Network,CCN)家族和结缔组织生长因子进行调控[39]。由此表明,YAP或TAZ 缺失会降低骨细胞介导的骨基质重塑。 在此基础上,ZARKA等[40]使用MLO-Y4细胞(小鼠骨样细胞),利用小干扰RNA转染YAP、TAZ后进行机械负荷实验。当机械负荷上升时,YAP和TAZ蛋白增加;YAP和TAZ被沉默时,趋化因子CXCL3和巨噬细胞集落刺激因子CSF1水平下调,阻断了部分骨细胞诱导的基因增加,这表明YAP/TAZ是MLO-Y4骨细胞中机械诱导趋化因子的中介。这些观察结果显示,YAP/TAZ在骨细胞介导的骨重塑起着重要作用。 2.3.3 通过YAP/骨形态发生蛋白2轴介导巨噬细胞促进间充质干细胞成骨 巨噬细胞作为免疫调节中不可或缺的存在,对促进骨组织愈合有重要作用[41-42]。有研究发现巨噬细胞可能对机械刺激敏感,其表型可由机械刺激调节。关于巨噬细胞机械反应的研究表明,巨噬细胞可被机械拉伸迅速激活,随后分泌各种细胞因子以应对炎性环境[43]。巨噬细胞从细胞外环境接收到机械信号,然后通过机械转导转化为生化信号,最终导致细胞行为和基因水平的变化[44]。 DONG等[45]研究发现将机械牵拉的巨噬细胞与骨髓间充质干细胞共培养后,成骨的相关蛋白表达升高,说明机械刺激后的巨噬细胞能促进成骨分化;检测其巨噬细胞亚型主要表达M2型巨噬细胞,分泌的白细胞介素10和转化生长因子β等抗炎因子也有升高。M2型巨噬细胞可以促进组织再生,而白细胞介素10和转化生长因子β能抑制破骨细胞的形成并支持骨形成。在其研究中还发现,机械拉伸使巨噬细胞中核YAP和骨形态发生蛋白2表达显著表达;而在巨噬细胞中沉默YAP后,机械拉伸诱导的骨形态发生蛋白2水平的没有升高,共培养的骨髓间充质干细胞钙沉积和碱性磷酸酶活性下降,这些结果证明了YAP/骨形态发生蛋白2轴在机械拉伸巨噬细胞后诱导的骨髓间充质干细胞成骨过程中起重要作用。结果表明在机械刺激下,巨噬细胞通过YAP/骨形态发生蛋白2轴诱导间充质干细胞成骨。 2.3.4 YAP/TAZ对破骨细胞的调控 破骨细胞来源于单核/巨噬细胞谱系,其活性受到多种激素和细胞因子的错综复杂的调节,其中由肿瘤坏死因子超家族成员核转录因子κB受体激活蛋白配体(receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand,RANKL)激活为主,现研究认为RANKL是作为驱动破骨细胞发育和激活成熟破骨细胞的关键信号[46]。当破骨细胞过度形成和/或活化的过程的不平衡是骨质疏松症和其他溶骨性疾病的主要原因。现有研究发现YAP和TAZ参与破骨细胞的分化和功能调控。 YAP1对破骨细胞分化和功能有调控作用。ZHAO等[47]使用小鼠胫骨和股骨中分离出的骨髓巨噬细胞及RAW264.7细胞系培养破骨细胞,发现YAP1的表达和活性在破骨细胞分化过程中受到调控;使用短发夹RNA沉默YAP1后显著降低了RANKL诱导的破骨细胞分化,观察到抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶阳性的多核破骨细胞形成减少,检测破骨细胞标记基因表达明显受损。对未沉默YAP1的骨髓巨噬细胞使用YAP-转录增强缔合域抑制剂维替泊芬后,破骨细胞分化和功能表达同样受到影响。说明YAP1可以调控破骨细胞的形成分化,而这种功能依赖于YAP1-转录增强缔合域的结合。这项研究表明YAP1在破骨细胞分化和功能中有重要作用。 TAZ抑制破骨细胞分化和功能。YANG等[48]发现在骨质疏松患者的骨髓和破骨细胞中,TAZ基因表达下降,提示TAZ可能在骨质疏松的发病机制中发挥了作用。敲除TAZ后观察到新生小鼠有骨质疏松的症状,将其骨髓巨噬细胞体外培养后发现抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶阳性多核破骨细胞比同窝未敲除TAZ基因的小鼠多。用慢病毒转染WT型小鼠的骨髓巨噬细胞使其过度表达或沉默TAZ,结果证明,TAZ抑制RANKL诱导的破骨细胞分化,证实了TAZ对RANKL诱导的破骨细胞形成分化具有抑制作用。 上述研究结果说明,YAP/TAZ对促进间充质干细胞成骨分化、调控骨细胞重塑、参与巨噬细胞极化以促进干细胞成骨分化和调控破骨细胞分化以及功能激活有着重要作用。但目前暂时没有系统性对YAP/TAZ在骨组织中细胞作用的研究,并且选择观察的细胞类型暂未统一,无法较好地比较研究结果。后续的实验研究应当更加系统和完善。期望后续研究能将现有的实验结果转换化,利用YAP/TAZ在骨组织细胞中的功能特点,进行治疗骨疾病方面的研究,见表2。 "

2.4 YAP/TAZ参与骨形成 2.4.1 YAP/TAZ对发育时期的骨骼形态的重要性 Hippo通路可以调节器官的形态、组织生长大小和维持稳态,作为其核心因子的YAP/TAZ同样在骨骼发育中起重要作用。KEGELMAN等[49]在研究过程中发现在使用Osx-Cre敲除YAP和TAZ(YAPcKO;TAZcKO)的小鼠均有胸腔畸形和继发骨折,新生鼠死亡率达到99%,仅有一只雌性小鼠能活到第56天,但患有脊柱侧弯、颅骨畸形和全身性的自发性骨折,而且同窝新生鼠的骨骼体积和骨组织矿物密度相较于野生型YAPWT;TAZWT少。虽然YAPcHET;TAZcKO和YAPcKO;TAZcHET的小鼠死亡率相对于YAP和TAZ均缺失的纯合子低,但在出生的10 d之内,上述基因型的小鼠均发生自发性的股骨骨折,其中YAPcHET;TAZcKO的小鼠股骨骨折发生率更高;虽然所有组骨折均有自主愈合,但均发现敲除YAP或TAZ基因的小鼠骨折处发现肥大软骨细胞过渡区有空腔,提示肥大软骨细胞死亡过多或者骨祖细胞数量的招募不足。 XIONG等[50]用Prx1-Cre和Osx-Cre敲除YAP和TAZ基因后,育种鼠在围产期期间都发生流产或胚胎患有骨骼畸形、胸腔出血等情况。VANYAI等[51]研究发现,使用Col2α1cre+ve敲除YAP和TAZ(Yapfl/ fl;Tazfl/fl)的小鼠在胚胎时期(E17.5)与同窝新生小鼠的对照比较,发现其胚胎标本有骨骼发育畸形,如脊柱畸形、桶状胸和胸骨以及鼻骨形态异常等情况。LI等 [52]使用Col2-Cre条件性敲除TAZ(TAZf/f)后发现,新生的小鼠幼崽表现出生长迟缓和颅骨、肋骨、胸骨胸骨发育不全,和四肢骨骼相较于对照组更短,骨小梁数量和厚度降低并且骨矿化下降,说明TAZ的缺失降低了小鼠中骨形成矿物质沉积率;在4月龄的TAZf/f小鼠也发现其关节形态不佳。上述研究提示YAP/TAZ参与骨骼形态的发育发展,敲除后会导致骨骼形成异常,导致严重的骨骼畸形甚至死亡。 2.4.2 YAP/TAZ在成骨不同阶段的功能 YAP/TAZ在成骨不同阶段发挥功能不同。XIONG等[50]使用Prx1-Cre、Osx-Cre和DMP1-Cre条件性敲除YAP和TAZ,研究在成骨细胞不同分化阶段YAP/TAZ对其影响。 