Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (4): 619-625.doi: 10.12307/2023.261
Previous Articles Next Articles
Hippo signaling pathway in the regulation of spinal cord injury
Tao Xin1, 2, Xu Yi1, Song Zhiwen1, Liu Jinbo1
- 1The Third Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Changzhou 213003, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, People’s Hospital of Liyang, Changzhou 213300, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2022-03-16Accepted:2022-05-09Online:2023-02-08Published:2022-06-23 -
Contact:Liu Jinbo, MD, Chief physician, Professor, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Changzhou 213003, Jiangsu Province, China Song Zhiwen, Master, Physician, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Changzhou 213003, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Tao Xin, Doctoral candidate, Associate chief physician, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Changzhou 213003, Jiangsu Province, China; Department of Orthopedics, People’s Hospital of Liyang, Changzhou 213300, Jiangsu Province, China Xu Yi, Master candidate, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Changzhou 213003, Jiangsu Province, China Tao Xin and Xu Yi contributed equally to this article. -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China (General Program), No. 81972048 (to LJB); National Natural Science Foundation of China (Youth Project), No. 81901247 (to SZW)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Tao Xin, Xu Yi, Song Zhiwen, Liu Jinbo. Hippo signaling pathway in the regulation of spinal cord injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 619-625.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
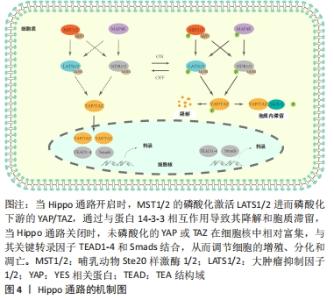
2.1 Hippo信号通路的概述 Hippo通路最初在果蝇细胞中发现,经过数十年的探索,研究证实其在细胞生长、分化、增殖和凋亡过程发挥重要作用,同时参与调控器官的形成发育、体积以及维持稳态[9-10];此外,Hippo通路参与细胞接触性抑制(细胞因互相接触而停止生长的一种生物学特性)的调节,YAP的过表达会导致细胞接触性抑制的丧失[11];Hippo信号通路还参与了各种肿瘤的发生,在许多类型的肿瘤中存在Hippo通路的失活[12-14]。 Hippo通路核心分子在果蝇中主要包括Hpo、Sav、Wts、Mats及Yki蛋白,对应的人类同源蛋白分别为Mst1/2、WW45、Lats、Mob1及YAP蛋白。在上游信号输入因子如Merlin作用下[15],启动核心激酶级联反应,首先MST1/2被活化,活化的MST1/2与WW45(SAV)结合后磷酸化LATS1/2,LATS1/2 进一步与MOB1形成复合物,最后磷酸化YAP/TAZ,磷酸化的YAP/TAZ被14-3-3蛋白募集并停留在细胞质中[16],此后,磷酸化的YAP/TAZ继续被CK1δ/ε 磷酸化,发生SCFβ-TRCP介导的YAP/TAZ泛素化降解[17];当Hippo信号通路被阻断或失活,YAP/TAZ不能被磷酸化,未被磷酸化的YAP/TAZ迁移进入细胞核。作为转录激活因子,与其他转录因子如TEAD结合,促进下游诸如Cyclin E、AXL、CTGF、Cyr61等靶基因的表达,从而发挥其调控细胞增殖以及细胞凋亡的作用。除了以上分子组成的经典Hippo信号级联模型,AGC丝氨酸/苏氨酸NDR1/2激酶(STK38/STK38L)和Ste20-like MAP4K家族成员也是Hippo通路重要的新成员,其中MAP4K激酶家族可激活磷酸化LATS1/2,从而通过磷酸化YAP/TAZ激活Hippo通路[18]。NDR1/2激酶可通过被核心分子MST1/2激活,进而磷酸化YAP,激活Hippo通路[19-20],见图4。 "

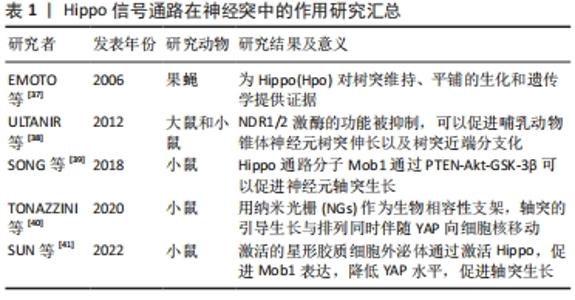
