Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (2): 322-328.doi: 10.12307/2022.1028
Exercise regulates lactic acid metabolism
Zhu Miaomiao1, 2, Kong Fanming1, Zhao Qian3
- 1Sport Coaching College, Beijing Sport University, Beijing 100084, China; 2Liaocheng No. 1 Experimental School, Liaocheng 252001, Shandong Province, China; 3College of Physical Science, Qufu Normal University, Qufu 273165, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2021-12-15Accepted:2022-02-11Online:2023-01-18Published:2022-06-20 -
Contact:Kong Fanming, PhD candidate, Sport Coaching College, Beijing Sport University, Beijing 100084, China -
About author:Zhu Miaomiao, Master, Sport Coaching College, Beijing Sport University, Beijing 100084, China; Liaocheng No. 1 Experimental School, Liaocheng 252001, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:Beijing Sport University School-level Projects, Nos. 2018PT007 and 20211021 (to KFM [project participant])
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhu Miaomiao, Kong Fanming, Zhao Qian. Exercise regulates lactic acid metabolism[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 322-328.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
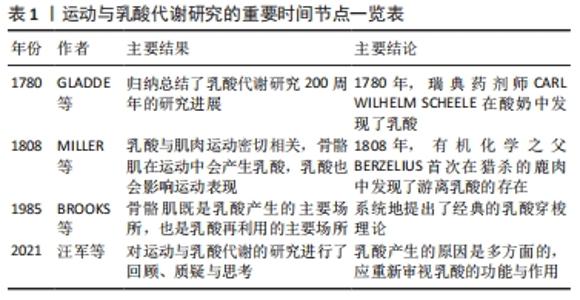
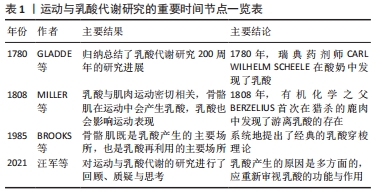
2.2 乳酸概述 2.2.1 乳酸简介与研究概况 乳酸为三碳分子,既是糖酵解供能系统代谢的终末产物,也是糖酵解过程的中间产物,可作为有氧供能系统的重要氧化基质,在供能体系中至关重要。乳酸为酸性物质,类属于羧酸,其分子式为C3H6O3,根据其在人体中的不同部位可分为血乳酸、肌乳酸等;运动训练实践中常用的乳酸指标有乳酸阈(lactic acid,LT)、个体乳酸阈、最大乳酸稳态(maximal lactate steady state,MLSS)等[8];骨骼肌细胞并不是乳酸的唯一来源,血液中的红细胞也可以产生乳酸;随着可穿戴设备的不断发展,非入侵式检测的方法在运动科学领域得到应用。其中汗液中乳酸的检测较为广泛并可作为反映组织受损的预警指标,但目前研究报道中汗液乳酸与血液乳酸相关性较低[9-10]。此外,人体的某些肠道菌群也可以通过无氧呼吸产生乳酸[11]。根据其在体内的存在状态可分为游离状态的乳酸和非游离状态的乳酸。 1780年,瑞典药剂师CARL WILHELM SCHEELE在酸奶中发现了乳酸[3]。运动与乳酸代谢的研究起点始于肌肉化学领域。1808年,有机化学之父BERZELIUS首次在猎杀的鹿肉中发现了游离乳酸的存在[4,12]。但在其后近百年的时间内,囿于测试设备、检测仪器等相关技术手段的落后,加之相关理论薄弱、认知水平有限等主客观条件的限制,运动与乳酸代谢的研究举步维艰。蛙作为乳酸代谢的典型模式生物,对该领域的研究发挥了重要作用。直到1907年FLETCHER和HOPKINS的经典实验使得运动与乳酸代谢的研究取得了标志性进展,并在“两栖类动物的肌乳酸”这一经典论著中明确提出肌肉收缩时产生乳酸[13-14]。该文的核心观点是肌肉疲劳状态下乳酸累积、富氧状态下乳酸消失以及乳酸可以再利用,并指出氧气可以延缓但不能阻止蛙肌在体外收缩时兴奋性丧失。“肌肉收缩时产生乳酸”这一论断的提出有力地促进了运动科学领域中“氧债”学说、运动性疲劳的产生机制以及运动后过量氧耗等理论的发展与完善。 2.2.2 乳酸应用的方法学因素 作为衡量运动员运动量以及新陈代谢的重要指标,在运动科学领域乳酸的检测具有重要的作用[15]。运动时骨骼肌是产生乳酸的主要场所,直接测定肌乳酸需要依靠肌肉活检,该技术因创伤性大、设备技术要求高、测试过程繁琐等局限,限制了其在实践中的应用与推广。血乳酸测试通过采集指尖和耳垂部位的血液(一般以μL为单位),可以间接反映骨骼肌乳酸的状况,且具有创伤小、测试过程相对简单等优点,近些年便携式血乳酸测试仪的普及更是有力推动了乳酸在实践中的应用。