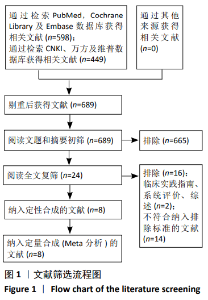
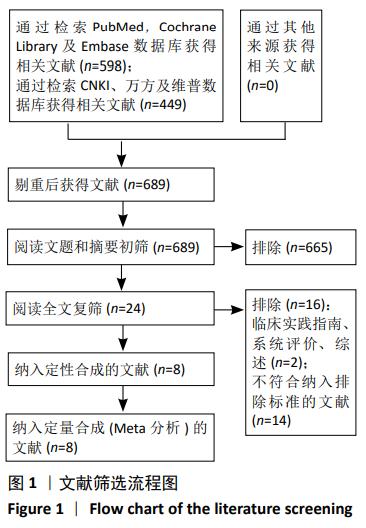
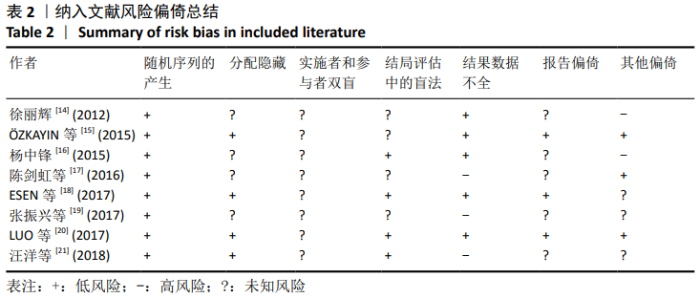
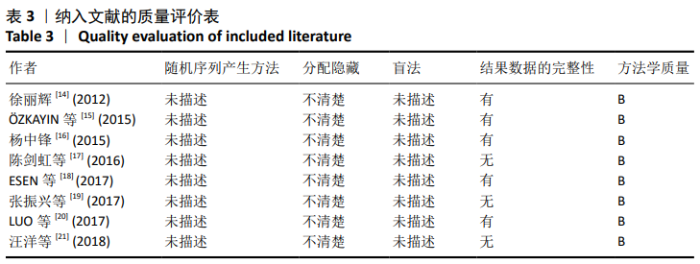
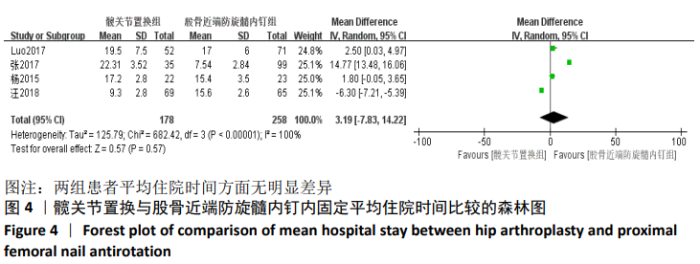
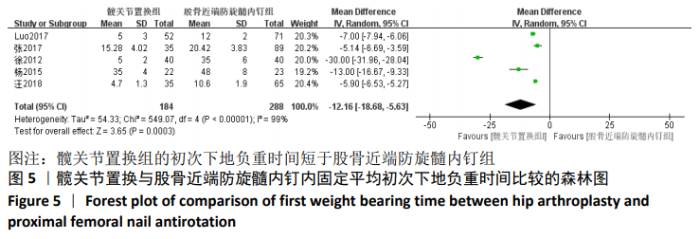
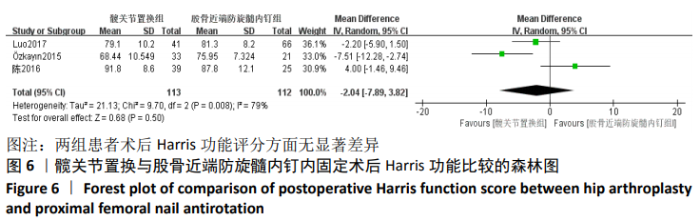
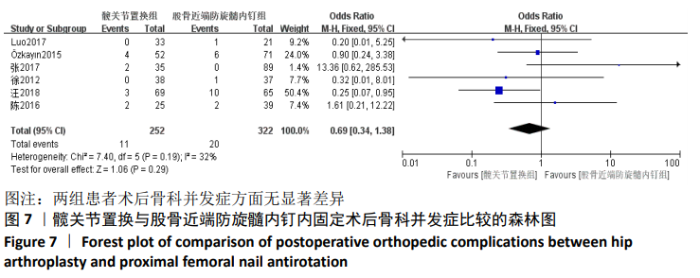
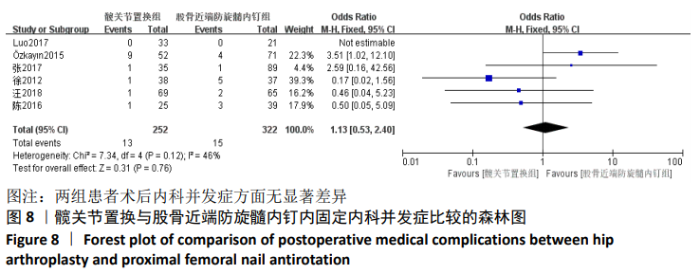
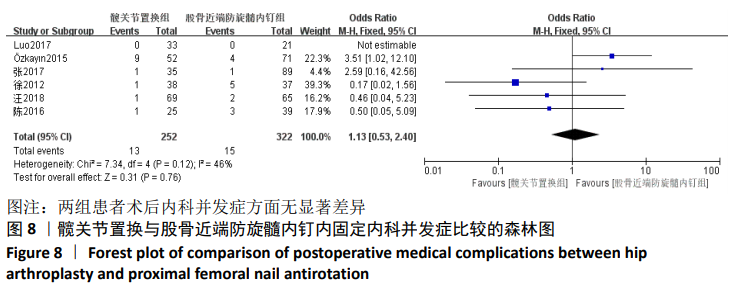
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (9): 1452-1457.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.4016
Previous Articles Next Articles
Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis
Chen Junming1, Yue Chen2, He Peilin1, Zhang Juntao3, Sun Moyuan3, Liu Youwen2
- 1Key Laboratory of Orthopedic Traumatology of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Rehabilitation of Ministry of Education, Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Fuzhou 350100, Fujian Province, China; 2Department of Hip Injury Center, Luoyang Orthopedic Hospital of Henan Province, Luoyang 471002, Henan Province, China; 3Henan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2020-03-27Revised:2020-04-01Accepted:2020-05-13Online:2021-03-28Published:2020-12-16 -
Contact:Liu Youwen, Professor, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Hip Injury Center, Luoyang Orthopedic Hospital of Henan Province, Luoyang 471002, Henan Province, China -
About author:Chen Junming, Master candidate, Key Laboratory of Orthopedic Traumatology of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Rehabilitation of Ministry of Education, Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Fuzhou 350100, Fujian Province, China Yue Chen, MD, Attending physician, Department of Hip Injury Center, Luoyang Orthopedic Hospital of Henan Province, Luoyang 471002, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81804126; the Special Project of Scientific Research on Traditional Chinese Medicine in Henan Province, No. 2016ZY2089
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457.
share this article
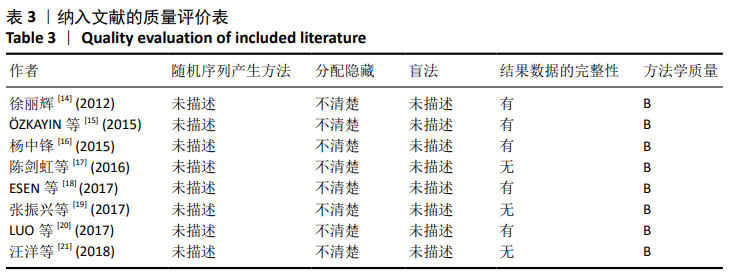
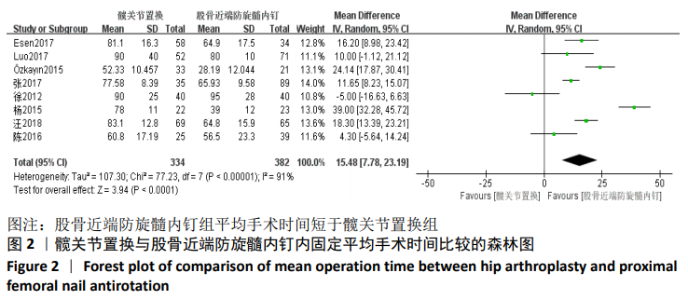
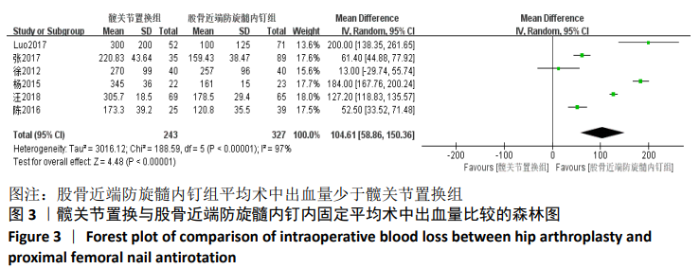
| [1] SANDOWSKI C, LUBBEKE A, SAUDAN M, et al. Treatment of reverse obligue and transverse intertrochanteric fractures with use of an intramedullary nail or a 95°screw-place, a prospectives, randomized study. Bone Joint Surg (Am). 2002;84-(A):372-381. [2] CHIRODIAN N, ARCH B, PARKER MJ. Sliding hip screw fixation of tro-chanteric hip fractures: outcome of 1024 procedures. Injury. 