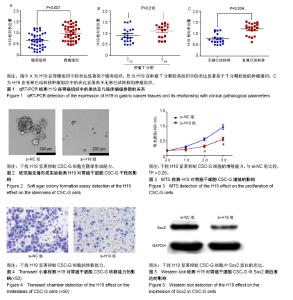
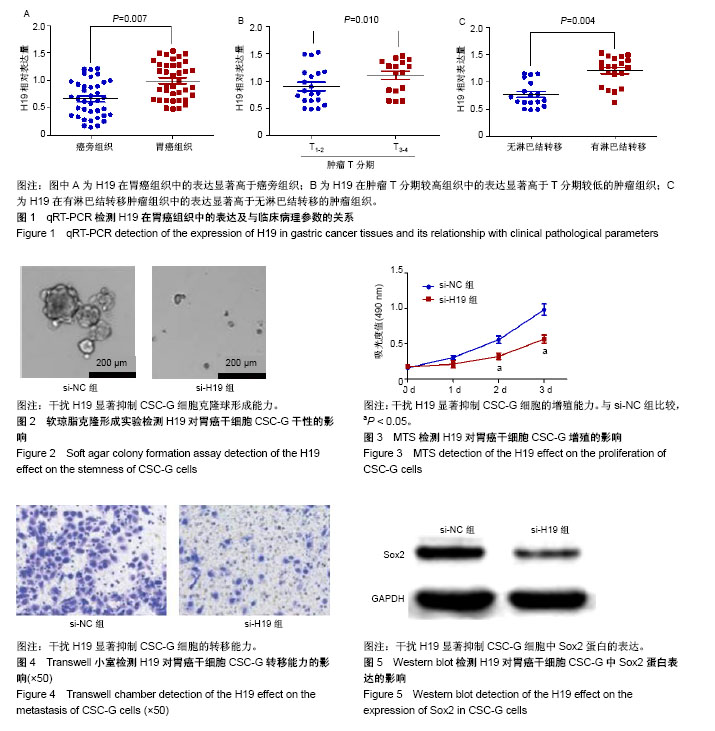
| [1] Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65(1):5-29.[2] Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66(2):115-132.[3] Berger H, Marques MS, Zietlow R, et al. Gastric cancer pathogenesis. Helicobacter. 2016;21 Suppl 1:34-38.[4] Leal MF, Assumpção PP, Smith MC, et al. Searching for Gastric Cancer Biomarkers Through Proteomic Approaches. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Research. 2014; 3(3): 989-995.[5] 颜涛,王枭雄,王春雷,等.肿瘤干细胞及肿瘤可塑性和异质性的研究进展[J].中国微侵袭神经外科杂志,2017,22(3):142-144.[6] Malhotra S, Freeberg MA, Winans SJ, et al. A Novel Long Non-Coding RNA in the hTERT Promoter Region Regulates hTERT Expression. Noncoding RNA. 2017;4(1): E1.[7] Hagan M, Zhou M, Ashraf M, et al. Long noncoding RNAs and their roles in skeletal muscle fate determination. Noncoding RNA Investig. 2017; pii: 24.[8] Pan B, Shi ZJ, Yan JY, et al.Long non-coding RNA NONMMUG014387 promotes Schwann cell proliferation after peripheral nerve injury.Neural Regen Res. 2017;12(12): 2084-2091.[9] Diamantopoulos MA, Tsiakanikas P, Scorilas A. Non-coding RNAs: the riddle of the transcriptome and their perspectives in cancer. Ann Transl Med. 2018;6(12):241.[10] Zhao M, Wang S, Li Q, et al. MALAT1: A long non-coding RNA highly associated with human cancers. Oncol Lett. 2018;16(1): 19-26.[11] Zhang L, Zhou Y Huang T, et al. The Interplay of LncRNA-H19 and Its Binding Partners in Physiological Process and Gastric Carcinogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 2017; 18(2):E450.[12] Collette J, Le Bourhis X, Adriaenssens E. Regulation of Human Breast Cancer by the Long Non-Coding RNA H19. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(11): E2319.[13] Shima H, Kida K, Adachi S, et al. Lnc RNA H19 is associated with poor prognosis in breast cancer patients and promotes cancer stemness. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2018;170(3): 507-516.[14] Li W, Jiang P, Sun X, et al. Suppressing H19 Modulates Tumorigenicity and Stemness in U251 and U87MG Glioma Cells. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2016;36(8):1219-1227.[15] 钟李锋.长链非编码RNA H19在胃癌干细胞中的表达及功能研究[D].福州:福建医科大学,2015.[16] 白金铭,张炫,乔佳欢,等.胃癌的发病机制及其防治方法[J].吉林医药学院学报,2018,39(4):310-312.[17] Kanaji S, Suzuki S, Matsuda Y, et al. Recent updates in perioperative chemotherapy and recurrence pattern of gastric cancer. Ann Gastroenterol Surg. 2018;2(6):400-405.[18] Reid PA, Wilson P, Li Y, et al. Current understanding of cancer stem cells: Review of their radiobiology and role in head and neck cancers. Head Neck. 2017;39(9):1920-1932.[19] 骆黎静,张宇迪,卢丹,等.肿瘤干细胞学说的应用前景与争议[J].中国临床医生杂志,2018,46(11):1274-1278.[20] Feng Y, Spezia M, Huang S, et al. Breast cancer development and progression: Risk factors, cancer stem cells, signaling pathways, genomics, and molecular pathogenesis. Genes Dis. 2018;5(2):77-106.[21] Ren J, Ding L, Zhang D, et al. Carcinoma-associated fibroblasts promote the stemness and chemoresistance of colorectal cancer by transferring exosomal lncRNA H19. Theranostics. 2018;8(14):3932-3948.