Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (8): 1229-1236.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2991
Previous Articles Next Articles
Role and mechanism of Guilu Erxianjiao in treatment of osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology
Geng Qiudong1, Ge Haiya1, Wang Heming1, 2, 3, Li Nan1, 2
- 1College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Fuzhou 350122, Fujian Province, China; 2Key Laboratory of Orthopedics & Traumatology and Rehabilitation of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Ministry of Education, Fuzhou 350122, Fujian Province, China; 3Rehabilitation Hospital Affiliated to Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Fuzhou 350003, Fujian Province, China
-
Received:2020-05-14Revised:2020-05-19Accepted:2020-06-01Online:2021-03-18Published:2020-12-12 -
Contact:Li Nan, MD, Professor, Master’s supervisor, College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Fuzhou 350122, Fujian Province, China; Key Laboratory of Orthopedics & Traumatology and Rehabilitation of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Ministry of Education, Fuzhou 350122, Fujian Province, China -
About author:Geng Qiudong, Master candidate, College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Fuzhou 350122, Fujian Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81973880; the Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province, No. 2019J01349
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Geng Qiudong, Ge Haiya, Wang Heming, Li Nan. Role and mechanism of Guilu Erxianjiao in treatment of osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1229-1236.
share this article
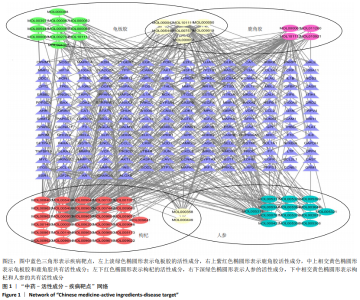
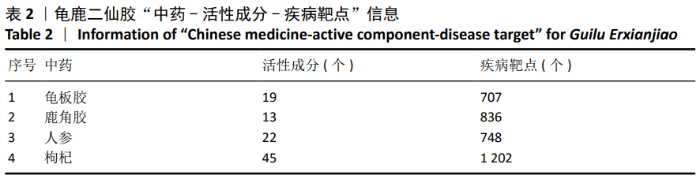
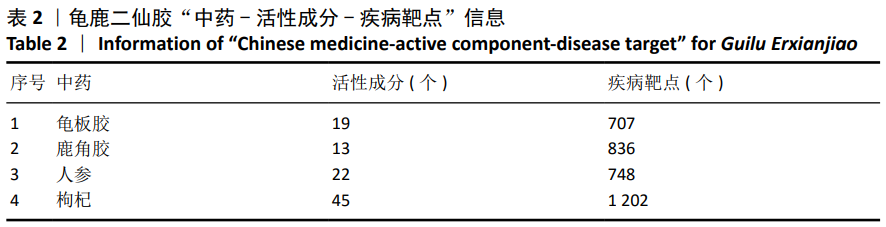
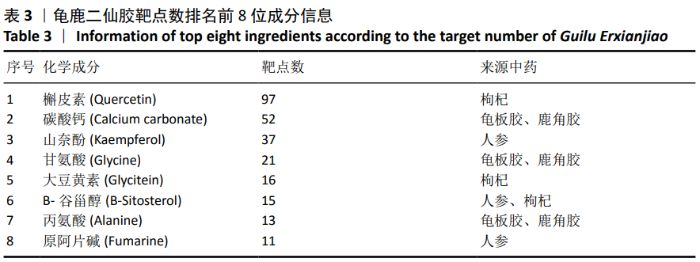
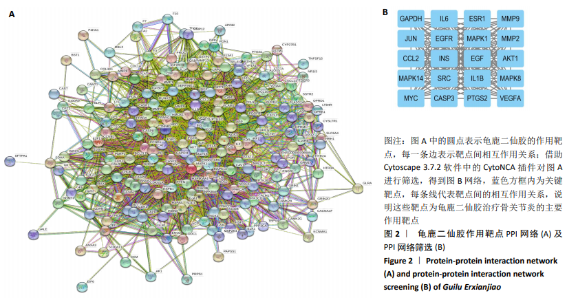
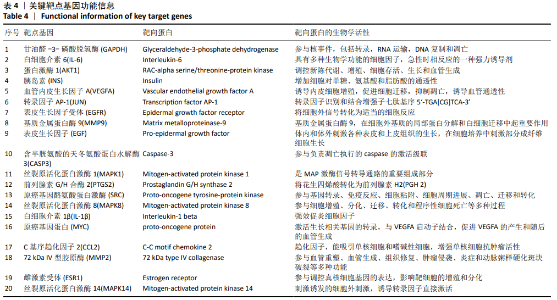
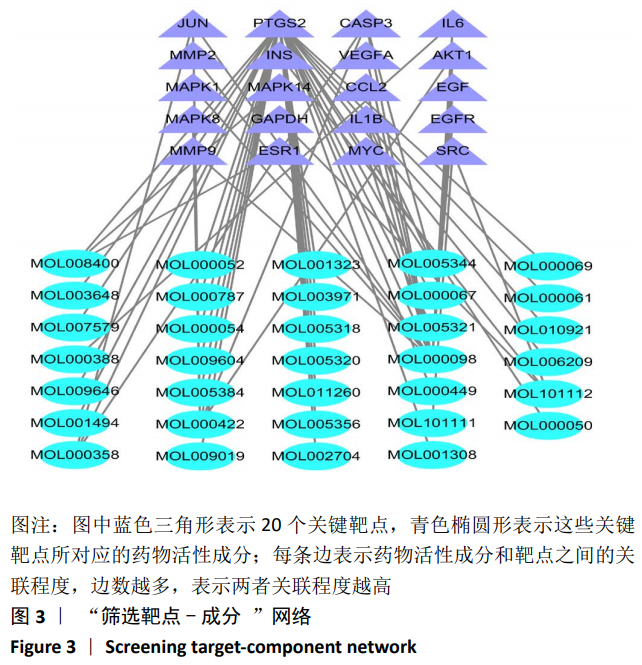
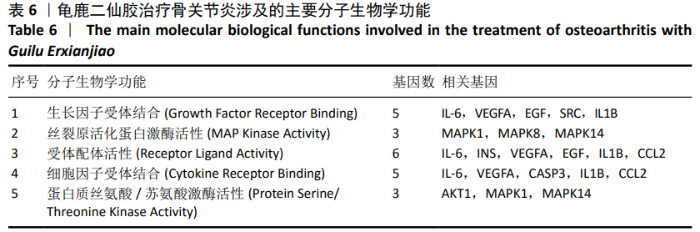
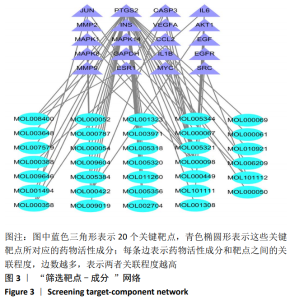
