Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (2): 300-306.doi: 10.12307/2022.1004
Previous Articles Next Articles
An osteoarthritis model in vitro: characteristics and new design idea
Li Mingxiu1, Wang Xuan1, Yang Jie2, Li Yi2
- 1The Second Clinical Medical College of Shaanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Xianyang 712046, Shaanxi Province, China; 2Department of Foot and Ankle Surgery, Honghui Hospital Affiliated to Medical College of Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710054, Shaanxi Province, China
-
Received:2021-12-11Accepted:2022-03-10Online:2023-01-18Published:2022-06-20 -
Contact:Li Yi, MD, Chief physician, Department of Foot and Ankle Surgery, Honghui Hospital Affiliated to Medical College of Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710054, Shaanxi Province, China -
About author:Li Mingxiu, Master candidate, the Second Clinical Medical College of Shaanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Xianyang 712046, Shaanxi Province, China -
Supported by:Bureau-level Scientific Research Project of Xi’an Health Bureau in 2018, No. J201802027 (to LY); Shaanxi Provincial Social Development Science and Technology Project, No. 2016SF-333 (to LY); Shaanxi Provincial Key Research and Development Program, No. 2020SF-099; Shaanxi Provincial Innovation Ability Support Plan - Innovation Talent Promotion Plan - Science and Technology Innovation Team, No. 2021TD-59
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Mingxiu, Wang Xuan, Yang Jie, Li Yi. An osteoarthritis model in vitro: characteristics and new design idea[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 300-306.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
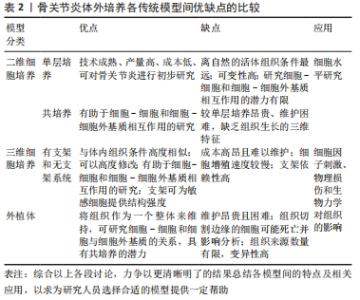
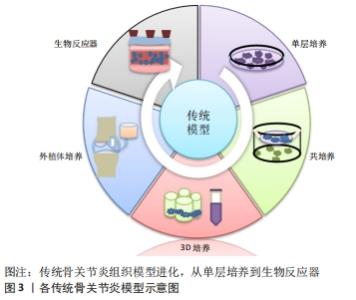
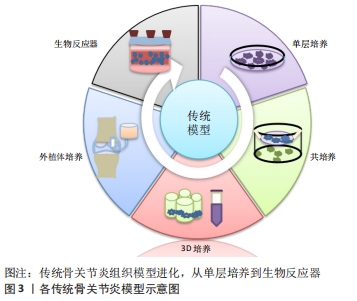
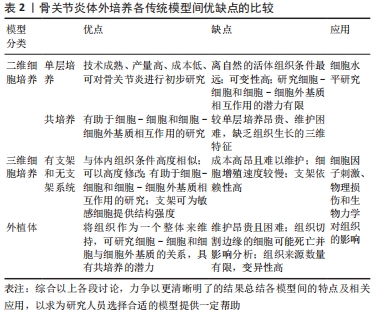
2.1.1 二维(2D)细胞模型 2D细胞模型可分为单层培养(单个细胞系培养)和共培养(两个或更多细胞系在单层中一起培养)。 单层培养:单层细胞培养是一种成熟、经济有效的方法,允许使用单一细胞来源进行多种实验治疗,并允许严格控制研究条件,可以获得相对快速、可靠和高产量的结果。细胞来源可以是从老鼠、牛到人类不等,可以是永生化细胞系或从动物或人供体关节组织分离的原代细胞。组织工程中使用的大多数人体细胞是从患者身上分离出来的成体原代细胞。但成体原代细胞寿命有限,增殖率低,分离过程复杂。 单层培养最常用的细胞系有:RAW 264.7巨噬细胞、人原代滑膜细胞和人关节软骨细胞等,不同的细胞系分泌不同的因子或对细胞因子刺激的反应不同。有研究发现单层模型(尤其是人类细胞系)直接与细胞靶点相对应,可在局部用药案例中用于细胞毒性和增殖的测试[14];细胞因子刺激方面,如白细胞介素1β通过提高基质金属蛋白酶、透明质酸酶和聚糖酶来对关节软骨进行酶降解,以诱导骨关节炎表型,从而可以筛选出软骨保护化合物来减弱关节软骨降解中所涉及的分解代谢因子(如白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α和一氧化氮)等[15]。有研究用白细胞介素1β对软骨细胞进行负性诱导,并给予细胞黄檀糖苷作为联合治疗,证明了活性成分黄檀糖苷可阻止白细胞介素1β诱导的效应[16]。 单层培养模型可用于对单个信号通路的研究,如某新型抑制剂对Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的研究发现Wnt/β-catenin通路在软骨形成和保护中具有关键作用[17];有研究用不同剂量的大黄素和白细胞介素1β处理大鼠软骨细胞,结果发现大黄素可以通过抑制ERK和 wnt/β-catenin 通路以及下调一系列炎症递质在软骨细胞中的表达,促进软骨细胞的增殖[18],而单层细胞培养很容易被转染来操纵基因和蛋白质的表达[19]。 原代细胞或永生化细胞系在玻璃或聚苯乙烯塑料瓶中的平面上培养使得细胞可以在等量的营养物质和生长因子下发育和增殖。然而,由于缺乏组织模拟特性,研究细胞-细胞和细胞-细胞外基质相互作用的潜力有限,如实际的软骨组织需要三维细胞生长,与细胞外基质相互作用,在少量传代后,当细胞表型和形态从正交形状改变为细长形状,类似成纤维细胞样软骨细胞时,细胞就会发生去分化。众所周知,这种表型产生Ⅰ型胶原纤维,而不是与关节软骨一致的Ⅱ型胶原纤维,因此使用单层模型来评估Ⅱ型胶原和骨胶蛋白定量软骨生长时比较困难。不仅如此,使用这些模型来研究承重和机械实验也较为困难[20]。如上段所述,原代细胞培养较使用细胞系昂贵,源材料难以获得,且在它们经历去分化和失去其独特表型之前传代的频率有限。