Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (19): 3030-3035.doi: 10.12307/2022.382
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of miR-7-5p on stem cell-like properties of human gastric cancer SGC-7901 cells
Guo Junfu, Li Xiangnan, Ma Tianchi, Miao Lanying
- Teaching and Experiment Center, Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenyang 110847, Liaoning Province, China
-
Received:2021-06-04Revised:2021-07-16Accepted:2021-08-24Online:2022-07-08Published:2021-12-28 -
Contact:Miao Lanying, Professor, Senior experimentalist, Teaching and Experiment Center, Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenyang 110847, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Guo Junfu, MD, Senior experimentalist, Master’s supervisor, Teaching and Experiment Center, Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenyang 110847, Liaoning Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China (Youth Project), No. 81803855 (to GJF); Liaoning Province Doctoral Initiation Project, No. 2019-BS-166 (to GJF); Shenyang Youth Science and Technology Innovation Talent Support Program, No. RC190078 (to GJF)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Guo Junfu, Li Xiangnan, Ma Tianchi, Miao Lanying. Effects of miR-7-5p on stem cell-like properties of human gastric cancer SGC-7901 cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(19): 3030-3035.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
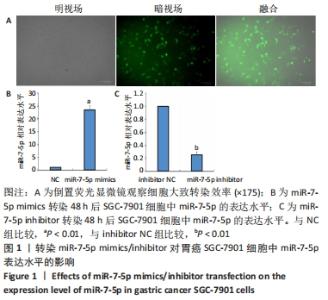
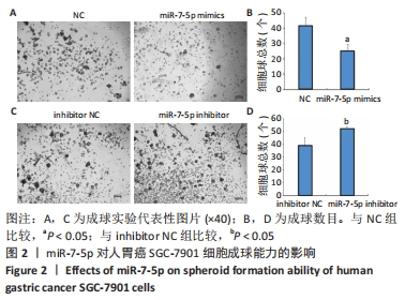
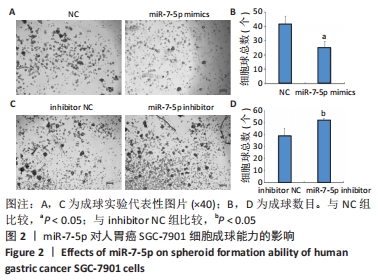
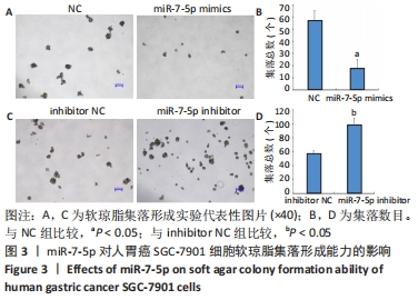
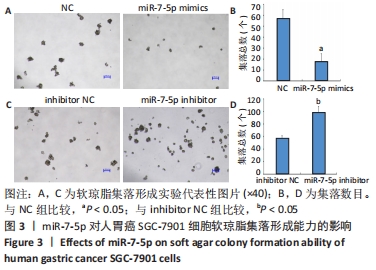
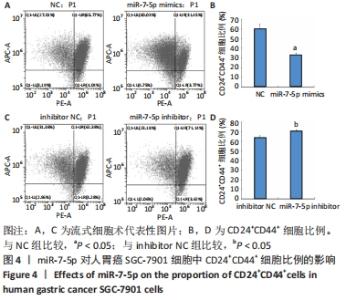
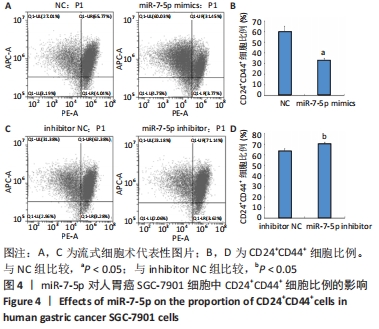
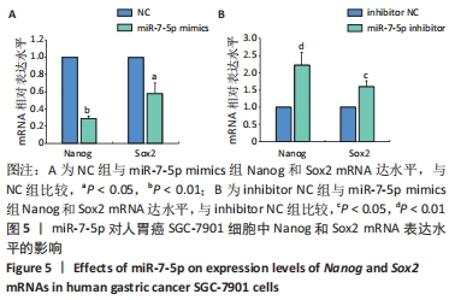
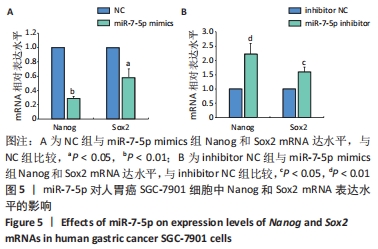
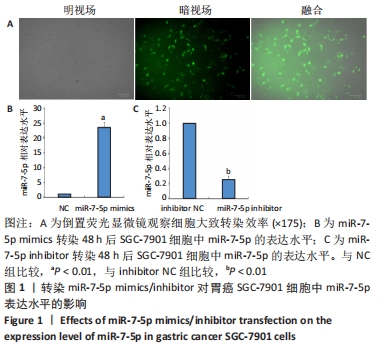
2.1 转染miR-7-5p mimics/inhibitor对人胃癌SGC-7901细胞中miR-7-5p表达水平的影响 为探讨miR-7-5p对胃癌细胞干样特性的影响,该研究首先通过转染miR-7-5p mimics/inhibitor过表达或抑制人胃癌SGC-7901细胞中的miR-7-5p。转染4 h后,通过倒置荧光显微镜观察SGC-7901细胞内的荧光情况,发现绝大部分细胞内都能看到绿色荧光,见图1A,提示细胞转染成功。转染48 h后,RT-qPCR检测结果显示,与NC组比较,miR-7-5p mimics组细胞中miR-7-5p表达水平显著上调(P < 0.01),见图1B;而与inhibitor NC组相比,miR-7-5p inhibitor组细胞中miR-7-5p表达水平则明显下调(P < 0.01),见图1C。结果提示,miR-7-5p mimics/inhibitor能够有效增加或抑制miR-7-5p的表达。"
| [1] SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL RL, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209-249. [2] CARLOMAGNO N, INCOLLINGO P, TAMMARO V, et al. Diagnostic, Predictive, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Molecular Biomarkers in Third Millennium: A Breakthrough in Gastric Cancer. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:7869802. [3] CHAN WL, YUEN KK, SIU SW, et al. Third-line systemic treatment versus best supportive care for advanced/metastatic gastric cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2017; 116:68-81. [4] CLARKE MF, DICK JE, DIRKS PB, et al. Cancer stem cells--perspectives on current status and future directions: AACR Workshop on cancer stem cells. Cancer Res. 2006;66(19):9339-9344. [5] GZIL A, ZARĘBSKA I, BURSIEWICZ W, et al. Markers of pancreatic cancer stem cells and their clinical and therapeutic implications. Mol Biol Rep. 2019;46(6):6629-6645. [6] BRUNGS D, AGHMESHEH M, VINE KL, et al. Gastric cancer stem cells: evidence, potential markers, and clinical implications. J Gastroenterol. 2016;51(4):313-326. [7] WANG D, LU P, ZHANG H, et al. Correction: Oct-4 and Nanog promote the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of breast cancer stem cells and are associated with poor prognosis in breast cancer patients. Oncotarget. 2021;12(10):1024-1025. [8] 马颖光,张自森,于泳,等.miR-513a-3p靶向鼠双微体基因2对胃癌细胞增殖迁移侵袭的影响[J].中华肿瘤杂志,2020,32(1):30-36. [9] 孙梦瑶,蔡思,王杰,等.外泌体miRNAs在胃癌中的作用[J].中华检验医学杂志,2018,41(7):499-502. [10] MI Y, ZHANG D, JIANG W, et al. miR-181a-5p promotes the progression of gastric cancer via RASSF6-mediated MAPK signalling activation. Cancer Lett. 2017;389:11-22. [11] TROSCHEL FM, BÖHLY N, BORRMANN K, et al. miR-142-3p attenuates breast cancer stem cell characteristics and decreases radioresistance in vitro. Tumour Biol. 2018;40(8):1010428318791887. [12] ZHANG GF, WU JC, WANG HY, et al. Overexpression of microRNA-205-5p exerts suppressive effects on stem cell drug resistance in gallbladder cancer by down-regulating PRKCE. Biosci Rep. 2020;40(9): BSR20194509. [13] 龚立刚,艾成思,王梦萍.miR-486-5p靶向FOXO1抑制结肠癌干细胞干性的初步研究[J].安徽医科大学学报,2020,55(4):528-533. [14] JIN HF, WANG JF, SHAO M, et al. Down-Regulation of miR-7 in Gastric Cancer Is Associated With Elevated LDH-A Expression and Chemoresistance to Cisplatin. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:555937. [15] HU C, ZHU S, WANG J, et al. Schistosoma japonicum MiRNA-7-5p Inhibits the Growth and Migration of Hepatoma Cells via Cross-Species Regulation of S-Phase Kinase-Associated Protein 2. Front Oncol. 2019;9:175. [16] 章凯,王建洪,罗小邹.miRNA-7在鼻咽癌中的表达及临床意义[J].中国耳鼻咽喉头颈外科,2018,25(9):478-480. [17] 刘华松,来金宇,郭家龙,等.miRNA-7过表达对食管癌细胞TE-1顺铂敏感性的影响及机制研究[J].湖北医药学院学报,2019,38(4): 356-360. [18] 王妹,姜钧耀,杜雨軒,等.miR-7低表达导致非小细胞肺癌细胞吉非替尼耐药的作用机制[J].医学研究生学报,2020,33(5):460-465. [19] YE T, YANG M, HUANG D, et al. MicroRNA-7 as a potential therapeutic target for aberrant NF-κB-driven distant metastasis of gastric cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019;38(1):55. [20] XIE J, CHEN M, ZHOU J, et al. miR-7 inhibits the invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer cells by suppressing epidermal growth factor receptor expression. Oncol Rep. 2014;31(4):1715-1722. [21] 谷泽慧,任立群,李琪,等.奥沙利铂通过调控miRNA-7-5p/RAF-1促进胃癌SGC-7901细胞凋亡的研究[J].肿瘤防治研究,2020,47(3): 175-180. [22] LIN J, LIU Z, LIAO S, et al. Elevated microRNA-7 inhibits proliferation and tumor angiogenesis and promotes apoptosis of gastric cancer cells via repression of Raf-1. Cell Cycle. 2020;19(19):2496-2508. [23] 葛雯.