Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (1): 76-82.doi: 10.12307/2022.981
Previous Articles Next Articles
Safety and efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of ischemic stroke: a meta-analysis
Hu Fei1, Wang Jie2
- 1Graduate School of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China; 2The First Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China
-
Received:2021-11-20Accepted:2021-12-31Online:2023-01-08Published:2022-06-14 -
Contact:Wang Jie, MD, Chief physician, The First Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China -
About author:Hu Fei, Master, Graduate School of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Hu Fei, Wang Jie. Safety and efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of ischemic stroke: a meta-analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 76-82.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

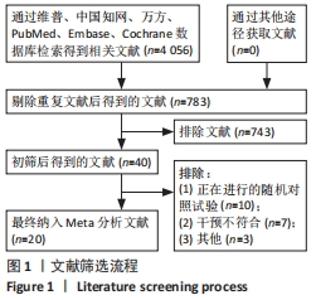
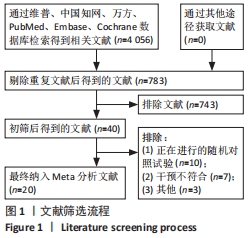
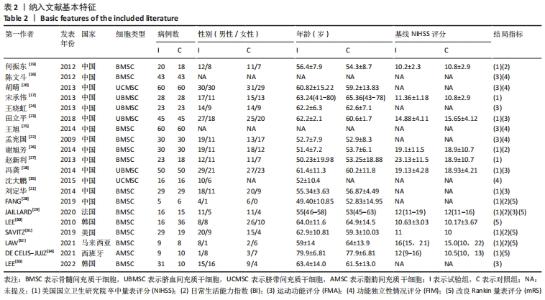
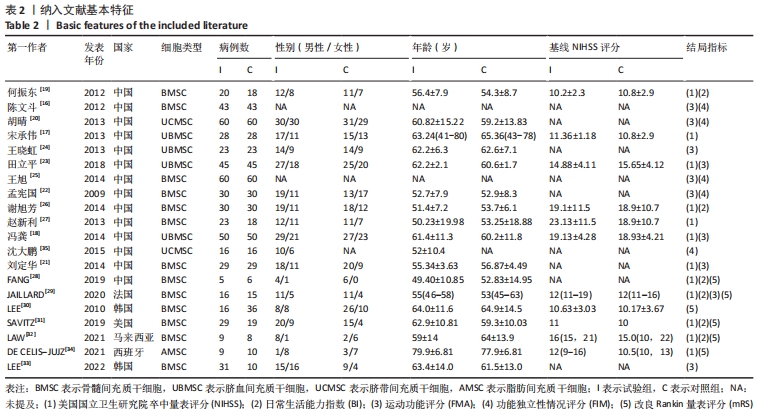
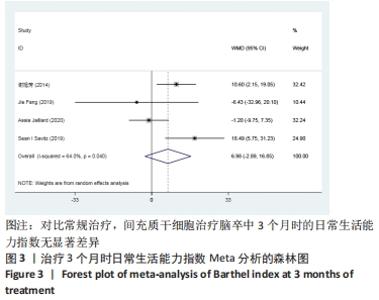
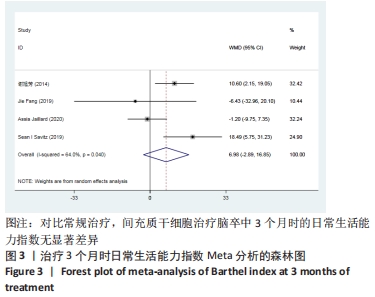
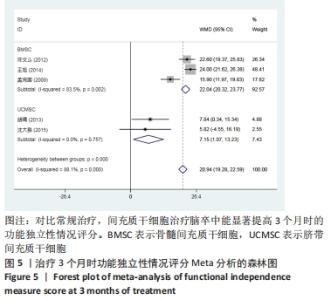
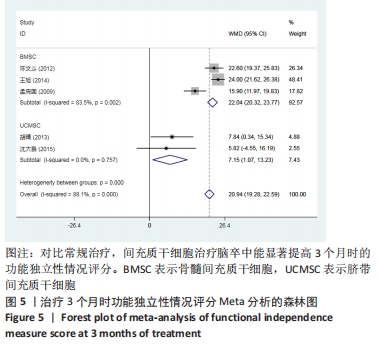
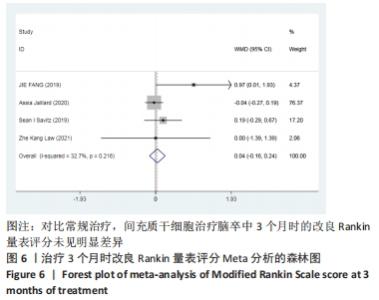
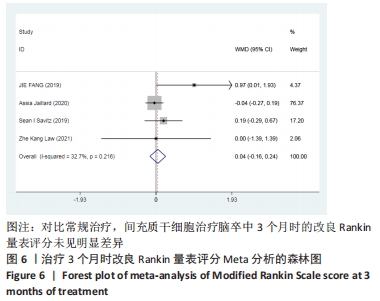
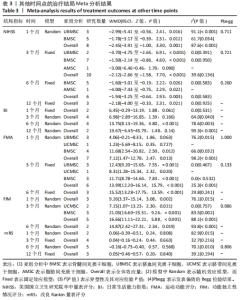
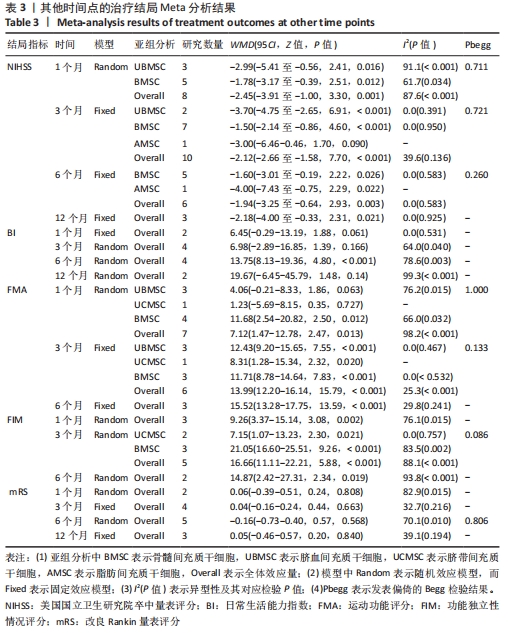
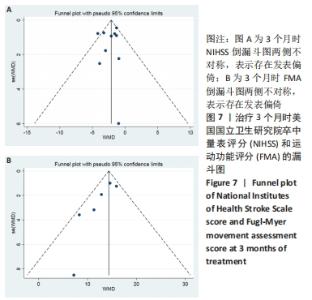
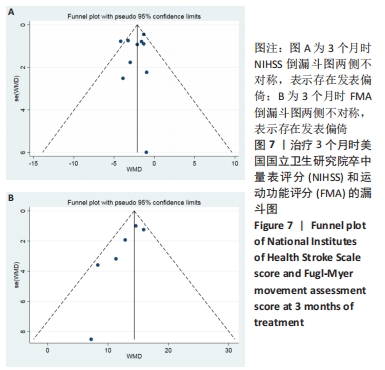
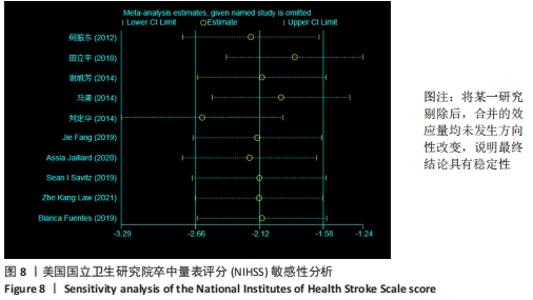
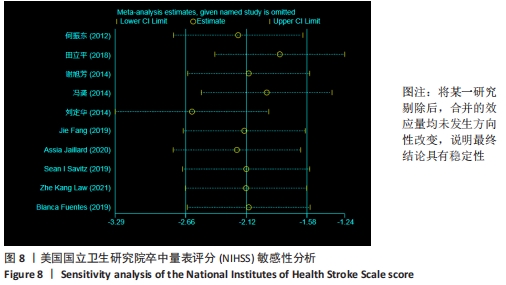
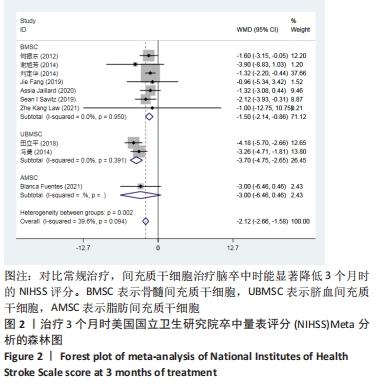
2.3 纳入研究的偏倚风险 所纳入文献均为随机对照试验,然而1篇文献随机方法不合理[17],2篇文献为开放标签[29,32],在分配隐藏、受试者和干预者施盲、结局评价者施盲方面。总的来说,纳入文献的质量令人满意。 2.4 Meta分析结果 2.4.1 美国国立卫生研究院卒中量表评分(NIHSS)的Meta分析 总共有10篇文献报告了治疗前和治疗3个月后患者神经功能缺损的NIHSS量表评分[18-19, 21,23,26,28-29,31-32,34],质性检验(I2=39.6%,P=0.094),认为两者具有同质性,故采用固定效应模型的Meta分析。合并效应量WMD=-2.12(95%CI:-2.66至-1.58,Z=7.70,P < 0.001),表明对比常规治疗,间充质干细胞治疗脑卒中时能显著降低3个月时的美国国立卫生研究院卒中量表评分,见图2。"
| [1] WANG W, JIANG B, SUN H, et al. Prevalence, Incidence, and Mortality of Stroke in China: Results from a Nationwide Population-Based Survey of 480 687 Adults. Circulation. 2017;135(8):759-771. [2] STURM JW, DEWEY HM, DONNAN GA, et al. Handicap after stroke: how does it relate to disability, perception of recovery, and stroke subtype?: the north North East Melbourne Stroke Incidence Study (NEMESIS). Stroke. 2002;33(3):762-768. [3] LIU JC, HUANG HY, HSU YT. Hyperthyroidism and thrombophilia in cerebral arterial and venous thrombosis: a case report and critical review. Neurologist. 