有研究发现在Prx1-Cre条件下,YAP单倍体缺失和TAZ完全缺失(YAPf/+;TAZf/f)的小鼠骨骼发育正常。对5周龄小鼠和12周龄股骨的Micro-CT分析显示:YAPf/+;TAZf/f 小鼠的股骨松质骨体积和皮质厚度的相较其他小鼠增加;组织形态学分析显示:YAPf/+;TAZf/f小鼠的成骨细胞数量、矿化表面和骨形成率增加,而破骨细胞数量没有变化;二者生长板的总体厚度、增殖区宽度和肥大区宽度没有显著差异。这表明青春期和成年期的YAPf/+,TAZf/f小鼠骨细胞生物状态没有明显改变。将该基因小鼠细胞体外培养,发现YAP和TAZ会抑制成骨细胞祖细胞中的Wnt信号传导和Runx2活性。这些结果说明,在成骨祖细胞时期YAP 和 TAZ 的表达减少会增加骨量。在Osx-Cre条件下敲除YAP和TAZ(YAPf/f;TAZf/f),促进了12周龄小鼠椎体致密骨的成骨和骨形成,雌性小鼠还表现出成骨细胞数量和矿化表面明显增加,说明在间充质干细胞和成骨祖细胞时期,YAP/TAZ表达抑制会增加骨形成。 然而,与XIONG等[50]研究结果相反,KEGELMAN等[49]发现从Osx-Cre小鼠中敲除YAP和TAZ会降低骨量,发现小鼠成骨细胞数量减少和破骨细胞数量增加。这2项研究结果的差异可能来源以下几个方面:首先是二者比较对象不同,XIONG等[50]是将YAP/TAZ条件性敲除小鼠与仅携带Osx-Cre基因小鼠进行了比较,有研究指出,Osx-Cre小鼠出生后容易表现出骨骼质量欠佳甚至骨折[53];然后是观察骨骼的发育阶段不同,在Xiong的研究中开始敲除YAP/TAZ是在小鼠鼠龄3周时开始的,而后者是从育种一开始就敲除了YAP和TAZ。 最后,XIONG等[50]使用DMP1-Cre作为观察成熟成骨细胞和骨细胞的介导,敲除YAP和TAZ的(YAPf/f;TAZf/f)后发现同样5周龄和12周龄的小鼠,二者骨松质体积和骨皮质厚度相较于Prx1-Cre和Osx-Cre条件性敲除YAP和TAZ的小鼠有所减少;成骨细胞数量下降、骨形成率降低,导致矿化表面和附着矿物率降低。KEGELMAN等[38]在另一项研究也得到相似的结果。研究结果说明,与成熟的成骨细胞和骨细胞相比,YAP和TAZ 在骨祖细胞中发挥不同的功能。由此可见,YAP/TAZ在成骨不同阶段发挥功能不同。 2.4.3 YAP/TAZ参与颅颌面骨发育 YAP/YAZ在颅颌面发育过程中也有着重要作用。WANG 等[54]发现了YAP/TAZ在神经嵴细胞发育颅颌面的小鼠中,使用Wnt1Cre和Wnt1Cre2SOR单独敲除YAP或TAZ小鼠胚胎都出现颅面结构不全、下颌骨间充质结构紊乱和严重致死率的情况。早期有报道指出,在家族遗传性唇腭裂的基因中发现YAP1功能突变[55]。GOODWIN等[56]研究发现在Osx-Cre和Col2-Cre条件下敲除YAP和TAZ(YAPfl/fl;TAZfl/fl)的小鼠,发现在胚胎发育中缺少YAP和TAZ会导致小鼠胚胎腭突融合延迟伴区域性细胞增殖减少,说明YAP/TAZ的缺失会导致小鼠上腭间充质缺失导致腭裂,但下颌骨无明显异常。这项研究说明YAP/TAZ参与腭突融合并反驳了异常下颌骨会导致腭突融合失败的说法。 上述研究结果表明,YAP/TAZ在体内实验中对骨骼形态和颌面部形态发育有着重要作用,在成骨不同阶段有着相反作用,对于探索骨形成的机制和颌面部畸形病因有了新的研究方向,见表3。 "
| [1] QIN L, LIU W, CAO H, et al. Molecular mechanosensors in osteocytes. Bone Res. 2020;8:23. [2] MOYA I M, HALDER G. Hippo-YAP/TAZ signalling in organ regeneration and regenerative medicine. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2019;20(4):211-226. [3] KOVAR H, BIERBAUMER L, RADIC-SARIKAS B. The YAP/TAZ Pathway in Osteogenesis and Bone Sarcoma Pathogenesis. Cells. 2020;9(4):972. [4] HARVEY KF, PFLEGER CM, HARIHARAN IK. The Drosophila mst ortholog, hippo, restricts growth and cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis. Cell. 2003;114(4):457-467. [5] ZHAO B, WEI X, LI W, et al. Inactivation of YAP oncoprotein by the Hippo pathway is involved in cell contact inhibition and tissue growth control. Genes Dev. 2007;21(21):2747-2761. [6] ALSAMMAN S, CHRISTENSON SA, YU A, et al. Targeting acid ceramidase inhibits YAP/TAZ signaling to reduce fibrosis in mice. Sci Transl Med. 2020;12(557):eaay8798. [7] STEIN C, BARDET AF, ROMA G, et al. YAP1 exerts its transcriptional control via TEAD-mediated activation of enhancers. PLoS Genet. 2015; 11(8):e1005465. [8] ZHANG H, LIU CY, ZHA ZY, et al. TEAD transcription factors mediate the function of TAZ in cell growth and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Biol Chem. 2009;284(20):13355-13362. [9] VOLTES A, HEVIA CF, ENGEL-PIZCUETA C, et al. Yap/Taz-TEAD activity links mechanical cues to progenitor cell behavior during zebrafish hindbrain segmentation. Development. 