2005;36(6):793-800. [3] KESMEZACAR H, AYHAN E, UNLU MC, et al. Predictors of mortality in elderly patients with an intertrochanteric or a femoral neck fracture. Trauma. 2010;68(1):153-158. [4] SHIN KH, HONG SH, HAN SB, Posterior fully threaded positioning screw prevents femoral neck collapse in Garden I or II femoral neck fractures. Injury. 2020;51:1031-1037. [5] CHOI HJ, KIM E, SHIN YJ, et al. The timing of surgery and mortality in elderly hip fractures: a retrospective, multicenteric cohort study. Indian J Orthop. 2014;48(6):599-604. [6] SIMMERMACHER RK, LJUNGQVIST J, BAIL H, et al. The new proximal femoral nail antirotation (PFNA) in daily practice: results of amulticentre clinical study. Injury. 2008;39(8):932-939. [7] PARK-WYLLIE LY, MAMDANI MM, JUURLINK DN, et al. Bi-sphosphonate use and risk of subtrochanteric or femoral shaft fractures in older wormen. JAMA. 2011;305(8):783-789. [8] WANG C, WANG Q. Helical blade compression failure occurred during PFNA implantation: a rare case and ingenious solution. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019;98(30):e16584. [9] MIN BW, LEE KJ, OH JK, et al. The Treatment Strategies for Failed Fixation of Intertrochanteric Fractures. Injury. 2019;50(7):1339-1346. [10] YU C, JIANG LH, CAI DW, et al. PFNA and InterTAN Intramedullary Nailing in Elderly Patients With Femoral Intertrochanteric Fractures: a Meta Analysis. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2019;32(2):120-129. [11] YUE C, WEI R, LIU Y. Perioperative systemic steroid for rapid recovery in total knee and hip arthroplasty: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. J Orthop Surg Res. 2017;12(1):100. [12] YUE C, KANG P, PEI F. Comparison of Direct Anterior and Lateral Approaches in Total Hip Arthroplasty: a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA). Medicine (Baltimore). 2015; 94(50):e2126. [13] JU JB, ZHANG PX, JIANG BG. Hip Replacement as Alternative to Intramedullary Nail in Elderly Patients with Unstable Intertrochanteric Fracture: a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Orthop Surg. 2019;11(5):745-754. [14] 徐丽辉.股骨近端防旋髓内钉、动力髋螺钉及人工关节置换治疗高龄股骨粗隆间骨折的疗效对比[J].中国老年学杂志,2012,32(24): 5596-5598. [15] ÖZKAYIN N, OKCU G, AKTUGLU K. Intertrochanteric femur fractures in the elderly treated with either proximal femur nailing or hemiarthroplasty: a prospective randomised clinical study. Injury. 2015,46(Suppl 2):S3-8. [16] 杨中锋.老年股骨粗隆间骨折的外科治疗及其临床疗效观察[J].医学综述,2015,2(21):757-759. [17] 陈剑虹,李顺东,童培建,等.