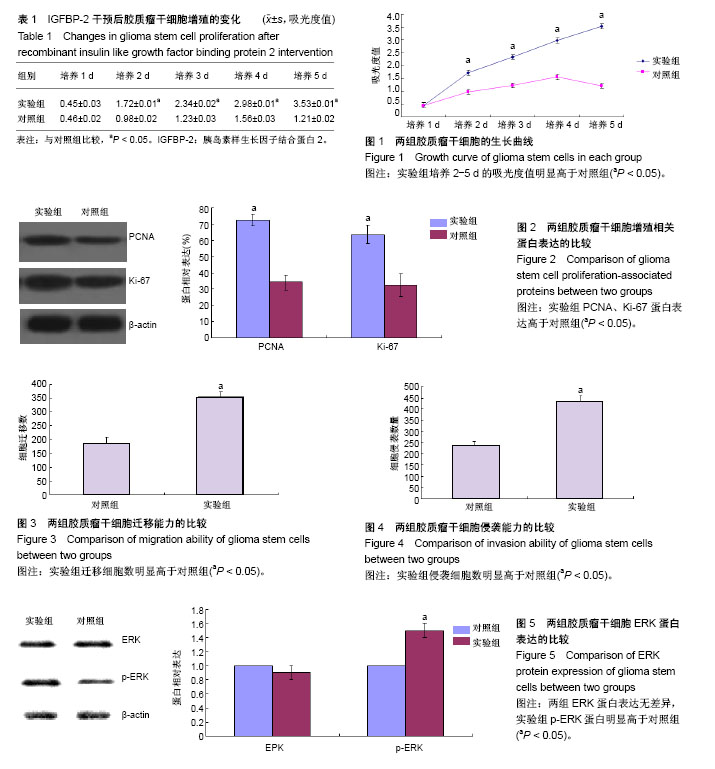
| [1] Holly JMP, Broadhurst J, MansorR,et al. Hyperglycemia Promotes TMPRSS2-ERG Gene Fusion in Prostate Cancer Cells via Upregulating Insulin-Like Growth Factor-Binding Protein-2. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2017;8:305.[2] 高松,郝继辉.胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白2在肿瘤恶性生物学行为中的作用及其临床应用[J].中国肿瘤临床, 2017,44(16): 826-830.[3] Xi G, Wai C, DeMambro V, et al. IGFBP-2 directly stimulates osteoblast differentiation.J Bone Miner Res. 2014;29(11): 2427-2438.[4] Milanesi E, Zanardini R, Rosso G, et al. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 2 in bipolar disorder: An expression study in peripheral tissues. World J Biol Psychiatry. 2017:1-9.[5] 李芳.胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白2与恶性肿瘤研究进展[J].临床合理用药杂志,2011,4(14):151-152.[6] 邵婉珍,王森,郭雄.胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白-2在骨软骨疾病发生发展中的作用[J].国外医学(医学地理分册), 2017,38(3): 302-304.[7] Han S, Meng L, Han S, et al. Plasma IGFBP-2 levels after postoperative combined radiotherapy and chemotherapy predict prognosis in elderly glioblastoma patients.PLoS One. 2014;9(4):e93791.[8] Hassan WA, Bjerre M, Hjortebjerg R, et al. Letter to the editor concerning 'Elevated serum antibodies against insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-2 allow detecting early-stage cancers: evidences from glioma and colorectal carcinoma studies’. Ann Oncol. 2015;26(1):252-253. [9] 魏亚辉,侯保秋.IGF-2及IGFBP-2与脑神经胶质瘤侵袭能力的相关性分析[J].昆明医科大学学报,2015,36(5):92-95.[10] 刘小兵.脑胶质瘤VEGF,bFGF,IGFBP-2在血浆和脑脊液的定量分析及意义[D].石家庄:河北医科大学,2010.[11] Zheng S, Houseman EA, Morrison Z, et al. DNA hypermethylation profiles associated with glioma subtypes and EZH2 and IGFBP2 mRNA expression. Neuro Oncol. 2011;13(3):280-289.[12] Yang P, Yan W, Zhang W, et al. Whole-genome messenger RNA profiling reveals genes involved in malignant progression of glioma. Zhonghua Yi XueZaZhi. 2013;93(1): 5-7. [13] Elmlinger MW, Deininger MH, Schuett BS, et al. In vivo expression of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-2 in human gliomas increases with the tumor grade. Endocrinology. 2001;142(4):1652-1658.[14] 李法平,陈帅奇,王艳波,等.免疫磁珠法分离膀胱癌CDl33+细胞及生物学行为研究[J].中华实验外科杂志, 2014,31(12): 2697-2699.[15] 邢艳玲,吴静.蛋白激酶Cζ抑制剂对皮肤鳞癌细胞A-431增殖和侵袭的影响[J].天津医药,2017,45(6): 566-570.[16] 吴爱兵,黎明春,麦宗炯,等.CK2α通过PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β信号通路调控肺腺癌A549细胞的侵袭及迁移[J].中国肺癌杂志, 2017, 20(4):233-238.[17] Shi Z, Henwood MJ, Bannerman P, et al. Primary pigmented nodular adrenocortical disease reveals insulin-like growth factor binding protein-2 regulation by protein kinase A. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2007;17(2):113-121.[18] 许淑芬,刘磊,方艳秋,等.IGFBP-2在卵巢肿瘤组织中的表达及临床意义[J].中国妇幼保健,2013,28(27):4537-4539.[19] 杨海成,王秦豪,刘喜平,等.IGFBP2在肿瘤发生发展中的作用[J]. 医学分子生物学杂志,2015,12(3):233-237.[20] 蔡文品,梁世周.血清胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白2在直肠癌早期诊断中的价值[J].