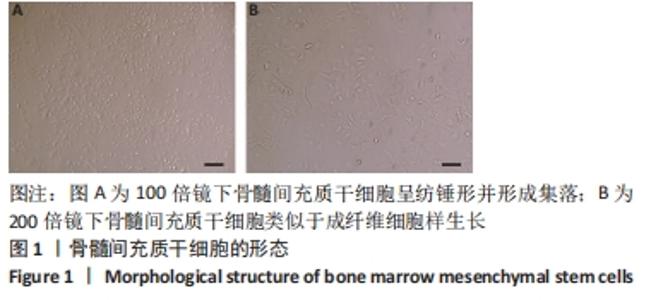
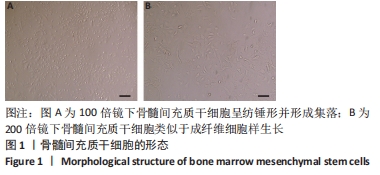
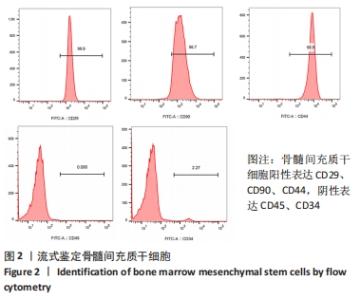
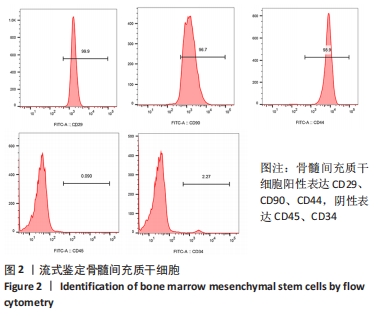
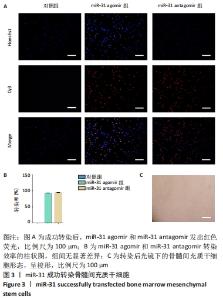
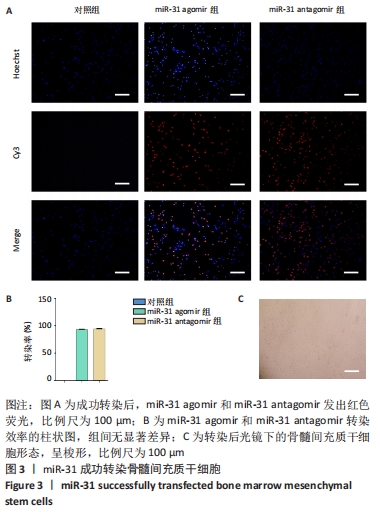
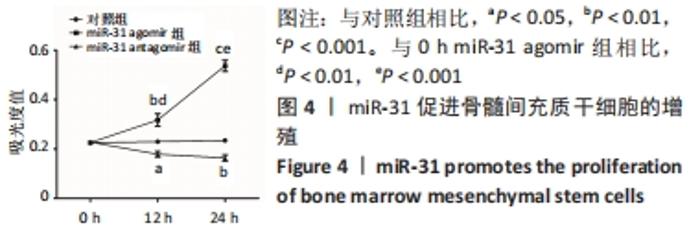
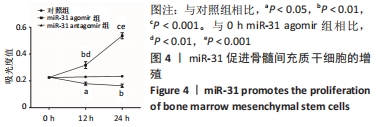
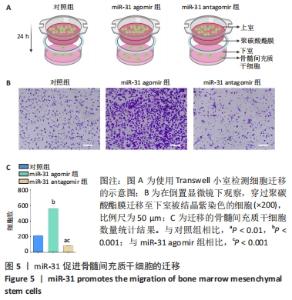
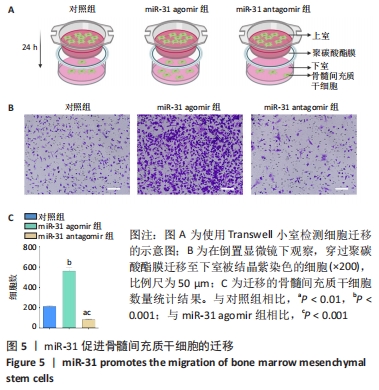
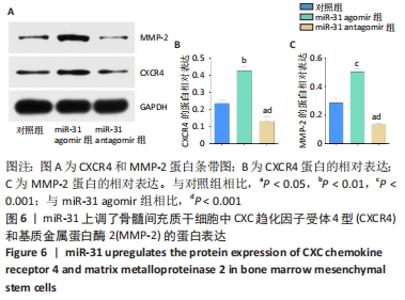
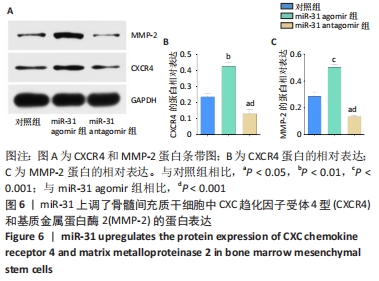
[1] LIU H, LI R, LIU T, et al. Immunomodulatory Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front Immunol. 2020;11:1912.