肿瘤干细胞与microRNA的关系[J].中国医药指南,2015,13(1): 47-48. [24] TAKAISHI S, OKUMURA T, TU S, et al. Identification of gastric cancer stem cells using the cell surface marker CD44. Stem Cells. 2009;27(5): 1006-1020. [25] BERINDAN-NEAGOE I, MONROIG PDEL C, PASCULLI B, et al. MicroRNAome genome: a treasure for cancer diagnosis and therapy. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64(5):311-336. [26] XUE X, FEI X, HOU W, et al. miR-342-3p suppresses cell proliferation and migration by targeting AGR2 in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Lett. 2018;412:170-178. [27] ZHU Y, GU J, LI Y, et al. MiR-17-5p enhances pancreatic cancer proliferation by altering cell cycle profiles via disruption of RBL2/E2F4-repressing complexes. Cancer Lett. 2018;412:59-68. [28] SUN X, LI J, SUN Y, et al. miR-7 reverses the resistance to BRAFi in melanoma by targeting EGFR/IGF-1R/CRAF and inhibiting the MAPK and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways. Oncotarget. 2016;7(33):53558-53570. [29] XU N, LIAN YJ, DAI X, et al. miR-7 Increases Cisplatin Sensitivity of Gastric Cancer Cells Through Suppressing mTOR. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2017;16(6):1022-1030. [30] ZHOU N, HAO S, HUANG Z, et al. MiR-7 inhibited peripheral nerve injury repair by affecting neural stem cells migration and proliferation through cdc42. Mol Pain. 2018;14:1744806918766793. [31] CHANG YL, ZHOU PJ, WEI L, et al. MicroRNA-7 inhibits the stemness of prostate cancer stem-like cells and tumorigenesis by repressing KLF4/PI3K/Akt/p21 pathway. Oncotarget. 2015;6(27):24017-24031. [32] JIA B, LIU W, GU J, et al. MiR-7-5p suppresses stemness and enhances temozolomide sensitivity of drug-resistant glioblastoma cells by targeting Yin Yang 1. Exp Cell Res. 2019;375(1):73-81. [33] PAN M, LI M, YOU C, et al. Inhibition of breast cancer growth via miR-7 suppressing ALDH1A3 activity concomitant with decreasing breast cancer stem cell subpopulation. J Cell Physiol. 2020;235(2):1405-1416. [34] NGUYEN PH, GIRAUD J, CHAMBONNIER L, et al. Characterization of Biomarkers of Tumorigenic and Chemoresistant Cancer Stem Cells in Human Gastric Carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2017;23(6):1586-1597. [35] ISHIMOTO T, NAGANO O, YAE T, et al. CD44 variant regulates redox status in cancer cells by stabilizing the xCT subunit of system xc(-) and thereby promotes tumor growth. Cancer Cell. 2011;19(3):387-400. [36] HONG Y, QIN H, LI Y, et al. FNDC3B circular RNA promotes the migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells via the regulation of E-cadherin and CD44 expression. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(11):19895-19910. [37] ZENG JF, MA XQ, WANG LP, et al. MicroRNA-145 exerts tumor-suppressive and chemo-resistance lowering effects by targeting CD44 in gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2017;23(13):2337-2345. [38] LIU G, LIU GX, FANG Y,et al. Clinicopathological and prognostic value of CD24 expression in breast cancer: a meta-analysis. Int J Biol Markers. 