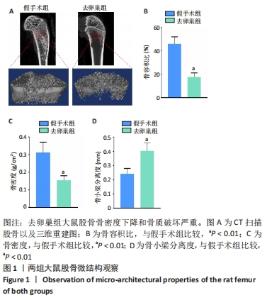
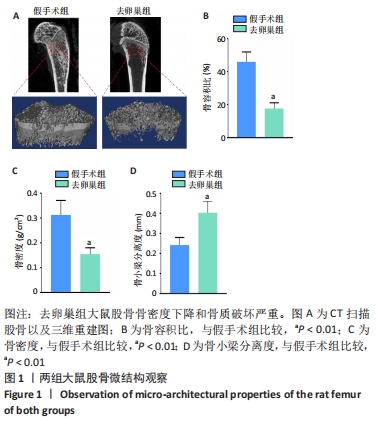
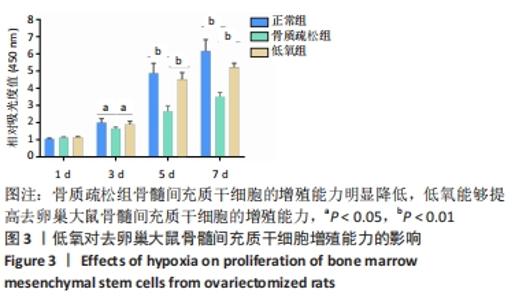
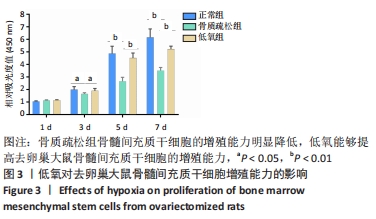
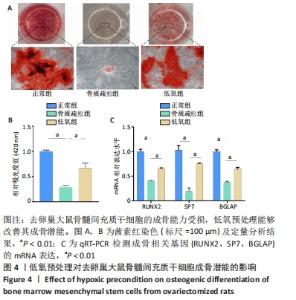
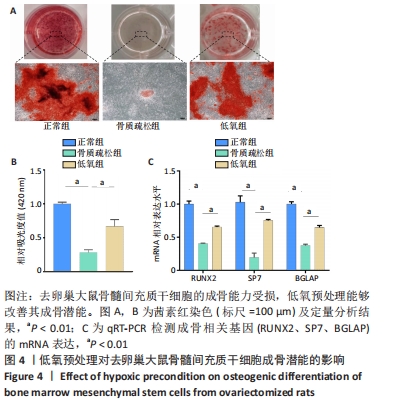
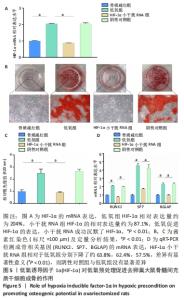
[1] EASTELL R, O’NEILL TW, HOFBAUER LC, et al. Postmenopausal osteoporosis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16069.
[2] BUCKLEY L, HUMPHREY MB. Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis. N Engl J Med. 2018;379(26):2547-2556.
[3] LIANG C, PENG S, LI J, et al. Inhibition of osteoblastic Smurf1 promotes bone formation in mouse models of distinctive age-related osteoporosis. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):3428.
[4] CRANE JL, CAO X. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and TGF-beta signaling in bone remodeling. J Clin Invest. 2014;124(2):466-472.
[5] RODRÍGUEZ JP, GARAT S, GAJARDO H, et al. Abnormal osteogenesis in osteoporotic patients is reflected by altered mesenchymal stem cells dynamics. J Cell Biochem. 1999;75(3):414-423.
[6] GRAYSON WL, ZHAO F, BUNNELL B, et al. Hypoxia enhances proliferation and tissue formation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;358(3):948-953.
[7] MALDA J, KLEIN TJ, UPTON Z. The roles of hypoxia in the in vitro engineering of tissues. Tissue Eng. 2007;13(9):2153-2162.
[8] ROSOVÁ I, DAO M, CAPOCCIA B, et al. Hypoxic preconditioning results in increased motility and improved therapeutic potential of human mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells. 2008;26(8):2173-2182.
[9] SEMENZA GL. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1: master regulator of O2 homeostasis. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1998;8(5):588-594.
[10] SEMENZA GL. Regulation of mammalian O2 homeostasis by hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 1999;15:551-578.
[11] BIANCO P, CAO X, FRENETTE PS, et al. The meaning, the sense and the significance: translating the science of mesenchymal stem cells into medicine. Nat Med. 2013;19(1):35-42.
[12] KULAK CA, BORBA VC, JORGETTI V, et al. Skeletal microstructural abnormalities in postmenopausal women with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Bone Miner Res. 2010;25(9):1931-1940.
[13] KJENSLI A, MOWINCKEL P, RYG MS, et al. Low bone mineral density is related to severity of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Bone. 2007;40(2):493-497.
[14] ADAS-OKUMA MG, MAEDA SS, GAZZOTTI MR, et al. COPD as an independent risk factor for osteoporosis and fractures. Osteoporos Int. 2020;31(4):687-697.
[15] HU X, YU SP, FRASER JL, et al. Transplantation of hypoxia-preconditioned mesenchymal stem cells improves infarcted heart function via enhanced survival of implanted cells and angiogenesis. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2008;135(4):799-808.
[16] PARK IH, KIM KH, CHOI HK, et al. Constitutive stabilization of hypoxia-inducible factor alpha selectively promotes the self-renewal of mesenchymal progenitors and maintains mesenchymal stromal cells in an undifferentiated state. Exp Mol Med. 2013;45(9):e44.
[17] YAN Z, SHEN D, LIAO J, et al. Hypoxia Suppresses TGF-B1-Induced Cardiac Myocyte Myofibroblast Transformation by Inhibiting Smad2/3 and Rhoa Signaling Pathways. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;45(1):250-257.
[18] PRALL WC, HAASTERS F, HEGGEBÖ J, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells from osteoporotic patients feature impaired signal transduction but sustained osteoinduction in response to BMP-2 stimulation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;440(4):617-622.
[19] EZASHI T, DAS P, ROBERTS RM. Low O2 tensions and the prevention of differentiation of hES cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(13): 4783-4788.
[20] POUYSSÉGUR J, DAYAN F, MAZURE NM. Hypoxia signalling in cancer and approaches to enforce tumour regression. Nature. 2006;441(7092): 437-443.
[21] KE Q, COSTA M. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1). Mol Pharmacol. 2006;70(5):1469-1480.
|