[2] KARL T, GARNER B, CHENG D. The therapeutic potential of the phytocannabinoid cannabidiol for Alzheimer’s disease. Behav Pharmacol. 2017;28(2 and 3-Spec Issue):142-160.
[3] LI H, WANG C, HE T, et al. Mitochondrial Transfer from Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells to Motor Neurons in Spinal Cord Injury Rats via Gap Junction. Theranostics. 2019;9(7):2017-2035.
[4] RA JC, SHIN IS, KIM SH, et al. Safety of intravenous infusion of human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells in animals and humans. Stem Cells Dev. 2011;20(8):1297-1308.
[5] JACKSON JS, GOLDING JP, CHAPON C, et al. Homing of stem cells to sites of inflammatory brain injury after intracerebral and intravenous administration: a longitudinal imaging study. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2010; 1(2):17.
[6] AHUJA CS, NORI S, TETREAULT L, et al. Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury-Repair and Regeneration. Neurosurgery. 2017;80(3S):S9-S22.
[7] ZHAO T, ZHANG ZN, RONG Z, et al. Immunogenicity of induced pluripotent stem cells. Nature. 2011;474(7350):212-215.
[8] CHAVAKIS E, DIMMELER S. Homing of progenitor cells to ischemic tissues. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011;15(4):967-980.
[9] BARTEL DP. Metazoan MicroRNAs. Cell. 2018;173(1):20-51.
[10] LU Z, HE Q, LIANG J, et al. miR-31-5p Is a Potential Circulating Biomarker and Therapeutic Target for Oral Cancer. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2019;16:471-480.
[11] BURKERT J, WRIGHT NA, ALISON MR. Stem cells and cancer: an intimate relationship. J Pathol. 2006;209(3):287-297.
[12] 王菲,原一桐,高渊涛,等.tdTomato转基因小鼠的建系及其在细胞示踪方面的应用研究[J].中国实验动物学报,2020,28(1):1-9.
[13] 赵碧春,原一桐,杜若琛,等.神经干细胞联合骨髓间充质干细胞移植对小鼠脊髓损伤的修复作用[J]. 神经解剖学杂志,2021,37(2): 168-174.
[14] COURTINE G, SOFRONIEW MV. Spinal cord repair: advances in biology and technology. Nat Med. 2019;25(6):898-908.
[15] QUADRI SA, FAROOQUI M, IKRAM A, et al. Recent update on basic mechanisms of spinal cord injury. Neurosurg Rev. 2020;43(2):425-441.
[16] GAZDIC M, VOLAREVIC V, HARRELL CR, et al. Stem Cells Therapy for Spinal Cord Injury. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(4):1039.
[17] WU LL, PAN XM, CHEN HH, et al. Repairing and Analgesic Effects of Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell Transplantation in Mice with Spinal Cord Injury. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:7650354.