但同时也应注意,在运动实践中,只有当肌乳酸和血乳酸达到平衡时,血乳酸反映肌乳酸的代谢情况才有意义。 肌乳酸和血乳酸之间浓度的相对平衡所需时间与运动方式、运动强度、运动持续时间等动力学因素有关。短时间(2.0-3.0 min)、最大强度运动时,肌乳酸生成速率较快,虽然肌乳酸与血乳酸之间的浓度梯度差值较大,但是调控乳酸易化扩散的相关转运蛋白和酶活性还未达到最大,因此血乳酸最大值出现在运动结束后10-12 min;长时间(40 min以上)或大强度持续时间较长的间歇运动中,全身血液循环较快、血液灌流较为均匀,各部位乳酸浓度差较小,因此运动后血乳酸达到峰值的时间相对较短。 运动结束后何时取血检测血乳酸受运动方式、运动强度以及运动水平等因素的影响,性别、年龄、膳食、药物以及取血位置等也是影响乳酸测定的因素,因此目前尚无严格统一标准[16]。有研究认为,运动中骨骼肌产生的乳酸可透过细胞膜进入血液形成血乳酸[17],血乳酸从生成到血管内的时间大约为2 min。目前一般在运动后3-5 min后测定乳酸水平。此外,在乳酸测试时为确保测试过程的安全性,采血环节应由专业医护人员或取得相关采血资质的人员进行,避免出现交叉感染。 2.3 运动与乳酸的生成 人体运动是生物能转换成机械能的过程,能量代谢是促进身体健康和提升运动表现的总机关,任何活动均需要消耗一定的能量[18]。乳酸作为机体重要的代谢底物,由能量连续统一体理论可知,无论是静息或安静状态还是进行任何强度的运动,肌肉都不断产生和清除乳酸[19]。有研究报道,视网膜、红细胞、骨髓质等也可以通过糖酵解过程产生乳酸释放能量[20]。当运动中磷酸原供能系统大量消耗,同时有氧氧化产生能量的速率不能满足机体所需能量时的糖酵解增强,乳酸产生也随之增多。人体每天产生乳酸的量为15-20 mmol/kg。 "
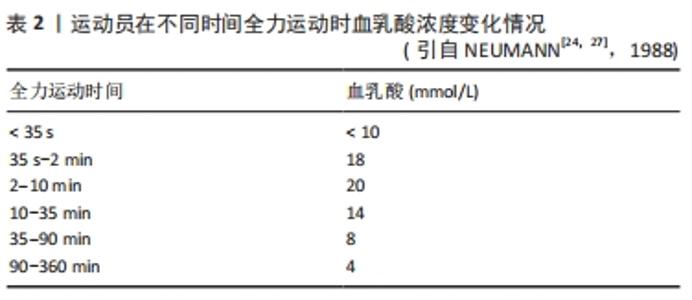
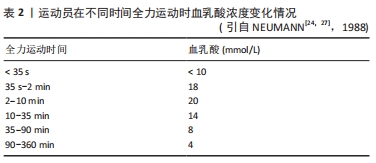
2.3.1 乳酸的生成条件 既往研究认为,糖类在无氧、缺氧或氧供不足的情况下经过一定的化学变化分解成乳酸。如20世纪20-80年代,将运动时乳酸增多的原因归咎于运动肌缺氧造成无氧糖酵解加强。1923年,ARCHIBALD VIVIAN HILL提出,肌肉中乳酸累积的原因可能是缺氧。经典“氧债”学说和“无氧阈”概念的提出,更是将乳酸与缺氧联系在一起。随后的研究表明,缺氧可能并不是乳酸累积的原因,乳酸更有可能是缺氧的副产物,并且乳酸还可以作为燃料重新参与供能[7]。 近些年的研究表明,缺氧不是乳酸产生的必要条件,如同位素示踪和磁共振波谱(MRS)技术已经证明,完全有氧条件下也可以产生乳酸,且乳酸代谢的动态范围明显超过葡萄糖和脂质。J?BSIS等[21]研究发现,肌肉在充分氧合的条件下也会产生乳酸。肌肉乳酸增多时,线粒体内还原型烟酰胺腺嘌呤二核苷酸(NADH)是下降的,说明呼吸链中氧化磷酸化顺利,线粒体并不缺氧。CONNETT等[22]通过测定狗骨骼肌收缩时的肌红蛋白氧饱和度发现,在氧分压远高于线粒体呼吸的临界阈时乳酸生成速率已加快。此外,机体在极量运动时对能量需求较大,即使氧供充足,高速度的能量需求使肌肉进行无氧糖酵解代谢,从而快速产生大量能量。因此缺氧不是肌肉产生乳酸的唯一或真正原因。上述现象提示,缺氧不是乳酸产生的必要条件,但乳酸的变化受体内氧气供应状况的影响。 2.3.2 运动时间与运动强度 在诸多影响乳酸代谢的动力学因素中,运动时间与运动强度是最为活跃的,且两者始终处于动态变化之中,因此有必要对其进行单独分析。运动强度是决定运动效应的关键因素,同时也是调控乳酸代谢的核心因素[23]。有文献报道,35 s-10 min的全力运动时血乳酸最高[24],其他时间全力运动时血乳酸浓度都较低,见表2。人体各生理学指标会随运动强度的增加或降低而发生动态变化,在次最大强度运动中肌肉乳酸水平升高可能与糖酵解速率加快、乳酸产生与清除失衡以及快肌纤维的募集增加等因素有关。全程马拉松运动中的乳酸产生量较低,100 km和180 km自行车个人赛后血乳酸水平差异不明显[25],这可能是由于高水平耐力运动员的乳酸再利用率较高,同时也是高水平运动员运动过程中能量节省化的体现。上述现象说明,利用乳酸指标监控以糖酵解供能为主的运动项目效度较高,而在监控运动时间较短或运动时间较长的运动项目时效度较低[26]。 "
运动强度一般指单位时间内完成的运动量,它是决定运动效应的关键因素,同时也是影响乳酸代谢的核心因素,可用最大摄氧量(VO2max)、心率、功率和速度等表示。以VO2max为例,美国运动医学会认为< 64%VO2max为中低强度、65%-90% VO2max为较高强度、≥91% VO2max为高强度[28]。 安静状态下仅有少量的乳酸生成,血乳酸浓度约为1 mmol/L,安静时肌乳酸的生成速率约为1 mmol/kg湿肌[20,25]。在一定强度范围内,血乳酸的增加与运动强度呈正比。低强度(< 40% VO2max)运动时,由于此时机体主要募集慢肌纤维参与工作,肌红蛋白和循环系统提供的氧气可以满足有氧代谢供能,不会引起明显的肌乳酸堆积,血乳酸浓度变化也很小。此状态下乳酸增加主要发生在运动开始阶段和加速冲刺阶段。当运动强度增大到50%-65% VO2max时,肌乳酸开始堆积;如果运动强度进一步增大,肌乳酸会以函数曲线升高,血乳酸也随之增加。 当运动强度增加至75%-85% VO2max持续运动时,运动开始后5-15 min肌乳酸积累达到峰值,然后逐渐下降。