Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (1): 121-129.doi: 10.12307/2022.731
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of inflammatory reaction mediated by microglia polarization in spinal cord injury
Shi Xu1, Li Ruiyu1, Zhang Bing1, Chen Qi2, Zuo Hua2
- 1Medical College of Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang 212000, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang 212000, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2021-09-22Accepted:2021-10-22Online:2023-01-08Published:2022-06-06 -
Contact:Zuo Hua, Master, Chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang 212000, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Shi Xu, Master candidate, Medical College of Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang 212000, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:Social Development Guiding Science and Technology Plan Project of Zhenjiang, No. FZ2020077 (to ZH)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Shi Xu, Li Ruiyu, Zhang Bing, Chen Qi, Zuo Hua. Effect of inflammatory reaction mediated by microglia polarization in spinal cord injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 121-129.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
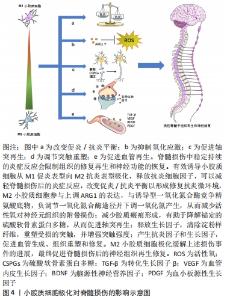
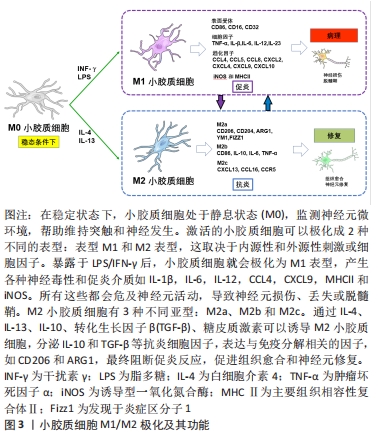
2.1 小胶质细胞 2.1.1 小胶质细胞的生理功能 小胶质细胞和巨噬细胞是两个容易混淆的概念。这两类细胞在时空分布上存在差异,它们既相互联系又相互区别[4]。小胶质细胞是一种胶质细胞,占中枢神经系统细胞总数的5%-10%。更重要的是,小胶质细胞也是驻留在中枢神经系统的组织巨噬细胞的一员[5]。其他类型的中枢神经系统巨噬细胞包括脑膜巨噬细胞、血管周围巨噬细胞和脉络丛巨噬细胞。在不同的解剖区域,这些组织巨噬细胞表现出形态上的异质性[6-7]。随着流式细胞术和单细胞测序等分子诊断技术的发展,小胶质细胞的标记分子有重要的更新,主要有CD45(低中度表达)、CD11b、Tmem119和P2RY12[8]。在中枢神经系统损伤部位,巨噬细胞来源于小胶质细胞和血源性巨噬细胞,损伤的中枢神经系统中激活后不能通过它们的形态或抗原标记来区分,所以这些细胞在之前的许多文献中被称为巨噬细胞/小胶质细胞。这些标记分子可有效地区分小胶质细胞和巨噬细胞,为小胶质细胞的进一步研究奠定了基础。 小胶质细胞起源于胚胎卵黄囊中的髓系祖细胞。像外周巨噬细胞一样,小胶质细胞有能力改变其形态,从而影响中枢神经系统的生理和病理条件[9]。小胶质细胞有很长的胞浆突起,与星形胶质细胞、神经元和血管直接接触,因此小胶质细胞可以执行监测功能,并持续感知其微环境的细微变化。它们通过吞噬作用快速有效地清除病原体、死亡细胞、碎片或异常蛋白,从而维持中枢神经系统的动态平衡[10-11]。小胶质细胞分支直接与轴突终末、棘突、星形胶质细胞突起和突触裂隙相互作用,促进突触的消除、修剪或成熟,从而有助于神经元网络的形成和保护[4]。此外,小胶质细胞有助于少突胶质前体细胞存活和髓鞘形成,其分泌的营养因子有助于神经元存活和轴突生长[12]。因此小胶质细胞在调节中枢神经系统的发育和稳态方面发挥着上述重要作用,对于小胶质细胞功能的探索和调控在中枢神经系统疾病的治疗领域具有不可忽视的研究价值。 2.1.2 小胶质细胞极化 在内源性刺激下,活化的小胶质细胞可以表现出致病和保护作用:M1促炎表型和M2抗炎表型,此2个不同的极化状态依赖于特定的微环境。这2种不同表型的小胶质细胞具有相反的特性。M1表型与促炎细胞因子和趋化因子的表达有关,这些因子促进慢性神经炎症、吞噬作用、氧化应激和神经退行性变,并抑制再生[5]。由于M1小胶质细胞常参与常见的炎症反应,因此在许多体内和体外实验中被广泛研究。暴露于细菌衍生物如脂多糖或感染相关信号如干扰素γ后可诱导M1表型,脂多糖和干扰素γ是诱导M1极化的经典活化配体[13]。神经元的机械损伤导致嘌呤代谢物、高迁移率族蛋白B1和热休克蛋白等因子的释放,这些因子调节促炎细胞因子的释放和Toll样受体的激活,从而诱导M1表型。随后,产生了高水平的促炎递质,包括表面受体、细胞因子、趋化因子、诱导型一氧化氮合酶和主要组织相容性复合体Ⅱ,它们是宿主防御的重要组成部分[14-15]。 M1小胶质细胞虽然在体内主要参与先天性免疫系统第一道防线的形成,能够抑制外来病原体或异常蛋白、核酸和细胞碎片的侵入,但也具有一定的神经毒性,不仅发挥先天免疫作用,还可加重中枢神经系统不同区域的神经炎症反应和神经元损伤[16]。而M2小胶质细胞可增强营养因子,降解神经毒性蛋白,减轻炎症反应,吞噬老化损伤的细胞器和代谢片段,促进神经元存活和神经突起外生长[17]。进一步研究发现,炎性微环境中M2小胶质细胞有3种不同亚型:M2a、M2b和M2c,这些亚型具有不同的特征,并在不同的微环境中诱导产生[7,18]。白细胞介素4或白细胞介素13诱导的M2a亚型主要与寄生虫免疫、生长刺激、组织修复、胶原形成和Th2细胞、嗜酸性粒细胞的募集有关。到目前为止,已经检测到不同的M2a特异性表面标记物,如CD206,ARG1,Ym1和Fizz1[19-20]。M2b亚型的极化与Fcγ受体、Toll样受体和免疫复合物的触发密切相关。M2b亚型与促炎和抗炎功能、B细胞类转换和抗体产生以及调节性T细胞的募集有关[21]。M2c极化对白细胞介素10、转化生长因子β、糖皮质激素等特异性抗炎因子有响应作用。M2c极化细胞显示CCL16,CXCL13和CCR5等趋化因子上调,同时参与片段清除、促愈合功能和铁螯合[22-23],见图3。 "
小胶质细胞表现出上述两种不同的极化表型,有人提出这是一种机体的自我修复尝试,帮助恢复健康稳定的内环境。随着对小胶质细胞极化过程的深入研究和理解,局部小胶质细胞群体的极化状态很可能是相互重叠的,而不是许多研究报道中以特定表型单独存在。在脊髓损伤动物实验中,损伤后早期观察到大多数小胶质细胞为M1表型,仅有一小部分表现为一过性的M2极化。脊髓损伤后,几种M1/M2标志物的表达较正常明显上调,但变化趋势不同。经典M2标志物ARG1仅在短时间内处于高表达状态,随后迅速下降,伤后1周恢复正常。与未损伤的脊髓相比,另一个经典的M2标记物CD206在损伤后2周持续高表达。而M1标志物CD16和CD32的表达虽然在伤后短时间内迅速升高,并在损伤后一两周内达到高峰,但在2-4周内迅速下降,仅接近正常水平。此外,作为M1标志物之一的诱导型一氧化氮合酶在伤后第3天才出现一过性升高。在脊髓损伤后的慢性期,M1表型的小胶质细胞占主导地位,导致组织修复能力下降和持续性神经炎症[7,16]。不同表型的小胶质细胞作为一个多功能的整体,不能以独立的、持续活跃的状态存在,其表型间转化的动态平衡偏向于M1型无疑是脊髓损伤后慢性炎症持续存在的潜在原因。调控小胶质细胞M2极化来发挥其修复抗炎特性或许可以延缓疾病进展和改善预后,这也可能是未来脊髓损伤的潜在治疗靶点。 2.2 小胶质细胞极化如何影响脊髓损伤 "