2.2 Hippo信号通路在中枢神经系统中的表达和作用机制 2.2.1 Hippo通路分子在神经系统细胞中存在广泛高表达 Cheng等[21]利用小鼠大脑皮质神经胶质、神经元和血管细胞的RNA-Seq转录组测序[22],经过研究表明Hippo信号通路核心组分,除了MST1和MST2,其余均在脑内大多数细胞类型中高表达,包括星形胶质细胞、神经元、少突胶质祖细胞、新形成的少突胶质细胞、有髓鞘的少突胶质细胞、小胶质细胞和内皮细胞。共转录因子YAP在星形胶质细胞中存在显著高表达,其促增殖能力是反应性星形胶质细胞增生功能的基础。 2.2.2 Hippo信号通路在中枢神经系统中参与调控神经发育 Hippo信号通路能够调控细胞的增殖、分化,在生物的器官发育过程中尤为重要。对于神经系统发育的影响,该通路依然作用显著,Poon等[23]在果蝇中研究发现,抑制Hippo通路能够增加幼虫胚胎后期成脑的体积,并且Hippo信号通路调控脑形成大小的作用是通过其底物Yorki(YAP同源物)实现的。该研究发现Hippo通路调节脑的大小是通过3种方式:增强神经干细胞的增殖能力、延长胚胎后期神经发生的时间、加快神经干细胞的细胞周期速度。另外一项研究也证实了Hippo信号通路参与调控神经系统的发育和器官大小,肝脏激酶B1(liver kinaseB1,LKB1)作为调节细胞极性、细胞增殖和应激反应的一种肿瘤抑制激酶[24],其与AMP依赖的蛋白激酶(adenosine 5‘-monophosphate -activated protein kinase,AMPK)通过调控核心激酶级联或直接通过AMPK磷酸化YAP,抑制哺乳动物细胞和癌症模型中细胞的YAP活性[25-26]。Gailite等[27]也发现LKB1能够抑制果蝇视叶神经细胞的Hippo通路,LKB1功能缺失能够诱导YAP靶基因的表达,从而加速细胞分裂和促进组织生长,同样的现象在中央大脑中也被证实。 2.2.3 Hippo通路调控神经细胞的分化和增殖 越来越多的研究表明,Hippo通路在调控神经干细胞分化中发挥着重要作用。在神经干细胞中,LATS1/2激酶的失活通过诱导YAP/TAZ活化,引起大量细胞凋亡,并上调一系列与细胞生长和增殖相关的基因[28]。当细胞接受到外界机械刺激时,YAP/TAZ能作为转录激活因子,介导下游靶基因表达,参与神经干细胞分化[29]。神经干细胞从静止态到激活,是对损伤做出应对进而维持组织稳态,Mts的抑制可以增强神经干细胞中的Hippo信号,此外Hippo或Warts的缺失诱导果蝇神经系统中神经干细胞的生长和增殖,表明Hippo信号在维持神经干细胞静止中起关键作用[30]。 神经嵴细胞的发育具有多潜能性,Hippo信号通路可以影响神经嵴分化以及细胞增殖。Kumar等[31]在鸟类胚胎中采用蛋质粒电穿孔法降低或上调YAP基因活性,研究YAP对骨形成蛋白(bone morphogenetic protein,BMP)、Wnt蛋白的影响,证实它们之间互相作用进而调控鸟类胚胎发育过程中神经嵴的迁移。深入研究发现,Hippo通路在神经嵴诱导、迁移、增殖、存活和分化中存在关键功能[32]。 Hippo信号通路同时也影响其他神经细胞分化,Jukam等[33]在果蝇感光细胞中研究发现,Yki通过抑制其负调控因子Warts,而促进其正调控因子Melted,实现自身的正反馈,从而引起神经细胞“全或无”的分化形式,使细胞分化成分别对蓝、绿光敏感的2种表型。此外,有研究发现神经干细胞中的YAPs是介导皮质星形胶质细胞分化与增殖的必要条件[34]。 综上所述,在神经系统的发育过程中,YAP起着核心调控作用。YAP的激活提高神经细胞的增殖能力进而增加器官的体积,同时YAP介导神经细胞分化。机体对YAP的调控,维持着神经细胞增殖、分化之间的动态平衡。 2.3 Hippo信号通路在脊髓损伤中的作用及机制 2.3.1 Hippo信号通路在神经突中的作用 神经元分化出轴突,并与树突彼此形成突触,在体内形成广泛而庞大的连接,神经元的连接保证了神经系统在传递信号时信息的完整性和及时性。而在脊髓损伤后,损伤部位轴突和树突的再生功能往往受到很大程度上的抑制,一是由于细胞的损伤造成神经突功能丧失,二是由于受到抑制性微环境的影响(胶质瘢痕形成、炎症刺激、氧化应激等) [35-36],而Hippo通路主要在减少抑制性微环境影响中发挥调控作用。 Emoto等[37]在果蝇Ⅳ类树枝状化神经元(drosophila class Ⅳ dendritic arborization neurons)中,发现Hpo(Mst1/2同源物)通过下游2个底物Trc(属于NDR家族)、Wts(LATS1/2同源物)激酶,分别调控树突的排列以及树突形态的维持,但是Hpo对轴突没有明显的影响。另有研究发现NDR1/2激酶(MOB1的下游因子,与LATS1/2激酶同属NDR家族)的功能被抑制,可以促进哺乳动物锥体神经元树突伸长以及树突近端分支化[38]。该研究进一步证实,NDR1/2对树突的影响是分别通过接头蛋白相关激酶1(AP-2 associated kinase1,AAK1)、Rabin8(a GDP/GTP exchange factor of Rab8 GTPase)进行调控的。除了NDR家族,Mob1分子也影响轴突生长,SONG等[39]发现PTEN-Akt-GSK-3β轴可以调控Mob1,其中GSK-3β介导Mob1的泛素化降解。过表达Mob1可以促进神经元轴突生长指标NF200以及GAP43表达,并在细胞和动物实验取得了一致的结果,提示Mob1在促进轴突伸长中的重要作用。 Hippo通路介导轴突导向生长也被运用到组织工程学方法中,TONAZZINI等[40]使用纳米光栅作为生物相容性支架,研究PC12细胞和原代海马神经元的细胞间相互接触作用,他们发现轴突引导生长与纳米光栅的横向距离相关,并且轴突的引导生长与排列同时伴随YAP向细胞核移动。另外,SUN等[41]提取星形胶质细胞外泌体和脂多糖预激活的星形胶质细胞外泌体,证实脂多糖预激活的星形胶质细胞外泌体的作用强于星形胶质细胞外泌体,深入研究机制发现其通过激活Hippo通路,促进MOB1表达,降低YAP水平,促进轴突的生长。 以上研究提示,Hippo家族在调控神经元神经突起方面发挥了重要的作用。在神经元发育过程中,Trc、Wts分别调控树突的排列以及树突形态的维持,而抑制NDR1/2能够促进树突的伸长。至于MOB1促进神经元轴突伸长的具体机制还有待研究。未来可以关注MOB1是否通过影响NDR激酶或YAP调控轴突的伸长,以及YAP在神经干细胞和神经元中的更多潜在作用及其作用机制,利用细胞组织工程学手段引导轴突导向生长,见表1。 "
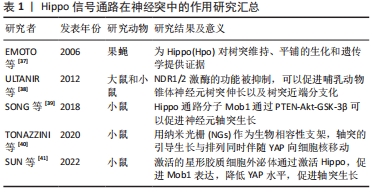
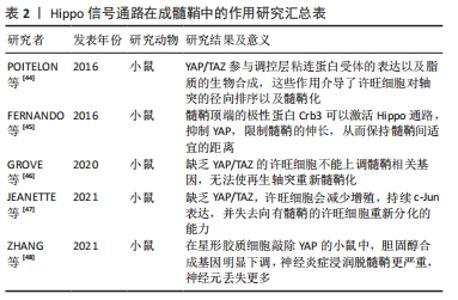
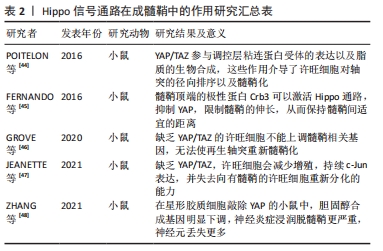