2.2 疾病靶点筛选结果 将所得结果进行综合删除重复项后,得到骨关节炎相关靶点2 612个。 2.3 网络构建与结果分析 得到201个共有靶点,对应龟鹿二仙胶活性成分69个。利用Cytoscape 3.7.2软件构建“中药-活性成分-疾病靶点”网络图见图1。靶点数排名前8位的成分为槲皮素(quercetin)、碳酸钙(calcium Carbonate)、山奈酚(kaempferol)、甘氨酸(glycine)、大豆黄素(glycitein)、β-谷甾醇(β-sitosterol)、丙氨酸(alanine)和原阿片碱(fumarine),见表3,这些可能为龟鹿二仙胶治疗骨关节炎的有效成分。将映射所得的201个靶点利用String构建PPI网络,其产生相互作用的网络有201个节点,3 543条边,所得PPI网络导入Cytoscape 3.7.2软件,使用CytoNCA插件进行拓扑分析,得到20个靶点的网络,见图2。对这20个靶点进行分析,明确此20个靶点的基本功能信息,见表4。将这20个靶点所对应的成分进行网络构建得到图3所示网络,根据degree值大小筛选前8位的成分为槲皮素、山奈酚、人参皂苷Rh2、β-谷甾醇、大豆黄素、原阿片碱、碳酸钙和花生四烯酸盐,结合前面所得到的前8位成分取交集后得到槲皮素、山奈酚、β-谷甾醇、大豆黄素、原阿片碱和碳酸钙6个成分,提示这6个成分可能为龟鹿二仙胶治疗骨关节炎的关键成分。"

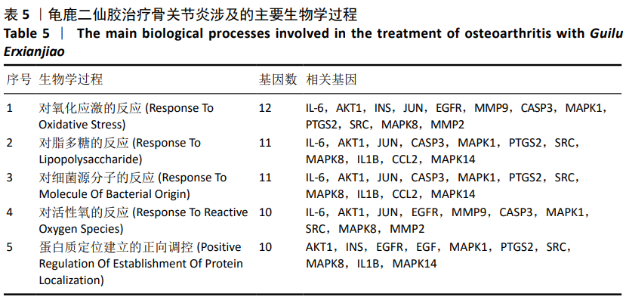
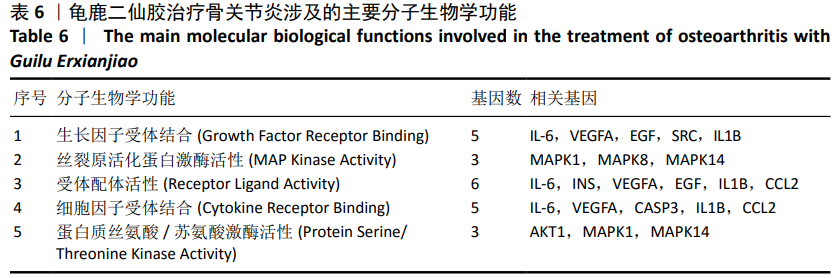
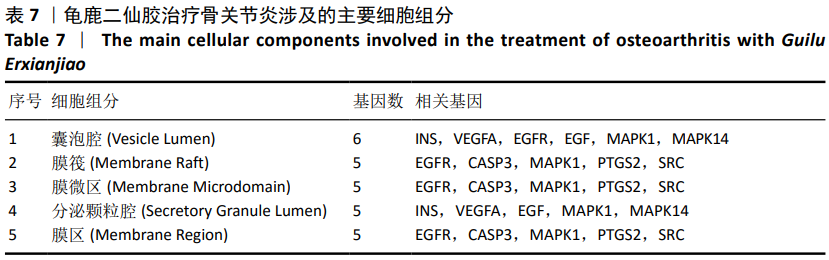
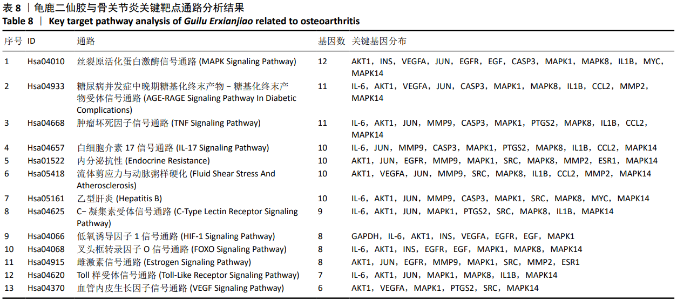
2.4 GO富集分析 将2.3中得到的20个靶点利用R语言软件借助Bioconductor数据包library(org.Hs.eg.db)对这20个靶点进行ID转换,然后运用R语言进行GO分析得到1 550个条目,其中生物学过程占1 512个,分子生物学功能占21个,细胞组分占17个,显示龟鹿二仙胶治疗骨关节炎主要与对氧化应激的反应、对脂多糖的反应、对细菌起源分子的反应、对活性氧的反应及细胞蛋白质定位建立的正调控等生物学过程以及生长因子受体结合、丝裂原活化蛋白激酶活性、受体配体活性、细胞因子受体结合、蛋白质丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶活性等分子生物学功能密切相关,其过程涉及细胞内囊泡、膜筏、膜微区、内质网腔及核染色质等细胞组分。其主要生物学过程、分子生物学功能、细胞组分参与的基因见表5-7。"

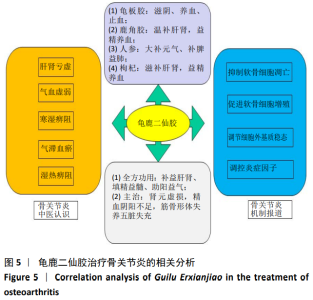
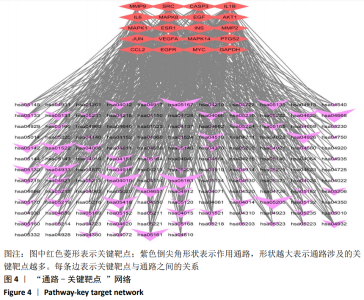
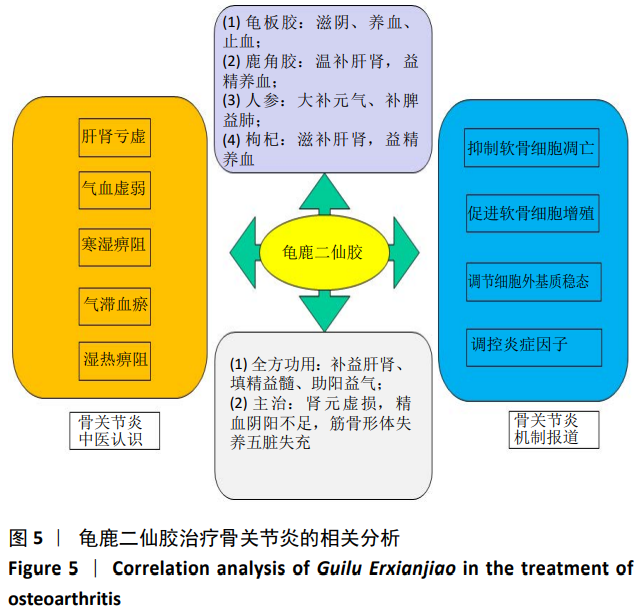
2.6 龟鹿二仙胶治疗骨关节炎的化学成分及作用机制的文献验证 通过检索共纳入文献17篇[8-11, 19-31]。分析所得文献,明晰龟鹿二仙胶的功用主治和方中单味药的功效,以及此方治疗骨关节炎的中医认识及作用机制,见图5。文献报道龟鹿二仙胶全方、拆方及其单药中主要化学成分槲皮素、山奈酚和甘氨酸等对骨关节炎均具有治疗作用[8-11, 19-26];大豆黄素可能通过对成骨细胞的增殖作用,抑制破骨性骨吸收,防治骨关节炎的发生和进展[27-28];人参皂苷能通过增高Bcl-2/Bax的比值、提高软骨细胞中Ⅱ型胶原基因的表达、抑制基质金属蛋白酶13的表达来改善骨关节炎患者症状[29-31]。其治疗骨关节炎的机制主要与对炎症介质、基质金属蛋白酶表达量和Ⅱ型胶原基因的调控相关,说明龟鹿二仙胶治疗骨关节炎可能与炎症、软骨代谢、细胞凋亡与增殖等通路有关。"
| [1] SILVERWOOD V, BLAGOJEVIC-BUCKNALL M, JINKS C, et al. Current evidence on risk factors for knee osteoarthritis in older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015; 23(4):507-515. [2] LANE NE, BRANDT K, HAWKER G, et al. OARSI-FDA initiative: defining the disease state of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2011; 19(5):478-482. [3] 中医骨伤科临床诊疗指南·膝痹病(膝骨关节炎)[J].康复学报,2019,29(3):1-7. [4] 林嘉辉,陈炳艺,李楠.