2015;19(2):53-55. [4] CHAVALI S, SHUKLA U, CHAUTA S. Traumatic subclavian arterial thrombosis presenting with cerebral infarct--a case report. Heart Lung Circ. 2014;23(10):e202-e206. [5] OU C, HUANG W, YUEN MM. A computational model based on fibrin accumulation for the prediction of stasis thrombosis following flow-diverting treatment in cerebral aneurysms. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2017;55(1):89-99. [6] LI T, XIA M, GAO Y, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells: an overview of their potential in cell-based therapy. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2015;15(9):1293-1306. [7] MISHRA PJ, BANERJEE D. Activation and Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1554:201-209. [8] CHANG F, XIONG W, WANG D, et al. Facilitation of ultrasonic microvesicles on homing and molecular mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in cerebral infarction patients. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017;21(17):3916-3923. [9] DING DC, CHANG YH, SHYU WC, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells: a new era for stem cell therapy. Cell Transplant. 2015;24(3):339-347. [10] ANKRUM JA, ONG JF, KARP JM. Mesenchymal stem cells: immune evasive, not immune privileged. Nat Biotechnol. 2014;32(3):252-260. [11] UCCELLI A, MORETTA L, PISTOIA V. Mesenchymal stem cells in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8(9):726-736. [12] PORADA CD, Almeida-Porada G. Mesenchymal stem cells as therapeutics and vehicles for gene and drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2010;62(12):1156-1166. [13] SCUTERI A, MILOSO M, FOUDAH D, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells neuronal differentiation ability: a real perspective for nervous system repair? Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2011;6(2):82-92. [14] WANG X, KIMBREL EA, IJICHI K, et al. Human ESC-derived MSCs outperform bone marrow MSCs in the treatment of an EAE model of multiple sclerosis. Stem Cell Reports. 2014; 3(1):115-130. [15] HATANO S. Experience from a multicentre stroke register: a preliminary report. Bull World Health Organ. 1976;54(5):541-553. [16] 陈文斗,李江涛,张效北,等.骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗脑梗死临床分析[J].吉林医学,2012,33(21):4522. [17] 宋承伟,汪萍,胡晓琴,等.脐带血间充质干细胞移植治疗脑梗死的临床疗效观察[J].临床合理用药杂志,2013,6(5): 69-70. [18] 冯龚,田国萍,李莉,等.人脐带血间充质干细胞治疗脑梗死的临床疗效研究[J].实用心脑肺血管病杂志,2014,22(1): 28-30. [19] 何振东.骨髓间充质干细胞移植改善脑梗死患者神经功能机制研究[J].亚太传统医药,2012,8(12):126-127. [20] 胡晴,曹梦莹,李瑞芳,等. 脐带间充质干细胞治疗脑梗死的安全性与有效性[J].