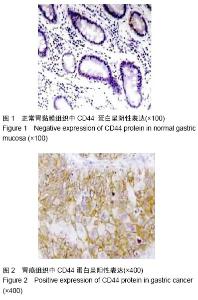
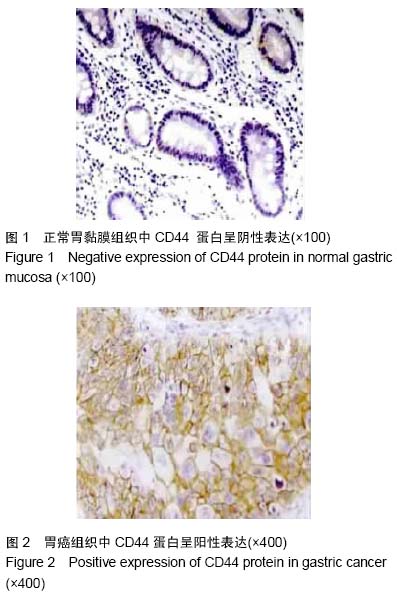
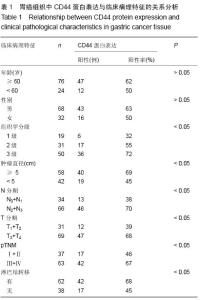
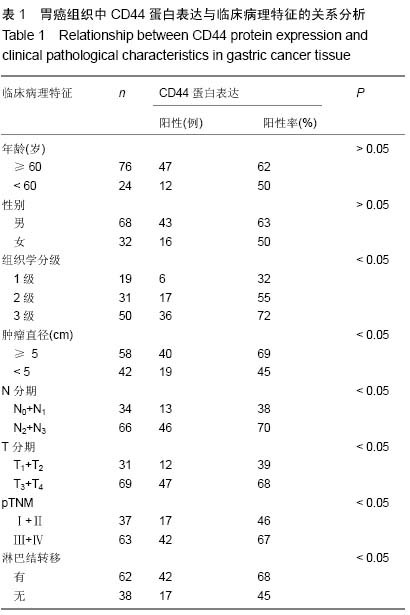
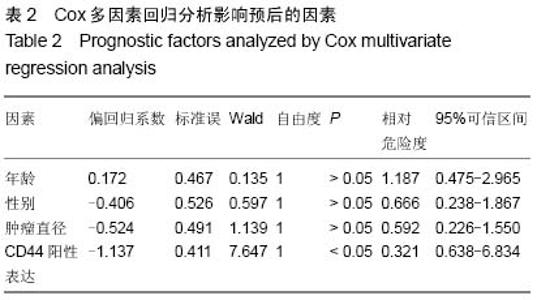
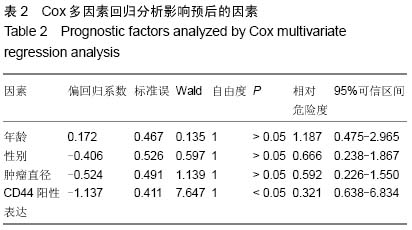
| [1] 王军,张勇,任芳,等.干细胞标志物CD44与胃癌临床病理特征的相关性研究[J].现代肿瘤医学,2013,21(3):585-588.
[2] 张岩松,李德春,李敏,等.CD44在胃癌组织及腹膜转移灶中的表达及其意义[J].江苏医药,2012,38(1):91-92.
[3] 谢建伟,黄昌明,郑朝辉,等.肿瘤干细胞表面标记物CD44在胃癌中的表达及其意义[J].中华胃肠外科杂志,2013,16(11): 1107-1112.
[4] 吴琼.MicroRNA-17-92促进胃癌干细胞自我更新及增殖的分子机制[D].西安:第四军医大学,2013.
[5] 周志华,张建东,徐桂芳,等.基于克隆形态分选胃癌干细胞及其对氟尿嘧啶敏感性的检测[J].中华胃肠外科杂志,2013,16(4): 376-380.
[6] 杨宏琼,周志华,张尤历,等.人胃癌细胞株SGC-7901的克隆形态观察及含肿瘤干细胞克隆的鉴定[J].中华肿瘤杂志,2013, 35(3): 164-169.
[7] 匡弢,王雷,宋文,等.胃癌肿瘤干细胞的分离与成脂分化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(36):6718-6721.
[8] 周雨,易德保,蒋传命,等.老年患者胃癌组织中CD44和ABCG2的表达及相关性[J].中国老年学杂志,2014,34(24):7042-7044.
[9] 宁志丰,王春,刘复兴,等.hMLH1和干细胞标志物CD44在胃癌的表达及相互间的关系[J].解剖学研究,2012,34(5):343-346.
[10] 张岩松,李德春,李敏,等.从腹腔游离癌细胞中分离胃癌干细胞的可行性及其意义[J].中国普通外科杂志,2012,21(4):474-476.
[11] 荣黎,吴小翎.胃癌侧群细胞耐药性研究及干细胞相关基因检测[J].世界科技研究与发展,2011,33(6):1081-1084.
[12] 陈军.胃癌干细胞干性特性及化疗药物对其影响的初步研究[D].重庆:第三军医大学,2013.