龟鹿二仙胶治疗骨关节炎的研究概况[J].中华中医药杂志, 2017,32(12):5509-5512. [5] 姜灵.龟鹿二仙胶汤治疗肝肾亏虚型膝关节骨性关节炎的临床疗效研究[D].大连:大连医科大学,2016. [6] 刘俊锋.龟鹿二仙胶汤对膝骨关节炎早期干预的临床研究[D].成都:成都中医药大学, 2013. [7] 张农.龟鹿二仙胶治疗老年增生性骨关节炎的临床观察[J].中医临床研究,2012,4(13): 79-80. [8] 余添赐.龟鹿二仙胶不同提取部位对体外培养豚鼠关节软骨细胞活性的影响[D].福州:福建中医药大学,2014. [9] 李楠,杜江,黄远鹏,等.龟鹿二仙胶及其拆方对SD大鼠膝骨关节炎的影响[J].中华中医药杂志,2013,28(6):1677-1680. [10] 杜江,黄远鹏,李奕修,等.龟鹿二仙胶及其拆方对去势骨关节炎大鼠血清雌二醇浓度及膝关节软骨细胞Ⅱ型胶原表达的影响[J].中医正骨,2013,25(3):11-20. [11] 杜江,黄远鹏,李奕修,等.龟鹿二仙胶及其拆方对去势骨关节炎大鼠关节软骨中Bax和Bcl-2的影响[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志, 2013,21(3):4-7. [12] 刘艾林,杜冠华.网络药理学:药物发现的新思想[J].药学学报,2010,45(12):1472-1477. [13] 许海玉,黄璐琦,卢鹏,等.基于体内ADME过程和网络药理学的中药现代研究思路[J].中国中药杂志,2012,37(2):142-145. [14] Xu X, Zhang W, Huang C, et al. A novel chemometric method for the prediction of human oral bioavailability. Int J Mol Sci. 2012; 13(6):6964-6982. [15] LI J, ZHAO P, LI Y, et al. Systems pharmacology-based dissection of mechanisms of Chinese medicinal formula Bufei Yishen as an effective treatment for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Sci Rep. 2015;5(1):15290. [16] 侯磊,李晓宇,黄娜娜,等.四逆散干预焦虑症作用机制的网络药理学分析[J].中草药, 2019,50(21):5154-5161. [17] SZKLARCZYK D, MORRIS J H, COOK H, et al. The STRING database in 2017: quality-controlled protein–protein association networks, made broadly accessible. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017; 45(D1):D362-D368. [18] 张新雨,黄娜娜,孙凯滨,等.柴胡龙骨牡蛎汤治疗原发性高血压作用网络与机制预测[J].中草药,2019,50(21):5162-5169. [19] KANZAKI N, SAITO K, MAEDA A, et al. Effect of a dietary supplement containing glucosamine hydrochloride, chondroitin sulfate and quercetin glycosides on symptomatic knee osteoarthritis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J Sci Food Agric. 2012;92(4):862-869. [20] LEYVA-LOPEZ N, GUTIERREZ-GRIJALVA E P, AMBRIZ-PEREZ D L, et al. Flavonoids as cytokine modulators: a possible therapy for inflammation-related diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(6):921. [21] QIU L, LUO Y, CHEN X. Quercetin attenuates mitochondrial dysfunction and biogenesis via upregulated AMPK/SIRT1 signaling pathway in OA rats. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;103:1585-1591. [22] BRITTI D, CRUPI R, IMPELLIZZERI D, et al. A novel composite formulation of palmitoylethanolamide and quercetin decreases inflammation and relieves pain in inflammatory and osteoarthritic pain models. BMC Vet Res. 2017;13(1): 229. [23] HALEAGRAHARA N, HODGSON K, MIRANDA-HERNANDEZ S, et al. Flavonoid quercetin-methotrexate combination inhibits inflammatory mediators and matrix metalloproteinase expression, providing protection to joints in collagen-induced arthritis. Inflammopharmacology. 2018;26(5): 1219-1232. [24] HU Y, GUI Z, ZHOU Y, et al. Quercetin alleviates rat osteoarthritis by inhibiting inflammation and apoptosis of chondrocytes, modulating synovial macrophages polarization to M2 macrophages. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019; 145:146-160. [25] ZHUANG Z, YE G, HUANG B. Kaempferol Alleviates the Interleukin-1beta-Induced Inflammation in Rat Osteoarthritis Chondrocytes via Suppression of NF-kappaB. Med Sci Monit. 2017;23:3925-3931. [26] de PAZ-LUGO P, LUPIANEZ JA, MELENDEZ-HEVIA E. High glycine concentration increases collagen synthesis by articular chondrocytes in vitro: acute glycine deficiency could be an important cause of osteoarthritis. Amino Acids. 2018,50(10):1357-1365. [27] 王志平,禹博,刘明皓,等.大豆苷元对人成骨细胞经典的雌激素受体信号通路的调节作用[J].武警后勤学院学报(医学版), 2018,27(3):200-203. [28] 王健,陶海荣.雌激素及相关化合物干预骨关节炎作用机制:关节保护与骨软骨细胞的修复[J].中国组织工程研究,2014, 18(33):5372-5376. [29] 黎立,李晓旭,司裕,等.人参皂苷Rb2保护关节软骨细胞对抗氧化应激的作用机制研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2018,26(9): 845-849. [30] WANG W, ZENG L, WANG ZM, et al. Ginsenoside Rb1 inhibits matrix metalloproteinase 13 through down-regulating Notch signaling pathway in osteoarthritis. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2015;240(12):1614-1621. [31] 段超.人参皂苷Rg1防治兔膝关节骨性关节炎的实验研究[D].武汉:湖北中医药大学, 2016. [32] 黄威,尹宗生.