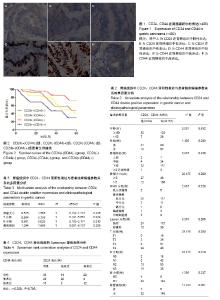
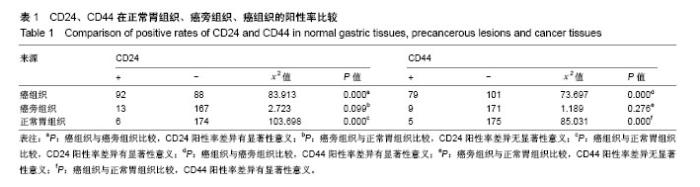
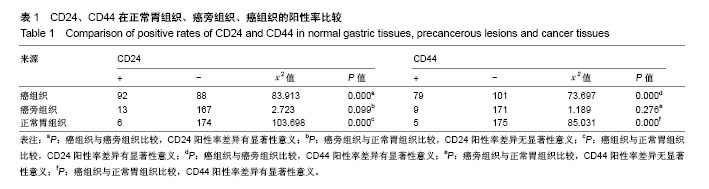
| [1] Takaishi S, Okumura T, Tu S, et al. Identification of gastric cancer stem cells using the cell surface marker CD44. Stem Cells. 2009; 27(5):1006-1020.[2] Plentz RR, Barat S, Chen X, et al. Notch and wnt-beta catenin pathways as targets of γ-secretase inhibitor IX (GSI) mediated therapy in CD44+ gastric cancer (GC) cells. J Clin Oncol. 2016; 34(4) :99.[3] Chen W, Zhang X, Chu C, et al. Identification of CD44+ cancer stem cells in human gastric cancer. Hepatogastroenterology. 2013;60(124):949-954.[4] Park JW, Um H, Yang H, et al. Proteogenomic analysis of NCC-S1M, a gastric cancer stem cell-like cell line that responds to anti-PD-1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;484(3):631-635.[5] Miao ZF, Xu H, Xu HM, et al. DLL4 overexpression increases gastric cancer stem/progenitor cell self-renewal ability and correlates with poor clinical outcome via Notch-1 signaling pathway activation. Cancer Med. 2017;6(1):245-257.[6] Sun M, Zhou W, Zhang YY, et al. CD44+ gastric cancer cells with stemness properties are chemoradioresistant and highly invasive. Oncol Lett. 2013;5(6):1793-1798.[7] Shitara K, Doi T, Nagano O, et al. Dose-escalation study for the targeting of CD44v+ cancer stem cells by sulfasalazine in patients with advanced gastric cancer (EPOC1205). Gastric Cancer. 2017;20(2):341-349.[8] Li K, Dan Z, Nie YQ. Gastric cancer stem cells in gastric carcinogenesis, progression, prevention and treatment. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20(18):5420-5426.[9] 李禄椿. Notch1信号转导通路对CD44+胃癌细胞生物学特性的影响[D]. 重庆:重庆医科大学, 2014.[10] 李威,姜波健,俞继卫. CD44与CD133蛋白在胃癌组织中的表达及其临床意义[J].中国普外基础与临床杂志,2014,21(1):21-28.[11] 许峰峰,杨世斌,肖隆斌,等.上皮细胞黏附分子、CD24在胃癌组织的表达及临床意义[J].中华实验外科杂志,2012,29(9):1831-1833.[12] Mao J, Fan S, Ma W, et al. Roles of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in the gastric cancer stem cells proliferation and salinomycin treatment. Cell Death Dis. 2014;5:e1039.[13] Nishikawa S, Konno M, Hamabe A, et al. Aldehyde dehydrogenase high gastric cancer stem cells are resistant to chemotherapy. Int J Oncol. 2013;42(4):1437-1442.[14] Yao HJ, Zhang YG, Sun L, et al. The effect of hyaluronic acid functionalized carbon nanotubes loaded with salinomycin on gastric cancer stem cells. Biomaterials.2014;35(33): 9208-9223.[15] Izumiya M, Kabashima A, Higuchi H, et al. Chemoresistance is associated with cancer stem cell-like properties and epithelial-to- mesenchymal transition in pancreatic cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 2012;32(9):3847-3853.[16] 周志华,张建东,徐桂芳,等. 基于克隆形态分选胃癌干细胞及其对氟尿嘧啶敏感性的检测[J].中华胃肠外科杂志,2013,16(4) : 376-380.[17] 陈军. 胃癌干细胞干性特性及化疗药物对其影响的初步研究[D]. 重庆:第三军医大学, 2013.[18] 王佳佳,孙立新,孙力超,等. 人胃癌CD90+干细胞可能影响胃癌的转移和患者的预后[J]. 中国肿瘤生物治疗杂志,2013, 20(2): 230-236.[19] Samadani AA, Akhavan-Niaki H. Interaction of sonic hedgehog (SHH) pathway with cancer stem cell genes in gastric cancer. Med Oncol. 2015;32(3):48.[20] 恽艳. 肿瘤干细胞标志Lgr5和CD44在胃癌中的表达及临床病理意义[D]. 苏州:苏州大学,2014.