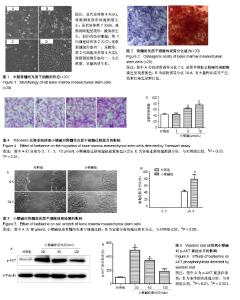
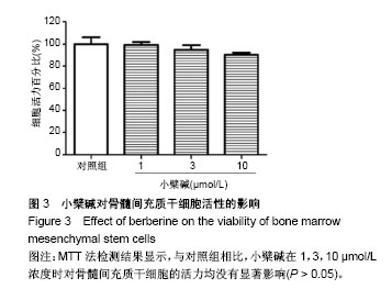
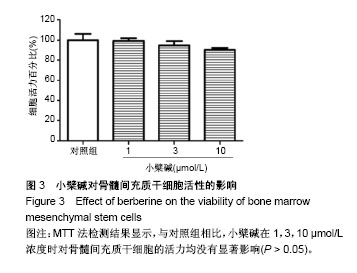
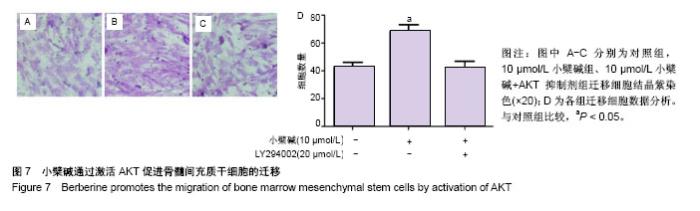
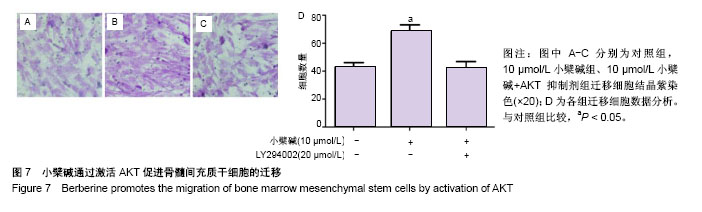
| [1] Barry FP.Mesenchymal stem cell therapy in joint disease.Novartis Found Symp. 2003;249:86-96. [2] Ng TK, Fortino VR, Pelaez D, et al. Progress of mesenchymal stem cell therapy for neural and retinal diseases.World J Stem Cells. 2014;6(2):111-119. [3] Zhao D, Liu B, Wang B, et al. Autologous bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells associated with tantalum rod implantation and vascularized iliac grafting for the treatment of end-stage osteonecrosis of the femoral head.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015: 240506. [4] Cui D, Li H, Xu X, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Cartilage Regeneration of TMJ Osteoarthritis.Stem Cells Int. 2017;2017: 5979741. [5] Prockop DJ.Marrow stromal cells as stem cells for nonhematopoietic tissues.Science. 1997;276(5309):71-74. [6] Temenoff JS, Mikos AG.Review: tissue engineering for regeneration of articular cartilage.Biomaterials. 2000;21(5):431-440. [7] Wakitani S, Goto T, Pineda SJ, et al. Mesenchymal cell-based repair of large, full-thickness defects of articular cartilage.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1994;76(4):579-592. [8] Lauffenburger DA, Horwitz AF.Cell migration: a physically integrated molecular process.Cell. 1996;84(3):359-369. [9] Chavakis E, Urbich C, Dimmeler S.Homing and engraftment of progenitor cells: a prerequisite for cell therapy.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2008;45(4):514-522. [10] Bing W, Pang X, Qu Q, et al. Simvastatin improves the homing of BMSCs via the PI3K/AKT/miR-9 pathway.J Cell Mol Med. 2016; 20(5):949-961. [11] Wang Y, Chen J, Fan W, et al. Stromal cell-derived factor-1α and transforming growth factor-β1 synergistically facilitate migration and chondrogenesis of synovium-derived stem cells through MAPK pathways.Am J Transl Res. 2017;9(5):2656-2667. [12] Chen M, Tan M, Jing M, et al. Berberine protects homocysteic acid-induced HT-22 cell death: involvement of Akt pathway.Metab Brain Dis. 2015;30(1):137-142. [13] Zhang C, Li C, Chen S, et al. Berberine protects against 6-OHDA-induced neurotoxicity in PC12 cells and zebrafish through hormetic mechanisms involving PI3K/AKT/Bcl-2 and Nrf2/HO-1 pathways.Redox Biol. 2017;11:1-11. [14] Wang Z, Chen Z, Chen T, et al. Berberine attenuates inflammation associated with delayed-type hypersensitivity via suppressing Th1 response and inhibiting apoptosis. Inflammation. 2016;40(1): 221-231.[15] Wang SF, Wu MY, Cai CZ, et al. Autophagy modulators from traditional Chinese medicine: Mechanisms and therapeutic potentials for cancer and neurodegenerative diseases.