2019;146(14):dev176735. [10] PAVEL M, RENNA M, PARK SJ, et al. Contact inhibition controls cell survival and proliferation via YAP/TAZ-autophagy axis. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):2961. [11] ARAGONA M, PANCIERA T, MANFRIN A, et al. A mechanical checkpoint controls multicellular growth through YAP/TAZ regulation by actin-processing factors. Cell. 2013;154(5):1047-1059. [12] PEREIRA D, RICHERT A, MEDJKANE S, et al. Cell geometry and the cytoskeleton impact the nucleo-cytoplasmic localisation of the SMYD3 methyltransferase. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):20598. [13] DUPONT S, MORSUT L, ARAGONA M, et al. Role of YAP/TAZ in mechanotransduction. Nature. 2011;474(7350):179-183. [14] WADA K, ITOGA K, OKANO T, et al. Hippo pathway regulation by cell morphology and stress fibers. Development. 2011;138(18):3907-3914. [15] LI H, RAGHUNATHAN V, STAMER W D, et al. Extracellular matrix stiffness and TGFβ2 regulate YAP/TAZ activity in human trabecular meshwork cells. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;10:844342. [16] GUO Y, QIAO Y, QUAN S, et al. Relationship of matrix stiffness and cell morphology in regulation of osteogenesis and adipogenesis of BMSCs. Mol Biol Rep. 2022;49(4):2677-2685. [17] YANG X, CHEN Z, CHEN C, et al. Bleomycin induces fibrotic transformation of bone marrow stromal cells to treat height loss of intervertebral disc through the TGFβR1/Smad2/3 pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):34. [18] KIM MS, JIN W. TrkB-induced inhibition of R-SMAD/SMAD4 activation is essential for TGF-β-mediated tumor suppressor activity. Cancers (Basel). 2020;12(4):1048. [19] STRASEN J, SARMA U, JENTSCH M, et al. Cell-specific responses to the cytokine TGFβ are determined by variability in protein levels. Mol Syst Biol. 2018;14(1):e7733. [20] LABIBI B, BASHKUROV M, WRANA JL, et al. Modeling the control of TGF-β/Smad nuclear accumulation by the hippo pathway effectors, Taz/Yap. iScience. 2020;23(8):101416. [21] HIEMER SE, SZYMANIAK AD, VARELAS X. The transcriptional regulators TAZ and YAP direct transforming growth factor β-induced tumorigenic phenotypes in breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 2014;289(19):13461-13474. [22] VARELAS X, SAMAVARCHI-TEHRANI P, NARIMATSU M, et al. The Crumbs complex couples cell density sensing to Hippo-dependent control of the TGF-β-SMAD pathway. Dev Cell. 2010;19(6):831-844. [23] SZETO SG, NARIMATSU M, LU M, et al. YAP/TAZ are mechanoregulators of TGF-β-Smad signaling and renal fibrogenesis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016;27(10):3117-3128. [24] LIU W, CUI Y, SUN J, et al. Transforming growth factor-β1 up-regulates connexin43 expression in osteocytes via canonical Smad-dependent signaling pathway. Biosci Rep. 2018;38(6):BSR20181678. [25] QIN Z, XIA W, FISHER GJ, et al. YAP/TAZ regulates TGF-β/Smad3 signaling by induction of Smad7 via AP-1 in human skin dermal fibroblasts. Cell Commun Signal. 