Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (1): 152-159.doi: 10.12307/2022.965
Previous Articles Next Articles
Potential of mesenchymal stem cell preconditioning strategies in the treatment of severe burn injury
Lou Hanxiao, Liu Wenjun, Liu Jun, Wang Xin, Zhang Gaofei, Wang Di, Li Jiamei
- Department of Burns, Second Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Kunming 650188, Yunnan Province, China
-
Received:2021-11-24Accepted:2022-01-29Online:2023-01-08Published:2022-06-14 -
Contact:Liu Wenjun, MD, Associate professor, Department of Burns, Second Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Kunming 650188, Yunnan Province, China -
About author:Lou Hanxiao, Master, Department of Burns, Second Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Kunming 650188, Yunnan Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82060349 (to LWJ); Kunming Medical Joint Special Project, No. 2018FE001(-242) (to LWJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Lou Hanxiao, Liu Wenjun, Liu Jun, Wang Xin, Zhang Gaofei, Wang Di, Li Jiamei. Potential of mesenchymal stem cell preconditioning strategies in the treatment of severe burn injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 152-159.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
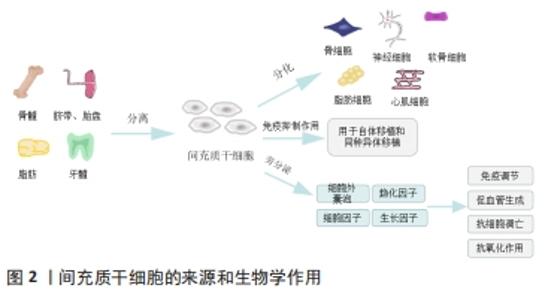
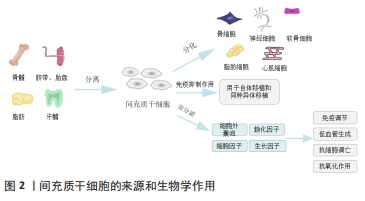
2.1 烧伤病理生理学 根据烧伤后组织损伤的严重程度和烧伤创面的血流变化程度,烧伤创面从中心到周围可分为3个区域,即凝固坏死区、淤滞区和充血区[8]。烧伤后48-72 h,淤滞区可因缺血缺氧、炎症反应和组织水肿等转化为坏死区,大面积坏死组织诱导患者机体出现免疫抑制状态。创面延迟愈合使创面长时间裸露,极易滋生致病菌,导致局部甚至全身感染,易发生脓毒血症,进而合并多器官功能障碍[9]。核因子κB是一种转录激活蛋白,在严重烧伤后被立即激活,调节多种炎症递质的释放,如肿瘤坏死因子α,诱导受损组织周围细胞凋亡[10]。坏死烧伤组织还可以释放大量损伤相关分子模式(damage-associated molecular pattern,DAMP)以及病原相关分子模式(pathogen-associated molecular pattern,PAMP),DAMP和PAMP通过Toll样受体/核因子κB途径激活炎症递质,引起全身炎症反应综合征[11]。烧伤后24-72 h,为对抗体内低温,儿茶酚胺、应激激素和炎症递质驱动烧伤患者发生高代谢反应,加速糖酵解、脂肪分解和蛋白水解。高代谢和持续炎症状态导致严重烧伤患者体质量下降、创面延迟愈合、胰岛素抵抗、免疫抑制、器官功能障碍和增生性瘢痕[12]。 2.2 严重烧伤的临床治疗方案和挑战 早期切痂是局部和全层皮肤烧伤治疗的金标准[13],对于清除烧伤创面中的细菌、有害物质、抑制局部炎症反应至关重要。同时,可以通过降低患者死亡率和住院时间显著改善严重烧伤患者的预后[14]。切痂后进行自体皮肤移植。但是Ⅲ度烧伤面积大于50%总体表面积的烧伤患者,供体皮肤非常有限[15],即使可以在一段时间内重复采集供体部位皮肤,但是供体部位皮肤愈合缓慢,并伴有额外的瘢痕和色素沉着会影响皮肤移植的质量和疗效[16]。感染也会导致皮肤移植失败甚至脓毒症,是严重烧伤后患者死亡的最常见原因[17]。多药耐药性微生物和真菌是抗感染治疗中的一个重大挑战[18],临床上采取了各种措施来控制和治疗多药耐药性,但该类致病菌仍在继续进化以抵抗新型抗生素的治疗效果。同时,严重烧伤后的患者因液体平衡改变、高动力循环、肝肾功能障碍显著降低了抗生素在组织中的浓度[19],最终导致机体耐药或治疗失败。严重烧伤后瘢痕治疗的挑战在于如何加深对瘢痕形成机制的理解来寻找新的治疗靶点。目前增生性瘢痕的治疗有赖于手术和负压压力疗法[20]。转化生长因子β被证明参与了瘢痕疙瘩和增生性瘢痕形成机制,然而到目前为止,只有转化生长因子β3被证明可以注射到手术创面以调节转化生长因子β通路,显著改善瘢痕外观[21]。在过去几十年中,尽管严重烧伤的治疗取得了重大进展,但为了继续优化目前的烧伤治疗方案,应首先研究如何加速创面愈合、减轻烧伤引起的高代谢分解反应、控制全身感染和缩短功能恢复的总时间,以提高严重烧伤患者的预后。 2.3 间充质干细胞的生物学作用 近年来干细胞治疗成为国内外研究的热点,间充质干细胞因其具有自我更新、高度增殖与多向分化的能力,成为组织再生与修复的希望。间充质干细胞极易从骨髓、牙龈、脂肪、脐带、胎盘等组织中被分离出来,并且可以实现高效的体外扩增[6]。它不仅能够在特定的环境中分化为脂肪细胞、骨细胞、软骨细胞、肝细胞、内皮细胞、心肌细胞、神经细胞等[22],而且还具有免疫抑制作用,常用来进行自体移植和同种异体移植[23]。间充质干细胞主要通过旁分泌细胞外囊泡、趋化因子、细胞因子和生长因子等发挥免疫调节、促血管生成、抗细胞凋亡和抗氧化作用[24-25],促进创面愈合和组织再生[26],见图2。"
脂肪来源间充质干细胞旁分泌的细胞外囊泡经多次静脉注射,可以抑制2型糖尿病大鼠模型体内促炎细胞因子白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α的表达,还能增加抗炎细胞因子白细胞介素10的分泌[27]。除了发挥抗炎作用, 在小鼠烫伤模型中通过皮下注射含有人羊膜间充质干细胞的条件培养基,可抑制急性热应激诱导的皮肤细胞凋亡,促进创面血管形成,从而显著促进烧伤创面愈合[28]。FOUBERT等[29]将自体脂肪来源间充质干细胞喷洒在红色杜洛克猪模型的皮肤损伤表面,分别在伤后的第2个月和第6个月与未喷洒间充质干细胞的创面进行对比,间充质干细胞组减少了创面的胶原沉积,改善了瘢痕沉着和表皮重塑,增加了弹性纤维长度,减少了增生性瘢痕。 2.4 间充质干细胞在严重烧伤中的临床应用 2005年至今,研究报道了几项基于间充质干细胞治疗烧伤的临床病例,见表1[30-32]。 "
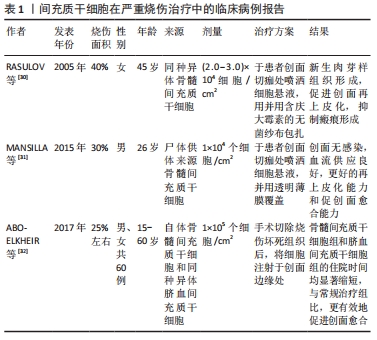
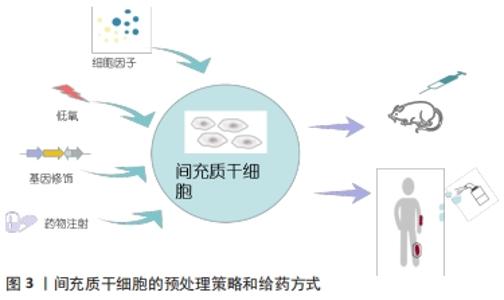
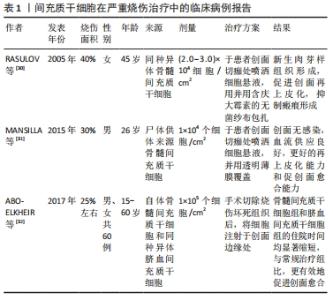