血乳酸变化趋势与肌乳酸基本一致,其机制可能是由于内脏器官存在生理惰性导致氧利用率较低,机体的呼吸机能和有氧代谢相关酶活性达到最高水平需要数分钟时间。短时间最大强度运动时,高速度的能量需求刺激了糖酵解速率的提高,一般运动至30-60 s时糖酵解速率达到最大。 血乳酸浓度随着运动强度的递增呈现出动态变化,乳酸浓度出现急剧增加的拐点所对应的乳酸浓度称为乳酸阈[29]。乳酸阈与有氧能力存在着高度正相关,且测试方便、遗传度较低、可训练性较高,因此是评价耐力训练水平的重要指标。血乳酸阈为4 mmol虽存在个体差异,但仍为学者们普遍接受[30],并认为应理性认识4 mmol,它只是反映乳酸浓度的“数量级”,而不是实践中公认的“金标准”[31-32]。乳酸阈形成的机制可能与局部肌肉供氧不足、运动单位募集改变、儿茶酚胺的非线性增加以及乳酸的清除率降低等有关。对乳酸阈的概念应科学理解,乳酸阈的出现并不表示运动强度达到这一阈值时工作肌才开始产生乳酸或工作肌才开始以无氧糖酵解的方式供能,而表示为无氧糖酵解供能比例明显增加,但运动时供能方式是否以无氧代谢为主尚存争议。 2.3.3 运动水平与乳酸生成 乳酸的生成与运动水平相关,并受运动项目的影响。一般而言,耐力训练可有效增强机体生成、清除和利用乳酸的能力[33]。完成相同亚极量强度定量负荷时,高水平耐力运动员的乳酸生成率低、清除率高、细胞缓冲能力强,因而其血乳酸浓度增高相对较小。这可能与高水平运动员的血浆肾上腺素、去甲肾上腺素的增多相对较少,糖酵解供能比例较低有关。耐力训练使骨骼肌线粒体数量增多、体积增大、氧化酶活性增强,氧化乳酸的能力提高,使乳酸清除速率提高;同时较高的三磷酸腺苷/二磷酸腺苷(ATP/ADP)比值抑制糖原分解,抑制了乳酸的生成。上述现象是运动员对耐力训练的有益适应,这是由于耐力项目运动表现提升的总体思路是提高脂肪酸氧化比例,减少肌糖原利用,进而提高运动能力。HODGETTS等[34]研究发现,血液中乳酸含量的增加可能会阻止脂肪组织释放游离脂肪酸,从而影响运动中脂肪的供能比例。虽然乳酸会抑制脂肪氧化,但高水平耐力运动员清除乳酸能力强,其后半程脂肪供能比例大,更有利于糖原节省,所以运动表现更好。 此外,对于以糖酵解供能为主的运动项目,如400 m、100 m和200 m游泳、1 000 m皮划艇等速度耐力型项目,运动结束后乳酸生成量越大,则糖酵解供能能力和速度耐力越强,进而运动水平越高。 2.4 运动与乳酸消除 为了维持体内酸碱平衡和供能能力,机体在产生乳酸的同时也在消除乳酸。乳酸堆积过多会导致体液的酸碱平衡紊乱,缓冲系统的作用、神经和体液因素对肺、肾功能的调节是维持体液pH值相对稳定的重要机制。具体而言,乳酸消除主要是通过有氧氧化、重新合成葡萄糖或糖原(即糖异生)、转变为脂肪酸或氨基酸以及随汗液或尿液排出体外等途径。由于转变为脂肪酸或氨基酸以及随汗液或尿液排出体外等途径所占比例较少,在此主要论述有氧氧化和糖异生2个部分。 "
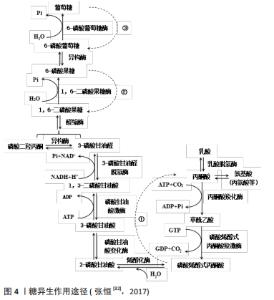
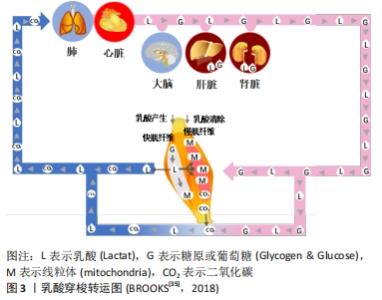
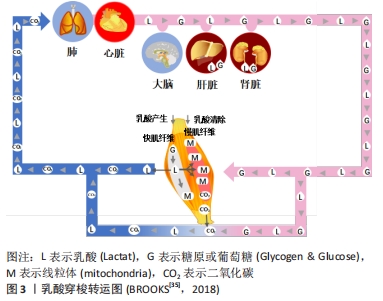
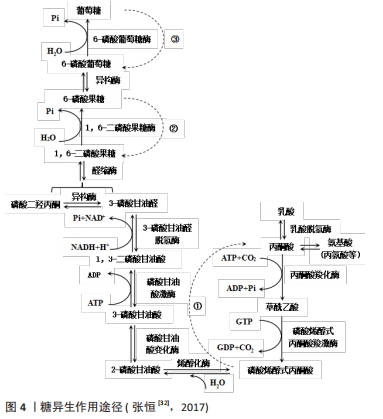
乳酸穿梭转运的方式分为工作肌中乳酸穿梭和肌肉-血管中乳酸穿梭。骨骼肌是乳酸穿梭的主要部位。运动中肌肉产生的乳酸借助肌纤维与血液中乳酸和[H+]浓度梯度,穿越肌细胞膜弥散进入毛细血管,在通过血液循环将其转运至心肌、肝脏、肾脏和非运动肌重新利用。乳酸穿梭形式与运动强度有关,当运动强度低于乳酸阈或通气阈时,肌肉产生的乳酸在其内部便可以清除;当运动强度加大时,工作肌中乳酸穿梭不能完全清除,多余的乳酸会随血液扩散至肝脏和肾脏等器官清除。 快肌纤维被大量募集是产生乳酸的重要原因,同时慢肌纤维又可以消耗乳酸,因此骨骼肌的乳酸穿梭系统可使乳酸氧化再利用。其过程如下:运动过程中Ⅱb型快肌纤维产生的乳酸可通过乳酸穿梭系统穿梭进邻近的Ⅱa型快肌纤维和Ⅰ型慢肌纤维,之后通过三羧酸循环释放能量合成ATP。 此外,既往研究认为乳酸主要是通过乳酸循环或科里氏循环清除,即只有在氧气供应较低时,丙酮酸的主要去处才是乳酸。新近研究发现,线粒体作为细胞代谢的能量工厂,在乳酸代谢中同样扮演着重要角色[36],有关线粒体进行乳酸代谢的机制还有待于进一步研究。 2.4.2 糖异生 能量是人体一切生命活动发生、发展和变化的动力[37]。人体内糖的储量有限,共400-500 g,正常人每小时可由肝释放出葡萄糖210 mg/kg体质量,马拉松跑时平均每分钟要消耗糖5 g,如果不及时补充糖类,正常情况下十几小时肝糖原便被耗尽,马拉松运动员将在90-95 min出现糖的总排空[37]。实践中即使禁食24 h,血糖仍可以维持正常范围,长期饥饿时也仅略有下降。这时除了周围组织减少对葡萄糖的利用外,肝脏、肾脏等将氨基酸、乳酸等作为新的肌肉燃料转变为葡萄糖的异生过程也发挥了重要作用。如新近研究发现,高CO2水平下柠檬酸合酶会取代柠檬酸裂解酶,从而产生三羧酸循环(tricarboxylic acid cycle,TCA)逆向运行现象[38]。三羧酸循环逆向运行会使每一圈循环消耗的ATP当量减少,并促进糖类、脂肪和氨基酸等能源物质的合成增加。 所谓糖异生(gluconeogenesis)一般指非糖化合物(乳酸、甘油、生糖氨基酸等)转变为葡萄糖或糖原的过程[37]。