永生化软骨细胞与原代细胞相比,细胞外基质成分的分泌却显著减少[20]。虽然细胞系的细胞材料来源限制少得多,但是它们的永生化性质使细胞避免了衰老。该段所述各点都降低了单层模型作为真实细胞模型的可靠性。 共培养:共培养是指在单层细胞培养的基础上,将2种及以上的细胞共同培养,是一种改进细胞间关系的研究方法,可以使用跨孔板等模型同时进行多种实验,并可生成关于病理机制的大量数据。跨孔板可将可溶性因子分泌到周围介质中,用于研究细胞与细胞之间的相互作用,如当软骨细胞和滑膜细胞与脂肪来源的间充质干细胞一起共培养时,促炎细胞因子包括白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、白细胞介素8和肿瘤坏死因子α的表达显著降低[20],细胞间通过细胞间钙和旁分泌信号发生交互维持关节软骨细胞的内环境稳态,由于保存了这些细胞间信号通路,关节软骨中抗炎或软骨保护分子的作用评估的准确性更高[21]。此外,软骨细胞和滑液之间的相互作用确保了生长因子、调节肽和营养物质在它们之间的流动;损伤软骨与滑膜共培养时,对滑膜细胞产生保护作用,如减少局灶性细胞丢失和软骨细胞簇形成[22]。软骨细胞培养模型支持软骨细胞和软骨下成骨细胞之间相互作用的研究,如与成骨细胞孵育的软骨细胞通过旁分泌信号帮助维持细胞生理和表型,这是研究软骨保护(减缓软骨降解)在骨重建中的作用的一个有效模型[23]。 虽然同时培养不同类型的细胞在维持细胞内环境稳态和表型方面有优势,但是也具有类似单层培养的一些缺点:平面培养和缺乏生长结构;维护不同的多孔环境成本较高;不能准确地模拟生理条件,产生有限的细胞外基质样环境,从而导致细胞形态的改变[24]。此外,不同类型的细胞需要不同的培养条件,如果它们一起培养,就会相互受到影响,如骨关节炎成骨细胞与健康藻酸盐珠包埋软骨细胞的共培养导致向软骨细胞肥大和基质矿化的表型转变,这在用白细胞介素1、白细胞介素6或抑瘤素-M刺激的健康成骨细胞中不会发生,进一步证明了人工刺激细胞的局限性和自然患病细胞的表型差异[25]。 2.1.2 三维(3D)细胞模型 此模型保留了2D细胞模型的优点,同时提供了与生理条件更相似的可定制环境,能够维持细胞的表型[26-27]。进而能够独立识别和调节导致疾病发生和进展的细胞和分子因素,研究它们在特定疾病发展中的作用,从而有助于进一步研究组织生理学和病理生理学。3D细胞模型可分为无支架模型(细胞生长在颗粒中)和有支架模型(细胞生长在外部平台中)。 无支架的三维细胞模型:无支架的三维细胞培养是指细胞通过沉淀法、悬滴法或搅拌法等在悬浮液中自发聚集形成颗粒。它不受支架性质的影响,较其他3D培养更稳定且经济,它可以维持细胞在各个维度的生长和细胞外基质的合成。细胞可以在锥形管或多孔板中一起离心,也可以使用生物反应器在搅拌下培养。诱导细胞聚集形成软骨组织样颗粒后,经过特定的培养时间,颗粒大小可达5 mm[28]。这些颗粒可以模拟整个关节组织,为细胞到细胞和细胞到细胞外基质的关系提供深入的了解。它可被用来研究体外软骨细胞再分化和骨髓干细胞分化。如,有研究报道,关节软骨细胞和髌下脂肪垫衍生的间充质干细胞与壳聚糖/透明质酸纳米颗粒的颗粒共培养促进软骨细胞分化,同时抑制软骨细胞的增殖,防止间充质干细胞肥大[29]。还有研究利用骨髓间充质干细胞进行软骨形成颗粒培养,表明含有成纤维细胞生长因子2的培养基可能有助于创建稳定可靠的无支架软骨样细胞片[30]。3D颗粒还可以评价关节内给药系统的应用效果,其通过Ⅱ型胶原、聚集蛋白聚糖和基质金属蛋白酶的糖胺聚糖含量定量和基因表达来评估白细胞介素1β刺激后的软骨形成和软骨保护作用[31]。 使用这种体外培养方法时必须考虑如下缺点:培养基中添加了大量的生长因子和软骨稳定剂,较单层培养成本更高;颗粒的生存期很短,营养物质难以穿透颗粒,导致其核心细胞死亡[32]。培养在颗粒中的细胞增殖能力大幅下降,颗粒中心的细胞可能被剥夺营养和氧气,虽可用来维持非肥大软骨细胞,但是可能会导致细胞凋亡,而且已经有研究表明了低氧会减少骨形成[20]。 悬挂式细胞培养是一种颗粒形成技术,将细胞制粒后在2D表面上以倒置的方式培养,重力帮助细胞保持悬浮状态,可减少极化的机会。与单层和典型的颗粒培养方式相比,促进了体内类圆形的形态,同时性别决定因子同源盒9信使核糖核酸水平增加。还可诱导蛋白多糖4、信使核糖核酸及其相关的蛋白润滑素表达上调,可为健康的关节间隙中提供润滑。 带支架的三维细胞模型:在工程化的体外模型中,3D组织支架应在体外精细地模仿细胞外基质框架,让细胞像在体内一样进行黏附、扩散、增殖、分化、成熟和产生细胞外基质等行为。它可以在强度、相互连接的孔隙率、弹性、生物化学和生物功能方面进行修改,以更好地模拟天然组织特异性微结构[33]。这使其成为骨关节炎中负载和承重的良好模型。用于制造支架的生物材料可以是天然的或人造的,支架可大致分为水凝胶和固态支架。最常用的支架是水凝胶,因为其含水量高,并且具有广泛的机械和物理化学特性,能够更好地模拟细胞外基质。 从海藻酸盐、明胶、壳聚糖和透明质酸等材料中提取的生物水凝胶可以促进软骨细胞的存活和增殖,以及Ⅱ型胶原、聚集素和性别决定因子同源盒9的表达,这些标记物在单层培养中通常会减少[34-35]。生物水凝胶还能够支持软骨细胞增殖和细胞外基质的产生,以及成骨细胞的生长和矿化,有利于研究骨软骨界面的活性[36]。然而生物水凝胶可能会因生产批次不同而性能不同。合成水凝胶具有更大的灵活性和化学修饰可调节性,且与生物水凝胶一样具有组织培养所需要的特性,研究表明,合成水凝胶(如衍生自聚乙二醇的水凝胶)可塑性好,稳定性高,如,它能够集成到机械负荷系统中,该系统能够引导人类间充质干细胞分化为关节软骨、钙化软骨和细胞外基质组织[37],而且它来源较广,降低了其生产过程中发生变化的可能性[38]。 相对于2D模型,合成水凝胶可以促进软骨形成、增加关键软骨细胞标志物(如Ⅱ型胶原)和非胶原蛋白(如骨钙素)的表达[39]。合成水凝胶也可以通过化学修饰进行微调,如将软骨形成分子引入水凝胶包埋细胞,促进软骨生成的生物素转化生长因子β3,以及Ⅱ型胶原和黏多糖表达[40]。利用合成水凝胶进行软骨修复的研究较多,如有人开发的骨关节炎藻酸盐及丝/藻酸盐基支架能够保持软骨细胞的功能和代谢活性,有利于后续软骨疾病抗炎药物的筛选[41]; 有研究证实热可逆凝胶化聚合物支架为软骨组织的生长提供了合适的环境,使骨关节炎软骨细胞能够以最佳水平分泌并保留透明质酸,可作为体外培养的支架材料[42];还有研究报告了一种空的自组装透明质酸纳米颗粒,在体外对透明质酸酶消化具有抵抗力,对原代关节软骨细胞中的分解代谢基因表达具有减弱作用,可以作为骨关节炎的潜在治疗剂[43];此外,有人开发了用于骨软骨组织再生的双相支架,它的组织特异性差异特征支持原代软骨细胞和成骨细胞的生长和增殖,并有利于新组织在其各自阶段形成,具有明显的界面区域[44]。 水凝胶(合成或生物)的性质和黏度很重要,将对细胞反应产生影响,如生物过程本质上是动态的,而大多数体外模型是静态的,这需要通过使用具有时变特性的支架来模拟疾病进展的动态。有研究设计了一种水凝胶,通过引导其交联反应来呈现细胞随时间变化对动态变硬的响应[45]。