RASULOV等[30]在2005年首次使用同种异体来源骨髓间充质干细胞治疗烧伤面积占总体表面积40%,ⅢB级烧伤的1例45岁女性患者。研究人员于患者烧伤后29 d,在创面切痂处局部给予间充质干细胞悬液喷洒,并用含庆大霉素的无菌纱布包扎。随后在治疗第3天通过肉眼观察到创面边缘新生的血管化肉芽样组织,患者的创面愈合速度加快,创面边缘上皮化加强,降低了增生性瘢痕的风险。2015年MANSILLA等[31]使用尸体供体来源的骨髓间充质干细胞,治疗烧伤面积占总体表面积30%的26岁男性患者,在患者入院切痂后,立即将细胞喷洒至创面上。治疗后的第5天,创面出现明显的肉芽组织样外观,间充质干细胞治疗再次表现出惊人的再上皮化能力和促创面愈合能力;在出院后的3年随访期间,患者未出现不良反应,间充质干细胞治疗区域几乎没有瘢痕或畸形,无功能性后遗症。2份临床病例报告均证明了间充质干细胞在促进创面愈合方面的治疗潜力。但由于只有1例患者,缺乏阴性对照组,无法确定局部应用间充质干细胞与创面愈合过程的因果关系,忽略了评估创面愈合质量的方法。在最近一项研究中,研究人员招募了60例近期烧伤面积高达25%总体表面积的患者,随机分为常规治疗组(早期切痂和自体皮肤移植)、自体骨髓来源间充质干细胞治疗组和同种异体来源脐血间充质干细胞(通过局部注射或喷洒细胞悬液)治疗组,随后对患者进行随访,以评估创面愈合情况、早期和晚期并发症的发生率以及住院时间,结果显示传统早期切痂和自体皮肤移植组中5%的烧伤患者、骨髓间充质干细胞组中55%的患者和脐血间充质干细胞组中30%的患者均未出现晚期并发症。与常规对照组相比,骨髓间充质干细胞组和脐血间充质干细胞组的住院时间均显著缩短,骨髓和脐血来源间充质干细胞可以有效促进严重烧伤的创面愈合,且骨髓间充质干细胞组和脐血间充质干细胞组间无差异[32]。以上研究均证明了间充质干细胞促进严重烧伤后创面愈合的有效性,患者接受治疗后未发现并发症,证明了间充质干细胞治疗严重烧伤创面的安全性。 2.5 间充质干细胞临床应用的局限性 尽管间充质干细胞在促进烧伤创面愈合中显示出了治疗潜力,但是目前仍然难以应用于临床治疗中。在进行动物实验时,一般烧伤造模成功后就立即通过局部或静脉注射的方法使用间充质干细胞[28-29],但在临床治疗中却难以实现,特别是在进行自体皮肤移植的情况下,可能会发生免疫排斥[31]。另外,由于移植环境的病理变化,间充质干细胞在移植后几天会发生细胞凋亡[33],主要原因是间充质干细胞从培养皿中被分离出来时,遭受第一次氧化应激损伤,导致细胞存活率下降。当间充质干细胞被移植到烧伤创面中,由于创面微环境炎症因子富集、营养物质匮乏、缺氧缺血导致缺乏细胞外基质的支持和黏附,同时激活细胞凋亡信号通路,致使间充质干细胞再一次面临氧化应激损伤,从而发生失巢凋亡[25]。已有研究证明间充质干细胞的体外预处理策略可以突破这种局限性,如细胞因子预处理、低氧预处理、基因修饰和药物预处理,给药方式常为静脉注射或局部使用[33-36],见图3。 "

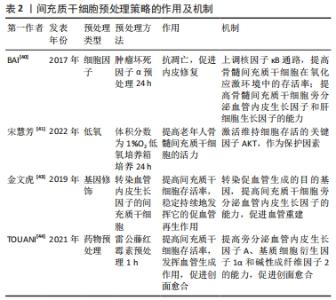
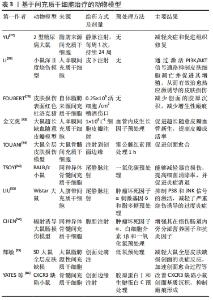
2.6 间充质干细胞的预处理策略 预处理策略是指在移植受损组织前对间充质干细胞进行优化,使间充质干细胞短暂接触低剂量的有毒因子或药物,增加其压力耐受性,改善细胞对特定环境的反应能力[37]。这些策略可以通过诱导细胞表达抗凋亡基因,从而提高间充质干细胞的存活率,促进细胞因子和生长因子的分泌以增加其作用效力。1986年REIMER等[38-39]首次应用预处理的方法,将心肌暴露于重复短周期缺氧中,成功提高了心肌缺血的恢复能力。越来越多的研究证明,预处理策略可以提高间充质干细胞在受损组织中的存活率和生物学效应。细胞因子已被证明可以提高移植后间充质干细胞的存活率。肿瘤坏死因子α预处理24 h,可以通过上调核因子κB通路促进骨髓间充质干细胞在氧化应激损伤中的抗凋亡作用和旁分泌血管内皮生长因子和肝细胞生长因子,从而促进内皮修复[40]。已有研究证实,低氧预处理同样具有促进骨髓间充质干细胞存活、组织修复等作用。宋慧芳等[41]研究表明低氧预处理(体积分数1%O2,体积分数5%CO2的低氧培养箱)24 h后的老年人自体骨髓来源间充质干细胞条件培养基,通过激活维持细胞存活的关键因子AKT,来提高老年人骨髓间充质干细胞活力,并通过旁分泌作用减轻氧化应激损伤模型中H9C2心肌细胞的损伤。此外,基因修饰可以通过上调或下调天然基因,重新编码间充质干细胞,从而调控其自身天然特定所需产物(如促炎/抗炎递质和细胞因子)的产生,或通过插入目的基因使间充质干细胞能够表达用于特定治疗的因子[42]。金文虎等[43]通过建立大鼠超长缺血随意皮瓣模型后,立即皮下注射血管内皮生长因子修饰的人羊膜间充质干细胞,皮瓣存活率要高于只注射人羊膜间充质干细胞,并可稳定持续地发挥它的促血管再生作用,此方法可用来改善随意皮瓣中远部位的缺血耐受力及成活能力。药物预处理也可以增强间充质干细胞在体外和体内的活力和促血管生成能力。TOUANI等[44]应用天然强效抗氧化药物雷公藤红素对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞预处理1 h,显著提高了间充质干细胞注射创面后的细胞活力和旁分泌血管内皮生长因子A、基质细胞衍生因子1α和碱性成纤维因子2的能力,发挥血管生成作用,促进创面愈合。预处理策略还可以针对疾病激活特定的信号通路,定制相应的细胞疗法[45]。在体外模拟2型糖尿病的过程中,利用干扰素γ和肿瘤坏死因子α预处理的骨髓间充质干细胞可通过 JAK1/JAK2信号通路完全逆转长期暴露于棕榈酸酯导致的间充质干细胞免疫调节功能降低的局面[46]。目前,各种预处理策略在体内和体外实验中得到广泛应用,见表2。"

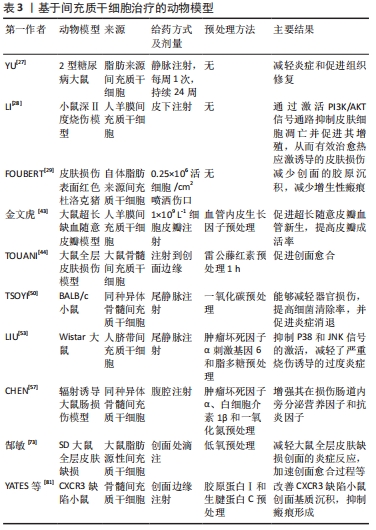
2.7.1 治疗创面感染 引起烧伤创面感染的细菌可分为革兰阴性菌和革兰阳性菌。金黄色葡萄球菌作为一种革兰阳性菌,是导致烧伤创面感染的主要原因,也是引起脓毒症的常见原因[47]。病原体随着抗生素的使用和创新不断进化,提高当前可用的局部或全身抗生素药物的有效性,对于降低严重烧伤患者的发病率和死亡率至关重要。间充质干细胞已被证明可以通过分泌抗微生物肽,包括抗菌肽、β-防御-2和铁调素直接发挥抗菌作用[48]。2016年,SUNG等[49]在小鼠大肠杆菌感染模型中证明了大肠杆菌预处理后的人脐血间充质干细胞可以通过Toll样受体4信号途径旁分泌β-防御-2,发挥其在体外和体内对大肠杆菌的抗菌作用。TSOYI等[50]在脓毒症小鼠模型中发现,脓毒症后6 h经尾静脉注射一氧化碳预处理后的同种异体骨髓间充质干细胞,与未预处理的间充质干细胞相比,不但保留了其治疗效果,提高了细胞存活率,并且促进中性粒细胞和腹膜中巨噬细胞对革兰阴性大肠杆菌、革兰阳性粪肠球菌的吞噬作用,小鼠的肝肾功能也有所恢复,提示预处理间充质干细胞可能对脓毒症未来的治疗具有重大意义。革兰阴性菌(铜绿假单胞菌、不动杆菌和不动杆菌灭活的脂多糖)和B型葡萄球菌肠毒素也可以作为间充质干细胞的预处理剂,显著提高细胞存活率和细菌清除率。体外研究表明,B型葡萄球菌肠毒素和脂多糖预处理均增强了的抗菌活性,这可能与抗菌肽、铁调素的分泌增加有关[51]。目前这些预处理策略仅限应用于动物模型中,并且间充质干细胞没有与抗菌药的药代动力学和临床患者的治疗标准结合使用,仍需要对其安全性和有效性进一步验证。 2.7.2 减轻过度炎症反应 严重烧伤后,DAMP、PAMP和应激激素通过G蛋白偶联受体激活JNK信号通路,并启动炎症级联反应[52]。轻度炎症预处理可诱导间充质干细胞分泌抗炎因子,LIU等[53]研究发现,经肿瘤坏死因子α刺激基因6和脂多糖预处理的人脐带间充质干细胞经尾静脉注射到实验烧伤大鼠体内后,可通过抑制P38和JNK信号通路来减轻严重烧伤引起的肝、肾、肺、心和脾中炎性细胞浸润,抑制全身过度炎症,发挥良好的抗炎作用。用白细胞介素1预处理的人骨髓间充质干细胞与脂多糖刺激后的小胶质细胞共培养后,小胶质细胞中炎症递质和凋亡蛋白均明显减少[54]。巨噬细胞作为组织损伤中的主要促炎递质,可以根据微环境极化为M1表型或M2表型[55]。M1型巨噬细胞的促炎反应依赖于Toll样受体和核因子κB 的激活,导致氧化应激和细胞凋亡;而M2型巨噬细胞会募集STAT3或其他转录因子,抑制炎症并促进组织重塑。Ti等[56]将脂多糖预处理2 d后的人脐带间充质干细胞上清液注射到糖尿病小鼠创面边缘,上调了创面边缘抗炎因子的表达并促进M2型巨噬细胞的活化,有效减轻了炎症并促进皮肤创面愈合。同样,在辐射诱导的大鼠肠损伤模型中,用肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β和一氧化氮预处理大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞进行异体移植,可增强其在损伤肠道内旁分泌营养因子和抗炎因子[57]。这些预处理策略有助于最大限度地发挥间充质干细胞在炎症环境中的抗炎能力,改善移植微环境炎症因子富集状态。 2.7.3 调节免疫系统 严重烧伤后,先天性免疫系统被激活,随后免疫细胞浸润,细胞因子产生。