Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (5): 674-678.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2997
Previous Articles Next Articles
MicroRNA-138-5p regulates chondrocyte proliferation and autophagy
Ma Zetao, Zeng Hui, Wang Deli, Weng Jian, Feng Song
- Department of Orthopedics, Peking University Shenzhen Hospital, Shenzhen 518036, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2020-04-07Revised:2020-05-07Accepted:2020-06-05Online:2021-02-18Published:2020-11-28 -
Contact:Zeng Hui, MD, Chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Peking University Shenzhen Hospital, Shenzhen 518036, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Ma Zetao, Associate chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Peking University Shenzhen Hospital, Shenzhen 518036, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the Scientific Research Plan of Shenzhen, No. JCYJ20170307111755218
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ma Zetao, Zeng Hui, Wang Deli, Weng Jian, Feng Song. MicroRNA-138-5p regulates chondrocyte proliferation and autophagy[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 674-678.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
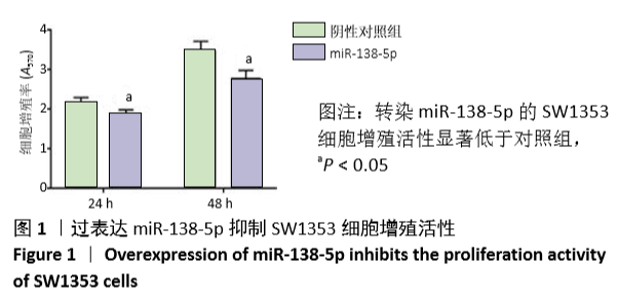
2.1 过表达miR-138-5p抑制软骨细胞的增殖mRNA活性 为了研究miR-138-5p对体外培养的SW1353细胞系增殖活性的影响,在对照组细胞中转染阴性对照miRNA,实验组细胞转染miR-138-5p模拟物。在培养24 h及48 h时收集细胞,用CCK-8试剂盒检测细胞增殖活性。结果发现,培养24 h细胞增殖率分别为:对照组(2.15±0.13)%,实验组(1.87±0.11)%,P=0.047;培养48 h 细胞增殖率分别为:对照组(3.48±0.23)%;实验组(2.79±0.19)%,P=0.016。从结果中可以看出,转染miR-138-5p的SW1353细胞增殖活性显著低于对照组,该结果提示在细胞中miR-138-5p表达的上调会抑制软骨细胞的增殖(图1)。"

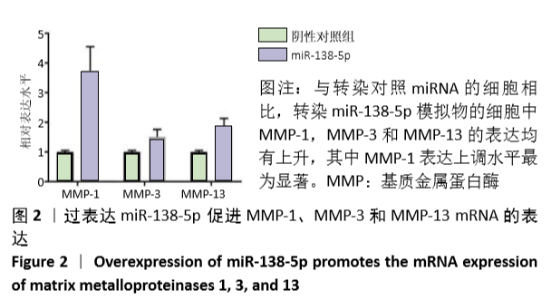
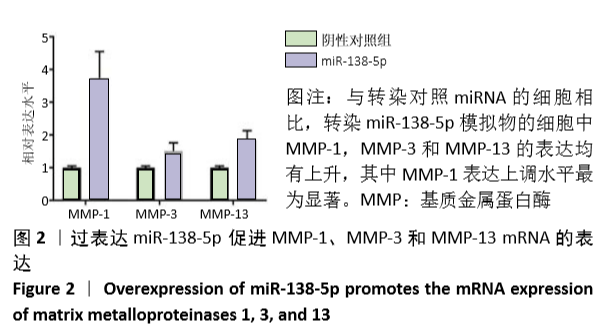
2.2 过表达miR-138-5p促进基质金属蛋白酶mRNA表达 软骨细胞通常通过分泌金属蛋白酶降解细胞外基质,引发软骨退化。为了研究miR-138-5p对软骨细胞基质金属蛋白酶表达水平的影响,设计合成了靶向基质金属蛋白酶1,3和13 mRNA的上下游引物,通过荧光定量PCR实验检测其在细胞内的表达水平。结果表明,与转染对照miRNA的细胞相比,转染miR-138-5p模拟物的细胞中基质金属蛋白酶1、基质金属蛋白酶3和基质金属蛋白酶13 miRNA的表达水平均有上升。其中基质金属蛋白酶1相对表达水平升高了(3.74±0.81)倍(P=0.004 3),基质金属蛋白酶3相对表达水平升高了(1.52±0.25)倍(P=0.024 2),基质金属蛋白酶13相对表达水平升高了(1.84±0.29)倍(P=0.007 8),基质金属蛋白酶1表达上调水平最为显著。这些结果表明,细胞内上调表达的miR-138-5p会促进软骨细胞基质金属蛋白酶的分泌(图2)。"
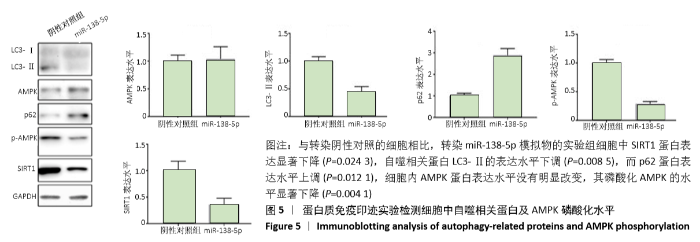
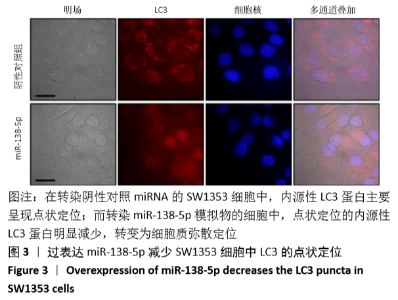
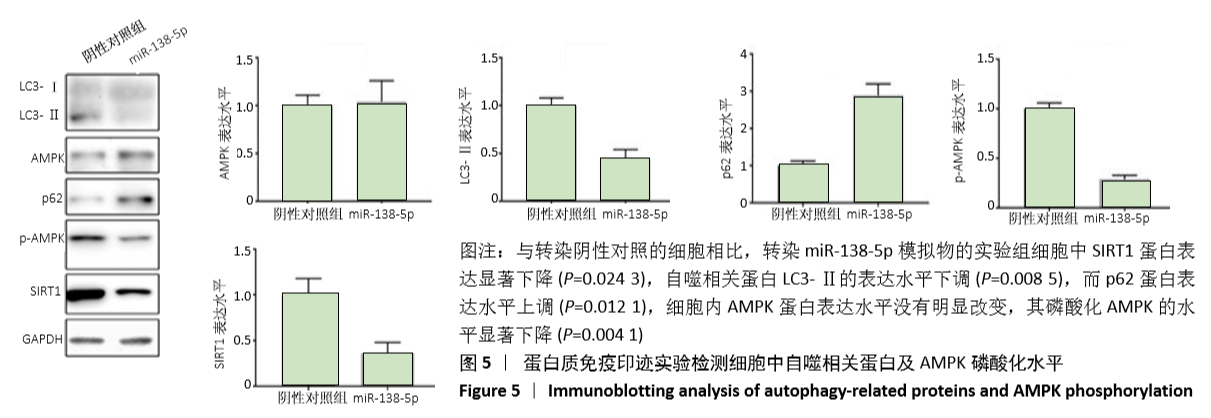
2.5 miR-138-5p影响SIRT1/AMPK信号通路 为了研究miR-138-5p是否可以通过直接靶向SIRT1影响其表达,进而影响AMPK信号通路,利用蛋白质免疫印迹实验检测了各组细胞LC3、p62、AMPK、p-AMPK及SIRT1蛋白的表达水平。结果发现,与转染阴性对照的细胞相比,转染miR-138-5p模拟物的实验组细胞中SIRT1蛋白表达水平显著下降(P=0.024 3),进一步说明miR-138-5p可以直接调控SIRT1的表达水平。另外,结果还发现自噬相关蛋白LC3-II的表达水平下调(P=0.008 5),而p62蛋白表达水平上调(P=0.012 1),这也进一步证实过表达miR-138-5p可以抑制软骨细胞的自噬活性。此外,还发现,尽管细胞内AMPK蛋白表达水平没有明显改变,但其磷酸化AMPK的水平显著下降(P=0.004 1),这提示过表达miR-138-5p 影响了AMPK的激活(图5)。"