中华全科医学, 2017,15(2):308-310.[21] 许淑芬,刘磊,方艳秋,等.RNAi技术沉默IGFBP-2基因对人乳腺癌细胞株MCF-7增殖的影响[J].中国妇幼保健, 2013,28(28): 4719-4721.[22] 郭兆刚,欧绍武.IGFBP-2对人胶质瘤细胞的恶性增殖和细胞周期进程的影响[J].解剖科学进展, 2014,20(3):279-282,287.[23] Han S, Li Z, Master LM, et al. Exogenous IGFBP-2 promotes proliferation, invasion, and chemoresistance to temozolomide in glioma cells via the integrin β1-ERK pathway. Br J Cancer. 2014;111(7):1400-1409. [24] 韩圣,吴安华,王运杰.IGFBP-2对U251细胞增殖和ERK1/2磷酸化及核转移的影响[J].山东医药,2010,50(8):10-12.[25] Russo VC, Schütt BS, Andaloro E, et al. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-2 binding to extracellular matrix plays a critical role in neuroblastoma cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. Endocrinology. 2005;146(10):4445-4455. [26] 邓裕佳.胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白-2与胶质瘤的研究进展[J].国际神经病学神经外科学杂志, 2017,44(2):217-220.[27] 张萌萌,郑丽华,张香梅,等. TET1与肿瘤侵袭转移关系的研究进展[J].国际外科学杂志,2018,45(1):65-68.[28] 杜媛鲲,米源,陈阁,等. Gli通过PI3K/AKT途径促进肺腺癌A549细胞侵袭转移的研究[J].河北医科大学学报,2018,39(1):24-28.[29] Zhao YD, Zhang QB, Chen H,et al.Research on human glioma stem cells in China.Neural Regen Res. 2017;12(11): 1918-1926.[30] Han S, Li Z, Master LM, et al. Exogenous IGFBP-2 promotes proliferation, invasion, and chemoresistance to temozolomide in glioma cells via the integrin β1-ERK pathway. Br J Cancer. 2014;111(7):1400-1409. [31] 杨雅芝,张小燕,李剑.间充质干细胞衰老相关信号通路[J].中国实验血液学杂志, 2018,26(1):307-310.[32] Ren H, Ma J, Si L, et al. Low dose of acacetin promotes breast cancer MCF-7 cells proliferation through the activation of ERK/ PI3K /AKT signaling pathway. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov.2018 Apr 20. [Epub ahead of print][33] Brunetti JE, Foscaldi S, Quintana VM, et al. Role of the ERK1/2 Signaling Pathway in the Replication of Junín and Tacaribe Viruses. Viruses. 2018;10(4): E199.[34] Jin XL, Li PF, Zhang CB,et al.Electroacupuncture alleviates cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury via modulation of the ERK1/2 signaling pathway.Neural Regen Res. 2016;11(7): 1090-1098.[35] 刘盟盟.Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK信号通路在肿瘤中的研究进展[J].东方食疗与保健,2017,(5):220.[36] 王杰.KIF15通过MEK-ERK信号通路促进胰腺癌细胞的增殖及侵袭转移[D].贵阳:贵州医科大学,2017.[37] Cincin ZB, Kiran B, Baran Y, et al. Hesperidin promotes programmed cell death by downregulation of nongenomic estrogen receptor signalling pathway in endometrial cancer cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;103:336-345.[38] Noeparast A, Giron P, De Brakeleer S, et al. Type II RAF inhibitor causes superior ERK pathway suppression compared to type I RAF inhibitor in cells expressing different BRAF mutant types recurrently found in lung cancer. Oncotarget. 2018;9(22):16110-16123.[39] 陈丽莎,徐永成,余志金,等.JMJD2B通过ERK-MAPK途径影响人结直肠癌细胞的恶性表型[J].南京医科大学学报(自然科学版), 2015,35(7):962-967.[40] 吴忱莼,李留霞,郭瑞霞,等.阻断丝裂原活化蛋白激酶信号通路对卵巢癌细胞增殖和侵袭能力的影响[J].肿瘤, 2015,35(4): 384-389,403. |