先天免疫反应通常是有益的,但过度激活会导致细胞因子风暴、多器官功能衰竭,甚至死亡。这种过度的免疫反应受DAMP和PAMP 的调节[58]。DAMP和PAMP 是免疫细胞主动分泌或受损细胞被动释放的内源性分子,可识别Toll样受体和NOD样受体(nucleotide binding oligomerization domain like receptors,NLR),受体结合其特定配体导致下游炎症通路的激活[59]。最近研究表明,在Toll样受体的各种配体中,用聚肌苷酸[poly(I:C)](一种Toll样受体3配体)预处理的小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞进行自体移植,能显著诱导吲哚胺-2,3-双加氧酶,改善葡聚糖硫酸钠诱导的小鼠炎症性结肠炎[60]。当免疫系统遭到破坏时,脂多糖作为配体,与Toll样受体4结合诱导细胞内发生信号级联反应,增加炎性细胞因子的释放和活性氧的产生。最近,RUHL等[61]发现,大麻二酚处理后可以对骨髓间充质干细胞发挥温和的免疫抑制,使间充质干细胞有效地发挥抗氧化应激损伤的作用。间充质干细胞表达的B7同系物1(B7-H1)与CD28相互作用,阻断了体液和细胞介导的免疫反应所需的T细胞通路,发挥免疫抑制作用[62]。ZHOU等[63]证明了间充质干细胞与T细胞之间比率的重要性,根据比率的高低可以在体外刺激或抑制T细胞的扩增。间充质干细胞可以在较低的比率下刺激活化的CD4+和CD8+T细胞亚群的增殖,而在较高的比率下则刺激T细胞发挥免疫抑制作用。根据烧伤病理环境的变化,调控间充质干细胞与T细胞之间比率也是调节免疫状态的一种治疗策略。 2.7.4 缓解高代谢状态 严重烧伤后,患者体内发生应激反应,儿茶酚胺、糖皮质激素、胰高血糖素和多巴胺(从大脑释放)的持续释放可能导致急性高分解代谢状态。随后促炎递质如细胞因子、趋化因子和急性期蛋白(即白细胞介素1、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子)的持续释放可能进一步导致中度至重度烧伤患者的高代谢状态。代谢亢进也会导致负氮平衡、免疫功能受损和创面愈合延迟。严重烧伤后胰高血糖素大量释放,导致患者持续高血糖,并发生胰岛素抵抗[64]。人端粒酶反转录酶转染间充质干细胞(human telomerase reverse transcriptase mesenchymal stem cell,hTERT-MSC)是骨髓来源的永生化细胞系,通过转染含有人端粒酶反转录酶基因的反转录病毒产生。hTERT-MSC可通过胰内和静脉途径注射促进胰腺细胞的分裂,或促进其他胰腺细胞类型转化为β细胞来补充胰腺β细胞,提高机体胰腺β细胞的增殖率和胰岛素敏感性,从而显示出逆转高血糖的潜力[65]。另一项研究中,炎症因子预处理后的人脐带间充质干细胞也可以抑制代谢紊乱,显著改善了烧伤大鼠模型因严重烧伤引起的体温过低[53]。在严重烧伤后的创面愈合过程中,切痂、外科清创、理疗和换药会显著增加患者的疼痛程度,疼痛引起的恐惧和焦虑情绪会导致患者应激激素升高,缓解疼痛也可以降低患者高代谢状态[66]。目前临床上主要应用阿片类药物和非类固醇抗炎药等治疗疼痛,然而这些方法只减轻了不到50%的患者30%-40%的疼痛[67]。近年来,间充质干细胞为疼痛,特别是神经损伤引起的神经病理性疼痛提供了一种可能的治疗方法[68]。四氢大麻酚是大麻的主要成分,通过激活大麻受体2型增强间充质干细胞的免疫调节作用。四氢大麻酚预处理的小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞,可以在热痛觉过敏和机械性痛觉超敏中发挥镇痛作用,同时显著降低促炎因子的释放。用大麻受体2型激动剂预处理间充质干细胞也可以增强慢性收缩损伤模型的抗氧化应激作用[69]。上述研究结果表明,预处理的间充质干细胞会为烧伤患者的疼痛治疗提供新的策略。 2.7.5 促进创面愈合 严重烧伤导致创面延迟愈合是治疗的主要障碍。在创面愈合阶段,细胞因子和生长因子激活角质细胞和成纤维细胞,角质细胞和成纤维细胞在创面上迁移,帮助和恢复血管网重建,这是创面愈合过程中的重要步骤。预处理策略可促进间充质干细胞旁分泌营养因子和促生长因子,以改善创面微环境,加速局部创面愈合。转化生长因子β1是一种在创面愈合和纤维化中起着重要作用的生长因子[70],转化生长因子β1预处理增强了其在创面中的分布以及整合素的表达和细胞黏附强度,能够明显促进创面愈合[71]。在另一项研究中,姜黄素作为一种天然膳食产品,对细胞的发生发展过程具有保护作用,低氧预处理结合姜黄素通过改变骨髓间充质干细胞线粒体嵴的形状,抑制线粒体细胞色素C释放,并抑制了细胞的凋亡信号,显著增加了骨髓间充质干细胞的存活率,同时加速小鼠皮肤创面愈合过程[72]。郜敏等[73]的研究表明,低氧预处理可以显著增强大鼠脂肪间充质干细胞的旁分泌能力,应用低氧预处理的大鼠脂肪间充质干细胞条件培养基可以减轻大鼠全层皮肤缺损创面的炎症反应、促进创面的再上皮化和胶原物质沉积,加速大鼠创面愈合的过程。间充质干细胞具有识别创面微环境中PAMP和DAMP的能力,并通过旁分泌效应对创面微环境的变化产生血管生成和组织修复的作用[74]。BASU等[75]用S100A8/A9(一种可以被间充质干细胞表达的Toll 样受体4识别的DAMP分子)预处理人脂肪组织来源间充质干细胞,通过局部注射在小鼠全层损伤的创面边缘,与未经预处理的间充质干细胞相比,可显著加速全层皮肤损伤小鼠的创面愈合。 2.7.6 抑制增生性瘢痕 烧伤可导致增生性瘢痕、皮肤挛缩。增生性瘢痕形成的具体机制并不明确,可能与肌成纤维细胞的异常生长和存活、细胞外基质沉积以及转化生长因子β信号过度激活有关[76]。皮下注射肿瘤坏死因子α刺激基因6预处理人骨髓间充质干细胞的细胞外囊泡可有效改善小鼠皮肤创面模型的瘢痕病理损伤,减少炎症分子分泌并减弱胶原沉积[77]。A型肉毒杆菌毒素可以通过在创面愈合期间防止肌肉和皮肤收缩[78],抑制增生性瘢痕导致的成纤维细胞生长,并影响转化生长因子β1的表达[79],最大限度地减少创面瘢痕形成。间充质干细胞条件培养基和A型肉毒素杆菌毒素均已被证明对增生性瘢痕有治疗作用,但是与单一疗法相比,间充质干细胞条件培养基和A型肉毒杆菌毒素的协同作用改变了成纤维细胞的骨架组成,抑制了成纤维细胞的增殖活性,促进了成纤维细胞凋亡,并显著抑制增生性瘢痕中成纤维细胞的收缩能力,改善了胶原纤维的排列和沉积[80]。增生性瘢痕也与遗传有关。最近一项研究发现,缺乏 CXC亚族趋化因子受体3(CXCR3)的小鼠会出现增生性瘢痕、表皮增厚、无组织真皮和血管过多的现象[80]。胶原蛋白Ⅰ是真皮细胞黏附的抑制因子,生腱蛋白C是一种在愈合期间表达上调的抗黏附基质细胞因子,YATES等[81]将hTERT-MSC置于含有胶原蛋白Ⅰ和生腱蛋白C的基质中,通过异种移植于CXCR3缺陷小鼠的创面中,不仅增强了成纤维细胞在创面中的增殖、迁移,促进创面愈合,减少了伤后的炎症,而且改善了CXCR3缺陷小鼠创面基质沉积,抑制瘢痕形成。 间充质干细胞的生物学作用有望在烧伤后减少过度炎症、加速创面愈合和减少瘢痕增生等方面提供新的潜力,见表3。 "
| [1] MASON SA, NATHENS AB, BYRNE JP, et al. Increased Rate of Long-term Mortality Among Burn Survivors: A Population-based Matched Cohort Study. Ann Surg. 2019;269(6):1192-1199. [2] PORTER C, HURREN NM, HERNDON DN, et al. Whole body and skeletal muscle protein turnover in recovery from burns. Int J Burns Trauma. 2013;3(1):9-17. [3] FARINA JA JR, ROSIQUE MJ, ROSIQUE RG. Curbing inflammation in burn patients. Int J Inflam. 2013;2013:715645. [4] MEIRELLES LDA S, FONTES AM, COVAS DT, et al. Mechanisms involved in the therapeutic properties of mesenchymal stem cells. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2009;20(5-6):419-427. [5] KIM KH, BLASCO-MORENTE G, CUENDE N, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells: properties and role in management of cutaneous diseases. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2017;31(3):414-423. [6] CHANG W, SONG BW, MOON JY, et al. Anti-death strategies against oxidative stress in grafted mesenchymal stem cells. Histol Histopathol. 2013;28(12):1529-1536. [7] MARANDA EL, RODRIGUEZ-MENOCAL L, BADIAVAS EV. Role of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Dermal Repair in Burns and Diabetic Wounds. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;12(1):61-70. [8] HUSSAIN A, DUNN KW. Predicting length of stay in thermal burns: a systematic review of prognostic factors. Burns. 2013;39(7):1331-1340. [9] SCHWACHA MG. Macrophages and post-burn immune dysfunction. Burns. 2003;29(1):1-14. [10] VAUGHN L, BECKEL N. Severe burn injury, burn shock, and smoke inhalation injury in small animals. Part 1: burn classification and pathophysiology. J Vet Emerg Crit Care (San Antonio). 2012;22(2):179-186. [11] D’ARPA P, LEUNG KP. Toll-Like Receptor Signaling in Burn Wound Healing and Scarring. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2017;6(10):330-343. [12] WILLIAMS FN, HERNDON DN, JESCHKE MG. The hypermetabolic response to burn injury and interventions to modify this response. Clin Plast Surg. 2009;36(4):583-596. [13] SHEVCHENKO RV, JAMES SL, JAMES SE. A review of tissue-engineered skin bioconstructs available for skin reconstruction. J R Soc Interface. 2010;7(43):229-258. [14] WOOD FM. Skin regeneration: the complexities of translation into clinical practise. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014;56:133-140. [15] HANSEN SL, VOIGT DW, WIEBELHAUS P, et al. Using skin replacement products to treat burns and wounds. Adv Skin Wound Care. 2001;14(1): 37-44; quiz 45-46. [16] BOYCE ST, KAGAN RJ, YAKUBOFF KP, et al. Cultured skin substitutes reduce donor skin harvesting for closure of excised, full-thickness burns. Ann Surg. 2002;235(2):269-279. [17] NORBURY W, HERNDON DN, TANKSLEY J, et al. Infection in Burns. Surg Infect (Larchmt). 2016;17(2):250-255. [18] BRANSKI LK, AL-MOUSAWI A, RIVERO H, et al. Emerging infections in burns. Surg Infect (Larchmt). 2009;10(5):389-397. [19] ROBERTS JA, ABDUL-AZIZ MH, LIPMAN J, et al. Individualised antibiotic dosing for patients who are critically ill: challenges and potential solutions. Lancet Infect Dis. 2014;14(6):498-509. [20] KWAN PO, TREDGET EE. Biological Principles of Scar and Contracture. Hand Clin. 2017;33(2):277-292. [21] FERGUSON MW, DUNCAN J, BOND J, et al. Prophylactic administration of avotermin for improvement of skin scarring: three double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase I/II studies. Lancet. 2009;373(9671):1264-1274. [22] FU X, LIU G, HALIM A, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Migration and Tissue Repair. Cells. 2019;8(8):784. [23] DJOUAD F, BOUFFI C, GHANNAM S, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells: innovative therapeutic tools for rheumatic diseases. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2009;5(7):392-399. [24] KUPCOVA SKALNIKOVA H. Proteomic techniques for characterisation of mesenchymal stem cell secretome. Biochimie. 2013;95(12):2196-2211. [25] LEE S, CHOI E, CHA MJ, et al. Cell adhesion and long-term survival of transplanted mesenchymal stem cells: a prerequisite for cell therapy. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015;2015:632902. [26] TAMAMA K, KERPEDJIEVA SS. Acceleration of Wound Healing by Multiple Growth Factors and Cytokines Secreted from Multipotential Stromal Cells/Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2012;1(4):177-182. [27] YU S, CHENG Y, ZHANG L, et al. Treatment with adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells exerts anti-diabetic effects, improves long-term complications, and attenuates inflammation in type 2 diabetic rats. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):333. [28] LI JY, REN KK, ZHANG WJ, et al. Human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells and their paracrine factors promote wound healing by inhibiting heat stress-induced skin cell apoptosis and enhancing their proliferation through activating PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):247. [29] FOUBERT P, ZAFRA D, LIU M, et al. Autologous adipose-derived regenerative cell therapy modulates development of hypertrophic scarring in a red Duroc porcine model. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1): 261. [30] RASULOV MF, VASILCHENKOV AV, ONISHCHENKO NA, et al. First experience of the use bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of a patient with deep skin burns. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2005; 139(1):141-144. [31] MANSILLA E, MARÍN GH, BERGES M, et al. Cadaveric bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells: first experience treating a patient with large severe burns. Burns Trauma. 2015;3:17. [32] ABO-ELKHEIR W, HAMZA F, ELMOFTY AM, et al. Role of cord blood and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in recent deep burn: a case-control prospective study. Am J Stem Cells. 2017;6(3):23-35. [33] ROBEY TE, SAIGET MK, REINECKE H, et al. Systems approaches to preventing transplanted cell death in cardiac repair. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2008;45(4):567-581. [34] SILVA LHA, ANTUNES MA, DOS SANTOS CC, et al. Strategies to improve the therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stromal cells in respiratory diseases. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):45. [35] MAJZUNOVA M, DOVINOVA I, BARANCIK M, et al. Redox signaling in pathophysiology of hypertension. J Biomed Sci. 2013;20(1):69. [36] 王国任,白志明.不同预处理策略促进间充质干细胞的归巢[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(28):4234-4242. [37] SART S, MA T, LI Y. Preconditioning stem cells for in vivo delivery. Biores Open Access. 2014;3(4):137-149. [38] REIMER KA, MURRY CE, YAMASAWA I, et al. Four brief periods of myocardial ischemia cause no cumulative ATP loss or necrosis. Am J Physiol. 1986;251(6 Pt 2):H1306-1315. [39] MURRY CE, JENNINGS RB, REIMER KA. Preconditioning with ischemia: a delay of lethal cell injury in ischemic myocardium. Circulation. 1986; 74(5):1124-1136. [40] BAI X, XI J, BI Y, et al. TNF-α promotes survival and migration of MSCs under oxidative stress via NF-κB pathway to attenuate intimal hyperplasia in vein grafts. J Cell Mol Med. 2017;21(9):2077-2091. [41] 宋慧芳,谈佳音,康毅,等.低氧预处理增强老年人骨髓间充质干细胞条件培养基对H9C2细胞氧化应激损伤的保护作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(1):1-6. [42] PARK JS, SURYAPRAKASH S, LAO YH, et al. Engineering mesenchymal stem cells for regenerative medicine and drug delivery. Methods. 2015; 84:3-16. [43] 金文虎,周爱婷,吴中桓,等.血管内皮生长因子基因修饰人羊膜间充质干细胞利于超长随意皮瓣的成活[J].