2017;32(2):e182-e189. [39] WANG JL, GUO CR, SU WY,et al. CD24 Overexpression Related to Lymph Node Invasion and Poor Prognosis of Colorectal Cancer. Clin Lab. 2018; 64(4):497-505. [40] LI Y, WANG R, XIONG S, et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts promote the stemness of CD24+ liver cells via paracrine signaling. J Mol Med (Berl). 2019;97(2):243-255. [41] WANG YC, WANG JL, KONG X, et al. CD24 mediates gastric carcinogenesis and promotes gastric cancer progression via STAT3 activation. Apoptosis. 2014;19(4):643-656. [42] TAKAHASHI M, NAKAJIMA M, OGATA H, et al. CD24 expression is associated with progression of gastric cancer. Hepatogastroenterology. 2013;60(124):653-658. [43] DENG W, GU L, LI X, et al. CD24 associates with EGFR and supports EGF/EGFR signaling via RhoA in gastric cancer cells. J Transl Med. 2016; 14:32. [44] FENG S, ZHENG Z, FENG L, et al. Proton pump inhibitor pantoprazole inhibits the proliferation, self‑renewal and chemoresistance of gastric cancer stem cells via the EMT/β‑catenin pathways. Oncol Rep. 2016;36(6):3207-3214. [45] ZHANG C, LI C, HE F, et al. Identification of CD44+CD24+ gastric cancer stem cells. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2011;137(11):1679-1686. [46] BASATI G, MOHAMMADPOUR H, EMAMI RAZAVI A. Association of High Expression Levels of SOX2, NANOG, and OCT4 in Gastric Cancer Tumor Tissues with Progression and Poor Prognosis. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2020;51(1):41-47. [47] XIAO Y, PAN J, GENG Q, et al. LncRNA MALAT1 increases the stemness of gastric cancer cells via enhancing SOX2 mRNA stability. FEBS Open Bio. 2019;9(7):1212-1222. [48] LI L, WEI X, WU B, et al. siRNA-mediated knockdown of ID1 disrupts Nanog- and Oct-4-mediated cancer stem cell-likeness and resistance to chemotherapy in gastric cancer cells. Oncol Lett. 2017;13(5):3014-3024. |
| [1] | Guo Junfu, Gao Xia, Chang Jiarong, Gao Shiqi, Miao Lanying. Effects of nuclear factor of activated T cells 5 on migration, invasion and cell cycle of human gastric cancer MGC803 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(17): 2732-2737. |
| [2] | Zhao Jiling, Peng Yi, Peng Zhiyong, Yu Guolong. Effects of human umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells secreting tumor necrosis factor alpha stimulating gene-6 protein on conversion of mouse bone marrow-derived macrophage subtypes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(13): 2012-2019. |
| [3] | Xu Guilan, Song Jiansheng, Yang Shijiang. Regulation of S100A4 gene silencing by ultrasound microbubbles on the stemness and epithelial-mesenchymal transformation of gastric cancer stem cells#br# [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4025-4031. |
