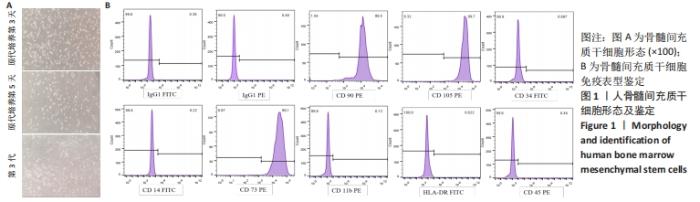
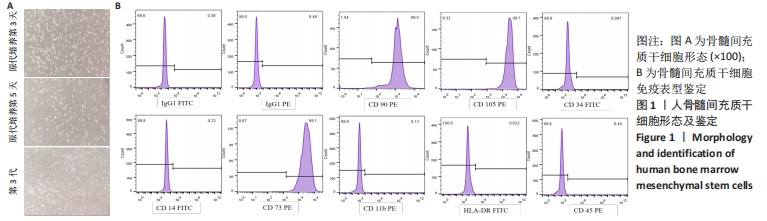
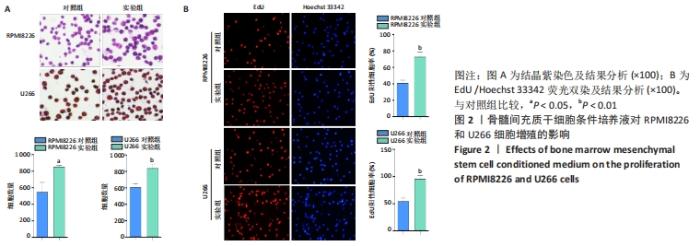
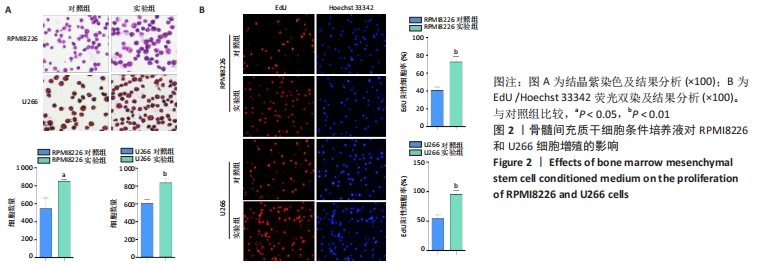
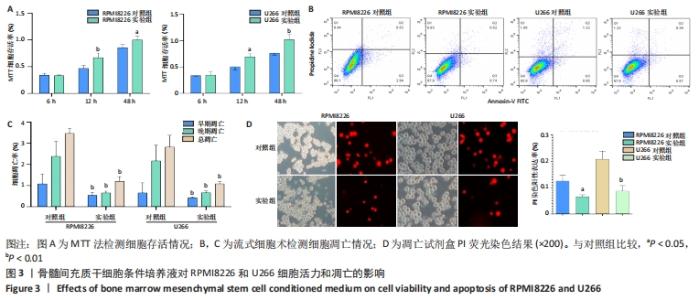
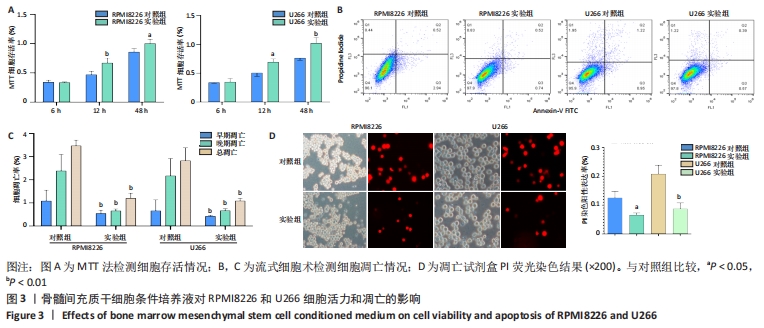
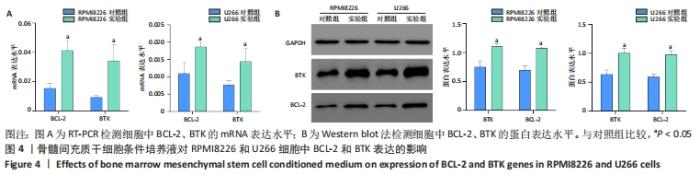
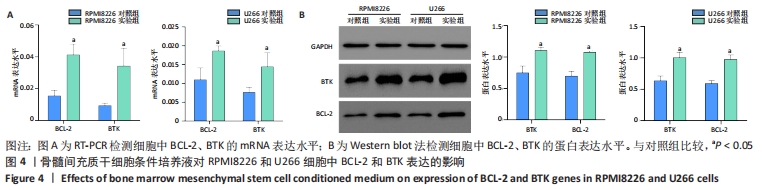
[1] BASAK GW, SRIVASTAVA AS, MALHOTRA R, et al. Multiple myeloma bone marrow niche. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2009;10(3):345-346.
[2] CHEN D, TANG P, LIU L, et al. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells promote cell proliferation of multiple myeloma through inhibiting T cell immune responses via PD-1/PD-L1 pathway. Cell Cycle. 2018;17(7):858-867.
[3] SU N, WANG P, LI Y. Role of Wnt/β-catenin pathway in inducing autophagy and apoptosis in multiple myeloma cells. Oncol Lett. 2016; 12(6):4623-4629.