2.3.2 Hippo信号通路在成髓鞘中的作用 髓鞘对神经元的功能是至关重要的,髓鞘介导了神经元信号的传递,保证了轴突与周围组织绝缘,避免了干扰,并且髓鞘形成“跳跃式传导”保证了动作电位的快速传递,甚至还能介导受损的轴突再生[42]。而在脊髓损伤后,受损的轴突不再有髓鞘包绕,少突胶质前体细胞虽大量增殖但不能分化成熟形成髓鞘[43]。研究表明,Hippo信号通路在髓鞘的形成中也有重要作用。 目前对于成髓鞘的研究主要在许旺细胞中展开,在髓鞘的伸长与抑制动态调控中均发挥作用。POITELON等[44]发现YAP/TAZ在许旺细胞早期增殖、神经生长以及成髓鞘过程中趋向于核定位,而在成熟的髓鞘中趋向于胞质定位,YAP/TAZ受到机械信号刺激而激活,激活后的YAP/TAZ与其共转录因子Tead促进许旺细胞的增殖,YAP/TAZ还参与调控层粘连蛋白受体的表达以及脂质的生物合成,这些作用介导了许旺细胞对轴突的径向排序以及髓鞘化。在轴突伸长过程中,髓鞘的伸长受到YAP的动态调控,YAP促进髓鞘伸长,而激活Hippo通路可以抑制YAP的功能,FERNANDO等[45]发现髓鞘顶端的极性蛋白Crb3可以激活Hippo通路,抑制YAP,限制髓鞘的伸长,从而保持髓鞘间适宜的距离。GROVE等[46]的发现进一步证实了YAP/TAZ的成髓鞘能力,在神经损伤后,成熟许旺细胞需要YAP/TAZ来恢复周围的髓鞘形成,成年小鼠神经损伤并发轴突退行性变时,YAP/TAZ显著消失,只有当轴突再生时,它们才会在许旺细胞中重新出现,缺乏YAP/TAZ的许旺细胞不能上调髓鞘相关基因,无法使再生轴突重新髓鞘化。JEANETTE等[47]也发现缺乏YAP/TAZ,许旺细胞会减少增殖, c-Jun表达持续,并失去向有髓鞘的许旺细胞重新分化的能力,他们的研究表明,YAP和TAZ是许旺细胞髓鞘化和再髓鞘化编程的潜在靶点。进一步研究发现YAP通过介导星形胶质细胞胆固醇合成影响髓鞘生长。胆固醇作为髓鞘的主要成分,主要在星形胶质细胞中合成,并运输到成年大脑中的少突胶质细胞和神经元,ZHANG等[48]在星形胶质细胞敲除YAP的小鼠中,通过RNA测序发现胆固醇合成基因明显下调,神经炎症浸润脱髓鞘更严重,神经元丢失更多。 通过以上研究结果看出,YAP/TAZ在外周髓鞘形成过程中是动态变化的。早期YAP/TAZ的激活促进许旺细胞增殖;在神经元轴突伸长的过程中,YAP的激活能够促使增生的髓鞘同时伸长,在成熟的髓鞘中,YAP/TAZ活性降低,更趋向于胞质定位。星形胶质细胞YAP对于髓鞘的合成至关重要,见表2。 "
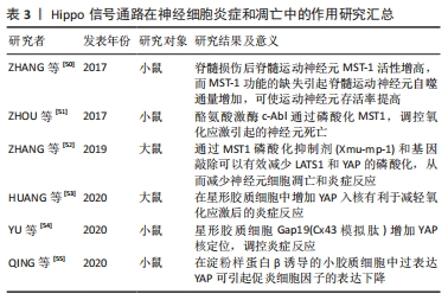
2.3.3 Hippo信号通路在神经细胞炎症和凋亡中的作用 在脊髓损伤后,脊髓的损伤部位迅速产生炎症反应。脊髓血管的破裂会导致脊髓神经细胞处于缺血缺氧状态,并产生大量炎症因子,介导脊髓的炎症反应并引起水肿[48]。该过程还募集中性粒细胞、巨噬细胞等趋向损伤部位,进一步加重炎症,导致损伤部位神经元的微环境急剧变化,并诱导神经元的凋亡及坏死[49]。在这一过程中,神经元Hippo通路相关信号分子发生了变化,参与了细胞凋亡、自噬等过程。 脊髓损伤发生后,MST-1通过诱导凋亡相关基因的表达,启动凋亡程序。ZHANG等[50]发现脊髓损伤后脊髓运动神经元MST-1活性增高,而MST-1功能的缺失引起脊髓运动神经元自噬通量增加,可使运动神经元存活率提高。他们在动物实验中也证实了MST-1功能的缺失可以促进脊髓损伤后功能改善和突触存活。通过Hippo的上游酪氨酸激酶c-Abl,磷酸化MST1,可以调控氧化应激引起的神经元死亡[51]。ZHANG等[52]的研究也证实MST1是一种促进细胞凋亡的激酶,大鼠脑出血损伤模型中,MST1的磷酸化在脑组织中显著增加,通过MST1磷酸化抑制剂(Xmu-mp-1)和基因敲除可以有效减少LATS1和YAP的磷酸化,从而减少神经元细胞凋亡和炎症反应。 除了神经元细胞,在其他神经细胞中Hippo通路对炎症反应也存在调控作用,HUANG等[53]研究发现,大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤模型中,通过Xmu-mp-1增加星形胶质细胞YAP核定位可以提高细胞活力,减少神经元死亡和反应性星形胶质细胞增生,同时减少炎性细胞因子的释放,从而减轻脑缺血再灌注损伤氧化应激后的炎症反应。同样是在星形胶质细胞中,YU等[54]发现连接蛋白43过表达加重脑出血损伤后细胞凋亡和炎症反应,使用连接蛋白43模拟肽Gap19可增加YAP的核转位,降低血肿周围组织的炎症细胞因子水平,并且YAP抑制剂维替波芬(VP)在体外可以逆转Gap19的抗炎作用,证实星形胶质细胞Gap19是通过YAP调控炎症反应。在小胶质细胞介导的中枢炎症反应中,QING等[55]用淀粉样蛋白β诱导的小胶质细胞促炎细胞因子产生,他们发现淀粉样蛋白β可降低小胶质细胞中YAP的表达。在小胶质细胞中过表达YAP可引起促炎细胞因子的表达下降。 因此,在脊髓损伤后,由于炎症或凋亡信号刺激,神经元中的MST1被激活。MST1通过诱导凋亡相关基因的表达,启动凋亡程序,通过抑制MST1有利于神经元的存活;同样在星形胶质细胞以及小胶质细胞中过表达YAP有利于减轻氧化应激后的炎症反应,由此可见,通过抑制Hippo通路可以减轻神经元凋亡和神经功能缺损,见表3。 "

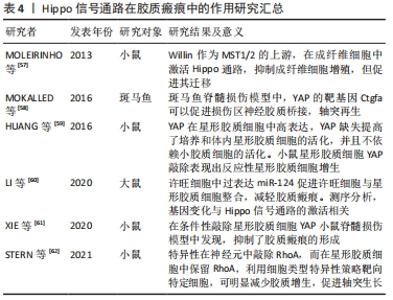
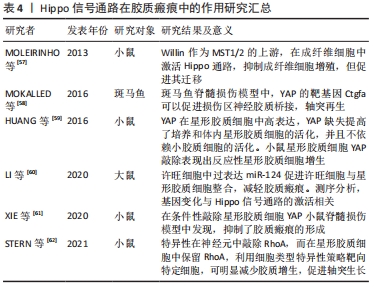
2.3.4 Hippo信号通路在胶质瘢痕中的作用 脊髓损伤后,胶质瘢痕的形成造成了神经元的继发损伤。胶质瘢痕由星形胶质细胞和成纤维细胞活化后产生,形成了神经元周围的硬基质,使轴突不能穿过瘢痕。同时该过程也形成了抑制性微环境,使神经元再生功能被抑制[56]。有研究显示,Hippo信号通路不仅参与瘢痕的形成,也介导了瘢痕形成后的机械信号转导。 激活Hippo可以调控成纤维细胞增殖和迁移,MST1/2的上游分子Willin在大鼠的坐骨神经中被发现,通过激活Hippo通路可引起LATS和YAP的磷酸化,MOLEIRINHO等[57]发现,Willin在坐骨神经中主要表达于成纤维细胞,并在成纤维细胞中激活Hippo通路,抑制成纤维细胞增殖,但能够促进成纤维细胞的迁移。有研究显示,肌成纤维细胞通过细胞表面整合素受体的机械传导感受细胞外基质张力,激活YAP和TAZ转位到胞核,促进包括结缔组织生长因子和血小板衍生生长因子在内的促生长基因的上调。结缔组织生长因子作为YAP的靶基因可以在斑马鱼脊髓损伤中促进损伤区神经胶质桥接、轴突再生[58]。 在星形胶质细胞活化介导胶质瘢痕增生中,Hippo通路发挥更重要的作用。HUANG等[59]发现YAP在星形胶质细胞中高表达,YAP缺失提高了体外和体内星形胶质细胞的活化,并且不依赖小胶质细胞的激活。小鼠星形胶质细胞YAP敲除表现出反应性星形胶质细胞增生。LI等[60]在许旺细胞中过表达miR-124促进了许旺细胞与星形胶质细胞整合,并可能减弱星形胶质细胞成胶质瘢痕的能力,转染miR-124的许旺细胞测序分析,基因变化与Hippo信号通路的激活相关。