武汉大学学报(医学版),2013,34(1): 55-60,70. [21] 刘定华,韩伯军,洪珊珊,等.自体骨髓间充质神经干细胞移植治疗脑梗死的疗效观察[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志, 2014,36(6):425-428. [22] 孟宪国,朱士文,高华,等.自体骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗脑梗死:6个月随访[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2009,13(32):6374-6378. [23] 田立平,王晶晶,赵凯龙.人脐带血间充质干细胞治疗脑梗死的临床效果观察[J].临床合理用药杂志,2018,11(26): 109-110. [24] 王晓虹,王苏平,徐广鑫,等.脐带血有核细胞治疗脑梗死后遗症近期疗效观察[J].转化医学杂志,2013,2(6):332-335. [25] 王旭,张志彬,贾芙蓉,等. 自体骨髓间充质干细胞介入移植治疗脑梗死临床研究[J].吉林医学,2014,35(2):237-239. [26] 谢旭芳,刘诗英,金光华,等.自体骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗脑梗死的临床分析[J].检验医学与临床,2014,11(21): 2955-2957. [27] 赵新利,王艳,张彩霞,等.骨髓间充质干细胞治疗在脑卒中的研究[J].环球中医药,2013(S2):157. [28] FANG J, GUO Y, TAN S, et al. Autologous Endothelial Progenitor Cells Transplantation for Acute Ischemic Stroke: A 4-Year Follow-Up Study. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2019;8(1):14-21. [29] JAILLARD A, HOMMEL M, MOISAN A, et al. Autologous Mesenchymal Stem Cells Improve Motor Recovery in Subacute Ischemic Stroke: a Randomized Clinical Trial. Transl Stroke Res. 2020;11(5):910-923. [30] LEE JS, HONG JM, MOON GJ, et al. A long-term follow-up study of intravenous autologous mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in patients with ischemic stroke. Stem Cells. 2010;28(6):1099-1106. [31] SAVITZ SI, YAVAGAL D, RAPPARD G, et al. A Phase 2 Randomized, Sham-Controlled Trial of Internal Carotid Artery Infusion of Autologous Bone Marrow-Derived ALD-401 Cells in Patients With Recent Stable Ischemic Stroke (RECOVER-Stroke). Circulation. 2019;139(2):192-205. [32] LAW ZK, TAN HJ, CHIN SP, et al. The effects of intravenous infusion of autologous mesenchymal stromal cells in patients with subacute middle cerebral artery infarct: a phase 2 randomized controlled trial on safety, tolerability and efficacy. Cytotherapy. 2021;23(9):833-840. [33] LEE J, CHANG WH, CHUNG JW, et al. Efficacy of Intravenous Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Motor Recovery After Ischemic Stroke: A Neuroimaging Study. Stroke. 2022;53(1):20-28. [34] DE CELIS-RUIZ E, FUENTES B, MONICHE F, et al. Allogeneic adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells in ischaemic stroke (AMASCIS-02): a phase IIb, multicentre, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial protocol. BMJ Open. 2021;11(8):e051790. [35] 沈大鹏.脐带间充质干细胞早期单次移植治疗对急性脑梗死的神经功能恢复[J]. 