糖异生过程不是糖酵解途径的简单逆转,而是涉及一系列生理、生化的酶促反应过程,见图4。乳酸作为公认的、最重要的进行糖异生作用基质,中低强度运动时可占全部糖异生的50%左右,这可能是由于乳酸不需要酶激活,可直接进入三羧酸循环;肝脏是进行糖异生的主要器官,心肌、骨骼肌(主要是慢肌)和肾脏也是进行糖异生的重要场所。其中,骨骼肌和心肌对乳酸的释放、摄取和利用主要依赖于一种特殊的跨膜转运蛋白,即单羧酸转运蛋白,慢肌纤维转运乳酸量比快肌纤维多,因此其单羧酸转运蛋白含量也较多。正常情况下,肾通过糖异生产生的葡萄糖量较少,仅占肝糖异生的10%,而饥饿五六周后由肾糖异生的葡萄糖达40 g/d,与肝糖异生的量接近持平[39]。糖异生的生理意义主要是维持血糖水平恒定、补充或恢复肝糖原以及维持体内酸碱平衡等。 "

2.4.3 恢复措施与乳酸消除 不同运动水平、不同运动项目的运动员的乳酸消除水平差异较大。高水平耐力运动员的乳酸清除速率要高于未经训练的普通人群,这可能与训练适应有关。运动中的积极性休息和运动后的整理活动可以促进乳酸的消除速率。如有文献报道,与被动性休息相比较,积极性休息能使乳酸的半时反应提高1倍[25];运动结束后骤然停止运动的消极性恢复时,乳酸清除速度为每分钟每100 mL体液2.0-3.0 mg,而积极性恢复时乳酸清除速率可以增加到每分钟每100 mL体液8 mg,为消极性恢复的两三倍[25]。其原因可能是积极性恢复时儿茶酚胺的调节重新增强,去甲肾上腺素通过对α-肾上腺素能受体的作用,使肝脏、肾脏等内脏器官的血管收缩,供血量减少,糖异生相对下降,血液更多流向心肌和骨骼肌等氧化乳酸较强的区域,从而更有利于乳酸氧化。还有研究认为,剧烈运动后即刻血液多停滞于外周骨骼肌,积极性恢复时骨骼肌的挤压作用加快了血液由运动器官至内脏器官的回流,促进了局部血液循环,增加了糖异生比例,进而改善了血液流变性。 积极性休息时的运动强度与运动方式、运动强度、运动水平等因素有关。BONEN等[40]报道,恢复期以32%VO2max强度运动时乳酸清除速率最快;另有研究报道,63%VO2max强度之前,血乳酸清除速率与运动强度呈正比关系,随着运动强度的进一步增大,乳酸清除速率反而降低[25]。这可能是由于运动强度增大引起乳酸增多所致。这提示,积极性恢复期的运动强度应较低,且注意运动水平的影响。目前的观点认为,积极性休息时以中低强度(< 60%VO2max)为宜,运动员比普通人略高。 2.5 乳酸的功能定位 2.5.1 乳酸有害论 乳酸是丙酮酸进一步代谢的产物,属于酸性物质,可析出H+,累积可引起pH值降低,加速疲劳的形成。其机制可能与糖酵解酶、磷酸果糖激酶等相关酶活性降低、肌钙蛋白对Ca2+敏感性降低、神经肌肉接点处的传递障碍、减缓Ca2+的重吸收以及影响横桥摆动周期等因素相关。文献报道,乳酸不仅是无氧条件下的代谢产物,也可能是人体最重要的能量载体;同时它还是癌细胞最重要的直接营养来源[41]。来自神经科学领域的证据表明,乳酸是神经元的关键能源和信号分子,乳酸的过量积累会破坏海马体神经再生,从而降低大脑的记忆和学习能力[42]。 2.5.2 乳酸无害论 近年来也有大量文献证明乳酸对人体有益,诸多学者不断为乳酸“正名”。如乳酸可以减缓癌症的发生,这可能与经常运动人群的乳酸清除能力较强,其机制可能是通过磷脂酰肌醇-3-激酶抑制乳酸脱氢酶A,降低“Warburg效应”,从而抑制癌细胞生长[43]。也有研究认为,乳酸可作为神经元的能源物质调节神经递质的释放,改善记忆过程,进而提高记忆力。运动性疲劳的堵塞学说认为,乳酸堆积会使H+浓度升高,这会通过抑制糖酵解能力、降低肌钙蛋白对Ca2+的敏感性以及抑制血红蛋白与氧气的结合等途径降低运动能力,进而产生运动性疲劳。产生上述误区的主要原因是,既往研究将乳酸增加等同于H+浓度增加。现今学者们已经认识到对骨骼肌力量产生抑制作用的是H+,不是乳酸,例如骨骼肌可以在没有酸中毒的情况下出现疲劳。此外,新近研究发现,高水平马拉松运动员运动后即刻乳酸产生量极少,变化率仅为4.8%,因此乳酸与运动性疲劳并不存在必然关系[44]。乳酸功能定位的演变趋势见表3。 "


综上所述,乳酸可作为重要的能量代谢底物和信号分子影响多组织器官的生理进程,既往学术界关于乳酸的功能与作用存在着诸多争议,并不断有学者为其“正名”,这为科学引导运动训练提供了更完善的生物学基础模型,同时也为科研人员了解、认识运动调控乳酸代谢提供了新思路。 2.6 运动调控乳酸变化的机制 运动对乳酸代谢的调控是一个多器官、多组织参与的生理生化调控过程,涉及神经、运动、循环、呼吸、消化和内分泌等系统。运动时心率增加、血流加大、耗氧量增加,能量需求快速增大,糖酵解速率加快、乳酸产生与清除速率失衡导致乳酸积累增加。运动时骨骼肌纤维被大量动员,尤其是快肌纤维的大量动员也是乳酸产生的重要原因;骨骼肌剧烈收缩诱导乳酸运输载体1/乳酸运输载体4(骨骼肌MCT1/MCT4)表达以促进乳酸的跨膜转运和氧化利用,也会调控乳酸的释放[45-46]。运动时交感神经兴奋,可调控去甲肾上腺素对α-肾上腺能受体的作用,使肝脏、肾脏等部位的血管收缩,供血量减少,血液更多流向骨骼肌等氧化乳酸较强的区域,从而使外周骨骼肌乳酸代谢加强。此外,乳酸作为代谢性应激反应的生物标志物,局部乳酸积累较多时,也会通过负反馈途径调控运动的强弱。另有研究从肠道菌群入手对乳酸与运动表现的关系进行了研究,如SCHEIMAN等[47]研究报道,高水平马拉松运动员体内如Veillonella细菌含量较高,它可以将运动代谢产生的乳酸转换为短链脂肪酸丙酸供人体利用来提高运动表现;将Veillonella菌群植入小鼠体内后可以发现小鼠的心率和氧利用率提高,进而有氧耐力明显提高。 但需要注意的是,运动调控乳酸代谢的变化是动态的、非线性的,受个体运动水平、体成分等因素的影响。长时间、系统的运动训练会使高水平运动员产生与清除乳酸的能力增强,这是机体对乳酸浓度变化的有益适应,其目的是为了使机体承受更高的运动负荷。另外,体成分也会对运动过程中的乳酸代谢产生影响,当体脂率过高时可能会抑制乳酸代谢,其内部机制尚不清楚,初步假设与G蛋白偶联受体(G ProteinCoupled Receptors 81,GPR81)的活性有关[48]。 "