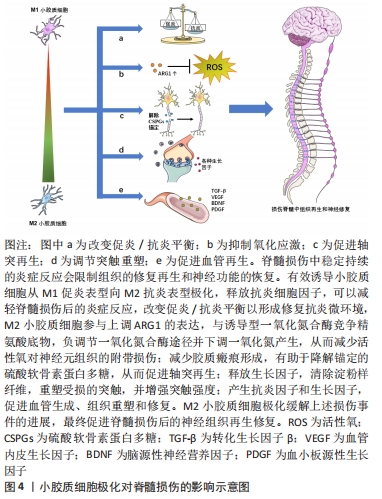
2.2.1 改变促炎与抗炎平衡 如上所述,在生理条件下,小胶质细胞处于M0静止表型。脊髓损伤之后,小胶质细胞活化,极化成M1促炎表型和M2抗炎表型,其中M1型比M2型占优势,此时促炎与抗炎之间平衡被打破。有研究发现抗炎因子如白细胞介素10、白细胞介素4、白细胞介素13和生长因子如胰岛素样生长因子1和转化生长因子β的释放促进M2小胶质细胞下调M1信号[7]。此外,进一步的证据表明,M2因子通过抑制经典调控炎症极化核转录因子κB途径抑制促炎细胞因子的产生[24]。总的来说,促进小胶质细胞的M2极化可以改善脊髓损伤微环境中的促炎症与抗炎平衡,发挥M2型小胶质细胞的修复抗炎特性。 2.2.2 氧化应激 氧化应激是脊髓损伤的重要环节,可直接和间接加速炎症反应,从而进一步增加氧化应激,最终改变膜通透性,诱发溶酶体解体和细胞坏死,导致脊髓继发性损伤[25]。M2小胶质细胞参与上调ARG1的表达,与诱导型一氧化氮合酶竞争精氨酸底物,负调节一氧化氮合酶途径并下调一氧化氮产生,从而减少活性氧对神经元组织的附带损伤,并参与损伤修复[26-27]。 2.2.3 轴突再生 轴突再生失败是中枢神经系统损伤后实现功能恢复的主要障碍。损伤后的轴突再生程度有限,促进轴突再生可以帮助重建受损的脊髓神经回路,促进功能恢复[28]。然而有体外实验证明了由脂多糖或干扰素γ激活的M1型小胶质细胞抑制神经突起生长并诱导营养不良神经元的轴突收缩[29]。除此以外,脊髓损伤后M1型小胶质细胞在体内外通过分泌白细胞介素1α、肿瘤坏死因子α和补体C1q来诱导星形胶质细胞发生形态学和行为学的改变,反应性星形胶质细胞增殖向损伤处迁移,形成胶质瘢痕,限制轴突的再生和细胞毒性炎症的扩散[30-31]。另一方面,硫酸软骨素蛋白多糖长期以来一直被认为是轴突再生和再髓鞘形成的抑制剂,KIGERL等[16]的研究发现M2型小胶质细胞有助于降解锚定的硫酸软骨素蛋白多糖并促进轴突再生。 2.2.4 突触重塑 大量证据表明,小胶质细胞在神经发育过程中可以调节突触可塑性,而且在中枢神经系统损伤后也是如此并直接调节突触活动[32-33]。小胶质细胞在受到促炎细胞因子刺激时,可以极化为M1表型,这对神经发生和突触可塑性有害,而M2型小胶质细胞可以释放生长因子,清除淀粉样纤维,并重塑受损的突触[11]。小胶质细胞极化后产生的趋化因子也是可塑性事件的重要调节剂,包括突触修剪和重塑[34]。除此以外,抗炎细胞因子不仅在调节神经元可塑性方面发挥重要作用,而且在增强突触强度方面也发挥着重要作用[28]。 2.2.5 血管生成 血管在脊髓的损伤和修复中起着至关重要的作用。虽然脊髓损伤后确实发生血管生成,但生成有限,无法提供足够数量的血管进行最大程度的修复[35]。目前了解到M1型小胶质细胞分泌丰富的促炎细胞因子,可参与发病机制并导致组织损伤,而M2小胶质细胞则倾向于产生抗炎因子和生长因子,比如转化生长因子β、血管内皮生长因子、脑源性神经营养因子和血小板源性生长因子,可以促进血管生成、组织重塑和修复[7,36]。 2.3 调控小胶质细胞极化的策略 "
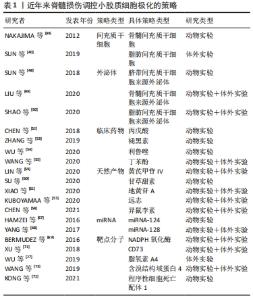
小胶质细胞极化在与脊髓损伤发展相关的一系列神经病理过程中发挥着不可或缺的作用。目前脊髓损伤治疗的综合策略包括细胞递送治疗、药物治疗和基因治疗等,同时在探索促进小胶质细胞M2极化的治疗策略方面的研究取得了相当大的进展。 2.3.1 间充质干细胞 间充质干细胞是一种多能异质细胞,其自我更新和向多系分化的特性可作为多种疾病的治疗来源[37]。间充质干细胞来源广泛,可来源于不同类型的组织,包括胎盘、脐带血、胎儿血、肝脏和骨髓等[38-40]。从上述来源获取细胞可以在收集容易、可获得性、保证增殖能力和相对较少的不良影响的情况下完成,这增加了它们的临床相关性。间充质干细胞分泌的免疫抑制细胞因子,如转化生长因子β、肿瘤坏死因子诱导基因6、前列腺素E2和抗炎白细胞介素,可诱导小胶质细胞代谢的改变,导致向抗炎小胶质细胞表型的转变。间充质干细胞体外培养结果显示,白细胞介素6、白细胞介素1β、巨噬细胞趋化蛋白1等M1标志物明显降低,而M2标志物显著增加,如白细胞介素10、白细胞介素4、CD206和ARG1[41]。有研究使用动物模型对体外获得的间充质干细胞进行体内验证。NAKAJIMA等[39]观察到骨髓间充质干细胞移植到大鼠脊髓损伤中心后白细胞介素4和白细胞介素13水平升高,肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6水平降低,结果表明,急性脊髓损伤后间充质干细胞移植通过将小胶质细胞表型从M1转移到M2,改变了炎症环境。这可能会降低亚急性/慢性损伤后抑制性瘢痕组织的作用,为轴突延伸和功能恢复提供良好的环境。此外,SUN等[40]研究发现,脂肪间充质干细胞可以阻断脂多糖诱导的小胶质细胞M1促炎表型,并诱导小胶质细胞M2抗炎表型,这可能与抑制TLR4/TRIF信号通路有关。当间充质干细胞调节小胶质细胞分化时,极化的小胶质细胞反过来影响间充质干细胞的分泌特性。对这些免疫调节机制的进一步研究可以促进脊髓损伤治疗的发展,利用间充质干细胞对小胶质细胞的调节和修复潜力,改变炎症反应的方向,从而调控炎症过程,限制过度的免疫防御机制,减少组织损伤,甚至增强自我修复能力,在损伤位点创造一个修复环境。然而,间充质干细胞直接移植入靶组织的局限性和挑战不容忽视。实验研究表明,移植的间充质干细胞的存活率很低[42],也存在其他相关风险包括免疫排斥、细胞去分化和肿瘤发生[43],所有这些都限制了其临床应用。只有规避上述的问题,才能更好地发挥间充质干细胞的优势。 2.3.2 外泌体 外泌体是指存在于多种细胞和体液中直径30-150 nm的小膜泡,比如内皮细胞、免疫细胞、血小板和平滑肌细胞等[44]。外泌体主要来源于细胞内溶酶体颗粒内陷形成的多囊泡,这些囊泡在囊泡外膜与细胞膜融合后释放到细胞外基质中[45]。当外泌体从宿主细胞分泌到受体细胞中时,外泌体可以通过它们携带的蛋白质、核酸和脂质来调节受体细胞的生物活性[46]。外泌体在中枢神经系统的细胞间通讯中起着至关重要的作用,如介导神经元和胶质细胞之间的通讯,促进神经元的修复和生长,以及调节免疫反应[47]。SUN等[48]证明,来自人脐带间充质干细胞的外泌体可以有效地诱导小胶质细胞从M1表型到M2表型极化,显著降低促炎细胞因子水平,如肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6、干扰素γ、粒细胞集落刺激因子、巨噬细胞趋化蛋白1和巨噬细胞炎性蛋白1α。进一步动物损伤模型研究发现,人脐带间充质干细胞来源的外泌体通过减轻损伤区域的炎症来促进脊髓损伤的愈合。此外,LIU等[49]通过多项实验发现,在脊髓损伤小鼠模型中移植骨髓间充质干细胞的外泌体可以促进小胶质细胞M2极化,在这些动物中,观察到脊髓损伤后损伤范围的缩小和功能行为的恢复。SHAO等[50]研究表明,来自脂肪间充质干细胞的外泌体有效地触发了小胶质细胞从M1表型向M2表型的极化,它们通过下调促炎细胞因子和上调抗炎细胞因子,具有强大的抗炎作用。上述实验结果有力地证实了外泌体具有调节小胶质细胞极化的能力。外泌体具有更好的跨越血脑屏障的能力,发挥与来源细胞相似的治疗效果和功能特性,并且全身移植后不良反应更少。尽管具体的潜在机制仍不清楚,外泌体巨大的治疗潜能有可能成为治疗脊髓损伤的一种新的选择。 2.3.3 临床药物 临床上对治疗脊髓损伤的药物开发从未停滞过。目前甲基强的松龙和米诺环素在临床试验中应用广泛,但是这些药物如何影响小胶质细胞极化仍有待阐明[51]。现在有一些药物正在处于脊髓损伤的临床前试验阶段。CHEN等[52]的研究发现用于治疗癫痫的丙戊酸可通过STAT1介导的核转录因子κB通路的乙酰化调节小胶质细胞极化来减轻炎症反应。ZHANG等[53]证实了褪黑素促进了小胶质细胞M1向M2 表型极化并减弱了脊髓中的炎症反应,从而极大地促进脊髓损伤后的功能恢复。利鲁唑是一类苯并噻唑类钠通道阻滞剂,具有神经保护作用和抗炎作用,适用于治疗肌萎缩侧索硬化。最近的一项研究表明,利鲁唑在脊髓损伤动物模型中上调了小胶质细胞M2型标记物水平并促进运动功能恢复[54]。