| [1] VINA ER, KWOH CK. Epidemiology of osteoarthritis: literature update. Curr Opin Rheumatol.2018; 30(2): 160-167. [2] SILVERWOOD V, BLAGOJEVIC-BUCKNALL M, JINKS C, et al. Current evidence on risk factors for knee osteoarthritis in older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2015; 23(4): 507-515. [3] PALMIERI-SMITH RM, CAMERON KL, DISTEFANO LJ, et al. The Role of Athletic Trainers in Preventing and Managing Posttraumatic Osteoarthritis in Physically Active Populations: a Consensus Statement of the Athletic Trainers’ Osteoarthritis Consortium. J Athl Train. 2017; 52(6): 610-623. [4] MARTEL-PELLETIER J, BARR A J, CICUTTINI F M, et al. Osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Dis Primers.2016; 2: 16072. [5] CHOI M C, JO J, PARK J, et al. NF-kappaB Signaling Pathways in Osteoarthritic Cartilage Destruction. Cells. 2019;8(7):734. [6] ZHANG M, LYGRISSE K, WANG J. Role of MicroRNA in Osteoarthritis. J Arthritis. 2017;6(2):239. [7] ZHOU ZB, DU D, HUANG GX, et al. Circular RNA Atp9b, a competing endogenous RNA, regulates the progression of osteoarthritis by targeting miR-138-5p. Gene.2018; 646: 203-209. [8] DUAN L,DUAN D,WEI W,et al.MiR-19b-3p attenuates IL-1beta induced extracellular matrix degradation and inflammatory injury in chondrocytes by targeting GRK6. Mol Cell Biochem. 2019; 459(1-2): 205-214. [9] LI B, BAI L, SHEN P, et al. Identification of differentially expressed microRNAs in knee anterior cruciate ligament tissues surgically removed from patients with osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Med.2017; 40(4): 1105-1113. [10] YUAN Y, ZHANG G Q, CHAI W, et al. Silencing of microRNA-138-5p promotes IL-1beta-induced cartilage degradation in human chondrocytes by targeting FOXC1: miR-138 promotes cartilage degradation. Bone Joint Res.2016;5(10): 523-530. [11] CARBALLO CB, NAKAGAWA Y, SEKIYA I, et al. Basic Science of Articular Cartilage. Clin Sports Med.2017; 36(3): 413-425. [12] KOPANSKA M, SZALA D, CZECH J, et al. MiRNA expression in the cartilage of patients with osteoarthritis. J Orthop Surg Res.2017; 12(1): 51. [13] CARAMES B, HASEGAWA A, TANIGUCHI N, et al. Autophagy activation by rapamycin reduces severity of experimental osteoarthritis[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2012, 71(4): 575-581. [14] CHENG NT, MENG H, MA LF, et al. Role of autophagy in the progression of osteoarthritis: The autophagy inhibitor, 3-methyladenine, aggravates the severity of experimental osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Med.2017; 39(5): 1224-1232. [15] QIN N, WEI L, LI W, et al. Local intra-articular injection of resveratrol delays cartilage degeneration in C57BL/6 mice by inducing autophagy via AMPK/mTOR pathway. J Pharmacol Sci.2017;134(3):166-174. [16] GUILAK F, NIMS