人工股骨头置换与股骨近端防旋髓内钉治疗高龄股骨转子间骨折的对比研究[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志, 2016, 24(2):18-21, 28. [18] ESEN E, DUR H, ATAOĞLU MB, et al. Evaluation of proximal femoral nail-antirotation and cemented,bipolar hemiarthroplasty with calcar replacement in treatment of intertrochanteric femoral fractures in terms of mortality and morbidity ratios. Eklem Hastalik Cerrahisi. 2017;28(1):35-40. [19] 张振兴,王荣,潘丕春,等.PFNA内固定与半髋关节置换治疗老年性股骨粗隆间骨折效果比较[J].齐鲁医学杂志,2017,32(2):192-194. [20] LUO X, HE S, ZENG D, et al. Proximal femoral nail antirotation versushemiarthroplasty in the treatment of senile intertrochanteric fractures: Casereport. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2017;38:37-42. [21] 汪洋,彭家全,唐春江,等.防旋转股骨近端髓内钉与人工关节置换治疗老年股骨转子间骨折的比较[J].重庆医学,2018,47(20):2706-2708, 2713. [22] 郝良,张忠林,王宝东,等.股骨转子间骨折:内固定装置改进、术式变化及其相关争议[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(18):2927-2935. [23] DUNG TT, HIEU ND, SON LM, et al. Primary Cementless Bipolar Long Stem Hemiarthroplasty for Unstable Osteoporotic Intertrochanteric Fracture in the Elderly Patients. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2019;7(24):4342-4346. [24] WU KL, XU YJ, ZHANG L, et al. Which implant is better for beginners to learn to treat geriatric intertrochanteric femur fractures: a randomised controlled trial of surgeons, metalwork, and patients. J Orthop Translat. 2020;21:18-23. [25] LEE YK, HA YC, CHANG BK, et al. Cementless bipolar hemiarthroplasty using a hydroxyatite-coated long sterm for osteoorotic unstable interochanteric fractures. Arthrpolasty. 2011;26(4):626-632. [26] CHAI W, KONG X, YANG M, et al. Robot-Assisted Total Hip Arthroplasty for Arthrodesed Hips. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2020;16:357-368. [27] KULACHOTE N, SA-NGASOONGSONG P, SIRISREETREERUX N, et al. Predicting Factors for Return to Prefracture Ambulatory Level in High Surgical Risk Elderly Patients Sustained Intertrochanteric Fracture and Treated With Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation (PFNA) With and Without Cement Augmentation. Geriatr Orthop Surg Rehabil. 2020;11: 2151459320912121. [28] ZHOU S, LIU J, ZHEN P, et al. Proximal femoral nail anti-rotation versus cementless bipolar hemiarthroplasty for unstable femoral intertrochanteric fracture in the elderly: a retrospective study. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders. 2019;20(1):1-7. [29] SMITH AM, MARDONES RM, SPERLING JW, et al. Early complications of operatively treated proximal humeralfractures. Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2007;16: 14-24. [30] 易善钧,潘有春,李廷林,等.特制股骨假体置换治疗老年股骨粗隆部不稳定骨折[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2014,12(21):1651-1653. [31] 宋继淳,韩城龙,岑怡彪,等.半髋关节置换与PFNA在治疗不稳定型股骨粗隆间骨折的临床分析[J].临床医学工程,2012,19(8):1276-1278. |