丁苯酞用于治疗缺血性中风的疗效和安全性在临床研究中得到证实。WANG等[55]验证了丁苯酞通过激活p38通路促进小胶质细胞M2极化发挥抗炎作用。小胶质细胞极化参与多种中枢神经系统疾病的发病机制,因此用于这些疾病的临床药物也可能对脊髓损伤中的小胶质细胞极化有着调控作用,并且临床药物应用于脊髓损伤的优势在于其安全性通过国家食品药品监督管理局的认证,缩短了进入临床试验的周期,值得进一步研究。 2.3.4 天然产物 天然产物因其低毒和高效在人类社会历史中作为替代治疗药物已经有了许多世纪的历史。天然产物可以从植物、动物、海洋生物和微生物中提取,具有近乎无限的生物结构多样性,例如较高的氧原子、sp3杂化结构或螺旋环碳原子和手性中心,这使得它们更容易干扰多个细胞信号通路,或以高选择性和高亲和力协调多个分子靶点[5,56]。迄今为止,一些细胞和动物模型实验表明,一系列天然产物及其衍生物可作为小胶质细胞极化调节剂,更有效地改善脊髓损伤的症状和病理进展。KUBOYAMAA等[57]发现活性草药远志在培养的小胶质细胞中诱导M2表型,改善了小鼠脊髓损伤模型的运动功能,并显示出上调M2型小胶质细胞和保护受损脊髓免受轴突变性的趋势。异鼠李素是一种天然的黄酮类化合物,从中药鼠李糖苷中分离得到,具有很强的抗炎作用。有研究发现异鼠李素通过Nrf2/HO-1通路减轻氧化应激和调节M1/M2小胶质细胞极化来促进脊髓损伤大鼠的功能恢复[58]。除此以外,有研究表示从中药黄芪的提取物黄芪甲苷Ⅳ[59]、甘草中分离出的甘草甜素[60]、以及从地黄中分离得到的地黄苷A也能够通过增加M2型小胶质细胞的极化减轻脊髓损伤后的小胶质细胞炎症反应[61]。与人工合成的药物相比,一系列天然产物及其衍生物可以作为小胶质细胞极化调节剂,其多样的生物结构和丰富的生物活性,在新药的探索和开发中发挥了相当大的作用。值得注意的是,尽管天然产物的潜力巨大,但是也具有不同程度的不良反应和有限的功效,需要经过更为严格的试验和验证才能用于临床。 2.3.5 miRNAs miRNAs是一类由19-23个核苷酸组成的内源性非编码RNA,在调节多种细胞生物学过程中发挥重要作用[62]。miRNAs通过与信使RNA的3’末端非翻译区结合刺激RNA干扰途径的降解或阻止靶基因的翻译,来负调控靶基因的表达[63-64]。最近,miRNAs在包括中枢神经系统疾病在内的许多疾病的发病机制中所起的作用受到特别重视。作为大脑中最丰富的miRNAs之一,miR-124不仅是神经系统发育所必需的,而且是参与调节小胶质细胞功能的关键因子[65]。据报道,高水平的miR-124被认为是维持小胶质细胞M0静止表型所必需的,miR-124的抑制会激活小胶质细胞[66]。HAMZEI等[67]证实了早期注射miR-124显著提高神经元存活率和M2型小胶质细胞/巨噬细胞的数量。YANG等[68]在脊髓损伤小鼠模型中发现BV2小胶质细胞中miR-128的表达下调。根据他们的结果,miR-128过表达显著提高小胶质细胞的存活率,并降低了炎性细胞因子的浓度。除此以外,过表达miR-128促进了小胶质细胞M1表型标志物CD86和CD32的下调和M2表型标志物 ARG1和CD206的上调。但是目前主要障碍是如何通过血脑屏障直接将miRNAs递送至病灶处,以及如何防止在递送过程中溶酶体活性降解外源性miRNAs。有人研究发现通过外泌体递送miR-216a-5p参与外泌体所介导的小胶质细胞极化,显示出外泌体和miRNAs 的组合治疗脊髓损伤的可能性[49]。脊髓损伤后发生的分子和细胞变化复杂交错,miRNAs表达的改变为深入了解这些变化的分子机制提供了更多的信息。确定小胶质细胞极化过程中起核心作用的优势miRNAs有望成为改善恢复脊髓损伤一种有吸引力的方法。 2.3.6 靶点分子 除了上述的主流调控策略之外,还有许多其他的方法可以诱导小胶质细胞的极化。BERMUDEZ等[69]的研究验证了在脊髓损伤中NADPH氧化酶表达与小胶质细胞极化表型的相关性,尤其是NOX2的抑制会限制小胶质细胞向M1表型的极化,使其偏向于M2表型。CD73是一种调节细胞外腺苷水平的5’-核苷酸酶,与免疫和炎症相关的脑发育疾病有着复杂的联系[70]。XU等[71]研究发现脊髓损伤后CD73表达上调,在CD73基因缺陷小鼠模型中M2型小胶质细胞减少并展现了较好的运动恢复。同时体外研究发现,沉默CD73会抑制了BV2细胞特有的小胶质细胞M2型标志物的表达,而过表达CD73则相反。程序性细胞死亡配体1可能通过抑制p38和ERK1/2的磷酸化调控小胶质细胞的极化进而减轻炎症反应[72]。随着对极化机制的深入研究,类似上述调控小胶质细胞的靶点分子还有脂氧素A4和含溴结构域蛋白4等[27,73]。 通过药物或基因修饰,改变脊髓损伤中靶点分子的表达来调控小胶质细胞的极化,从而揭示出可能在新型脊髓损伤治疗创新中靶向的其他分子和途径。 作者在此将选择性地列举了近年来在调控小胶质细胞向M2抗炎表型极化的主要策略相关研究,见表1。 "
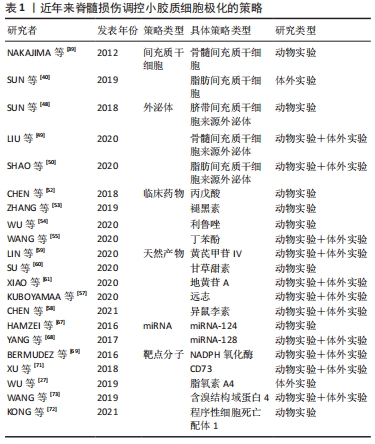
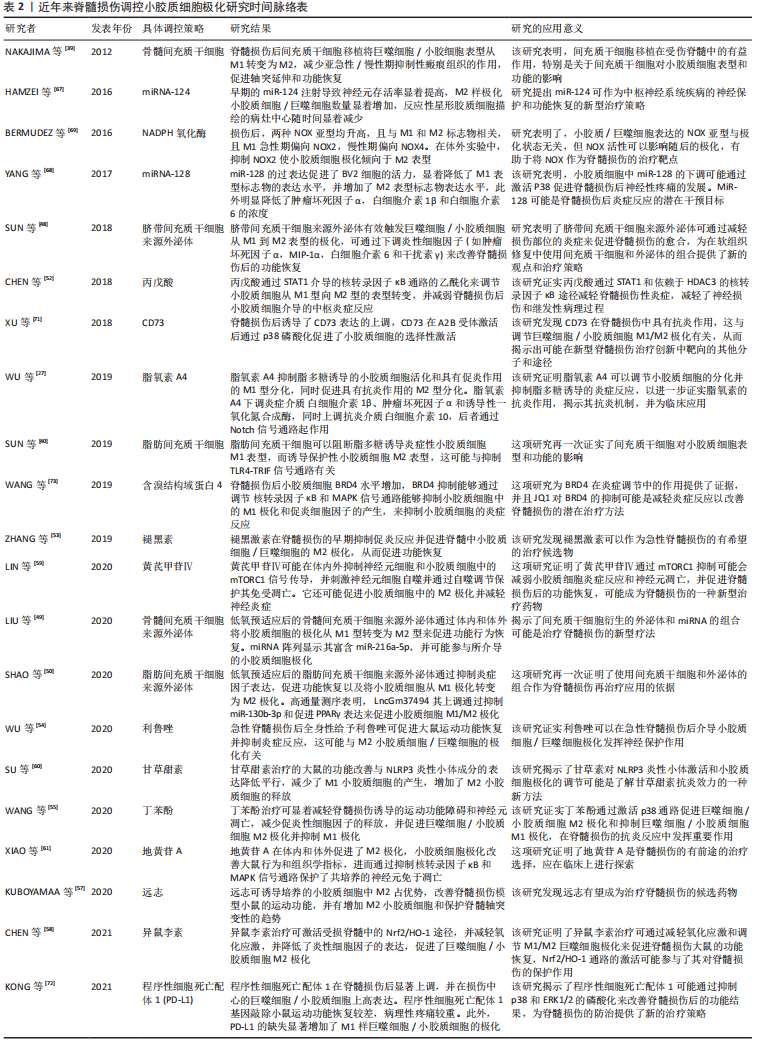
在2012年NAKAJIMA等[39]最先发现了骨髓间充质干细胞移植在受伤脊髓中的有益作用,并影响小胶质细胞表型和功能的;在2018年SUN等[48]使用脐带间充质干细胞来源外泌体有效触发巨噬细胞/小胶质细胞从M1到M2表型的极化,为脊髓损伤修复中使用间充质干细胞和外泌体的组合提供了新的观点和治疗策略;在2020年LIU等[49]验证了低氧预适应骨髓间充质干细胞外体穿梭miR-216a-5p通过移位小胶质细胞M1/M2极化修复创伤性脊髓损伤,揭示了间充质干细胞衍生的外泌体和miRNAs的组合可能是治疗脊髓损伤的新型疗法。上述3项研究也是对间充质干细胞作用机制的层层深入,并提示了组合疗法有利于更精确地调控小胶质细胞极化。作者进一步列举了近年来脊髓损伤调控小胶质细胞极化研究的具体信息,见表2。 "

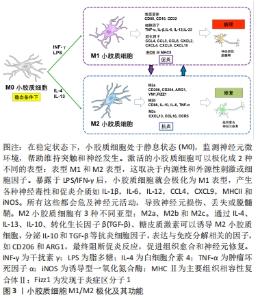
2.4 脊髓损伤后的炎症反应 脊髓损伤可以定义为外力直接或间接作用于脊髓造成的损伤。脊髓损伤包括原发性损伤和继发性损伤,导致渐进性感觉和功能损伤[2]。病变区域中心和周围组织一般发生一系列的病理生理变化,包括神经元和神经细胞死亡、血管破裂以及血脑屏障破坏。这些事件之后是一个漫长的继发性损伤阶段。根据损伤后时间的长短,继发性损伤可分为急性期、亚急性期和慢性期。继发性损伤的主要特征是出血、缺氧、神经胶质细胞活化、线粒体活性异常、外周免疫细胞浸润、星形胶质细胞增生和脱髓鞘、轴突变性以及囊肿形成等[74-75]。这些过程的级联加速了神经元的死亡,最终导致脊髓功能的丧失。 在正常生理条件下,小胶质细胞表现为M0静止型,胞质突起较长。当强烈的外部刺激或损伤,比如机械损伤或医源性损伤作用于脊髓时,会导致损伤相关的分子模式过表达,通常存在于受损部位的细胞内,发出损伤发生的信号[15,76],小胶质细胞被激活,并呈变形虫形态。这些激活的小胶质细胞表达高水平的CD45,通常与血液来源的巨噬细胞难以区分[10]。脊髓损伤后,巨噬细胞趋化蛋白1等细胞因子浓度明显上调,这些因子与细胞表面受体结合,进一步激活小胶质细胞[74,77],激活的小胶质细胞开始在损伤中心聚集和增殖,并导致一系列损伤后事件。小胶质细胞一旦被激活,就会释放炎症递质,包括细胞毒性物质如一氧化氮、氧自由基、蛋白水解酶、白细胞介素1、肿瘤坏死因子α和干扰素γ,这些炎性细胞因子表现出损害神经系统和加重组织损伤的细胞毒性[11]。中性粒细胞在损伤后6 h内开始聚集,淋巴细胞在6-12 h内开始聚集,巨噬细胞则在12-24 h内开始聚集[78]。随着血脑屏障的破坏,这些免疫细胞从循环中被招募到病变部位,遇到损伤相关的分子模式过表达的微环境,加重脊髓水肿和神经功能缺损[75,79]。在受伤的早期阶段,作为对外界刺激的反应,小胶质细胞暂时表现出一些有益的效应和自我修复尝试,最初的炎症反应可以帮助清除碎片,吞噬死亡的细胞,并分泌与再髓鞘相关的神经营养因子[80]。由于未知的原因,脊髓损伤的修复愈合和炎症不同于肌肉和皮肤等外周损伤。 在周围神经损伤中,清除病原体的促炎反应是暂时的,随着时间的推移会转变为抗炎修复反应,这涉及巨噬细胞表型转化和抗炎分子的释放[6]。然而,在损伤的脊髓中由于缺乏对抗炎和修复阶段诱导的有效调控,导致大多数巨噬细胞/小胶质细胞在持续炎症中保留促炎表型,从而限制了组织重塑、修复和功能恢复[77,79]。由小胶质细胞介导的稳定而持续的炎症反应,对脊髓损伤的预后至关重要。炎症反应过程中小胶质细胞向M2表型极化或至少向M2表型倾斜有利于抑制氧化应激反应、调节突触重塑以及促进轴突再生和血管生成,可能为脊髓损伤后神经组织的修复提供一种新的思路。 "