RJ, DICKS A, et al. Osteoarthritis as a disease of the cartilage pericellular matrix. Matrix Biol.2018;71-72:40-50. [17] POSEY KL, COUSTRY F, HECHT JT. Cartilage oligomeric matrix protein: COMPopathies and beyond. Matrix Biol.2018;71-72:161-173. [18] LI H, WANG D, YUAN Y, et al. New insights on the MMP-13 regulatory network in the pathogenesis of early osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017;19(1): 248. [19] MALEMUD CJ. Inhibition of MMPs and ADAM/ADAMTS[J]. Biochem Pharmacol.2019;165:33-40. [20] WU GW, CHEN J,HUANG YM,et al.Electroacupuncture Delays Cartilage Degeneration by Modulating Nuclear Factor-kappaB Signaling Pathway. Chin J Integr Med.2019;25(9):677-683. [21] WAN Y, LI W, LIAO Z, et al. Selective MMP-13 inhibitors: promising agents for the therapy of Osteoarthritis. Curr Med Chem. 2020;27(22): 3753-3769. [22] LEI J, FU Y, ZHUANG Y, et al. LncRNA SNHG1 Alleviates IL-1beta-induced Osteoarthritis by Inhibiting miR-16-5p-mediated p38 MAPK and NF-kappaB Signaling Pathways. Biosci Rep. 2019;39(9):BSR20191523. [23] LI Y, XIAO W, WU P, et al. The expression of SIRT1 in articular cartilage of patients with knee osteoarthritis and its correlation with disease severity. J Orthop Surg Res.2016;11(1):144. [24] SUN W, LI Y, WEI S. miR-4262 regulates chondrocyte viability, apoptosis, autophagy by targeting SIRT1 and activating PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in rats with osteoarthritis. Exp Ther Med.2018; 15(1): 1119-1128. [25] TIAN S, GUO X, YU C, et al. miR-138-5p suppresses autophagy in pancreatic cancer by targeting SIRT1. Oncotarget.2017; 8(7): 11071-11082. [26] CETRULLO S, D’ADAMO S, TANTINI B, et al. mTOR, AMPK, and Sirt1: Key Players in Metabolic Stress Management. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr.2015;25(1): 59-75. [27] VELAGAPUDI R, EL-BAKOUSH A, LEPIARZ I, et al. AMPK and SIRT1 activation contribute to inhibition of neuroinflammation by thymoquinone in BV2 microglia. Mol Cell Biochem.2017; 435(1-2): 149-162. [28] CHEN H, LIU X, CHEN H, et al. Role of SIRT1 and AMPK in mesenchymal stem cells differentiation[J]. Ageing Res Rev, 2014, 13: 55-64. [29] PRESNEAU N, DUHAMEL LA, YE H, et al. Post-translational regulation contributes to the loss of LKB1 expression through SIRT1 deacetylase in osteosarcomas. Br J Cancer.2017;117(3):398-408. [30] ZHANG X, HAN X, ZHANG P, et al.Morin attenuates oxidized low-density lipoprotein-mediated injury by inducing autophagy via activating AMPK signaling in HUVECs.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2019;46(11): 1053-1060. [31] XUE JF, SHI ZM, ZOU J, et al. Inhibition of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway promotes autophagy of articular chondrocytes and attenuates inflammatory response in rats with osteoarthritis. Biomed Pharmacother.2017;89: 1252-1261. |