| [1] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [2] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [3] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [4] | Jiang Yong, Luo Yi, Ding Yongli, Zhou Yong, Min Li, Tang Fan, Zhang Wenli, Duan Hong, Tu Chongqi. Von Mises stress on the influence of pelvic stability by precise sacral resection and clinical validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1318-1323. |
| [5] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [6] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [7] | Wei Wei, Li Jian, Huang Linhai, Lan Mindong, Lu Xianwei, Huang Shaodong. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [8] | Wang Jinjun, Deng Zengfa, Liu Kang, He Zhiyong, Yu Xinping, Liang Jianji, Li Chen, Guo Zhouyang. Hemostatic effect and safety of intravenous drip of tranexamic acid combined with topical application of cocktail containing tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [9] | Xiao Guoqing, Liu Xuanze, Yan Yuhao, Zhong Xihong. Influencing factors of knee flexion limitation after total knee arthroplasty with posterior stabilized prostheses [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1362-1367. |
| [10] | Huang Zexiao, Yang Mei, Lin Shiwei, He Heyu. Correlation between the level of serum n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and quadriceps weakness in the early stage after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1375-1380. |
| [11] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [12] | Wang Haiying, Lü Bing, Li Hui, Wang Shunyi. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: prediction of functional prognosis of patients based on spinopelvic parameters [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1393-1397. |
| [13] | Lü Zhen, Bai Jinzhu. A prospective study on the application of staged lumbar motion chain rehabilitation based on McKenzie’s technique after lumbar percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1398-1403. |
| [14] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [15] | Du Xiupeng, Yang Zhaohui. Effect of degree of initial deformity of impacted femoral neck fractures under 65 years of age on femoral neck shortening [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1410-1416. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 161
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 651
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||