[1] 李忠俊,相丽欣,叶兴德.间充质干细胞研究进展[J].中国输血杂志,2013,26(4):307-309.
[2] 王艳,张晋林,黄晓兵,等.脐带间充质干细胞研究现状与临床治疗[J].重庆医学,2013,42(18):2161-2163.
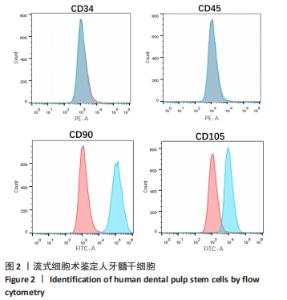
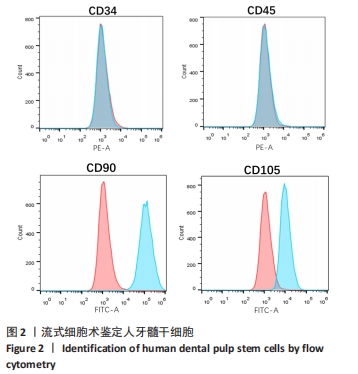
[3] 滕肇慧,KONG TS,左夏林.人体牙髓干细胞制备、保存及分析鉴定的研究进展[J].国际老年医学杂志,2020,41(2):129-132.
[4] GRONTHOS S, MANKANI M, BRAHIM J, et al. Postnatal human dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) in vitro and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97(25):13625-13630.
[5] POTDAR PD, JETHMALANI YD. Human dental pulp stem cells: Applications in future regenerative medicine. World J Stem Cells. 2015; 7(5):839-851.
[6] NISHINO Y, YAMADA Y, EBISAWA K, et al. Stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth (SHED) enhance wound healing and the possibility of novel cell therapy. Cytotherapy. 2011;13(5):598-605.
[7] ALIPOUR R, ADIB M, MASOUMI KARIMI M, et al. Comparing the immunoregulatory effects of stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth and bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2013;12(4):331-344.
[8] YILDIRIM S, ZIBANDEH N, GENC D, et al. The Comparison of the Immunologic Properties of Stem Cells Isolated from Human Exfoliated Deciduous Teeth, Dental Pulp, and Dental Follicles. Stem Cells Int. 2016; 2016:4682875.
[9] 刘伟,凌均棨.牙髓干细胞诱导分化为血管内皮细胞的研究进展[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2014,41(6):707-711.
[10] ZHANG W, WALBOOMERS XF, SHI S, et al. Multilineage differentiation potential of stem cells derived from human dental pulp after cryopreservation. Tissue Eng. 2006;12(10):2813-2823.
[11] 李鑫平,崔秋菊,曾曙光.β-磷酸三钙/壳聚糖水凝胶改性对牙髓干细胞生长与矿化的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(22): 3493-3499.
[12] WANG K, DISKIN SJ, ZHANG H, et al. Integrative genomics identifies LMO1 as a neuroblastoma oncogene. Nature. 2011;469(7329):216-220.
[13] MEAD B, LOGAN A, BERRY M, et al. Concise Review: Dental Pulp Stem Cells: A Novel Cell Therapy for Retinal and Central Nervous System Repair. Stem Cells. 2017;35(1):61-67.
[14] ZHANG J, LIAN M, CAO P, et al. Effects of Nerve Growth Factor and Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor Promote Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells to Neural Differentiation. Neurochem Res. 2017;42(4):1015-1025.
[15] 黄国梁,王倩玉,买雨晨.GM-CSF对猪卵丘细胞扩展相关基因表达的影响[J].现代畜牧兽医,2021(10):1-4.
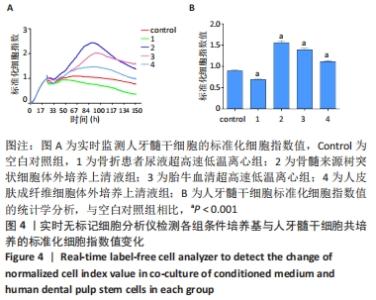
[16] 谢文静,凌敏,梁婕.RTCA与CCK-8法用于检测柴油废气颗粒物致支气管上皮细胞毒性的比较研究[J].生态毒理学报,2021,16(2): 187-194.
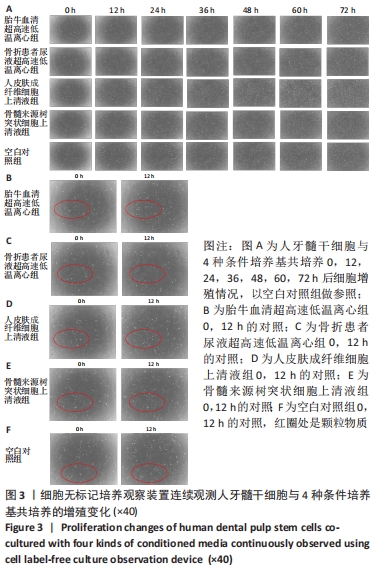
[17] TRUKHAN IS, DREMINA TN, LOZOVSKAYA EA. Assessment of Potential Cytotoxicity During Vital Observation at the BioStation CT. Acta Biomedica Scientifica. 2018;3(6):48-53.
[18] 李超然,黄桂林,王帅.间充质干细胞来源外泌体促进损伤组织修复与再生的应用与进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(1):133-139.
[19] VALADI H, EKSTRÖM K, BOSSIOS A, et al. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9(6):654-659.
[20] MONTECALVO A, LARREGINA AT, SHUFESKY WJ, et al. Mechanism of transfer of functional microRNAs between mouse dendritic cells via exosomes. Blood. 2012;119(3):756-766.
[21] RAPOSO G, NIJMAN HW, STOORVOGEL W, et al. B lymphocytes secrete antigen-presenting vesicles. J Exp Med. 1996;183(3):1161-1172.
[22] HO DH, YI S, SEO H, et al. Increased DJ-1 in urine exosome of Korean males with Parkinson’s disease. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:704678.
|