| [1] KUMAR R, LIM J, MEKARY RA, et al. Traumatic spinal injury: global epidemiology and worldwide volume. World Neurosurg. 2018;113: e345-e363. [2] AHUJA CS, WILSON JR, NORI S, et al. Traumatic spinal cord injury. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3:17018. [3] PRIEBE MM, CHIODO AE, SCELZA WM, et al. Spinal cord injury medicine. 6. Economic and societal issues in spinal cord injury. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2007;88(3 Suppl 1):S84-S88. [4] LONDON A, COHEN M, SCHWARTZ M. Microglia and monocyte-derived macrophages: functionally distinct populations that act in concert in CNS plasticity and repair. Front Cell Neurosci. 2013;7:34. [5] JIN X, LIU MY, ZHANG DF, et al. Natural products as a potential modulator of microglial polarization in neurodegenerative diseases. Pharmacol Res. 2019;145:104253. [6] MEDZHITOV R. Origin and physiological roles of inflammation. Nature. 2008;454(7203):428-435. [7] DAVID S, KRONER A. Repertoire of microglial and macrophage responses after spinal cord injury. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2011;12(7):388-399. [8] JURGA AM, PALECZNA M, KUTER KZ. Overview of general and discriminating markers of differential microglia phenotypes. Front Cell Neurosci. 2020;14:198. [9] KIERDORF K, ERNY D, GOLDMANN T, et al. Microglia emerge from erythromyeloid precursors via Pu.1- and Irf8-dependent pathways. Nat Neurosci. 2013;16(3):273-280. [10] XU L, HE D, BAI Y. Microglia-Mediated Inflammation and Neurodegenerative Disease. Mol Neurobiol. 2016;53(10):6709-6715. [11] GAUDET AD, FONKEN LK. Glial cells shape pathology and repair after spinal cord injury. Neurotherapeutics. 2018;15(3):554-577. [12] HAGEMEYER N, HANFT KM, AKRIDITOU MA, et al. Microglia contribute to normal myelinogenesis and to oligodendrocyte progenitor maintenance during adulthood. Acta Neuropathol. 2017;134(3):441-458. [13] YANG Z, LIU B, YANG LE, et al. Platycodigenin as potential drug candidate for alzheimer’s disease via modulating microglial polarization and neurite regeneration. Molecules. 2019. doi: 10.3390/molecules24183207. [14] MILICH LM, RYAN CB, LEE JK. The origin, fate, and contribution of macrophages to spinal cord injury pathology. Acta Neuropathol. 2019; 137(5):785-797. [15] KIGERL KA, LAI W, WALLACE LM, et al. High mobility group box-1 (HMGB1) is increased in injured mouse spinal cord and can elicit neurotoxic inflammation. Brain Behav Immun. 2018;72:22-33. [16] KIGERL KA, GENSEL JC, ANKENY DP, et al. Identification of two distinct macrophage subsets with divergent effects causing either neurotoxicity or regeneration in the injured mouse spinal cord. J Neurosci. 2009; 29(43):13435-13444. [17] ORTEGA-GóMEZ A, PERRETTI M, SOEHNLEIN O. Resolution of inflammation: an integrated view. EMBO Mol Med. 2013;5(5):661-674. [18] SHAPOURI-MOGHADDAM A, MOHAMMADIAN S, VAZINI H, et al. Macrophage plasticity, polarization, and function in health and disease. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(9):6425-6440. [19] FENN AM, HALL JC, GENSEL JC, et al. IL-4 signaling drives a unique arginase+/IL-1β+ microglia phenotype and recruits macrophages to the inflammatory CNS: consequences of age-related deficits in IL-4Rα after traumatic spinal cord injury. J Neurosci. 2014;34(26):8904-8917. [20] LITTLEFIELD A, KOHMAN RA. Differential response to intrahippocampal interleukin-4/interleukin-13 in aged and exercise mice. Neuroscience. 