中国组织工程研究, 2019,23(21):3349-3356. [44] TOUANI FK, BORIE M, AZZI F, et al. Pharmacological Preconditioning Improves the Viability and Proangiogenic Paracrine Function of Hydrogel-Encapsulated Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. Stem Cells Int. 2021;2021:6663467. [45] HU C, LI L. Preconditioning influences mesenchymal stem cell properties in vitro and in vivo. J Cell Mol Med. 2018;22(3):1428-1442. [46] BOLAND L, BURAND AJ, BROWN AJ, et al. IFN-γ and TNF-α Pre-licensing Protects Mesenchymal Stromal Cells from the Pro-inflammatory Effects of Palmitate. Mol Ther. 2018;26(3):860-873. [47] LACHIEWICZ AM, HAUCK CG, WEBER DJ, et al. Bacterial Infections After Burn Injuries: Impact of Multidrug Resistance. Clin Infect Dis. 2017;65(12):2130-2136. [48] GORMAN E, MILLAR J, MCAULEY D, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells for acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), sepsis, and COVID-19 infection: optimizing the therapeutic potential. Expert Rev Respir Med. 2021;15(3):301-324. [49] SUNG DK, CHANG YS, SUNG SI, et al. Antibacterial effect of mesenchymal stem cells against Escherichia coli is mediated by secretion of beta- defensin- 2 via toll- like receptor 4 signalling. Cell Microbiol. 2016;18(3):424-436. [50] TSOYI K, HALL SR, DALLI J, et al. Carbon Monoxide Improves Efficacy of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells During Sepsis by Production of Specialized Proresolving Lipid Mediators. Crit Care Med. 2016;44(12):e1236-e1245. [51] SAEEDI P, HALABIAN R, FOOLADI AAI. Antimicrobial effects of mesenchymal stem cells primed by modified LPS on bacterial clearance in sepsis. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(4):4970-4986. [52] KADDOURA I, ABU-SITTAH G, IBRAHIM A, et al. Burn injury: review of pathophysiology and therapeutic modalities in major burns. Ann Burns Fire Disasters. 2017;30(2):95-102. [53] LIU L, SONG H, DUAN H, et al. TSG-6 secreted by human umbilical cord-MSCs attenuates severe burn-induced excessive inflammation via inhibiting activations of P38 and JNK signaling. Sci Rep. 2016;6:30121. [54] REDONDO-CASTRO E, CUNNINGHAM C, MILLER J, et al. Interleukin-1 primes human mesenchymal stem cells towards an anti-inflammatory and pro-trophic phenotype in vitro. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):79. [55] HUANG J, SHEN XD, YUE S, et al. Adoptive transfer of heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1)-modified macrophages rescues the nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor (Nrf2) antiinflammatory phenotype in liver ischemia/reperfusion injury. Mol Med. 2014;20(1):448-455. [56] TI D, HAO H, TONG C, et al. LPS-preconditioned mesenchymal stromal cells modify macrophage polarization for resolution of chronic inflammation via exosome-shuttled let-7b. J Transl Med. 2015;13:308. [57] CHEN H, MIN XH, WANG QY, et al. Pre-activation of mesenchymal stem cells with TNF-α, IL-1β and nitric oxide enhances its paracrine effects on radiation-induced intestinal injury. Sci Rep. 2015;5:8718. [58] COMISH PB, CARLSON D, KANG R, et al. Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns and the Systemic Immune Consequences of Severe Thermal Injury. J Immunol. 2020;205(5):1189-1197. [59] JESCHKE MG, VAN BAAR ME, CHOUDHRY MA, et al. Burn injury. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2020;6(1):11. [60] RYU DB, LIM JY, LEE SE, et al. Induction of Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase by Pre-treatment with Poly(I:C) May Enhance the Efficacy of MSC Treatment in DSS-induced Colitis. Immune Netw. 2016;16(6):358-365. [61] RUHL T, KIM BS, BEIER JP. Cannabidiol restores differentiation capacity of LPS exposed adipose tissue mesenchymal stromal cells. Exp Cell Res. 2018;370(2):653-662. [62] SHENG H, WANG Y, JIN Y, et al. A critical role of IFNgamma in priming MSC-mediated suppression of T cell proliferation through up-regulation of B7-H1. Cell Res. 2008;18(8):846-857. [63] ZHOU Y, DAY A, HAYKAL S, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells augment CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell proliferation through a CCL2 pathway. Cytotherapy. 