与HUANG等发现不同,XIE等[61]在小鼠脊髓损伤模型中发现,星形胶质细胞的YAP表达升高并被激活,而条件性敲除YAP使星形胶质细胞增殖能力下降,抑制了胶质瘢痕的形成,这一过程抑制脊髓损伤后神经元的再生,不利于损伤后小鼠功能恢复,接着他们探究了YAP调控星形胶质细胞增殖的具体机制,发现是通过bFGF-RhoA-YAP-p27Kip1轴介导的。通过对RhoA-YAP轴的深入研究发现,RhoA在神经元和星形胶质细胞中以相反方式作用影响轴突再生,在神经元中,RhoA抑制轴突生长,而在星形胶质细胞中,RhoA通过驱动肌动蛋白微丝压紧而激活YAP信号,抑制星形胶质细胞增生,减少胶质瘢痕产生,从而促进轴突再生,因此,在神经元中敲除RhoA,而在星形胶质细胞中保留RhoA,利用细胞类型特异性策略靶向特定细胞,可明显减少胶质增生,促进轴突生长[62]。 综合以上研究,作者认为Hippo通路对于星形胶质细胞的增殖以及胶质瘢痕具有调控作用,但是具体调控方式有待进一步研究。作者认为在脊髓损伤早期星形胶质细胞形成有利于损伤部位的愈合,形成受损轴突的“避风港”,避免轴突接触炎性环境。但是在损伤后期炎症消退后,瘢痕的持续存在成为神经元再生的“壁垒”,不利于神经元再生,在瘢痕形成后,细胞外基质的硬度增加,通过机械信号激活YAP/TAZ,可能又促进成纤维细胞的增殖活化,形成恶性循环。因此,根据致伤时机以及细胞微环境合理调控胶质瘢痕非常重要,见表4。 "
| [1] LI HL, XU H, LI YL, et al. Epidemiology of traumatic spinal cord injury in Tianjin, China: An 18-year retrospective study of 735 cases. J Spinal Cord Med. 2019;42(6):778-785. [2] AHUJA CS, NORI S, TETREAULT L, et al. Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury-Repair and Regeneration. Neurosurgery. 2017;80(3S):S9-S22. [3] MCRAE J, SMITH C, EMMANUEL A, et al. The experiences of individuals with cervical spinal cord injury and their family during post-injury care in non-specialised and specialised units in UK. BMC Health Serv Res. 2020;20(1):783. [4] HACHEM LD, MOTHE AJ, TATOR CH. Unlocking the paradoxical endogenous stem cell response after spinal cord injury. Stem Cells. 2020;38(2):187-194. [5] O’SHEA TM, BURDA JE, SOFRONIEW MV. Cell biology of spinal cord injury and repair. J Clin Invest. 2017;127(9):3259-3270. [6] KIMURA T, HORIKOSHI Y, KURIYAGAWA C, et al. Rho/ROCK Pathway and Noncoding RNAs: Implications in Ischemic Stroke and Spinal Cord Injury. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(21):11573. [7] CHENG P, LIAO HY, ZHANG HH. The role of Wnt/mTOR signaling in spinal cord injury. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2022;25:101760. [8] ZAVVARIAN MM, ZHOU C, KAHNEMUYIPOUR S, et al. The MAPK Signaling Pathway Presents Novel Molecular Targets for Therapeutic Intervention after Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury: A Comparative Cross-Species Transcriptional Analysis. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(23):12934. [9] BUTTITTA LA, EDGAR BA. How size is controlled: from Hippos to Yorkies. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9(11):1225-1227. [10] YU FX, ZHAO B, GUAN KL. Hippo Pathway in Organ Size Control, Tissue Homeostasis, and Cancer. Cell. 2015;163(4):811-828. [11] ZHAO B, WEI X, LI W, et al. Inactivation of YAP oncoprotein by the Hippo pathway is involved in cell contact inhibition and tissue growth control. Genes Dev. 2007;21(21):2747-2761. [12] DEY A, VARELAS X, GUAN KL. Targeting the Hippo pathway in cancer, fibrosis, wound healing and regenerative medicine. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2020;19(7):480-494. [13] GONZÁLEZ-ALONSO P, ZAZO S, MARTÍN-APARICIO E, et al. The Hippo Pathway Transducers YAP1/TEAD Induce Acquired Resistance to Trastuzumab in HER2-Positive Breast Cancer. Cancers (Basel). 