[13] 曹亮.乳斑微转移模型在胃癌干细胞及前驱细胞研究中的作用及临床意义[D]. 大连:大连医科大学,2011.
[14] 卫勃.应激性反应原作用于MicroRNA与CD44之间表达平衡进而影响胃癌干细胞的表型形成的初步研究[D].北京:军医进修学院,2010.
[15] 蔡成,俞继卫,吴巨钢,等.TGF-β1诱导胃癌细胞上皮间质转化及促进干细胞特性获得的研究[J].国际外科学杂志,2012,39(12): 824-829.
[16] 周雨,胡程,段海瑞,等.CD44+胃癌细胞的获取及其干细胞特性的初步鉴定[J].大家健康:下旬版,2014,8(1):4-6.
[17] 侯杰,杨镛.胃癌干细胞表面标志物的研究进展[J].中国民族民间医药,2014,23(18):19-20.
[18] 荣黎,吴小翎.胃癌SGC-7901细胞株侧群细胞分选及生物学特性的初步研究[J].中国生物工程杂志,2011,31(11):38-43.
[19] 任芳.胃癌干细胞标志物与临床和病理的相关性研究[D].上海:上海交通大学,2012.
[20] Choi HS, Kim WT, Ryu CJ. Antibody approaches to prepare clinically transplantable cells from human embryonic stem cells: identification of human embryonic stem cell surface markers by monoclonal antibodies. Biotechnol J. 2014;9(7): 915-920.
[21] Zhu L, Ruan Z, Yin Y, et al. Expression and significance of DLL4--Notch signaling pathway in the differentiation of human umbilical cord derived mesenchymal stem cells into cardiomyocytes induced by 5-azacytidine. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2015;71(1):249-253.
[22] Dhanasekaran M, Indumathi S, Kanmani A, et al. Surface antigenic profiling of stem cells from human omentum fat in comparison with subcutaneous fat and bone marrow. Cytotechnology. 2012;64(5):497-509.
[23] 陈军,崔有宏,郝迎学,等.5-氟尿嘧啶及长春新碱对胃癌细胞SGC-7901干细胞相关特性的影响[J].第三军医大学学报,2013, 35(12):1247-1251.
[24] 恽艳.肿瘤干细胞标志Lgr5和CD44在胃癌中的表达及临床病理意义[D]. 苏州:苏州大学,2014.
[25] 李渊.CD44在胃癌发生中的作用[J].医学综述,2014,20(6): 1029-1033.
[26] 李霞,徐桂芳,张伟杰,等.胃癌干细胞的分离鉴定以及干细胞特性研究[J].胃肠病学,2014,19(9):517-522.
[27] Andrews TE, Wang D, Harki DA. Cell surface markers of cancer stem cells: diagnostic macromolecules and targets for drug delivery. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2013;3(2):121-142.
[28] Mohsen-Kanson T, Hafner AL, Wdziekonski B, et al. Expression of cell surface markers during self-renewal and differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;430(3):871-875.
[29] 陆国玉,吴晓飞,周蕾,等.CD133和CD44在胃腺癌中的表达及其与E-cadherin的关系[J].南方医科大学学报,2013,33(11):1632- 1642.
[30] Biddle A, Gammon L, Fazil B, et al. CD44 staining of cancer stem-like cells is influenced by down-regulation of CD44 variant isoforms and up-regulation of the standard CD44 isoform in the population of cells that have undergone epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. PLoS One. 2013;8(2): e57314.
[31] 孙艳花,孙艳丽,冉学红,等.黏附分子CD44表达对白血病细胞黏附、迁移及浸润的影响[J].中华血液学杂志,2013,34(1):60-63.
[32] 杨世斌,肖隆斌,许峰峰,等.EPCAM、CD44和CD24在胃癌组织中的表达及其临床意义[J].中国病理生理杂志,2012,28(7): 1224-1229.
[33] Hiscox S, Baruha B, Smith C, et al. Overexpression of CD44 accompanies acquired tamoxifen resistance in MCF7 cells and augments their sensitivity to the stromal factors, heregulin and hyaluronan. BMC Cancer. 2012 Oct 6;12:458.
[34] Gisina AM, Lupatov AY, Karalkin PA, et al. Subpopulation of colorectal adenocarcinoma cells co-expressing CD133 and cancer stem cells markers of other tumors. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2012;152(6):739-742.
[35] Idikio HA. Human cancer classification: a systems biology- based model integrating morphology, cancer stem cells, proteomics, and genomics. J Cancer. 2011;2:107-115.
[36] Martelli AM, Evangelisti C, Chiarini F, et al. The emerging role of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/ akt/mammalian target of rapamycin signaling network in cancer stem cell biology. Cancers (Basel). 2010;2(3):1576-1596.
[37] 杨家佳,张琳,郑茂金,等.肿瘤干细胞标记物CD44和EpCAM在胃癌中的表达及意义[J].徐州医学院学报,2014,34(10):661-664.
[38] 吴生华,俞继卫,姜波健.胃癌干细胞的研究现状[J].腹部外科, 2009,22(6):371-373.
[39] 孙晓彤.胃癌中肿瘤干细胞标志物的初步鉴定、表达及其临床病理学意义[D]. 兰州:兰州大学,2010. |