[22] Ding K, Liao Y, Gong D, et al. Effect of long non-coding RNA H19 on oxidative stress and chemotherapy resistance of CD133+ cancer stem cells via the MAPK/ERK signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;502(2):194-201.[23] 邹兴斌.胃癌干细胞制备方法及在胃癌侵袭转移中的机制[J].中国老年学杂志,2018,38(12):2968-2971.[24] Peng X, Liu G, Peng H, et al. SOX4 contributes to TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and stem cell characteristics of gastric cancer cells. Genes Dis. 2017; 5(1):49-61.[25] Chen L, Zhou Y, Li H. LncRNA, miRNA and lncRNA-miRNA interaction in viral infection. Virus Res. 2018;257:25-32.[26] Chen C, Cui Q, Zhang X, et al. Long non-coding RNAs regulation in adipogenesis and lipid metabolism: Emerging insights in obesity. Cell Signal. 2018;51:47-58.[27] Zarkou V, Galaras A, Giakountis A, et al. Crosstalk mechanisms between the WNT signaling pathway and long non-coding RNAs. Noncoding RNA Res. 2018;3(2):42-53.[28] Ji D, Zhong X, Jiang X, et al. The role of long non-coding RNA AFAP1-AS1 in human malignant tumors. Pathol Res Pract. 2018;214(10):1524-1531.[29] Li BL, Wan XP. The role of lncRNAs in the development of endometrial carcinoma. Oncol Lett. 2018;16(3):3424-3429.[30] Brannan CI, Dees EC, Ingram RS, et al. The product of the H19 gene may function as an RNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1990; 10(1):28-36.[31] Gabory A, Jammes H, Dandolo L. The H19 locus: role of an imprinted non-coding RNA in growth and development. Bioessays. 2010;32(6):473-480.[32] Ariel I, Sughayer M, Fellig Y, et al. The imprinted H19 gene is a marker of early recurrence in human bladder carcinoma. Mol Pathol. 2000;53(6):320-323.[33] 兰霞斌,张浩.长链非编码RNA H19在肿瘤中的研究进展[J].肿瘤学杂志,2017,23(12):1115-1120.[34] Yörüker EE, Keskin M, Kulle CB, et al. Diagnostic and prognostic value of circulating lncRNA H19 in gastric cancer. Biomed Rep. 2018;9(2):181-186.[35] Liu G, Xiang T, Wu QF, et al. Long Noncoding RNA H19-Derived miR-675 Enhances Proliferation and Invasion via RUNX1 in Gastric Cancer Cells. Oncol Res. 2016;23(3): 99-107.[36] 刘志坤,祝淑钗,苏景伟,等. RNA 干扰 MDC1 基因对食管癌细胞X线照后细胞周期及相关蛋白表达影响[J].中华放射肿瘤学杂志, 2015,24(6): 708-713.[37] Ooki A, Dinalankara W, Marchionni L, et al. Epigenetically regulated PAX6 drives cancer cells toward a stem-like state via GLI-SOX2 signaling axis in lung adenocarcinoma. Oncogene. 2018;37(45):5967-5981.[38] Zayed H, Petersen I. Stem cell transcription factor SOX2 in synovial sarcoma and other soft tissue tumors. Pathol Res Pract. 2018;214(7):1000-1007.[39] Maehara R, Fujikura K, Takeuchi K, et al. SOX2-silenced squamous cell carcinoma: a highly malignant form of esophageal cancer with SOX2 promoter hypermethylation. Mod Pathol. 2018;31(1):83-92.[40] Fujiki H, Sueoka E, Rawangkan A, et al. Human cancer stem cells are a target for cancer prevention using (-)-epigallocatechin gallate. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2017; 143(12):2401-2412.[41] Liu X, Qiao B, Zhao T, et al. Sox2 promotes tumor aggressiveness and epithelial?mesenchymal transition in tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Mol Med. 2018;42(3): 1418-1426. |