| [1] HUI S, GHERGUROVICH JM, MORSCHER RJ, et al. Glucose feeds the TCA cycle via circulating lactate. Nature. 2017;551(7678):115-118. [2] 王杨文洁,张缨.运动与骨骼肌单羧酸转运蛋白1和4研究进展[J].中国运动医学杂志,2020,39(10):820-824. [3] GLADDEN LB. 200th anniversary of lactate research in muscle. Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 2008;36(3):109-115. [4] MILLER BF, FATTOR JA, JACOBS KA, et al. Lactate and glucose interactions during rest and exercise in men: effect of exogenous lactate infusion. J Physiol. 2002;544(3):963-975. [5] BROOKS GA. Lactate: link between glycolytic and oxidative metabolism. Sports Med. 2007;37(4-5):341-343. [6] BROOKS GA. Glycolytic end product and oxidative substrate during sustained exercise in mammals–the “lactate shuttle”. Berlin: Springer-Verlag,1985. [7] 汪军,周越,孙君志,等.质疑与思考:运动生理学研究的十个问题[J].成都体育学院学报,2021,47(1):118-124. [8] BENEKE R. Anaerobic threshold, individual anaerobic threshold, and maximal lactate steady state in rowing. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1995; 27(6):863-867. [9] PROMPHET N, RATTANAWALEEDIROJN P, SIRALERTMUKUL K, et al. Non-invasive textile based colorimetric sensor for the simultaneous detection of sweat pH and lactate. Talanta. 2019;192:424-430. [10] JIA W, BANDODKAR AJ, VALDÉS-RAMÍREZ G, et al. Electrochemical tattoo biosensors for real-time noninvasive lactate monitoring in human perspiration. Anal Chem. 2013;85(14):6553-6560. [11] MICHAEL G. Eat, Move, Sleep, Repeat. Meyer & Meyer Sport. 2020. [12] 谢东山.乳酸代谢与乳酸穿梭理论发展[J].生物化工,2019,5(6): 135-141. [13] 许豪文.运动生物化学概论[M].北京:高等教育出版社,2001:98-99. [14] Fletcher WM. Lactic acid in amphibian muscle. J Physiol. 1907;35(4): 247-309. [15] 苏炳添,李健良,徐慧华,等.科学训练辅助:柔性可穿戴传感器运动监测应用[J].中国科学:信息科学,2022,52(1):54-74. [16] 杨锡让.实用运动生理学[M].北京:北京体育大学出版社,2007: 146-148. [17] 杨锡让,傅浩坚.运动生理学进展——质疑与思考[M].北京:北京体育大学出版社,2000:315-316. [18] 黎涌明,纪晓楠,资薇.人体运动的本质[J].体育科学,2014,34(2): 11-17. [19] 孔凡明,米靖,马杰.能量保护模式的概念释义、作用机制与训练启示[J].北京体育大学学报,2021,44(10):90-99. [20] 运动生物化学编写组.运动生物化学[M].