| [4] | Du Ruiling. Lutein regulates proliferation and apoptosis of gastric cancer stem cells through PI3K/AKT signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(29): 4593-4598. |
| [5] | Han Fang-zheng, Zhang Xiao-lin, Dong Wei-yi, Xie Yun-ting. Co-expression of CD24 and CD44 in gastric carcinoma and its influence on clinicopathological parameters and prognosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(29): 4625-4630. |
| [6] | Yuan Hang, Liu Bin, Tie Ya-teng, Sun Ya-min, Xin Qing, Su Qin-jun, Li Shuang-ming. Distribution and morphological characteristics of CD44+/SOX2+ cancer stem cells in colorectal carcinoma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(9): 1329-1333. |
| [7] | Zhang Ze, Zeng Xiang-yong, Duan Shan. Expression of tumor stem cell surface marker CD44 in gastric cancer tissues and its significance [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(45): 6760-6765. |
| [8] | Zhai Xiao-jian, Zhang Hao, Zhang Yi-ni, Ni Ming, Wang Zheng. Relationship between cell activity and multidrug resistance of CD44+CD24-/low breast cancer stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(32): 4758-4763. |
| [9] | Wu Gao-feng, Liu Xi-ping, Yang Bai-lin, Li Pei-qing, Ming Hai-xia, Zhang Wei. Morphology and proliferation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and expressions of CD34 and CD44 under stomach cancer microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(14): 2040-2045. |
| [10] | Li Shi-ting, Tao Wen-cheng. Effects of cancer stem cell surface marker CD44 in gastric cancer invasion and lymph node metastasis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(23): 3669-3673. |
| [11] | Zhou Bin, Zhang Fang-jie, Luo Wei, Gao Shu-guang, Zeng Chao, Xiong Yi-lin, Li Yu-sheng,. Effects of hyaluronic acid on osteopontin mRNA and CD44 mRNA expression in human osteoarthritic chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(38): 6172-6178. |
| [12] | Zhang Wei, Kang Hai-han, Zhang Yong-lei, Kong Ye, Hua Ya-wei. Different release properties and targeting effects of sustained-release drugs for the treatment of gastric cancer [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(8): 1481-1488. |
| [13] | Zhang Deng-cai, Liu Bin, Zhang Li-hua, Zhang Cai-lan, Yang Yan-li, Su Qin-jun, Shi Min, Dong Liang, Ha Ying-di . Morphology and distribution of CD44+/Oct4+ colorectal cancer stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(49): 8461-8467. |
| [14] | Xu Wen, Tian Chen, Li Fang, Xia Bing, Guo Qing, Zhang Yi-zhuo. In vitro proliferation and passage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells impact homing-associated factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(40): 7102-7109. |
| [15] | Chen Hao, Xu Lang. Signal pathway effects on gastric cancer stem cells and gastric cancer occurrence [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(14): 2532-2537. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||