高黏度可能在培养的细胞或组织中引起闭塞效应,产生缺氧现象,从而降低其生存能力分数[46]。水凝胶的生物相容性和无害性也是重要的特征。目前由可生物降解的聚合物组成的预制支架较受青睐,因为其生物相容性允许轻松地集成到生物系统中,例如使用聚己内酯应用在外科缝线和植入物中;它还具有低熔点,可提供理想的热塑性能,便于3D打印;其黏弹性也有利于细胞培养。然而,聚合物如聚己内酯是非骨诱导性的,最近的研究已经将骨诱导和机械支持分子(如羟基磷灰石和聚富马酸丙烯酯)添加进该聚合物,聚己内酯/羟基磷灰石/聚富马酸丙烯酯支架可促进间充质干细胞成骨诱导,增加钙沉积水平和Runt相关转录因子2表达,这标志了成骨细胞的分化,而且其不具有细胞毒性[47]。 水凝胶提供了适合体外建模的材料,但这些水凝胶的复合部分与天然细胞外基质中发现的材料不同,这可能会影响细胞的行为。此外,水凝胶含有很大的水成分,不适合模拟各种环境,如适合关节软骨但不适合体内细胞外基质含水量非常低的软骨下骨。因此,这种支架中成骨细胞的生长不能够准确地模拟体内环境。 带支架的3D细胞模型成本高昂,难以维护且难以标准化,细胞增殖、细胞迁移通常较慢,对其研究仍需要进一步的工作来确定其稳定性和可靠性。 2.1.3 外植体模型 外植体可被认为是最准确的骨关节炎体外模型,因为移植模型直接来源于体内组织(它们的来源可以是动物和人类),整个组织保持其形态和功能,并在其3D环境中维持细胞,可以帮助研究者们更好地了解细胞在其自然 3D 环境中的行为。可用于研究软骨,软骨下骨和滑膜等组织在关节炎中的作用,还可研究细胞因子、渗透压、物理损伤和生物应力对组织的影响。组织外植体模型可包含单个关节组织或骨软骨外植体或与滑膜或软骨下骨组织共培养的软骨外植体等。与骨软骨组织相比,骨外植体在受到脂多糖攻击时分泌的炎症递质水平增加,这表明骨软骨组织内的不同细胞可以相互影响[48]。用白细胞介素1β攻击的软骨外植体产生的肿瘤坏死因子α水平高于对照组,而骨软骨外植体的肿瘤坏死因子α分泌水平没有变化,这表明骨或滑膜的存在可能会降低肿瘤坏死因子α的表达,同时强调了在骨关节炎病理生理学分析中考虑所有关节组织的必要性[49];有研究开发了一种由软骨和骨骼2个分离的介质室组成的新型体外骨软骨培养模型,它允许延长骨软骨外植体的培养时间,同时保持软骨的结构、机械性能和组织含量至少56 d,这种模型可用于研究临床相关的软骨治疗或软骨再生机制[50]。 外植体模型仍存在必须解决的问题。如培养中组织的维护费用昂贵且难以控制,温度、pH值、湿度、培养基和补充物(如胰岛素加光照)等条件对保持外植体的活力至关重要;组织手术边缘的细胞可能死亡而影响分析;从组织提取中可能会产生分子改变;从每个供体分离的外植体数量有限,不同的来源可能会引起不同的反应,很难实现可行的复制[49]。因移植的组织是在人工环境中培养的,对手术切除后的机械效应或血管生成效应的研究有待完善。骨关节炎的分子变化通常只会在中晚期导致实际的身体症状,但采集的组织通常是健康样本,不具有病理性,实验过程中维持细胞和组织长期存活是一个挑战。有研究发现,生物反应器或组织模拟聚合物有助于使骨关节炎的状况维持稍长的时间[51],上述各模型间优缺点的比较见表2。 "
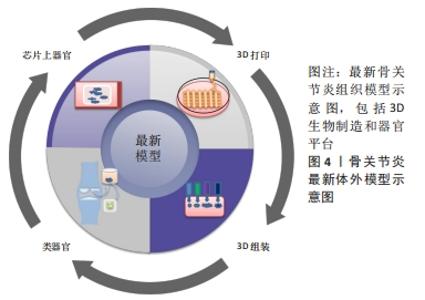
2.1.4 生物反应器模型 生物反应器的引入提高了细胞活力并开发了长期的体外培养模型,该模型可将主要组织的共培养物与诱导骨关节炎的物理化学因素相结合,研究特定条件下不同细胞的相互作用和机制。生物反应器是允许在受控环境下动态培养细胞的工具。动态培养使得细胞在基质中均匀分布,有利于细胞间相互作用;还可为细胞提供机械刺激,增加细胞增殖并减少坏死组织形成的机会。目前已经开发了多种生物反应器,如灌注生物反应器、旋转壁容器、旋转烧瓶和压缩系统,将其放置在三维支架环境中以帮助创建功能性组织[52]。有研究者开发了一种生物反应器,骨软骨单元中的软骨和骨被单独隔开,可以独立控制,允许特定的营养物质和微环境用于骨软骨组织的发育和维持[53]。还有人设计了计算导向的生物反应器,可以增加反应器体中细胞的灌注[54]。然而,模型还需进一步验证完善以更好地模拟体内条件。 2.2 骨关节炎体外模型的最新研究进展 3D生物制造和人体器官平台已被用于模拟人体病理生理状况,或可作为潜在的最先进的体外骨关节炎模型,见图4。"
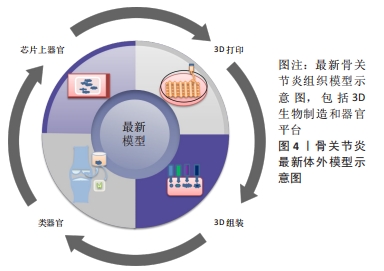

2.2.1 3D生物制造 3D生物制造是组织工程中的一种新兴策略,通过细胞和生物材料的精确沉积和组装来构建3D体外模型。 3D生物打印:它使用计算机辅助设计建模来沉积生物墨水 (由活细胞、生物材料和生长因子组成) 以逐层的方式制造3D结构。使用3D生物打印可开发仿生软骨组织,如有人报道了在聚乙二醇-藻酸盐-凝血酶水凝胶的自愈液中,含有人间充质干细胞的纤维蛋白原球体被生物打印形成纤维蛋白,以模拟软骨的细胞外基质来创造软骨微环境[55],现在的重点也正在向骨软骨组织缺损修复的研究方向发展,如有研究使用基于融合沉积模型的3D生物打印和纳米晶羟磷灰石来创建模仿骨软骨组织的分级孔隙结构,结果表明这种组织工程支架可以改善骨髓人间充质干细胞的黏附、生长和骨软骨分化[56]。3D生物打印的某些挑战限制了其广泛应用,例如低机械性能、相对较低的打印分辨率以及较长的打印时间。 生物组装:生物组装技术通过自动组装各种形状的预成型细胞-材料混合构建块来创建分层结构。细胞封装水凝胶经常用作构建块,因为它们可以改变其形式,并被分组成点状、线状和平面状组件[57]。 具有创造复杂解剖结构的能力,适用于软骨组织工程的研究,如有学者设计了一种自动化的3D生物组装平台,将预分化的软骨微组织或细胞负载的明胶基水凝胶微球插入3D绘制热塑性聚合物支架中,通过多步自底向上的生物组装策略制造来复杂的混合层次结构,结果表明这个平台支持组织融合、长期细胞活力和软骨特异性细胞外基质蛋白沉积[58]。然而生物组装却不能独立完成生物制造过程,因为此系统目前尚不成熟。 2.2.2 体外器官模型 随着组织工程领域的技术进步,在模拟复杂和动态的微环境方面器官模型的出现显示出巨大的潜力。类器官和芯片上器官是最近几年发展起来的2种不同的方法。 类器官:它是源自初级组织、胚胎干细胞和诱导多能干细胞的体外3D细胞簇,能够自我更新和自我组织,并表现出与起源组织相似的器官功能。类器官具有一定的优势,如基因组稳定、具有自我更新的干细胞的群,可以产生完全分化的后代、类器官可以无限扩展,冷冻保存为生物银行、并可使用类似于单层培养的技术轻松操作[59]。理论上具有模拟体外骨关节炎环境的巨大潜力,然而目前对应用于骨骼、软骨和骨软骨组织的类器官尚未进行过多探索。有学者开发了一种基于人骨膜衍生细胞自发生物组装的方法,允许在异位植入小鼠时大规模生产半自主愈伤组织类器官并形成骨微器官,再生骨表现出与天然骨相似的形态学特征,可用于骨缺损愈合的研究[60]。 芯片上器官:将炎症反应和免疫细胞等纳入体外疾病模型的微装置被称为器官芯片。它具有一定的可控性,允许营养和氧气的最佳供应,可以有效去除分解代谢产物,并使组织内的细胞极化和交流,可以创造复杂的生理微环境[61]。还可设置多房室装置以适合体外联合模型,因为不同的组织需要不同类型的机械和生物化学刺激。根据所涉及的细胞和组织的不同,模型可大致分为单组织软骨和多组织软骨。有研究建立了一种微生理芯片软骨模型,该模型允许对3D关节软骨微组织进行机械压缩,结果表明,超过30%生理压缩可以模拟骨关节炎发病机制中涉及的机械性能。压迫刺激软骨内稳态向分解代谢、炎症、肥大转变,基因表达谱类似于临床骨关节炎情况[62]。在重现自然的多组织相互作用方面,有研究开发了一种人诱导多能干细胞的微生理骨软骨组织芯片来模拟骨关节炎病理学,研究结果证明了正常和病理条件下芯片模型中骨和软骨组织之间的相互作用,可用于骨关节炎建模和筛选测试骨关节炎治疗药物[63]。 尽管有几项研究表明体外器官模型取得了令人信服的概念验证方法,但其转化意义和预测能力尚待在临床和药物环境中建立,所以体外器官模型需要进一步优化和持续创新。 "