北京:北京体育大学出版社,2013:65-66. [21] JÖBSIS FF, STAINSBY WN. Oxidation of NADH during contractions of circulated mammalian skeletal muscle. Respir Physiol. 1968;4(3):292-300. [22] CONNETT RJ, GAYESKI TE, HONIG CR. Lactate accumulation in fully aerobic, working, dog gracilis muscle. Am J Physiol. 1984;246(1 Pt 2):H120-128. [23] 田麦久,刘大庆.运动训练学[M].北京:人民体育出版社,2012: 42-45. [24] 翁锡全.运动训练生物化学[M].广东:广东高等教育出版社,2016: 28-30. [25] 张爱芳.实用运动生物化学[M].北京:北京体育大学出版社,2005: 54-63. [26] BISHOP D. Physiological predictors of flat-water kayak performance in women. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2000;82(1-2):91-97. [27] BRAND K, AICHINGER S, FORSTER S, et al. Cell-cycle-related metabolic and enzymatic events in proliferating rat thymocytes. Eur J Biochem. 1988;172(3):695-702. [28] FERGUSON B. ACSM’s Guidelines for Exercise Testing and Prescription 9th Ed.J Can Chiropr Assoc. 2014;58(3):328. [29] 运动医学名词审定分委员会.运动医学名词[M].北京:科学出版社,2019:40-41. [30] MADER A. Zur Beurteilung der sportartspezifischen Ausdauerleistungsfähigkeit im Labor. Sportarzt und Sportmedizin. 1976;27(4): S80-88. [31] 冯连世,冯美云,冯炜权,等.优秀运动员身体机能评定方法[M].北京:人民体育出版社,2003:104-117. [32] 张恒.应用生物化学[M].江苏:南京大学出版社,2017:203-207. [33] BROOKS GA. The tortuous path of lactate shuttle discovery: From cinders and boards to the lab and ICU. J Sport Health Sci. 2020;9(5): 446-460. [34] HODGETTS V, COPPACK SW, FRAYN KN, et al. Factors controlling fat mobilization from human subcutaneous adipose tissue during exercise. J Appl Physiol (1985). 1991;71(2):445-451. [35] BROOKS GA. The Science and Translation of Lactate Shuttle Theory. Cell Metab. 2018;27(4):757-785. [36] GLANCY B, KANE DA, KAVAZIS AN, et al. Mitochondrial lactate metabolism: history and implications for exercise and disease. J Physiol. 2021;599(3):863-888. [37] 严亨秀,盘强文.整合应用生理学[M].北京:科学出版社,2021: 164-168. [38] STEFFENS L, PETTINATO E, STEINER TM, et al. High CO2 levels drive the TCA cycle backwards towards autotrophy. Nature. 2021;592(7856): 784-788. [39] 查锡良,周春燕.生物化学[M].7版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2011: 224-226. [40] BONEN A, BELCASTRO AN. Comparison of self-selected recovery methods on lactic acid removal rates. Med Sci Sports. 1976;8(3):176-178. [41] DE LA CRUZ-LÓPEZ KG, CASTRO-MUÑOZ LJ, REYES-HERNÁNDEZ DO, et al. Lactate in the Regulation of Tumor Microenvironment and Therapeutic Approaches. Front Oncol. 