2013;15(10):1195-1207. [64] JESCHKE MG, GAUGLITZ GG, KULP GA, et al. Long-term persistance of the pathophysiologic response to severe burn injury. PLoS One. 2011;6(7):e21245. [65] KHATRI R, MAZUREK S, PETRY SF, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells promote pancreatic β-cell regeneration through downregulation of FoxO1 pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):497. [66] GRIGGS C, GOVERMAN J, BITTNER EA, et al. Sedation and Pain Management in Burn Patients. Clin Plast Surg. 2017;44(3):535-540. [67] HOSSEINI M, YOUSEFIFARD M, AZIZNEJAD H, et al. The Effect of Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell Transplantation on Allodynia and Hyperalgesia in Neuropathic Animals: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2015;21(9):1537-1544. [68] LIU L, HUA Z, SHEN J, et al. Comparative Efficacy of Multiple Variables of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Transplantation for the Treatment of Neuropathic Pain in Rats. Mil Med. 2017;182(S1):175-184. [69] XIE J, XIAO D, XU Y, et al. Up-regulation of immunomodulatory effects of mouse bone-marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells by tetrahydrocannabinol pre-treatment involving cannabinoid receptor CB2. Oncotarget. 2016;7(6):6436-6447. [70] GILBERT RWD, VICKARYOUS MK, VILORIA-PETIT AM. Signalling by Transforming Growth Factor Beta Isoforms in Wound Healing and Tissue Regeneration. J Dev Biol. 2016;4(2):21. [71] GHOSH D, MCGRAIL DJ, DAWSON MR. TGF-β1 Pretreatment Improves the Function of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in the Wound Bed. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2017;5:28. [72] WANG X, SHEN K, WANG J, et al. Hypoxic preconditioning combined with curcumin promotes cell survival and mitochondrial quality of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells, and accelerates cutaneous wound healing via PGC-1α/SIRT3/HIF-1α signaling. Free Radic Biol Med. 2020;159:164-176. [73] 郜敏,张杰,王际壮,等.低氧预处理大鼠脂肪源性间充质干细胞条件培养基对大鼠全层皮肤缺损创面愈合的影响[J].中华烧伤杂志,2020,36(9):803-812. [74] QI Y, JIANG D, SINDRILARU A, et al. TSG-6 released from intradermally injected mesenchymal stem cells accelerates wound healing and reduces tissue fibrosis in murine full-thickness skin wounds. J Invest Dermatol. 2014;134(2):526-537. [75] BASU A, MUNIR S, MULAW MA, et al. A Novel S100A8/A9 Induced Fingerprint of Mesenchymal Stem Cells associated with Enhanced Wound Healing. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):6205. [76] PENN JW, GROBBELAAR AO, ROLFE KJ. The role of the TGF-β family in wound healing, burns and scarring: a review. Int J Burns Trauma. 2012;2(1):18-28. [77] JIANG L, ZHANG Y, LIU T, et al. Exosomes derived from TSG-6 modified mesenchymal stromal cells attenuate scar formation during wound healing. Biochimie. 2020;177:40-49. [78] CHANG CS, WALLACE CG, HSIAO YC, et al. Botulinum toxin to improve results in cleft lip repair: a double-blinded, randomized, vehicle-controlled clinical trial. PLoS One. 2014;9(12):e115690. [79] XIAO Z, ZHANG F, LIN W, et al. Effect of botulinum toxin type A on transforming growth factor beta1 in fibroblasts derived from hypertrophic scar: a preliminary report. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2010; 34(4):424-427. [80] HU CH, TSENG YW, LEE CW, et al. Combination of mesenchymal stem cell-conditioned medium and botulinum toxin type A for treating human hypertrophic scars. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2020;73(3): 516-527. [81] YATES CC, RODRIGUES M, NUSCHKE A, et al. Multipotent stromal cells/mesenchymal stem cells and fibroblasts combine to minimize skin hypertrophic scarring. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):193. |