炎症与骨关节炎软骨退变[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2019,27(5):448-452. [33] SOHN DH, SOKOLOVE J, SHARPE O, et al. Plasma proteins present in osteoarthritic synovial fluid can stimulate cytokine production via Toll-like receptor 4. Arthritis Res Ther. 2012;14(1):R7. [34] CHOCKALINGAM PS, VARADARAJAN U, SHELDON R, et al. Involvement of protein kinase Czeta in interleukin-1beta induction of ADAMTS-4 and type 2 nitric oxide synthase via NF-kappaB signaling in primary human osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56(12):4074-4083. [35] 陈喜德,魏波,杨柳菁,等.不同病期骨关节炎大鼠关节软骨中caspase-3与细胞凋亡的相关性[J].广东医学,2018,39(2):181-186. [36] 冯顶丽,卓丽丹,芦笛,等.微小RNA调节间充质干细胞软骨分化机制的研究进展[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2018,45(6):640-645. [37] WU Y H, LIU W, ZHANG L, et al. Effects of microRNA-24 targeting C-myc on apoptosis, proliferation, and cytokine expressions in chondrocytes of rats with osteoarthritis via MAPK signaling pathway. J Cell Biochem. 2018; 119(10):7944-7958. [38] 邵进,张岩,王治,等.低氧诱导因子-1α参与骨发育及骨代谢调控的研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2015,21(3):349-355. [39] 田大川,李海乐,肖大伟,等.联合应用软骨再生支架与突变型HIF-1α修饰BMSCs分泌的外泌体对晚期软骨缺损修复的促进作用[J].吉林大学学报(医学版),2018,44(2): 216-222. [40] 马笃军,彭力平,余阗,等.牛膝总皂苷对骨关节炎模型兔软骨修复及低氧诱导因子1信号通路的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(27):4332-4337. [41] 孙志江.自噬在晚期糖基化终产物诱导的软骨细胞凋亡中的作用[D].兰州:兰州大学, 2018. [42] SORCI G, RIUZZI F, GIAMBANCO I, et al. RAGE in tissue homeostasis, repair and regeneration. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA). Mol Cell Res. 2013;1833(1):101-109. [43] 徐小磊.TLR4/Akt/FoxO1轴在白藜芦醇抗肥胖相关骨性关节炎中的作用研究[D].沈阳:中国医科大学,2019. |
| [1] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [2] | Jiang Yong, Luo Yi, Ding Yongli, Zhou Yong, Min Li, Tang Fan, Zhang Wenli, Duan Hong, Tu Chongqi. Von Mises stress on the influence of pelvic stability by precise sacral resection and clinical validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1318-1323. |
| [3] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [4] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [5] | Li Dadi, Zhu Liang, Zheng Li, Zhao Fengchao. Correlation of total knee arthroplasty efficacy with satisfaction and personality characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1346-1350. |