中国伤残医学,2015,23(2):26-28. [36] CAPLAN AI. Mesenchymal stem cells. J Orthop Res. 1991;9(5):641-650. [37] JIAO Y, LIU YW, CHEN WG, et al. Neuroregeneration and functional recovery after stroke: advancing neural stem cell therapy toward clinical application. Neural Regen Res. 2021;16(1):80-92. [38] BANG OY, LEE JS, LEE PH, et al. Autologous mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in stroke patients. Ann Neurol. 2005; 57(6):874-882. [39] JIANG Y, ZHU W, ZHU J, et al. Feasibility of delivering mesenchymal stem cells via catheter to the proximal end of the lesion artery in patients with stroke in the territory of the middle cerebral artery. Cell Transplant. 2013;22(12):2291-2298. [40] BEKER M, CAGLAYAN AB, BEKER MC, et al. Lentivirally administered glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor promotes post-ischemic neurological recovery, brain remodeling and contralesional pyramidal tract plasticity by regulating axonal growth inhibitors and guidance proteins. Exp Neurol. 2020;331:113364. [41] SHIOTA Y, NAGAI A, SHEIKH AM, et al. Transplantation of a bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell line increases neuronal progenitor cell migration in a cerebral ischemia animal model. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):14951. [42] FORBES LH, ANDREWS MR. Advances in human stem cell therapies: pre-clinical studies and the outlook for central nervous system regeneration. Neural Regen Res. 2021;16(4):614-617. [43] LIU J, CHUAH YJ, FU J, et al. Co-culture of human umbilical vein endothelial cells and human bone marrow stromal cells into a micro-cavitary gelatin-methacrylate hydrogel system to enhance angiogenesis. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019; 102:906-916. |
| [1] | Li Rui, Liu Zhen, Guo Zige, Lu Ruijie, Wang Chen. Aspirin-loaded chitosan nanoparticles and polydopamine modified titanium sheets improve osteogenic differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 374-379. |
| [2] | Ning Ziwen, Wang Xu, Shi Zhengliang, Qin Yihua, Wang Guoliang, Jia Di, Wang Yang, Li Yanlin. Meniscal injury repair methods for non-blood supply area [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 420-426. |
| [3] | Ma Munan, Xie Jun, Sang Yuchao, Huang Lei, Zhang Guodong, Yang Xiaoli, Fu Songtao. Electroacupuncture combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of chemotherapy-induced premature ovarian insufficiency in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 1-7. |
| [4] | Zhang Yujuan, Yuan Yitong, Du Ruochen, Tian Feng, Fu Yuan, Wang Chunfang. miR-31 promotes the proliferation and migration of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 66-71. |