2019;9:1143. [42] WANG J, CUI Y, YU Z, et al. Brain Endothelial Cells Maintain Lactate Homeostasis and Control Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis. Cell Stem Cell. 2019;25(6):754-767.e9. [43] XU K, YIN N, PENG M, et al. Glycolysis fuels phosphoinositide 3-kinase signaling to bolster T cell immunity. Science. 2021;371(6527):405-410. [44] 魏文哲,孙科,赵之光,等.模拟全程马拉松跑过程中能量代谢的变化[J].中国体育科技,2020,56(6):3-8. [45] THOMAS C, BISHOP DJ, LAMBERT K, et al. Effects of acute and chronic exercise on sarcolemmal MCT1 and MCT4 contents in human skeletal muscles: current status. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2012; 302(1):R1-14. [46] BENTON CR, YOSHIDA Y, LALLY J, et al. PGC-1alpha increases skeletal muscle lactate uptake by increasing the expression of MCT1 but not MCT2 or MCT4. Physiol Genomics. 2008;35(1):45-54. [47] SCHEIMAN J, LUBER JM, CHAVKIN TA, et al. Meta-omics analysis of elite athletes identifies a performance-enhancing microbe that functions via lactate metabolism. Nat Med. 2019;25(7):1104-1109. [48] 孙景权,严翊,叶建平,等.乳酸/GPR81信号通路调节脂肪酸利用的研究进展[J].北京体育大学学报,2016,39(10):71-75. [49] FERGUSON BS, ROGATZKI MJ, GOODWIN ML, et al. Lactate metabolism: historical context, prior misinterpretations, and current understanding. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2018;118(4):691-728. [50] OLIVER SG, WINSON MK, KELL DB, et al. Systematic functional analysis of the yeast genome. Trends Biotechnol. 1998;16(9):373-378. |
| [1] | Cheng Mingguang, Zhang Chaoyu, Zhuang Kangle, Ruan Peng, Zuo Yi, Zhou Zhengchun, Kong Xiang, Ge Jianjun, Cheng Guangcun. In vitro construction of Stanford type A aortic dissection 3D dynamic simulation diagram and individual tissue-engineered blood vessels [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 335-338. |
| [2] | Zhou Jie, Pei Xibo, Wan Qianbing. Advances and biological application of asymmetric dressings [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 434-440. |
| [3] | Chen Jingqiao, Li Ying, Meng Maohua, Xu Xingxing, Wang Qinying, Wang Huan, Lu Jing, Shu Jiayu, Dong Qiang. Research progress in platelet-rich fibrin in stomatology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 441-446. |
| [4] | Han Tao, Hao Jianqiang, Li Wenbo, Shi Jie, Gao Qiuming. Advantages and problems of antibiotic-loaded bone cements for bone and joint infections [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 470-477. |