2017;343:106-114. [21] MARTINEZ FO, SICA A, MANTOVANI A, et al. Macrophage activation and polarization. Front Biosci. 2008;13:453-461. [22] ORIHUELA R, MCPHERSON CA, HARRY GJ. Microglial M1/M2 polarization and metabolic states. Br J Pharmacol. 2016;173(4):649-665. [23] EHRCHEN J, STEINMüLLER L, BARCZYK K, et al. Glucocorticoids induce differentiation of a specifically activated, anti-inflammatory subtype of human monocytes. Blood. 2007;109(3):1265-1274. [24] LI XH, FU NS, XING ZM. MiR-100 suppresses inflammatory activation of microglia and neuronal apoptosis following spinal cord injury via TLR4/NF-κB pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(20):8713-8720. [25] FATIMA G, SHARMA VP, DAS SK, et al. Oxidative stress and antioxidative parameters in patients with spinal cord injury: implications in the pathogenesis of disease. Spinal Cord. 2015;53(1):3-6. [26] SONG C, HEPING H, SHEN Y, et al. AMPK/p38/Nrf2 activation as a protective feedback to restrain oxidative stress and inflammation in microglia stimulated with sodium fluoride. Chemosphere. 2020; 244:125495. [27] WU J, DING DH, LI QQ, et al. Lipoxin A4 regulates lipopolysaccharide-induced bv2 microglial activation and differentiation via the notch signaling pathway. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019;13:19. [28] VEZZANI A and VIVIANI B. Neuromodulatory properties of inflammatory cytokines and their impact on neuronal excitability. Neuropharmacology. 2015;96(Pt A):70-82. [29] KITAYAMA M, UENO M, ITAKURA T, et al. Activated microglia inhibit axonal growth through RGMa. PLoS One. 2011;6(9):e25234. [30] LIDDELOW SA, GUTTENPLAN KA, CLARKE LE, et al. Neurotoxic reactive astrocytes are induced by activated microglia. Nature. 2017; 541(7638):481-487. [31] ANDERSON MA, BURDA JE, REN Y, et al. Astrocyte scar formation aids central nervous system axon regeneration. Nature. 2016;532(7598): 195-200. [32] WEINHARD L, DI BARTOLOMEI G, BOLASCO G, et al. Microglia remodel synapses by presynaptic trogocytosis and spine head filopodia induction. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):1228. [33] PAOLICELLI RC, BOLASCO G, PAGANI F, et al. Synaptic pruning by microglia is necessary for normal brain development. Science. 2011; 333(6048):1456-1458. [34] ROMERO-SANCHIZ P, NOGUEIRA-ARJONA R, ARAOS P, et al. Variation in chemokines plasma concentrations in primary care depressed patients associated with Internet-based cognitive-behavioral therapy. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):1078. [35] OUDEGA M. Molecular and cellular mechanisms underlying the role of blood vessels in spinal cord injury and repair. Cell Tissue Res. 2012;349(1):269-288. [36] JIN S, YANG C, HUANG J, et al. Conditioned medium derived from FGF-2-modified GMSCs enhances migration and angiogenesis of human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):68. [37] MUNIR H, WARD LSC, MCGETTRICK HM. Mesenchymal stem cells as endogenous regulators of inflammation. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1060: 73-98. [38] IN’T ANKER PS, SCHERJON SA, KLEIJBURG-VAN DER KEUR C, et al. Isolation of mesenchymal stem cells of fetal or maternal origin from human placenta. Stem Cells. 2004;22(7):1338-1345. [39] NAKAJIMA H, UCHIDA K, GUERRERO AR, et al. Transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells promotes an alternative pathway of macrophage activation and functional recovery after spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma. 2012;29(8):1614-1625. [40] SUN J, LIU YL, LI C, et al. Effect of human adipose mesenchymal stem cells on phenotype polarization of mice microglia via TLR3/TRIF signal pathway. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2019;50(2):164-170. [41] CHO DI, KIM MR, JEONG HY, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells reciprocally regulate the M1/M2 balance in mouse bone marrow-derived macrophages. Exp Mol Med. 2014;46(1):e70. [42] DE BECKER A and RIET IV. Homing and migration of mesenchymal stromal cells: How to improve the efficacy of cell therapy? World J Stem Cells. 2016;8(3):73-87. [43] RODRIGUEZ R, RUBIO R, MENENDEZ P. Modeling sarcomagenesis using multipotent mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Res. 2012;22(1):62-77. [44] ORTEGA FG, ROEFS MT, DE MIGUEL PEREZ D, et al. Interfering with endolysosomal trafficking enhances release of bioactive exosomes. Nanomedicine. 2019;20:102014. [45] MATHIVANAN S, JI H, SIMPSON RJ. Exosomes: extracellular organelles important in intercellular communication. J Proteomics. 2010;73(10): 1907-1920. [46] FARAHANI M, RUBBI C, LIU L, et al. CLL exosomes modulate the transcriptome and behaviour of recipient stromal cells and are selectively enriched in miR-202-3p. PLoS One. 2015;10(10):e0141429. [47] GALLART-PALAU X, SERRA A, SZE SK. Enrichment of extracellular vesicles from tissues of the central nervous system by PROSPR. Mol Neurodegener. 2016;11(1):41. [48] SUN G, LI G, LI D, et al. hucMSC derived exosomes promote functional recovery in spinal cord injury mice via attenuating inflammation. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2018;89:194-204. [49] LIU W, RONG Y, WANG J, et al. Exosome-shuttled miR-216a-5p from hypoxic preconditioned mesenchymal stem cells repair traumatic spinal cord injury by shifting microglial M1/M2 polarization. J Neuroinflammation. 2020;17(1):47. [50] SHAO M, JIN M, XU S, et al. Exosomes from long noncoding RNA-Gm37494-ADSCs repair spinal cord injury via shifting microglial M1/M2 polarization. Inflammation. 2020;43(4):1536-1547. [51] CERQUEIRA SR, OLIVEIRA JM, SILVA NA, et al. Microglia response and in vivo therapeutic potential of methylprednisolone-loaded dendrimer nanoparticles in spinal cord injury. Small. 2013;9(5):738-749. [52] CHEN S, YE J, CHEN X, et al. Valproic acid attenuates traumatic spinal cord injury-induced inflammation via STAT1 and NF-κB pathway dependent of HDAC3. J Neuroinflammation. 2018;15(1):150. [53] ZHANG Y, LIU Z, ZHANG W, et al. Melatonin improves functional recovery in female rats after acute spinal cord injury by modulating polarization of spinal microglial/macrophages. J Neurosci Res. 2019; 97(7):733-743. [54] WU Q, ZHANG Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Riluzole improves functional recovery after acute spinal cord injury in rats and may be associated with changes in spinal microglia/macrophages polarization. Neurosci Lett. 2020;723:134829. [55] WANG L, WU JP, HE XJ. Butylphthalide has an anti-inflammatory role in spinal cord injury by promoting macrophage/microglia M2 polarization via p38 phosphorylation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2020;45(17): E1066-E1076. [56] HENKEL T, BRUNNE RM, MüLLER H, et al. Statistical investigation into the structural complementarity of natural products and synthetic compounds. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 1999;38(5):643-647. [57] KUBOYAMA T, KOMINATO S, NAGUMO M, et al. Recovery from spinal cord injury via M2 microglial polarization induced by Polygalae Radix. Phytomedicine. 2021;82:153452. [58] CHEN F, HU M, SHEN Y, et al. Isorhamnetin promotes functional recovery in rats with spinal cord injury by abating oxidative stress and modulating M2 macrophages/microglia polarization. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021;895:173878. [59] LIN J, PAN X, HUANG C, et al. Dual regulation of microglia and neurons by Astragaloside IV-mediated mTORC1 suppression promotes functional recovery after acute spinal cord injury. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(1):671-685. [60] SU XQ, WANG XY, GONG FT, et al. Oral treatment with glycyrrhizin inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation and promotes microglial M2 polarization after traumatic spinal cord injury. Brain Res Bull. 2020; 158:1-8. [61] XIAO S, WANG C, YANG Q, et al. Rea regulates microglial polarization and attenuates neuronal apoptosis via inhibition of the NF-κB and MAPK signalings for spinal cord injury repair. J Cell Mol Med. 2021; 25(3):1371-1382. [62] SUBRAMANIAM S, JEET V, CLEMENTS JA, et al. Emergence of microRNAs as key players in cancer cell metabolism. Clin Chem. 2019; 65(9):1090-1101. [63] ENGELS BM, HUTVAGNER G. Principles and effects of microRNA-mediated post-transcriptional gene regulation. Oncogene. 2006;25(46): 6163-6169. [64] PARK JH, SHIN C. MicroRNA-directed cleavage of targets: mechanism and experimental approaches. BMB Rep. 2014;47(8):417-423. [65] CHEN Y, SUN JX, CHEN WK, et al. miR-124/VAMP3 is a novel therapeutic target for mitigation of surgical trauma-induced microglial activation. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2019;4:27. [66] GUO Y, HONG W, WANG X, et al. MicroRNAs in microglia: how do MicroRNAs affect activation, inflammation, polarization of microglia and mediate the interaction between microglia and glioma? Front Mol Neurosci. 2019;12:125. [67] HAMZEI TAJ S, KHO W, RIOU A, et al. MiRNA-124 induces neuroprotection and functional improvement after focal cerebral ischemia. Biomaterials. 2016;91:151-165. [68] YANG Z, XU J, ZHU R, et al. Down-regulation of miRNA-128 contributes to neuropathic pain following spinal cord injury via activation of p38. Med Sci Monit. 2017;23:405-411. [69] BERMUDEZ S, KHAYRULLINA G, ZHAO Y, et al. NADPH oxidase isoform expression is temporally regulated and may contribute to microglial/macrophage polarization after spinal cord injury. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2016;77:53-64. [70] ANTONIOLI L, PACHER P, VIZI ES, et al. CD39 and CD73 in immunity and inflammation. Trends Mol Med. 2013;19(6):355-367. [71] XU S, ZHU W, SHAO M, et al. Ecto-5’-nucleotidase (CD73) attenuates inflammation after spinal cord injury by promoting macrophages/microglia M2 polarization in mice. J Neuroinflammation. 2018; 15(1):155. [72] KONG F, SUN K, ZHU J, et al. PD-L1 improves motor function and alleviates neuropathic pain in male mice after spinal cord injury by inhibiting MAPK pathway. Front Immunol. 2021;12:670646. [73] WANG J, CHEN J, JIN H, et al. BRD4 inhibition attenuates inflammatory response in microglia and facilitates recovery after spinal cord injury in rats. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23(5):3214-3223. [74] KWON BK, TETZLAFF W, GRAUER JN, et al. Pathophysiology and pharmacologic treatment of acute spinal cord injury. Spine J. 2004;4(4): 451-464. [75] AMBROZAITIS KV, KONTAUTAS E, SPAKAUSKAS B, et al. Pathophysiology of acute spinal cord injury. Medicina (Kaunas). 2006;42(3):255-261. [76] ZHANG X, MOSSER DM. Macrophage activation by endogenous danger signals. J Pathol. 2008;214(2):161-178. [77] GENSEL JC, ZHANG B. Macrophage activation and its role in repair and pathology after spinal cord injury. Brain Res. 2015;1619:1-11. [78] HAGGERTY AE, MALDONADO-LASUNCIóN I, OUDEGA M. Biomaterials for revascularization and immunomodulation after spinal cord injury. Biomed Mater. 2018;13(4):044105. [79] MALDONADO-LASUNCIóN I, VERHAAGEN J, OUDEGA M. Mesenchymal stem cell-macrophage choreography supporting spinal cord repair. Neurotherapeutics. 2018;15(3):578-587. [80] SHECHTER R, SCHWARTZ M. CNS sterile injury: just another wound healing? Trends Mol Med. 2013;19(3):135-143. |