2020; 12(5):1108. [14] HUANG Z, ZHOU JK, WANG K, et al. PDLIM1 Inhibits Tumor Metastasis Through Activating Hippo Signaling in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hepatology. 2020; 71(5): 1643-1659. [15] YIN F, YU JZ, ZHENG YG, et al. Spatial organization of Hippo signaling at the plasma membrane mediated by the tumor suppressor Merlin/NF2. Cell. 2013;154(6):1342-1355. [16] DONG JX, FELDMANN G, HUANG JB, et al. Elucidation of a universal size-control mechanism in Drosophila and mammals. Cell. 2007; 130(6):1120-1133. [17] ZHAO B, LI L, TUMANENG K, et al. A coordinated phosphorylation by Lats and CK1 regulates YAP stability through SCFβ-TRCP. Genes Dev. 2010;24(1):72-85. [18] MENG Z, MOROISHI T, MOTTIER-PAVIE V, et al. MAP4K family kinases act in parallel to MST1/2 to activate LATS1/2 in the Hippo pathway. Nat Commun. 2015;6:8357. [19] HERGOVICH A. The Roles of NDR Protein Kinases in Hippo Signalling. Genes (Basel). 2016;7(5):21. [20] EMOTO K. The growing role of the Hippo--NDR kinase signalling in neuronal development and disease. J Biochem. 2011;150(2):133-141. [21] CHENG J, WANG S, DONG Y, et al. The Role and Regulatory Mechanism of Hippo Signaling Components in the Neuronal System. Front Immunol. 2020;11:281. [22] ZHANG Y, CHEN K, SLOAN SA, et al. An RNA-sequencing transcriptome and splicing database of glia, neurons, and vascular cells of the cerebral cortex. J Neurosci. 2014;34(36):11929-11947. [23] POON CL, MITCHELL KA, KONDO S, et al. The Hippo Pathway Regulates Neuroblasts and Brain Size in Drosophila melanogaster. Curr Biol. 2016; 26(8):1034-1042. [24] SHACKELFORD DB, SHAW RJ. The LKB1-AMPK pathway: metabolism and growth control in tumour suppression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009;9(8): 563-575. [25] NGUYEN HB, BABCOCK JT, WELLS CD, et al. LKB1 tumor suppressor regulates AMP kinase/mTOR-independent cell growth and proliferation via the phosphorylation of Yap. Oncogene. 2013;32(35):4100-4109. [26] MO JS, MENG Z, KIM YC, et al. Cellular energy stress induces AMPK-mediated regulation of YAP and the Hippo pathway. Nat Cell Biol. 2015;17(4):500-510. [27] GAILITE I, AERNE BL, TAPON N. Differential control of Yorkie activity by LKB1/AMPK and the Hippo/Warts cascade in the central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015;112(37):E5169-5178. [28] LAVADO A, PARK JY, PARÉ J, et al. The Hippo Pathway Prevents YAP/TAZ-Driven Hypertranscription and Controls Neural Progenitor Number. Dev Cell. 2018;47(5):576-591.e8. [29] THOMPSON R, CHAN C. Signal transduction of the physical environment in the neural differentiation of stem cells. Technology (Singap World Sci). 2016;4(1):1-8. [30] DING R, WEYNANS K, BOSSING T, et al. The Hippo signalling pathway maintains quiescence in Drosophila neural stem cells. Nat Commun. 