[21] Soave A, John LM, Dahlem R, et al. The Impact of Tumor Diameter and Tumor Necrosis on Oncologic Outcomes in Patients With Urothelial Carcinoma of the Bladder Treated With Radical Cystectomy. Urology. 2015;86(1):92-98.[22] 池桢,黄昌明,郑朝辉,等. 肿瘤大小对T3期胃癌患者预后的影响[J]. 中华胃肠外科杂志, 2011, 14(2) :114-116.[23] 陆俊,黄昌明,郑朝辉,等. 肿瘤大小对早期胃癌病人预后的影响[J]. 中国实用外科杂志, 2012,32(9):758-761.[24] Stokes GN, Shelton JB Jr, Zahn CM, et al. Association of CD44 isoform immunohistochemical expression with myometrial and vascular invasion in endometrioid endometrial carcinoma. Gynecol Oncol. 2002;84(1):58-61.[25] Yildiz E, Gokce G, Kilicarslan H, et al. Prognostic value of the expression of Ki-67, CD44 and vascular endothelial growth factor, and microvessel invasion, in renal cell carcinoma. BJU Int. 2004; 93(7):1087-1093.[26] Wakamatsu Y, Sakamoto N, Oo HZ, et al. Expression of cancer stem cell markers ALDH1, CD44 and CD133 in primary tumor and lymph node metastasis of gastric cancer. Pathol Int. 2012;62(2): 112-119.[27] Nishikawa S, Konno M, Hamabe A, et al. Surgically resected human tumors reveal the biological significance of the gastric cancer stem cell markers CD44 and CD26. Oncol Lett. 2015; 9(5):2361-2367. [28] Watanabe T, Okumura T, Hirano K, et al. Circulating tumor cells expressing cancer stem cell marker CD44 as a diagnostic biomarker in patients with gastric cancer. Oncol Lett. 2017; 13(1):281-288.[29] Arima S, Kunimura T, Date H, et al. Expression of Standard CD44 in Advanced Gastric Cancer: Relationship with Metastasis to Lymph Nodes. Journal of Physical Chemistry. 2011; 22(3): 163-169.[30] Eom BW, Joo J, Park B, et al. Nomogram Incorporating CD44v6 and Clinicopathological Factors to Predict Lymph Node Metastasis for Early Gastric Cancer. PLoS One. 2016; 11(8): e0159424.[31] Zhou C, Ji J, Cai Q, et al. MTA2 enhances colony formation and tumor growth of gastric cancer cells through IL-11. BMC Cancer. 2015;15:343.[32] Müller W, Schneiders A, Heider KH, et al. Expression and prognostic value of the CD44 splicing variants v5 and v6 in gastric cancer. J Pathol. 1997;183(2):222-227.[33] Lee ES, Kim SH, Lee JY, et al. Radiologist performance in differentiating polypoid early from advanced gastric cancer using specific CT criteria: emphasis on dimpling sign. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009;193(6):1546-1555.[34] Yoon C, Park DJ, Schmidt B, et al. CD44 expression denotes a subpopulation of gastric cancer cells in which Hedgehog signaling promotes chemotherapy resistance. Clin Cancer Res. 2014; 20(15):3974-3988.[35] Nishikawa S, Konno M, Hamabe A, et al. Surgically resected human tumors reveal the biological significance of the gastric cancer stem cell markers CD44 and CD26. Oncol Lett. 2015; 9(5): 2361-2367.[36] 陈仕才,宋新明,陈志辉,等.CD133 和 CD44 在结直肠癌细胞中的表达及其与患者5年生存率的相关性分析[J].中国病理生理杂志, 2011,27(5):883-889.[37] 金可可,蒋仲荪,陈少贤,等.非小细胞肺癌患者 CD44及其变异体 V6 的测定[J].中国病理生理杂志,2001,17(11):1008-1092.[38] 杨世斌,肖隆斌,许峰峰,等. EPCAM、CD44和CD24在胃癌组织中的表达及其临床意义[J].中国病理生理杂志,2012,28(7): 1224-1229.[39] Bektas S, Bahadir B, Ucan BH, et al. CD24 and galectin-1 expressions in gastric adenocarcinoma and clinicopathologic significance. Pathol Oncol Res. 2010;16(4):569-577. |