2018;16(1):18. [26] MIRANDA MZ, BIALIK JF, SPEIGHT P, et al. TGF-β1 regulates the expression and transcriptional activity of TAZ protein via a Smad3-independent, myocardin-related transcription factor-mediated mechanism. J Biol Chem. 2017;292(36):14902-14920. [27] UEMURA M, NAGASAWA A, TERAI K. Yap/Taz transcriptional activity in endothelial cells promotes intramembranous ossification via the BMP pathway. Sci Rep. 2016;6:27473. [28] PARK JS, KIM M, SONG NJ, et al. A Reciprocal Role of the Smad4-Taz Axis in Osteogenesis and Adipogenesis of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Stem Cells. 2019;37(3):368-381. [29] LEE E, KO JY, KIM J, et al. Osteogenesis and angiogenesis are simultaneously enhanced in BMP2-/VEGF-transfected adipose stem cells through activation of the YAP/TAZ signaling pathway. Biomater Sci. 2019;7(11):4588-602. [30] KOPF J, PETERSEN A, DUDA GN, et al. BMP2 and mechanical loading cooperatively regulate immediate early signalling events in the BMP pathway. BMC Biol. 2012;10:37. [31] KLOSTERHOFF BS, VANTUCCI CE, KAISER J, et al. Effects of osteogenic ambulatory mechanical stimulation on early stages of BMP-2 mediated bone repair. Connect Tissue Res. 2022;63(1):16-27. [32] DENG M, LIU P, XIAO H, et al. Improving the osteogenic efficacy of BMP2 with mechano growth factor by regulating the signaling events in BMP pathway. Cell Tissue Res. 2015;361(3):723-731. [33] WEI Q, HOLLE A, LI J, et al. BMP-2 Signaling and mechanotransduction synergize to drive osteogenic differentiation via YAP/TAZ. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2020;7(15):1902931. [34] MATSUMOTO Y, LA ROSE J, KENT OA, et al. Reciprocal stabilization of ABL and TAZ regulates osteoblastogenesis through transcription factor RUNX2. J Clin Invest. 2016;126(12):4482-4496. [35] YANG JH, KIM SC, KIM KM, et al. Isorhamnetin attenuates liver fibrosis by inhibiting TGF-β/Smad signaling and relieving oxidative stress. Eur J Pharmacol. 2016;783:92-102. [36] KOMATSU N, KAJIYA M, MOTOIKE S, et al. Type I collagen deposition via osteoinduction ameliorates YAP/TAZ activity in 3D floating culture clumps of mesenchymal stem cell/extracellular matrix complexes. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):342. [37] LORTHONGPANICH C, THUMANU K, TANGKIETTRAKUL K, et al. YAP as a key regulator of adipo-osteogenic differentiation in human MSCs. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):402. [38] KEGELMAN CD, COULOMBE JC, JORDAN KM, et al. YAP and TAZ mediate osteocyte perilacunar/canalicular remodeling. J Bone Miner Res. 2020;35(1):196-210. [39] ZHAO G, HUANG B L, RIGUEUR D, et al. CYR61/CCN1 regulates sclerostin levels and bone maintenance. J Bone Miner Res. 2018;33(6): 1076-1089. [40] ZARKA M, ETIENNE F, BOURMAUD M, et al. Mechanical loading activates the YAP/TAZ pathway and chemokine expression in the MLO-Y4 osteocyte-like cell line. Lab Invest. 