2016;7:10510. [31] KUMAR D, NITZAN E, KALCHEIM C. YAP promotes neural crest emigration through interactions with BMP and Wnt activities. Cell Commun Signal. 2019;17(1):69. [32] ZHAO X, LE TP, ERHARDT S, et al. Hippo-Yap Pathway Orchestrates Neural Crest Ontogenesis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:706623. [33] JUKAM D, XIE B, RISTER J, et al. Opposite feedbacks in the Hippo pathway for growth control and neural fate. Science. 2013;342(6155): 1238016. [34] HUANG Z, XIONG WC. Neogenin-YAP signaling in neocortical astrocytic differentiation. Neurogenesis (Austin). 2016;3(1):e1248735. [35] PETROVA V, EVA R. The Virtuous Cycle of Axon Growth: Axonal Transport of Growth-Promoting Machinery as an Intrinsic Determinant of Axon Regeneration. Dev Neurobiol. 2018;78(10):898-925. [36] O’DONOVAN KJ. Intrinsic Axonal Growth and the Drive for Regeneration. Front Neurosci. 2016;10:486. [37] EMOTO K, PARRISH JZ, JAN LY, et al. The tumour suppressor Hippo acts with the NDR kinases in dendritic tiling and maintenance. Nature. 2006;443(7108):210-213. [38] ULTANIR SK, HERTZ NT, LI G, et al. Chemical genetic identification of NDR1/2 kinase substrates AAK1 and Rabin8 Uncovers their roles in dendrite arborization and spine development. Neuron. 2012;73(6): 1127-1142. [39] SONG Z, HAN X, ZOU H, et al. PTEN-GSK3β-MOB1 axis controls neurite outgrowth in vitro and in vivo. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2018;75(23):4445-4464. [40] TONAZZINI I, MASCIULLO C, SAVI E, et al. Neuronal contact guidance and YAP signaling on ultra-small nanogratings. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1): 3742. [41] SUN H, CAO X, GONG A, et al. Extracellular vesicles derived from astrocytes facilitated neurite elongation by activating the Hippo pathway. Exp Cell Res. 2022;411(1):112937. [42] POPLAWSKI GHD, LIE R, HUNT M, et al. Adult Rat Myelin Enhances Axonal Outgrowth From Neural Stem Cells. Sci Transl Med. 2018; 10(442):eaal2563. [43] BARNABÉ-HEIDER F, GÖRITZ C, SABELSTRÖM H, et al. Origin of new glial cells in intact and injured adult spinal cord. Cell Stem Cell. 2010; 7:470-482. [44] POITELON Y, LOPEZ-ANIDO C, CATIGNAS K, et al. YAP and TAZ control peripheral myelination and the expression of laminin receptors in Schwann cells. Nat Neurosci. 2016;19(7):879-887. [45] FERNANDO RN, COTTER L, PERRIN-TRICAUD C, et al. Optimal myelin elongation relies on YAP activation by axonal growth and inhibition by Crb3/Hippo pathway. Nat Commun. 2016;7:12186. [46] GROVE M, LEE H, ZHAO H, et al. Axon-dependent expression of YAP/TAZ mediates Schwann cell remyelination but not proliferation after nerve injury. Elife. 