| [1] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [2] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [3] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [4] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [5] | Peng Zhihao, Feng Zongquan, Zou Yonggen, Niu Guoqing, Wu Feng. Relationship of lower limb force line and the progression of lateral compartment arthritis after unicompartmental knee arthroplasty with mobile bearing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1368-1374. |
| [6] | Du Xiupeng, Yang Zhaohui. Effect of degree of initial deformity of impacted femoral neck fractures under 65 years of age on femoral neck shortening [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1410-1416. |
| [7] | Zhang Shangpu, Ju Xiaodong, Song Hengyi, Dong Zhi, Wang Chen, Sun Guodong. Arthroscopic suture bridge technique with suture anchor in the treatment of acromioclavicular dislocation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1417-1422. |
| [8] | Yuan Jiawei, Zhang Haitao, Jie Ke, Cao Houran, Zeng Yirong. Underlying targets and mechanism of Taohong Siwu Decoction in prosthetic joint infection on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1428-1433. |
| [9] | Zhou Jihui, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Multiple problems in the selection of implants for patellar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1440-1445. |
| [10] | Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [11] | Gu Xia, Zhao Min, Wang Pingyi, Li Yimei, Li Wenhua. Relationship between hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha and hypoxia signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1284-1289. |
| [12] | Yuan Mei, Zhang Xinxin, Guo Yisha, Bi Xia. Diagnostic potential of circulating microRNA in vascular cognitive impairment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1299-1304. |
| [13] | Li Jiacheng, Liang Xuezhen, Liu Jinbao, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Differential mRNA expression profile and competitive endogenous RNA regulatory network in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1212-1217. |
| [14] | Chai Le, Lü Jianlan, Hu Jintao, Hu Huahui, Xu Qingjun, Yu Jinwei, Quan Renfu. Signal pathway variation after induction of inflammatory response in rats with acute spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1218-1223. |
| [15] | Geng Qiudong, Ge Haiya, Wang Heming, Li Nan. Role and mechanism of Guilu Erxianjiao in treatment of osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1229-1236. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||