2021;101(12):1597-1604. [41] SCHLUNDT C, EL KHASSAWNA T, SERRA A, et al. Macrophages in bone fracture healing: Their essential role in endochondral ossification. Bone. 2018;106:78-89. [42] ZHANG F, HUAN L, XU T, et al. Inflammatory macrophages facilitate mechanical stress-induced osteogenesis. Aging (Albany NY). 2020; 12(4):3617-3625. [43] ATCHA H, MELI VS, DAVIS CT, et al. Crosstalk between CD11b and Piezo1 mediates macrophage responses to mechanical cues. Front Immunol. 2021;12:689397. [44] ATCHA H, JAIRAMAN A, HOLT JR, et al. Mechanically activated ion channel Piezo1 modulates macrophage polarization and stiffness sensing. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):3256. [45] DONG L, SONG Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Mechanical stretch induces osteogenesis through the alternative activation of macrophages. J Cell Physiol. 2021;236(9):6376-6390. [46] MCDONALD MM, KHOO WH, NG PY, et al. Osteoclasts recycle via osteomorphs during RANKL-stimulated bone resorption. Cell. 2021; 184(5):1330-1347. [47] ZHAO L, GUAN H, SONG C, et al. YAP1 is essential for osteoclastogenesis through a TEADs-dependent mechanism. Bone. 2018;110:177-186. [48] YANG W, LU X, ZHANG T, et al. TAZ inhibits osteoclastogenesis by attenuating TAK1/NF-kappaB signaling. Bone Res. 2021;9(1):33. [49] KEGELMAN CD, MASON DE, DAWAHARE JH, et al. Skeletal cell YAP and TAZ combinatorially promote bone development. FASEB J. 2018; 32(5):2706-2721. [50] XIONG J, ALMEIDA M, O’BRIEN CA. The YAP/TAZ transcriptional co-activators have opposing effects at different stages of osteoblast differentiation. Bone. 2018;112:1-9. [51] VANYAI HK, PRIN F, GUILLERMIN O, et al. Control of skeletal morphogenesis by the Hippo-YAP/TAZ pathway. Development. 2020; 147(21):dev187187. [52] LI Y, YANG S, QIN L, et al. TAZ is required for chondrogenesis and skeletal development. Cell Discov. 2021;7(1):26. [53] WANG L, MISHINA Y, LIU F. Osterix-Cre transgene causes craniofacial bone development defect. Calcif Tissue Int. 2015;96(2):129-137. [54] WANG J, XIAO Y, HSU CW, et al. Yap and Taz play a crucial role in neural crest-derived craniofacial development. Development. 2016; 143(3):504-515. [55] WILLIAMSON KA, RAINGER J, FLOYD JA, et al. Heterozygous loss-of-function mutations in YAP1 cause both isolated and syndromic optic fissure closure defects. Am J Hum Genet. 2014;94(2):295-302. [56] GOODWIN AF, CHEN CP, VO NT, et al. YAP/TAZ regulate elevation and bone formation of the mouse secondary palate. J Dent Res. 2020; 99(12):1387-1396. |
| [1] | Dang Yi, Du Chengyan, Yao Honglin, Yuan Nenghua, Cao Jin, Xiong Shan, Zhang Dingmei, Wang Xin. Hormonal osteonecrosis and oxidative stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1469-1476. |
| [2] | Long Guiyue, Li Dongdong, Liao Hongbing. Calcium phosphate cement/poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) degradation products promote osteoclast differentiation of mouse monocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1193-1198. |