2020;9:e50138. [47] JEANETTE H, MARZIALI LN, BHATIA U, et al. YAP and TAZ regulate Schwann cell proliferation and differentiation during peripheral nerve regeneration. Glia. 2021;69(4):1061-1074. [48] ZHANG J, XU X, LIU H, et al. Astrocytic YAP prevents the demyelination through promoting expression of cholesterol synthesis genes in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Cell Death Dis. 2021; 12(10):907. [49] GADANI SP, WALSH JT, LUKENS JR, et al. Dealing with Danger in the CNS: The Response of the Immune System to Injury. Neuron. 2015;87: 47-62. [50] ZHANG M, TAO W, YUAN Z, et al. Mst-1 deficiency promotes post-traumatic spinal motor neuron survival via enhancement of autophagy flux. Neurochem. 2017;143(2):244-256. [51] ZHOU L, ZHANG Q, ZHANG P, et al. c-Abl-mediated Drp1 phosphorylation promotes oxidative stress-induced mitochondrial fragmentation and neuronal cell death. Cell Death Dis. 2017;8(10): e3117. [52] ZHANG P, WANG T, ZHANG D, et al. Exploration of MST1-Mediated Secondary Brain Injury Induced by Intracerebral Hemorrhage in Rats via Hippo Signaling Pathway. Transl Stroke Res. 2019;10(6):729-743. [53] HUANG L, LI S, DAI Q, et al. Astrocytic Yes-associated protein attenuates cerebral ischemia-induced brain injury by regulating signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 signaling. Exp Neurol. 2020;333:113431. [54] YU H, CAO X, LI W, et al. Targeting connexin 43 provides anti-inflammatory effects after intracerebral hemorrhage injury by regulating YAP signaling. J Neuroinflammation. 2020;17(1):322. [55] QING J, LIU X, WU Q, et al. Hippo/YAP Pathway Plays a Critical Role in Effect of GDNF Against Aβ-Induced Inflammation in Microglial Cells. DNA Cell Biol. 2020;39(6):1064-1071. [56] BRADBURY EJ, BURNSIDE ER. Moving beyond the glial scar for spinal cord repair. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):3879. [57] MOLEIRINHO S, PATRICK C, TILSTON-LÜNEL AM, et al. Willin, an upstream component of the hippo signaling pathway, orchestrates mammalian peripheral nerve fibroblasts. PLoS One. 2013;8(4):e60028. [58] MOKALLED MH, PATRA C, DICKSON AL, et al. Injury-induced ctgfa directs glial bridging and spinal cord regeneration in zebrafish. Science. 2016;354(6312):630-634. [59] HUANG Z, WANG Y, HU G, et al. YAP Is a Critical Inducer of SOCS3, Preventing Reactive Astrogliosis. Cereb Cortex. 2016;26(5):2299-2310. [60] LI Z, YU Y, KANG J, et al. MicroRNA-124 Overexpression in Schwann Cells Promotes Schwann Cell-Astrocyte Integration and Inhibits Glial Scar Formation Ability. Front Cell Neurosci. 2020;14:144. [61] XIE C, SHEN X, XU X, et al. Astrocytic YAP Promotes the Formation of Glia Scars and Neural Regeneration after Spinal Cord Injury. J Neurosci. 2020;40(13):2644-2662. [62] STERN S, HILTON BJ, BURNSIDE ER, et al. RhoA drives actin compaction to restrict axon regeneration and astrocyte reactivity after CNS injury. Neuron. 2021;109(21):3436-3455.e9. |
| [1] | Li Shihao, Li Qi, Li Zhen, Zhang Yuanyuan, Liu Miaomiao, Ouyang Yi, Xu Weiguo. Plantar pressure and gait analysis in patients with anterior cruciate ligament injury and reconstruction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 626-631. |