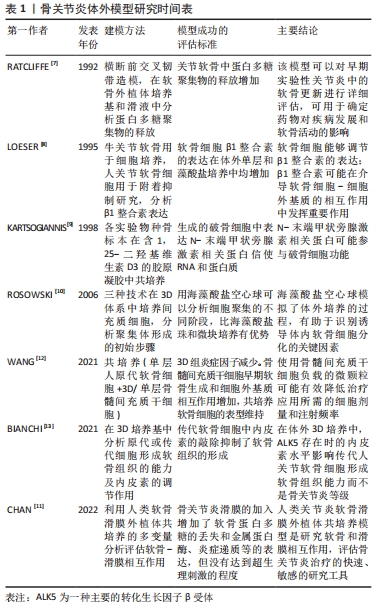
| [1] GBD 2017 DISEASE AND INJURY INCIDENCE AND PREVALENCE COLLABORATORS. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018;392(10159):1789-1858. [2] KING LK, MARCH L, Anandacoomarasamy A. Obesity & osteoarthritis. Indian J Med Res. 2013;138(2):185-193. [3] LOESER RF, GOLDRING SR, SCANZELLO CR, et al. Osteoarthritis: a disease of the joint as an organ. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64(6):1697-1707. [4] HUNTER DJ, BIERMA-ZEINSTRA S. Osteoarthritis. Lancet. 2019;393(10182):1745-1759. [5] THYSEN S, LUYTEN FP, LORIES RJ. Targets, models and challenges in osteoarthritis research. Dis Model Mech. 2015;8(1):17-30. [6] CADDEO S, BOFFITO M, SARTORI S. Tissue engineering approaches in the design of healthy and pathological in vitro tissue models. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2017;5:40. [7] RATCLIFFE A, BILLINGHAM ME, SAED-NEJAD F, et al. Increased release of matrix components from articular cartilage in experimental canine osteoarthritis. J Orthop Res. 1992;10(3):350-358. [8] LOESER RF, CARLSON CS, MCGEE MP. Expression of beta 1 integrins by cultured articular chondrocytes and in osteoarthritic cartilage. Exp Cell Res. 1995;217(2): 248-257. [9] KARTSOGIANNIS V, UDAGAWA N, NG KW, et al. Localization of parathyroid hormone-related protein in osteoclasts by in situ hybridization and immunohistochemistry. Bone. 1998;22(3):189-194. [10] ROSOWSKI M, FALB M, TSCHIRSCHMANN M, et al. Initiation of mesenchymal condensation in alginate hollow spheres--a useful model for understanding cartilage repair? Artif Organs. 2006;30(10):775-784. [11] CHAN MWY, GOMEZ-ARISTIZÁBAL A, MAHOMED N, et al. A tool for evaluating novel osteoarthritis therapies using multivariate analyses of human cartilage-synovium explant co-culture. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2022;30(1):147-159. [12] WANG B, LIU W, LI JJ, et al. A low dose cell therapy system for treating osteoarthritis: in vivo study and in vitro mechanistic investigations. Bioact Mater. 2021;7:478-490. [13] BIANCHI VJ, PARSONS M, BACKSTEIN D, et al. Endoglin level is critical for cartilage tissue formation in vitro by passaged human chondrocytes. Tissue Eng Part A. 2021;27(17-18):1140-1150. [14] SALGADO C, JORDAN O, ALLÉMANN E. Osteoarthritis in vitro models: applications and implications in development of intra-articular drug delivery systems. Pharmaceutics. 2021;13(1):60. [15] KOTHARI P, TRIPATHI AK, GIRME A. Caviunin glycoside (cafg) from dalbergia sissoo attenuates osteoarthritis by modulating chondrogenic and matrix regulating proteins. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021;282:114315. [16] LEE SA, MOON SM, HAN SH. Chondroprotective effects of aqueous extract of anthriscus sylvestris leaves on osteoarthritis in vitro and in vivo through MAPKS And Nf-Κb signaling inhibition. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;103:1202-1211. [17] DESHMUKH V, HU H, BARROGA C. A small-molecule inhibitor of the wnt pathway (sm04690) as a potential disease modifying agent for the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee. osteoarthritis cartilage. 2018;26(1):18-27. [18] LIU Z, LANG Y, LI L, et al. Effect of emodin on chondrocyte viability in an in vitro model of osteoarthritis. Exp Ther Med. 2018;16(6):5384-5389. [19] AL-MODAWI RN, BRINCHMANN JE, KARLSEN TA. Multi-pathway protective effects of micrornas on human chondrocytes in an in vitro model of osteoarthritis. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2019;17:776-790. [20] SAMVELYAN HJ, HUGHES D, STEVENS C. Models of osteoarthritis: relevance and new insights. Calcif Tissue Int. 2021;109(3):243-256. [21] BEEKHUIZEN M, BASTIAANSEN-JENNISKENS YM, KOEVOET W, et al. Osteoarthritic synovial tissue inhibition of proteoglycan production in human osteoarthritic knee cartilage: establishment and characterization of a long-term cartilage-synovium coculture. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63(7):1918-1927. [22] COPE PJ, OURRADI K, LI Y. Models of osteoarthritis: the good, the bad and the promising. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019;27(2):230-239. [23] BENAM KH, DAUTH S, HASSELL B, et al. Engineered in vitro disease models. Annu Rev Pathol. 2015;10:195-262. [24] ZHENG W, FENG Z, YOU S. Fisetin inhibits il-1β-induced inflammatory response in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes through activating sirt1 and attenuates the progression of osteoarthritis in mice. Int Immunopharmacol. 2017;45:135-147. [25] JOHNSON CI, ARGYLE DJ, CLEMENTS DN. In vitro models for the study of osteoarthritis. Vet J. 2016;209:40-49. [26] PARK H, LEE HJ, AN H, et al. Alginate hydrogels modified with low molecular weight hyaluronate for cartilage regeneration. Carbohydr Polym. 2017;162:100-107. [27] MOHAN N, MOHANAN PV, SABAREESWARAN A. Chitosan-Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogel For Cartilage Repair. Int J Biol Macromol. 2017;104(Pt B):1936-1945. [28] ZIADLOU R, BARBERO A, MARTIN I. Anti-inflammatory and chondroprotective effects of vanillic acid and epimedin c in human osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Biomolecules. 2020;10(6):932. [29] HUANG S, SONG X, LI T, et al. Pellet coculture of osteoarthritic chondrocytes and infrapatellar fat pad-derived mesenchymal stem cells with chitosan/hyaluronic acid nanoparticles promotes chondrogenic differentiation. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):264. [30] ITOKAZU M, WAKITANI S, MERA H, et al. Transplantation of scaffold-free cartilage-like cell-sheets made from human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells for cartilage repair: a preclinical study. Cartilage. 