| [3] | Huang Linke, Wei Linhua, Jiang Jie, Liu Qian, Chen Weiwei. Effects of estrogen combined with treadmill exercise on bone mass and articular cartilage in ovariectomized mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1166-1171. |
| [4] | Gao Yu, Han Jiahui, Ge Xin. Immunoinflammatory microenvironment after spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1300-1305. |
| [5] | Yang Yitian, Wang Lu, Yao Wei, Zhao Bin. Application of the interaction between biological scaffolds and macrophages in bone regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1071-1079. |
| [6] | Li Wenjie, You Aijia, Zhou Junli, Fang Sujuan, Li Chun. Effects of different dressings in the treatment of burn wounds: a network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1141-1148. |
| [7] | Wang Jinling, Huang Xiarong, Qu Mengjian, Huang Fujin, Yin Lingwei, Zhong Peirui, Liu Jin, Sun Guanghua, Liao Yang, Zhou Jun. Effects of exercise training on bone mass and bone microstructure in aged osteoporotic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 676-682. |
| [8] | Zhang Min, Zhang Xiaoming, Liu Tongbin. Application potential of naringin in bone tissue regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 787-792. |
| [9] | Tao Xin, Xu Yi, Song Zhiwen, Liu Jinbo. Hippo signaling pathway in the regulation of spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 619-625. |
| [10] | Li Rui, Liu Zhen, Guo Zige, Lu Ruijie, Wang Chen. Aspirin-loaded chitosan nanoparticles and polydopamine modified titanium sheets improve osteogenic differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 374-379. |
| [11] | Zhang Lichen, Chen Liang, Gu Yong. Inorganic ion bionic periosteum regulates immune microenvironment to promote bone repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 346-353. |
| [12] | Dai Xianglin, Zhang Wenfeng, Yao Xijun, Shang Jiaqi, Huang Qiujin, Ren Yifan, Deng Jiupeng. Barium titanate/polylactic acid piezoelectric composite film affects adhesion, proliferation, and osteogenic differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 367-373. |
| [13] | Chen Feng, Ren Guowu, Zhang Xiaoyun, Chen Yueping, Shi Rusheng. Receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa B ligand signal transduction mechanism and osteoclast activation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 293-299. |
| [14] | Zhang Jie, Tian Ai. Advances in the signaling pathway of M2 macrophages involved in bone regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 314-321. |
| [15] | Wei Tengfei, He Xiaoming, Wei Yurou, Zhan Zhiwei, He Mincong, He Wei, Wei Qiushi. Differential expression of Piezo1 in osseous tissue of steroid- and alcohol-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 270-275. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||