| [1] | Li Rui, Liu Zhen, Guo Zige, Lu Ruijie, Wang Chen. Aspirin-loaded chitosan nanoparticles and polydopamine modified titanium sheets improve osteogenic differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 374-379. |
| [2] | Ning Ziwen, Wang Xu, Shi Zhengliang, Qin Yihua, Wang Guoliang, Jia Di, Wang Yang, Li Yanlin. Meniscal injury repair methods for non-blood supply area [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 420-426. |
| [3] | Ma Munan, Xie Jun, Sang Yuchao, Huang Lei, Zhang Guodong, Yang Xiaoli, Fu Songtao. Electroacupuncture combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of chemotherapy-induced premature ovarian insufficiency in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 1-7. |
| [4] | Zhang Yujuan, Yuan Yitong, Du Ruochen, Tian Feng, Fu Yuan, Wang Chunfang. miR-31 promotes the proliferation and migration of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 66-71. |
| [5] | Gao Yixuan, Wang Lingfeng, Ba Te, Li Fang, Cao Shengjun, Li Junliang, Zhou Biao, Chen Qiang. Adipose-derived stem cells overexpressing growth hormone promote proliferation and migration of fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 8-14. |
| [6] | Liu Siqi, Wu Mingrui, Qiao Lingran, Xie Liying, Chen Siyu, Han Zhibo, Zuo Lin. Effects of hydrogel loaded with human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on diabetic wound repair in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 21-27. |
| [7] | Fu Chunmei, Zhang Pu, Wang Yang, Li Xiaolin, Xue Yan, Fu Jie, Zhang Cixian, Yang Yujuan, Duan Yaya, Feng Kai. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in the treatment of 24 patients with severe aplastic anemia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 15-20. |
| [8] | Wei Yanzhao, Zheng Xiaohan, Gao Shijun, Huang Ting, Wei Xufang, Chen Xinxu, Zhao Zhenqiang. Expression of autocrine macrophage migration inhibitory factor and its receptors of human embryonic stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 34-41. |
| [9] | Yang Yan, Wang Jingxian, Zhang Ronghong, Li Chen, Fan Anran, Cui Dongbing, Wu Shumei. Effects of conditioned media of different sources on the proliferation of human dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 49-53. |
| [10] | Lan Qian, Gu Yangcong, Xiao Xin, Bi Xueting, Li Na. Human periodontal ligament stem cells-derived exosomes interfere with the proliferation and differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 54-58. |
| [11] | Huang Wenjun, Zhou Yafei, Wang Jie, Li Huan, Zhang Yanmin, Zhou Rui. Establishment and identification of a protocol for highly efficient differentiation of hepatocytes from human pluripotent stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 28-33. |
| [12] | Zhao Jufen, Ma Rong, Cao Jia, Yu Chuanyang, Tao Xiang, Wang Jia, Wang Libin. Regulation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1 beta on stemness expression in breast cancer stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 59-65. |
| [13] | Feng Hao, Zhang Bin, Wang Jianping. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation can improve bone metabolism in osteoporotic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 72-75. |
| [14] | Huang Chuwen, Jiang Hua, Li Minqing. Complications and death causes of peripheral blood stem cell transplantation in the treatment of thalassemia major [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 42-48. |
| [15] | Liu Runyuan, Dong Ming, Han Wenqing, Dong Juhong, Niu Weidong. Application and progress of small extracellular vesicles in periodontal and pulp regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 83-90. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