2016;7(4):361-372. [31] CARON MM, EMANS PJ, COOLSEN MM. Redifferentiation of dedifferentiated human articular chondrocytes: comparison of 2d and 3d cultures. osteoarthritis cartilage. 2012;20(10):1170-1178. [32] NAKAGAWA Y, MUNETA T, OTABE K, et al. Cartilage derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells expresses lubricin in vitro and in vivo. PLoS One. 2016; 11(2):E0148777. [33] DUVAL K, GROVER H, HAN LH. Modeling physiological events in 2d vs. 3d cell culture. Physiology (Bethesda). 2017;32(4):266-277. [34] PRADAL J, ZULUAGA MF, MAUDENS P. Intra-articular bioactivity of a p38 mapk inhibitor and development of an extended-release system. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015;93:110-117. [35] GOLDRING SR, GOLDRING MB. Changes in the osteochondral unit during osteoarthritis: structure, function and cartilage-bone crosstalk. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016;12(11):632-644. [36] MAUDENS P, SEEMAYER CA, THAUVIN C. Nanocrystal-polymer particles: extended delivery carriers for osteoarthritis treatment. Small. 2018. doi:10.1002/Smll. 201703108. [37] STEINMETZ NJ, AISENBREY EA, WESTBROOK KK. Mechanical loading regulates human msc differentiation in a multi-layer hydrogel for osteochondral tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2015;21:142-153. [38] MAISANI M, PEZZOLI D, CHASSANDE O. Cellularizing hydrogel-based scaffolds to repair bone tissue: how to create a physiologically relevant micro-environment? J Tissue Eng. 2017;8:2041731417712073. [39] DEY P, SCHNEIDER T, CHIAPPISI L. Mimicking of chondrocyte microenvironment using in situ forming dendritic polyglycerol sulfate-based synthetic polyanionic hydrogels. Macromol Biosci. 2016;16(4):580-590. [40] STUDLE C, VALLMAJÓ-MARTÍN Q, HAUMER A. Spatially confined induction of endochondral ossification by functionalized hydrogels for ectopic engineering of osteochondral tissues. Biomaterials. 2018;171:219-229. [41] GALUZZI M, PERTEGHELLA S, ANTONIOLI B. Human engineered cartilage and decellularized matrix as an alternative to animal osteoarthritis model. Polymers (Basel). 2018;10(7):738. [42] KATOH S, YOSHIOKA H, SENTHILKUMAR R. Enhanced expression of hyaluronic acid in osteoarthritis-affected knee-cartilage chondrocytes during three-dimensional in vitro culture in a hyaluronic-acid-retaining polymer scaffold. Knee. 2021;29:365-373. [43] KANG LJ, YOON J, RHO JG, et al. Self-assembled hyaluronic acid nanoparticles for osteoarthritis treatment. Biomaterials. 2021;275:120967. [44] SINGH YP, MOSES JC, BHUNIA BK, et al. Hierarchically structured seamless silk scaffolds for osteochondral interface tissue engineering. J Mater Chem B. 2018; 6(36):5671-5688. [45] GUVENDIREN M, BURDICK JA. Stiffening hydrogels to probe short- and long-term cellular responses to dynamic mechanics. Nat Commun. 2012;3:792. [46] CAI Z, ZHANG H, WEI Y. Shear-thinning hyaluronan-based fluid hydrogels to modulate viscoelastic properties of osteoarthritis synovial fluids. Biomater Sci. 2019;7(8):3143-3157. [47] MALIKMAMMADOV E, TANIR TE, KIZILTAY A, et al. Pcl and pcl-based materials in biomedical applications. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2018;29(7-9):863-893. [48] GEURTS J, JURIĆ D, MULLER M. Novel ex vivo human osteochondral explant model of knee and spine osteoarthritis enables assessment of inflammatory and drug treatment responses. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(5):1314. [49] BYRON CR, TRAHAN RA. Comparison of the effects of interleukin-1 on equine articular cartilage explants and cocultures of osteochondral and synovial explants. Front Vet Sci. 2017;4:152. [50] SCHWAB A, MEEUWSEN A, EHLICKE F, et al. Ex vivo culture platform for assessment of cartilage repair treatment strategies. Altex. 2017;34(2):267-277. [51] BICHO D, PINA S, OLIVEIRA JM. In vitro mimetic models for the bone-cartilage interface regeneration. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1059:373-394. [52] AHMED S, CHAUHAN VM, GHAEMMAGHAMI AM, et al. New generation of bioreactors that advance extracellular matrix modelling and tissue engineering. Biotechnol Lett. 2019;41(1):1-25. [53] LIN H, LOZITO TP, ALEXANDER PG, et al. Stem cell-based microphysiological osteochondral system to model tissue response to interleukin-1β. Mol Pharm. 2014;11(7):2203-2212. [54] NICHOLS DA, SONDH IS, LITTLE SR, et al. Design and validation of an osteochondral bioreactor for the screening of treatments for osteoarthritis. Biomed Microdevices. 2018;20(1):18. [55] LDE MELO BAG, JODAT YA, MEHROTRA S, et al. 3D printed cartilage-like tissue constructs with spatially controlled mechanical properties. Adv Funct Mater. 2019;29(51):1906330. [56] NOWICKI MA, CASTRO NJ, PLESNIAK MW, et al. 3d printing of novel osteochondral scaffolds with graded microstructure. Nanotechnology. 2016;27(41):414001. [57] MORONI L, BURDICK JA, HIGHLEY C, et al. Biofabrication strategies for 3d in vitro models and regenerative medicine. Nat Rev Mater. 2018;3(5):21-37. [58] MEKHILERI NV, LIM KS, BROWN GCJ, et al. Automated 3d bioassembly of micro-tissues for biofabrication of hybrid tissue engineered constructs. Biofabrication. 2018;10(2):024103. [59] FATEHULLAH A, TAN SH, BARKER N. Organoids as an in vitro model of human development and disease. Nat Cell Biol. 2016;18(3):246-254. [60] NILSSON HALL G, MENDES LF, GKLAVA C, et al. Developmentally engineered callus organoid bioassemblies exhibit predictive in vivo long bone healing. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2019;7(2):1902295. [61] MOSIG AS. Organ-on-chip models: new opportunities for biomedical research. Future Sci Oa. 2016;3(2):FSO130. [62] OCCHETTA P, MAINARDI A, VOTTA E, et al. Hyperphysiological compression of articular cartilage induces an osteoarthritic phenotype in a cartilage-on-a-chip model. Nat Biomed Eng. 2019;3(7):545-557. [63] LIN Z, LI Z, LI EN, et al. Osteochondral tissue chip derived from ipscs: modeling oa pathologies and testing drugs. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2019;7:411. |