| [1] | Fang Xingyan, Tian Zhenli, Zhao Zheyi, Wen Ping, Xie Tingting. Effects of sodium arsenite on human umbilical vein endothelial cell injury and sphingosine kinases 1/sphingosine 1-phosphate signaling axis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-7. |
| [2] | Zhou Jie, Pei Xibo, Wan Qianbing. Advances and biological application of asymmetric dressings [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 434-440. |
| [3] | Chen Jingqiao, Li Ying, Meng Maohua, Xu Xingxing, Wang Qinying, Wang Huan, Lu Jing, Shu Jiayu, Dong Qiang. Research progress in platelet-rich fibrin in stomatology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 441-446. |
| [4] | Han Tao, Hao Jianqiang, Li Wenbo, Shi Jie, Gao Qiuming. Advantages and problems of antibiotic-loaded bone cements for bone and joint infections [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 470-477. |
| [5] | Zhang Lichen, Chen Liang, Gu Yong. Inorganic ion bionic periosteum regulates immune microenvironment to promote bone repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 346-353. |
| [6] | Dai Xianglin, Zhang Wenfeng, Yao Xijun, Shang Jiaqi, Huang Qiujin, Ren Yifan, Deng Jiupeng. Barium titanate/polylactic acid piezoelectric composite film affects adhesion, proliferation, and osteogenic differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 367-373. |
| [7] | Zhang Yujuan, Yuan Yitong, Du Ruochen, Tian Feng, Fu Yuan, Wang Chunfang. miR-31 promotes the proliferation and migration of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 66-71. |
| [8] | Liu Runyuan, Dong Ming, Han Wenqing, Dong Juhong, Niu Weidong. Application and progress of small extracellular vesicles in periodontal and pulp regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 83-90. |
| [9] | Xi Hualei, Xue Bing, Xu Wanqiu, Xu Xiaohang, Yao Lihong, Wang Xiumei. Neural differentiation and neural biomarker expression of dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 91-98. |
| [10] | Liu Zhuoran, Jiang Ming, Li Yourui. Extracellular vesicles in chronic periodontitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 99-104. |
| [11] | Zhu Zhenghuan, Zou Hongjun, Song Zhiwen, Liu Jinbo. Cellular microenvironment in nerve repair after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 114-120. |
| [12] | Guo Yujun, Lu Wenjun, Yang Shulong, Li Zhaozhu. Effect of urine-derived stem cells and their exosomes on kidney diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 138-144. |
| [13] | LIU Danni, SUN Guanghua, ZHOU Guijuan, LIU Hongya, ZHOU Jun, TAN Jinqu, HUANG Xiarong, PENG Ting, FENG Wei-bin, LUO Fu. Effect of electroacupuncture on apoptosis of neurons in cerebral cortex of rats with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury at "Shuigou" and "Baihui" points [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(在线): 1-6. |
| [14] | Zhu Chan, Han Xuke, Yao Chengjiao, Zhou Qian, Zhang Qiang, Chen Qiu. Human salivary components and osteoporosis/osteopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1439-1444. |
| [15] | Jin Tao, Liu Lin, Zhu Xiaoyan, Shi Yucong, Niu Jianxiong, Zhang Tongtong, Wu Shujin, Yang Qingshan. Osteoarthritis and mitochondrial abnormalities [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1452-1458. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||