| [6] | Wei Wei, Li Jian, Huang Linhai, Lan Mindong, Lu Xianwei, Huang Shaodong. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [7] | Wang Jinjun, Deng Zengfa, Liu Kang, He Zhiyong, Yu Xinping, Liang Jianji, Li Chen, Guo Zhouyang. Hemostatic effect and safety of intravenous drip of tranexamic acid combined with topical application of cocktail containing tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [8] | Xiao Guoqing, Liu Xuanze, Yan Yuhao, Zhong Xihong. Influencing factors of knee flexion limitation after total knee arthroplasty with posterior stabilized prostheses [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1362-1367. |
| [9] | Peng Zhihao, Feng Zongquan, Zou Yonggen, Niu Guoqing, Wu Feng. Relationship of lower limb force line and the progression of lateral compartment arthritis after unicompartmental knee arthroplasty with mobile bearing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1368-1374. |
| [10] | Huang Zexiao, Yang Mei, Lin Shiwei, He Heyu. Correlation between the level of serum n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and quadriceps weakness in the early stage after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1375-1380. |
| [11] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [12] | Wang Haiying, Lü Bing, Li Hui, Wang Shunyi. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: prediction of functional prognosis of patients based on spinopelvic parameters [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1393-1397. |
| [13] | Lü Zhen, Bai Jinzhu. A prospective study on the application of staged lumbar motion chain rehabilitation based on McKenzie’s technique after lumbar percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1398-1403. |
| [14] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [15] | Du Xiupeng, Yang Zhaohui. Effect of degree of initial deformity of impacted femoral neck fractures under 65 years of age on femoral neck shortening [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1410-1416. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||