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016;194:861-876. [16] de Oliveira JS, Abdalla FH, Dornelles GL, et al. Berberine protects against memory impairment and anxiogenic-like behavior in rats submitted to sporadic Alzheimer's-like dementia: Involvement of acetylcholinesterase and cell death.Neurotoxicology. 2016;57: 241-250. [17] Kumar A, Ekavali, Chopra K, et al. Current knowledge and pharmacological profile of berberine: An update.Eur J Pharmacol. 2015;761:288-297. [18] Wang N, Tan HY, Li L, et al. Berberine and Coptidis Rhizoma as potential anticancer agents: Recent updates and future perspectives.J Ethnopharmacol. 2015;176:35-48. [19] Ortiz LM, Lombardi P, Tillhon M, et al. Berberine, an epiphany against cancer.Molecules. 2014;19(8):12349-12367. [20] Lee HW, Suh JH, Kim HN, et al. Berberine promotes osteoblast differentiation by Runx2 activation with p38 MAPK.J Bone Miner Res. 2008;23(8):1227-1237. [21] Tao K, Xiao D, Weng J, et al. Berberine promotes bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells osteogenic differentiation via canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.Toxicol Lett. 2016; 240(1):68-80. [22] Sun Y, Li QF, Yan J, et al. Isoflurane Preconditioning Promotes the Survival and Migration of Bone Marrow Stromal Cells.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;36(4):1331-1345. [23] Hu YR, Ma H, Zou ZY, et al. Activation of Akt and JNK/Nrf2/NQO1 pathway contributes to the protective effect of coptisine against AAPH-induced oxidative stress. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;(85): 313-322.[24] Qin-Wei Z, Yong-Guang LI.Berberine attenuates myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury by suppressing the activation of PI3K/AKT signaling.Exp Ther Med. 2016;11(3):978-984. [25] Neirinckx V, Agirman G, Coste C, et al. Adult bone marrow mesenchymal and neural crest stem cells are chemoattractive and accelerate motor recovery in a mouse model of spinal cord injury.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015;6:211. [26] Schrepfer S, Deuse T, Reichenspurner H, et al. Stem cell transplantation: the lung barrier.Transplant Proc. 2007;39(2): 573-576. [27] Karp JM, Leng Teo GS.Mesenchymal stem cell homing: the devil is in the details.Cell Stem Cell. 2009;4(3):206-216. [28] Imenshahidi M, Hosseinzadeh H.Berberis Vulgaris and Berberine: An Update Review.Phytother Res. 2016;30(11):1745-1764. [29] Ma ZJ, Hu SL, Wang SS, et al. Effects and underlying mechanism of berberine on renal tubulointerstitial injury in diabetic rats. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2016;96(38):3072-3077. [30] Eo SH, Kim JH, Kim SJ.Induction of G?/M Arrest by Berberine via Activation of PI3K/Akt and p38 in Human Chondrosarcoma Cell Line.Oncol Res. 2014;22(3):147-157. [31] Song YC, Lee Y, Kim HM, et al. Berberine regulates melanin synthesis by activating PI3K/AKT, ERK and GSK3β in B16F10 melanoma cells.Int J Mol Med. 2015;35(4):1011-1016. |