[18] WANG Y, SUN X, LV J, et al. Stromal Cell-Derived Factor-1 Accelerates Cartilage Defect Repairing by Recruiting Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Promoting Chondrogenic Differentiation. Tissue Eng Part A. 2017;23(19-20):1160-1168.
[19] MENG Z, FENG G, HU X, et al. SDF Factor-1α Promotes the Migration, Proliferation, and Osteogenic Differentiation of Mouse Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Through the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway. Stem Cells Dev. 2021;30(2):106-117.
[20] LU TX, ROTHENBERG ME. MicroRNA. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018; 141(4):1202-1207.
[21] DONG H, LEI J, DING L, et al. MicroRNA: function, detection, and bioanalysis. Chem Rev. 2013;113(8):6207-6233.
[22] LEE RC, FEINBAUM RL, AMBROS V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 1993;75(5):843-854.
[23] CHANG W, WANG J, TAO D, et al. Identification of a novel miRNA from the ovine ovary by a combinatorial approach of bioinformatics and experiments. J Vet Med Sci. 2016;77(12):1617-1624.
[24] MARTÍNEZ G, FORMENT J, LLAVE C, et al. High-throughput sequencing, characterization and detection of new and conserved cucumber miRNAs. PLoS One. 2011;6(5):e19523.
[25] HARA ES, ONO M, EGUCHI T, et al. miRNA-720 controls stem cell phenotype, proliferation and differentiation of human dental pulp cells. PLoS One. 2013;8(12):e83545.
[26] GAY I, CAVENDER A, PETO D, et al. Differentiation of human dental stem cells reveals a role for microRNA-218. J Periodontal Res. 2014; 49(1):110-120.
[27] D’SOUZA W, KUMAR A. microRNAs in oral cancer: Moving from bench to bed as next generation medicine. Oral Oncol. 2020;111:104916.
[28] NAJI A, EITOKU M, FAVIER B, et al. Biological functions of mesenchymal stem cells and clinical implications. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019;76(17):3323-3348.
[29] KANG SK, SHIN IS, KO MS,et al. Journey of mesenchymal stem cells for homing: strategies to enhance efficacy and safety of stem cell therapy. Stem Cells Int. 2012;2012:342968.
[30] RODERFELD M. Matrix metalloproteinase functions in hepatic injury and fibrosis. Matrix Biol. 2018;68-69:452-462.
[31] STAMATOPOULOS A, STAMATOPOULOS T, GAMIE Z, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells for bone sarcoma treatment: Roadmap to clinical practice. J Bone Oncol. 2019;16:100231.
[32] MOREIN D, ERLICHMAN N, BEN-BARUCH A. Beyond Cell Motility: The Expanding Roles of Chemokines and Their Receptors in Malignancy. Front Immunol. 2020;11:952.
[33] LIM K, HYUN YM, LAMBERT-EMO K, et al. Neutrophil trails guide influenza-specific CD8⁺ T cells in the airways. Science. 2015;349(6252): aaa4352.
[34] YANG W, MA B. A Mini-Review: The Therapeutic Potential of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Relevant Signaling Cascades. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;14(3):214-218.
[35] MA C, WANG J, FAN L. Therapeutic effects of bone mesenchymal stem cells on oral and maxillofacial defects: a novel signaling pathway involving miR-31/CXCR4/Akt axis. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2019; 39(4):321-330.
[36] LV C, YANG S, CHEN X, et al. MicroRNA-21 promotes bone mesenchymal stem cells migration in vitro by activating PI3K/Akt/MMPs pathway. J Clin Neurosci. 2017;46:156-162.
[37] 李鹏飞. miR-31在脊髓源神经干细胞及向运动神经元样细胞分化中功能和机制的研究[D].太原:山西医科大学,2021.
[38] LI X, GAO Y, TIAN F, et al. miR-31 promotes neural stem cell proliferation and restores motor function after spinal cord injury. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2021;246(11):1274-1286.
|