| [5] | Liu Siqi, Wu Mingrui, Qiao Lingran, Xie Liying, Chen Siyu, Han Zhibo, Zuo Lin. Effects of hydrogel loaded with human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on diabetic wound repair in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 21-27. |
| [6] | Fu Chunmei, Zhang Pu, Wang Yang, Li Xiaolin, Xue Yan, Fu Jie, Zhang Cixian, Yang Yujuan, Duan Yaya, Feng Kai. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in the treatment of 24 patients with severe aplastic anemia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 15-20. |
| [7] | Feng Hao, Zhang Bin, Wang Jianping. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation can improve bone metabolism in osteoporotic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 72-75. |
| [8] | Huang Chuwen, Jiang Hua, Li Minqing. Complications and death causes of peripheral blood stem cell transplantation in the treatment of thalassemia major [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 42-48. |
| [9] | Huang Bin, Zheng Jinxu, Zhang Jun. Progress of non-coding RNAs in stem cell abnormality of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 130-137. |
| [10] | Zhang Jinglan, Zhang Binjing, Chen Yifei, Zhang Chenyue, Hu Zhiai, Hu Haikun. Biological effects of magnetic field on osteogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 145-151. |
| [11] | Lou Hanxiao, Liu Wenjun, Liu Jun, Wang Xin, Zhang Gaofei, Wang Di, Li Jiamei. Potential of mesenchymal stem cell preconditioning strategies in the treatment of severe burn injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 152-159. |
| [12] | Liu Wentao, Feng Xingchao, Yang Yi, Bai Shengbin. Effect of M2 macrophage-derived exosomes on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(在线): 1-6. |
| [13] | Liu Gang, Ma Chao, Wang Le, Zeng Jie, Jiao Yong, Zhao Yi, Ren Jingpei, Hu Chuanyu, Xu Lin, Mu Xiaohong. Ankle-foot orthoses improve motor function of children with cerebral palsy: a Meta-analysis based on 12 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1299-1304. |
| [14] | Yang Shenglin, Pu Xingwei, Luo Chunshan, Yang Jianwen. Neuroprotective effects of tetrandrine preconditioning in rabbits with spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1223-1227. |
| [15] | Zhao Jing, Liu Xiaobo, Zhang Yue, Zhang Jiaming, Zhong Dongling, Li Juan, Jin Rongjiang. Visualization analysis of neuromuscular electrical stimulation therapy based on CiteSpace: therapeutic effects, hot spots, and developmental trends [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1234-1241. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||