[4] RUSHWORTH SA, MURRAY MY, ZAITSEVA L, et al. Identification of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase as a therapeutic target in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2014;123(8):1229-1238.
[5] 黄淑娟.新型BTK抑制剂Abivertinib在急性髓细胞白血病中的应用及其作用机制研究[D].杭州:浙江大学,2020.
[6] XU S, DE VEIRMAN K, DE BECKER A, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells in multiple myeloma: a therapeutical tool or target? Leukemia. 2018; 32(7):1500-1514.
[7] CORRE J, MAHTOUK K, ATTAL M, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells are abnormal in multiple myeloma. Leukemia. 2007;21(5): 1079-1088.
[8] ZHANG XX, ZHANG LF, LIU L, et al. Effect of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Patients with Multiple Myelima on Migration of Myeloma Cells In Vitro. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2018;26(2):484-488.
[9] HECHT M, HEIDER U, KAISER M, et al. Osteoblasts promote migration and invasion of myeloma cells through upregulation of matrix metalloproteinases, urokinase plasminogen activator, hepatocyte growth factor and activation of p38 MAPK. Br J Haematol. 2007;138(4):446-458.
[10] LANDSKRON G, DE LA FUENTE M, THUWAJIT P, et al. Chronic inflammation and cytokines in the tumor microenvironment. J Immunol Res. 2014;2014:149185.
[11] JI LL, SONG G, JIANG LM, et al. Evaluation of conditioned medium from placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells as a storage medium for avulsed teeth: An in vitro study. Dent Traumatol. 2021;37(1):73-80.
[12] NATSUIZAKA M, KINUGASA H, KAGAWA S, et al. IGFBP3 promotes esophageal cancer growth by suppressing oxidative stress in hypoxic tumor microenvironment. Am J Cancer Res. 2014;4(1):29-41.
[13] HUI L, CHEN Y. Tumor microenvironment: Sanctuary of the devil. Cancer Lett. 2015;368(1):7-13.
[14] ZHANG YL, FU JX, ZHANG H, et al. Effects of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells on the Biological Characteristics of Migrating and Homing in Multiple Myeloma Cells. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2016;24(2):469-473.
[15] LI B, FU J, CHEN P, et al. Impairment in immunomodulatory function of mesenchymal stem cells from multiple myeloma patients. Arch Med Res. 2010;41(8):623-633.
[16] KIM YH, CHO KA, LEE HJ, et al. Conditioned Medium from Human Tonsil-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Enhances Bone Marrow Engraftment via Endothelial Cell Restoration by Pleiotrophin. Cells. 2020;9(1):221.
[17] 林清凡,解一新,陈婉清,等.人胎盘源间充质干细胞条件培养液可上调缺氧状态下BeWo 细胞活力和紧密连接因子的表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(31):4970-4975.
[18] 邱纪玲,王晓彤,周灏雯,等.间充质干细胞条件培养液修复多种疾病损伤的潜能[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(29):4743-4748.
[19] 田堃. P38 MAPK参与调节人脐带间充质干细胞对人白血病肿瘤细胞的生长抑制[D].北京:北京协和医学院,2011.
[20] ZHAO P, CHEN Y, YUE Z, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulate stemness of multiple myeloma cell lines via BTK signaling pathway. Leuk Res. 2017;57:20-26.
[21] SUZUKI K, SUN R, ORIGUCHI M, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells promote tumor growth through the enhancement of neovascularization. Mol Med. 2011;17(7-8):579-587.
[22] WANG Y, WU X, HU Y. Multiple Myeloma Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Inhibit CD8+ T Cell Function in a Process that May Implicate Fibroblast Activation Protein α. Iran J Immunol. 2019;16(4): 278-290.
[23] SCHINKE C, QU P, MEHDI SJ, et al. The Pattern of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Expression Is an Independent Marker of Outcome in Multiple Myeloma. Clin Cancer Res. 2018;24(12):2913-2919.
[24] ZHANG G, MIAO F, XU J, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow regulate invasion and drug resistance of multiple myeloma cells by secreting chemokine CXCL13. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2020;20(2): 209-217.
[25] 蒋铁斌,李昕,周俊,等.PDCD5在多发性骨髓瘤中的表达及其与BCL-2相关性[J].中南大学学报(医学版),2008,33(9):814-820.
[26] CHEN Q, RAY S, HUSSEIN MA, et al. Role of Apo2L/TRAIL and Bcl-2-family proteins in apoptosis of multiple myeloma. Leuk Lymphoma. 2003;44(7):1209-1214.
[27] ZHANG B, GOJO I, FENTON RG. Myeloid cell factor-1 is a critical survival factor for multiple myeloma. Blood. 2002;99(6):1885-1893.
[28] 黄来全,刘大翔.BTK与PKCβ在多发性骨髓瘤中表达及调控的信号通路机制研究[J].东南大学学报(医学版),2018,37(4):578-583.
[29] 张雯. Bruton’s酪氨酸激酶抑制剂联合硼替佐米对人多发性骨髓瘤细胞的作用及其机制[D].上海:第二军医大学,2017.
[30] 张亮,杜佳,周立为,等.依布硒诱导多发性骨髓瘤细胞凋亡及其机制的研究[J].第三军医大学学报,2014,36(2):110-114.
[31] DENG J, ISIK E, FERNANDES SM, et al. Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibition increases BCL-2 dependence and enhances sensitivity to venetoclax in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia. 2017;31(10):2075-2084.
|