| [2] | Zhou Jie, Pei Xibo, Wan Qianbing. Advances and biological application of asymmetric dressings [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 434-440. |
| [3] | Chen Jingqiao, Li Ying, Meng Maohua, Xu Xingxing, Wang Qinying, Wang Huan, Lu Jing, Shu Jiayu, Dong Qiang. Research progress in platelet-rich fibrin in stomatology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 441-446. |
| [4] | Han Tao, Hao Jianqiang, Li Wenbo, Shi Jie, Gao Qiuming. Advantages and problems of antibiotic-loaded bone cements for bone and joint infections [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 470-477. |
| [5] | Liu Gang, Deng Bowen, Jiang Shengyuan, Xu Lin, Fan Xiao, Tao Jingwei, Zhang Houjun, He Feng, Zhao Yi, Mu Xiaohong. Tetramethylpyrazine improves hemorheological indexes in rats with complete spinal cord transection: a dynamic observation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 282-286. |
| [6] | Chen Feng, Ren Guowu, Zhang Xiaoyun, Chen Yueping, Shi Rusheng. Receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa B ligand signal transduction mechanism and osteoclast activation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 293-299. |
| [7] | Li Mingxiu, Wang Xuan, Yang Jie, Li Yi. An osteoarthritis model in vitro: characteristics and new design idea [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 300-306. |
| [8] | Liu Yinghong, Yi Yating. Mechanism and implication of angiogenesis in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 307-313. |
| [9] | Zhang Jie, Tian Ai. Advances in the signaling pathway of M2 macrophages involved in bone regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 314-321. |
| [10] | Zhu Miaomiao, Kong Fanming, Zhao Qian. Exercise regulates lactic acid metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 322-328. |
| [11] | Zhang Yujuan, Yuan Yitong, Du Ruochen, Tian Feng, Fu Yuan, Wang Chunfang. miR-31 promotes the proliferation and migration of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 66-71. |
| [12] | Liu Runyuan, Dong Ming, Han Wenqing, Dong Juhong, Niu Weidong. Application and progress of small extracellular vesicles in periodontal and pulp regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 83-90. |
| [13] | Xi Hualei, Xue Bing, Xu Wanqiu, Xu Xiaohang, Yao Lihong, Wang Xiumei. Neural differentiation and neural biomarker expression of dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 91-98. |
| [14] | Liu Zhuoran, Jiang Ming, Li Yourui. Extracellular vesicles in chronic periodontitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 99-104. |
| [15] | Zhu Zhenghuan, Zou Hongjun, Song Zhiwen, Liu Jinbo. Cellular microenvironment in nerve repair after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 114-120. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||