| [1] | Sun Kexin, Zeng Jinshi, Li Jia, Jiang Haiyue, Liu Xia. Mechanical stimulation enhances matrix formation of three-dimensional bioprinted cartilage constructs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-7. |
| [2] | Zhou Jie, Pei Xibo, Wan Qianbing. Advances and biological application of asymmetric dressings [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 434-440. |
| [3] | Chen Jingqiao, Li Ying, Meng Maohua, Xu Xingxing, Wang Qinying, Wang Huan, Lu Jing, Shu Jiayu, Dong Qiang. Research progress in platelet-rich fibrin in stomatology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 441-446. |
| [4] | Han Tao, Hao Jianqiang, Li Wenbo, Shi Jie, Gao Qiuming. Advantages and problems of antibiotic-loaded bone cements for bone and joint infections [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 470-477. |
| [5] | Xie Pingjin, Luo Zhen, Lu Qigui, Guo Yanxing, Chen Qunqun, Li Feilong. Effect of ligustrazine and overexpression of miR-20b-5p on synovial, cartilage and subchondral bone angiogenesis in rats with early-stage knee osteoarthritis: a histological observation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 237-245. |
| [6] | Wang Huanhuan, Wang Qing, Tang Peng, Zhang Rui, Min Hongwei. Effects of extracorporeal shock wave on the proliferation and autophagy of chondrocytes from osteoarthritis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 252-257. |
| [7] | Chen Feng, Ren Guowu, Zhang Xiaoyun, Chen Yueping, Shi Rusheng. Receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa B ligand signal transduction mechanism and osteoclast activation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 293-299. |
| [8] | Liu Yinghong, Yi Yating. Mechanism and implication of angiogenesis in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 307-313. |
| [9] | Zhang Jie, Tian Ai. Advances in the signaling pathway of M2 macrophages involved in bone regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 314-321. |
| [10] | Zhu Miaomiao, Kong Fanming, Zhao Qian. Exercise regulates lactic acid metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 322-328. |
| [11] | Liu Runyuan, Dong Ming, Han Wenqing, Dong Juhong, Niu Weidong. Application and progress of small extracellular vesicles in periodontal and pulp regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 83-90. |
| [12] | Xi Hualei, Xue Bing, Xu Wanqiu, Xu Xiaohang, Yao Lihong, Wang Xiumei. Neural differentiation and neural biomarker expression of dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 91-98. |
| [13] | Liu Zhuoran, Jiang Ming, Li Yourui. Extracellular vesicles in chronic periodontitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 99-104. |
| [14] | Shi Xu, Li Ruiyu, Zhang Bing, Chen Qi, Zuo Hua. Effect of inflammatory reaction mediated by microglia polarization in spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 121-129. |
| [15] | Guo Yujun, Lu Wenjun, Yang Shulong, Li Zhaozhu. Effect of urine-derived stem cells and their exosomes on kidney diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 138-144. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||