| [5] | Dai Xianglin, Zhang Wenfeng, Yao Xijun, Shang Jiaqi, Huang Qiujin, Ren Yifan, Deng Jiupeng. Barium titanate/polylactic acid piezoelectric composite film affects adhesion, proliferation, and osteogenic differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 367-373. |
| [6] | Zhang Luyao, Yang Kang. Effects of different exercises on renal interstitial fibrosis in type 2 diabetic mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 200-207. |
| [7] | Wu Shuangshuang, Zhang Ying, Kou Xianjuan. Treadmill exercise improves cognitive dysfunction in diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 208-215. |
| [8] | Shui Xiaoping, Li Chunying, Li Mingjuan, Li Shunchang, Sun Junzhi, Su Quansheng. Effects of aerobic and resistance exercise on antioxidant stress index and brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression in the hippocampus of type 2 diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 264-269. |
| [9] | Chen Feng, Ren Guowu, Zhang Xiaoyun, Chen Yueping, Shi Rusheng. Receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa B ligand signal transduction mechanism and osteoclast activation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 293-299. |
| [10] | Li Mingxiu, Wang Xuan, Yang Jie, Li Yi. An osteoarthritis model in vitro: characteristics and new design idea [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 300-306. |
| [11] | Liu Yinghong, Yi Yating. Mechanism and implication of angiogenesis in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 307-313. |
| [12] | Zhang Jie, Tian Ai. Advances in the signaling pathway of M2 macrophages involved in bone regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 314-321. |
| [13] | Liu Runyuan, Dong Ming, Han Wenqing, Dong Juhong, Niu Weidong. Application and progress of small extracellular vesicles in periodontal and pulp regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 83-90. |
| [14] | Xi Hualei, Xue Bing, Xu Wanqiu, Xu Xiaohang, Yao Lihong, Wang Xiumei. Neural differentiation and neural biomarker expression of dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 91-98. |
| [15] | Liu Zhuoran, Jiang Ming, Li Yourui. Extracellular vesicles in chronic periodontitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 99-104. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||